Hybrid Lipid Nanoformulations for Hepatoma Therapy: Sorafenib Loaded Nanoliposomes—A Preliminary Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Sorafenib Functionalized Liposomes
2.2. Characterization of Liposomes
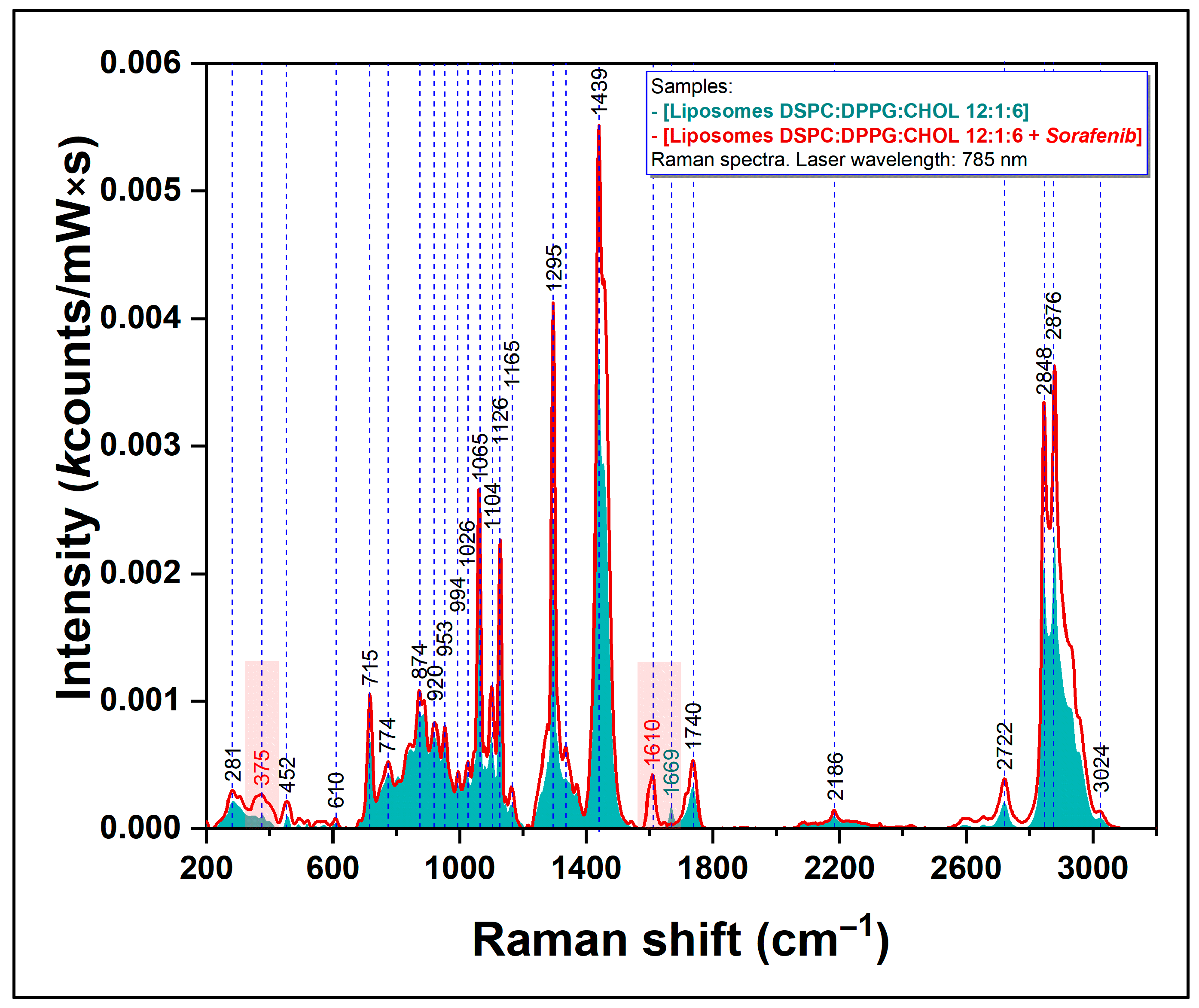
2.2.1. Raman Spectroscopy
- -
- Lipo and Lipo_SOR: excitation wavelength 785 nm, power at sample surface 113 mW, objective lens 50×, 60 acquisition points, integration time 40 s (exposure time 10 s and 4 signal accumulations).
- -
- SOR: excitation wavelength 785 nm, power at sample surface 11.3 mW, objective lens 50× lens, 20 acquisition points, integration time 40 s (exposure time 10 s and 4 signal accumulations).
2.2.2. Determination of Concentration, Zeta-Potential and Particle Size of Liposomes
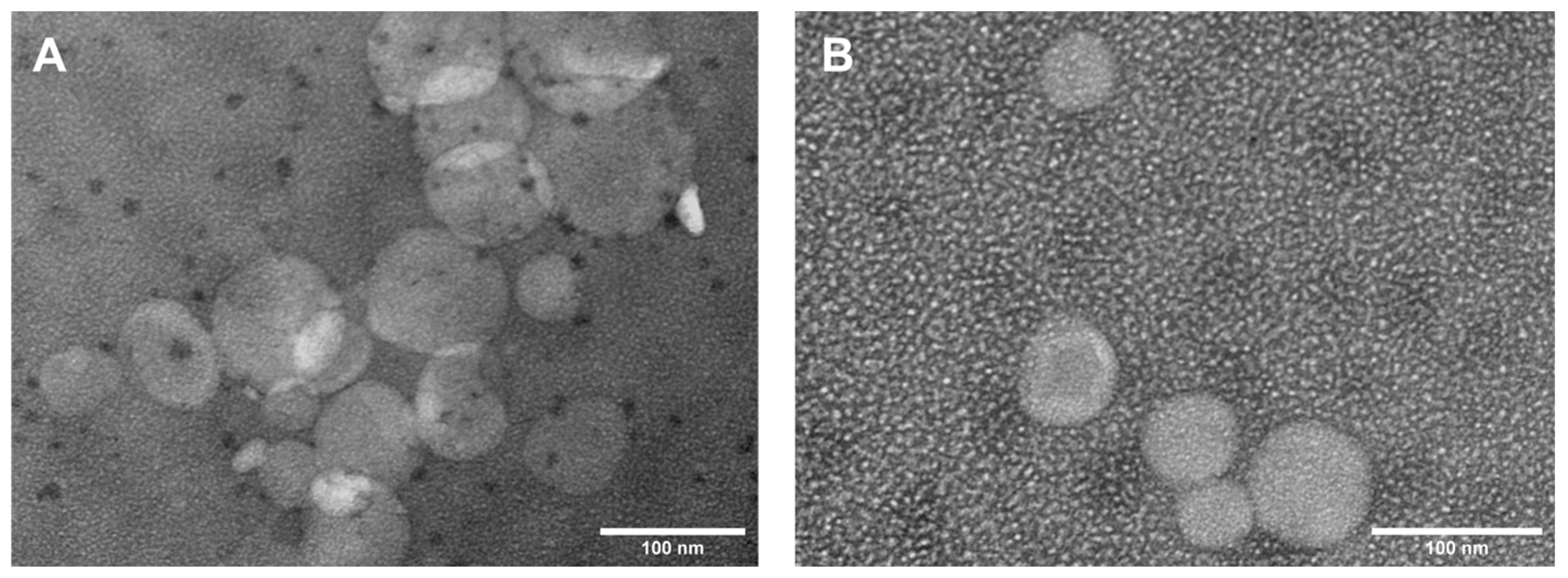
2.2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy Measurements
2.2.4. Sorafenib Encapsulation Efficiency
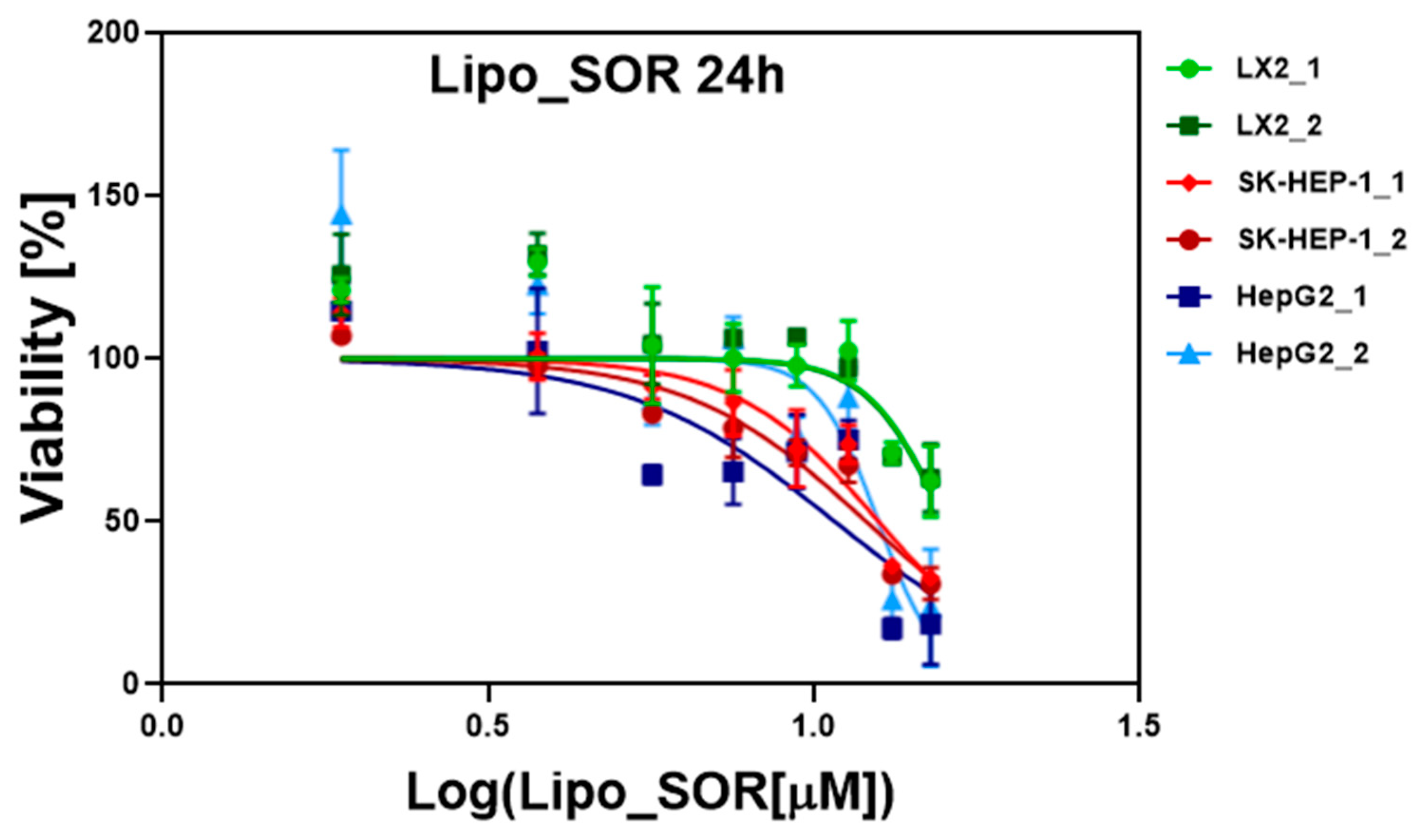
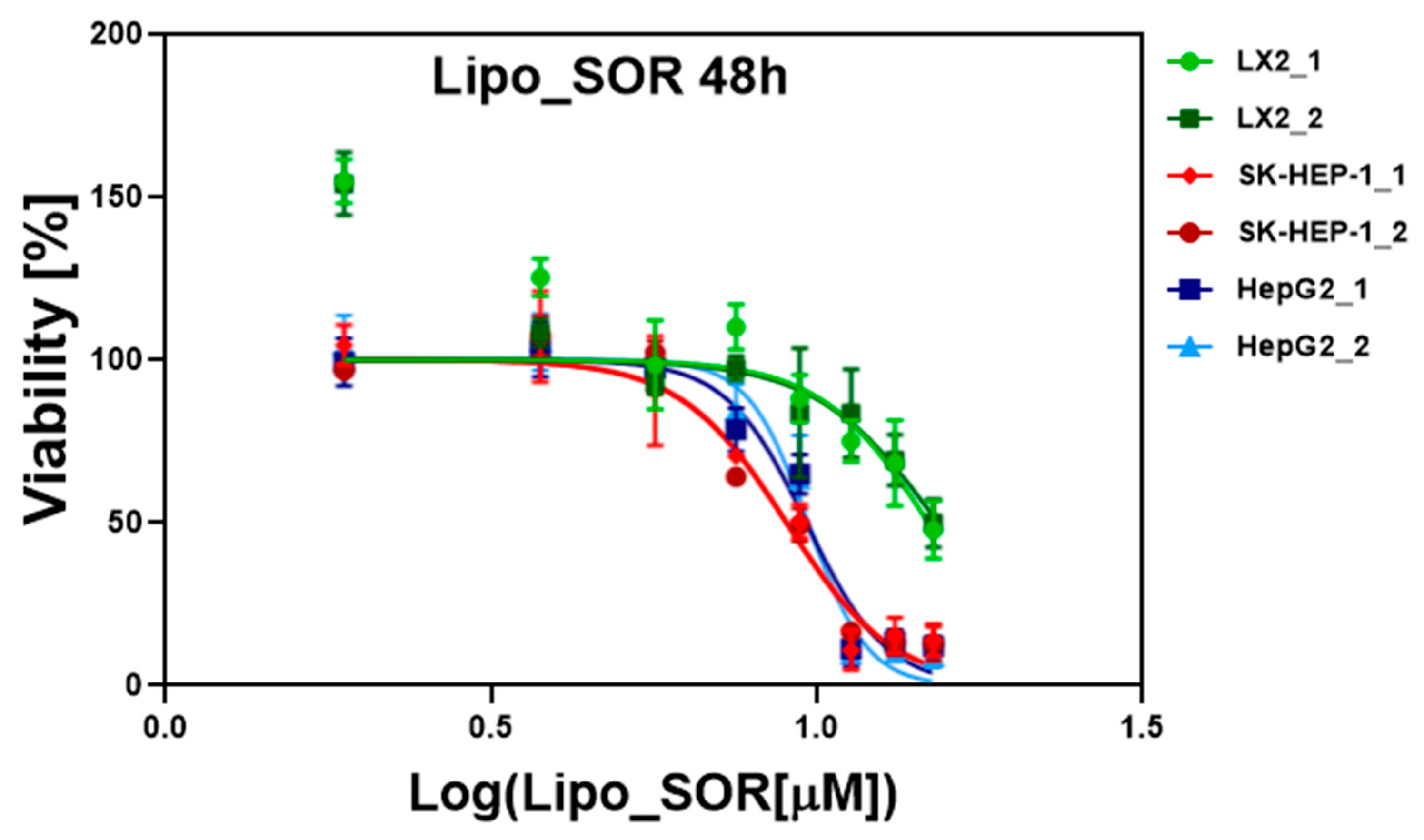
2.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies on Cell Cultures
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Liposomes
3.1.1. Evaluation of Sorafenib-Loaded Nanoliposome by Raman Spectroscopy
3.1.2. Determination of Concentration, Zeta-Potential and Particle Size of Liposomes
3.1.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
3.1.4. Encapsulation Efficiency
3.2. In Vitro Evaluation of Liposomes on Cell Cultures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, E.; Viatour, P. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Old friends and new tricks. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1898–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakrania, A.; Zheng, G.; Bhat, M. Nanomedicine in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A New Frontier in Targeted Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoul, J.-L.; Frenel, J.-S.; Raimbourg, J.; Gilabert, M. Current options and future possibilities for the systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic Oncol. 2019, 6, HEP11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Kudo, M.; Kawazoe, S.; Osaki, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Okusaka, T.; Tamai, T.; Suzuki, T.; Hisai, T.; Hayato, S.; et al. Phase 2 study of lenvatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M. Lenvatinib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2017, 6, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Tak, W.-Y.; Gasbarrini, A.; Santoro, A.; Colombo, M.; Lim, H.-Y.; Mazzaferro, V.; Wiest, R.; Reig, M.; Wagner, A.; et al. Regorafenib as second-line therapy for intermediate or advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Multicentre, open-label, phase II safety study. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.K.; Verslype, C.; Cohn, A.L.; Yang, T.-S.; Su, W.-C.; Burris, H.; Braiteh, F.; Vogelzang, N.; Spira, A.; Foster, P.; et al. Cabozantinib in hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of a phase 2 placebo-controlled randomized discontinuation study. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, K.-H.; Numata, K.; Stein, S.; Verret, W.; Hack, S.; Spahn, J.; Liu, B.; Huang, C.; et al. Randomised efficacy and safety results for atezolizumab (Atezo) + bevacizumab (Bev) in patients (pts) with previously untreated, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, ix187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Cai, M.; Lin, L.; Chen, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhu, K.; Shuai, X. Codelivery of sorafenib and GPC3 siRNA with PEI-modified liposomes for hepatoma therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 2468–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizesan, I.; Iacovita, C.; Pop, A.; Kiss, B.; Dudric, R.; Stiufiuc, R.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Loghin, F. The Effect of Zn-Substitution on the Morphological, Magnetic, Cytotoxic, and In Vitro Hyperthermia Properties of Polyhedral Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbălată, C.I.; Porfire, A.S.; Sesarman, A.; Rauca, V.-F.; Banciu, M.; Muntean, D.; Știufiuc, R.; Moldovan, A.; Moldovan, C.; Tomuță, I. A Screening Study for the Development of Simvastatin-Doxorubicin Liposomes, a Co-Formulation with Future Perspectives in Colon Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Știufiuc, G.F.; Toma, V.; Onaciu, A.; Chiș, V.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Știufiuc, R.I. Proving Nanoscale Chiral Interactions of Cyclodextrins and Propranolol Enantiomers by Means of SERS Measurements Performed on a Solid Plasmonic Substrate. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsman, M.; Sereti, V.; Andreassen, K.; Snipstad, S.; van Wamel, A.; Eliasen, R.; Berg, S.; Urquhart, A.J.; Andresen, T.L.; Davies, C.d.L. Ultrasound-mediated delivery enhances therapeutic efficacy of MMP sensitive liposomes. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocan, T.; Stiufiuc, R.; Popa, C.; Nenu, I.; Pestean, C.; Nagy, A.L.; Mocan, L.P.; Leucuta, D.C.; Hajjar, N.A.; Sparchez, Z. Percutaneous ultrasound guided PEG-coated gold nanoparticles enhanced radiofrequency ablation in liver. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snipstad, S.; Sulheim, E.; de Lange Davies, C.; Moonen, C.; Storm, G.; Kiessling, F.; Schmid, R.; Lammers, T. Sonopermeation to improve drug delivery to tumors: From fundamental understanding to clinical translation. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z. Advances in Nanoliposomes for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, A.D.; Horne, R.W. Negative staining of phospholipids and their structural modification by surface-active agents as observed in the electron microscope. J. Mol. Biol. 1964, 8, 660-IN10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, A.D.; Hill, M.W.; Miller, N.G.A. Preparation and use of liposomes as models of biological membranes. In Methods in Membrane Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1974; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Știufiuc, G.F.; Nițică, Ș.; Toma, V.; Iacoviță, C.; Zahn, D.; Tetean, R.; Burzo, E.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Știufiuc, R.I. Synergistical Use of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions for the Synthesis of a New Class of Multifunctional Nanohybrids: Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiufiuc, R.; Iacovita, C.; Stiufiuc, G.; Florea, A.; Achim, M.; Lucaciu, C.M. A new class of pegylated plasmonic liposomes: Synthesis and characterization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 437, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, F.; Li, P. Effectiveness of localized ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction with doxorubicin liposomes in H22 mouse hepatocellular carcinoma model. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, D.; Yu, J.; Dou, J.; Li, X.; Mu, M.; Liang, P. Chemotherapeutic Nanoparticle-Based Liposomes Enhance the Efficiency of Mild Microwave Ablation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Wen, J.; Qi, X.; Liu, J.; Lian, B.; Zhang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. GA&HA-Modified Liposomes for Co-Delivery of Aprepitant and Curcumin to Inhibit Drug-Resistance and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 2559–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, Z.-P.; Tian, G.-X.; Pan, R.-Y.; Xu, C.-M.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J. Liver-targeted liposomes for codelivery of curcumin and combretastatin A4 phosphate: Preparation, characterization, and antitumor effects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1789–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhao, P.; Wu, S.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Zheng, C.; Li, K.; Ma, X.; et al. Cisplatin and curcumin co-loaded nano-liposomes for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 545, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, T.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, J.; Yu, D.; Zhang, N. Sorafenib and gadolinium co-loaded liposomes for drug delivery and MRI-guided HCC treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 141, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.H.; Moon, H.; Lee, H.J.; Han, J.K. Combined treatment of sorafenib and doxorubicin-loaded microbubble-albumin nanoparticle complex for hepatocellular carcinoma: A feasibility study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Shang, F.; Chen, D.; Cao, T.; Wang, X.; Jiao, J.; He, S.; Liang, X. Protein liposomes-mediated targeted acetylcholinesterase gene delivery for effective liver cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Zhou, L.; Jin, H.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, D.; Jiang, Y. Sorafenib-Loaded Long-Circulating Nanoliposomes for Liver Cancer Therapy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1351046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannito, S.; Bincoletto, V.; Turato, C.; Pontisso, P.; Scupoli, M.T.; Ailuno, G.; Andreana, I.; Stella, B.; Arpicco, S.; Bocca, C. Hyaluronated and PEGylated Liposomes as a Potential Drug-Delivery Strategy to Specifically Target Liver Cancer and Inflammatory Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchet, B.; Billemont, B.; Cramard, J.; Benichou, A.S.; Chhun, S.; Harcouet, L.; Ropert, S.; Dauphin, A.; Goldwasser, F.; Tod, M. Validation of an HPLC-UV method for sorafenib determination in human plasma and application to cancer patients in routine clinical practice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stăncioiu, L.; Gherman, A.M.R.; Brezeștean, I.; Dina, N.E. Vibrational spectral analysis of Sorafenib and its molecular docking study compared to other TKIs. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1248, 131507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fong, D.W.F.; Yin, L.; Wong, Y.; Huang, W. Liposomes modulate docetaxel-induced lipid oxidization and membrane damage in human hepatoma cells. J. Liposome Res. 2009, 19, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quagliariello, V.; Masarone, M.; Armenia, E.; Giudice, A.; Barbarisi, M.; Caraglia, M.; Barbarisi, A.; Persico, M. Chitosan-coated liposomes loaded with butyric acid demonstrate anticancer and anti-inflammatory activity in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 41, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQahtani, S.A.; Harisa, G.I.; Badran, M.M.; AlGhamdi, K.M.; Kumar, A.; Salem-Bekhit, M.M.; Ahmad, S.F.; Alanazi, F.K. Nano-erythrocyte membrane-chaperoned 5-fluorouracil liposomes as biomimetic delivery platforms to target hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.H.; Park, S.S.; Lee, K.J.; Ju, E.J.; Park, J.; Ko, E.J.; Jung, J.; Kuroda, S.; Hong, S.-M.; Hwang, J.J.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of cisplatin-incorporated bio-nanocapsules as chemo-radiotherapy for human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamam, H.; Park, J.; Gadalla, H.H.; Masters, A.R.; Abdel-Aleem, J.A.; Abdelrahman, S.I.; Abdelrahman, A.A.; Lyle, L.T.; Yeo, Y. Development of Liposomal Gemcitabine with High Drug Loading Capacity. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2858–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, B.; Wei, H.; Pan, R.; Sun, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Tian, G. Galactose Modified Liposomes for Effective Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and Combretastatin A4. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlQahtani, S.A.; Harisa, G.I.; Alomrani, A.H.; Alanazi, F.K.; Badran, M.M. Improved pharmacokinetic and biodistribution of 5-fluorouracil loaded biomimetic nanoerythrocytes decorated nanocarriers for liver cancer treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagwani, S.; Jalalpure, S.; Dhamecha, D.; Jadhav, K.; Bohara, R. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of Resveratrol Loaded Cationic Liposomes for Targeting Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4969–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Xiao, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, T.; Su, Z.; Zhang, N. Ceramide-Fabricated Co-Loaded Liposomes for the Synergistic Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Chu, H.; Liu, X.; Dai, Y.; Wang, D. Doxorubicin and Lovastatin co-delivery liposomes for synergistic therapy of liver cancer. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Afzal, A.; Raza, S.M.; Bashir, S.; Madni, A.; Khan, M.W.; Ma, X.; Xiang, G. Liposomal co-delivered oleanolic acid attenuates doxorubicin-induced multi-organ toxicity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47136–47153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, A.W.; Szklaruk, J.; Lall, C.; Blair, K.J.; Kaseb, A.O.; Kamath, A.; Rohren, S.A.; Elsayes, K.M. Angiogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Pathophysiology, Targeted Therapy, and Role of Imaging. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2020, 7, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Particle Size (nm) | Percentage (%) | Concentration (NP/mL) | Zeta-Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipo | 183 | 93.3 | 5.3 × 1012 | 5.05 |
| 734 | 6.6 | |||
| Lipo_SOR | 127–320 | 70.7 | 9.2 × 1010 | 11.29 |
| 724–960 | 29.3 |
| Treatment_Time | LX2 Cells | SK-HEP-1 Cells | HepG2 Cells |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOR_24 h | 18.695 | 16.935 | 16.95 |
| SOR_48 h | 16.3 | 13.935 | 15.145 |
| Lipo_24 h | - | - | - |
| Lipo_48 h | - | - | - |
| Lipo_SOR_24 h | 15.76 | 12.25 | 11.615 |
| Lipo_SOR_48 h | 15.02 | 8.96 | 9.63 |
| Cell Lines | Lipo_SOR 24 vs. 48 h | SOR 24 vs. 48 h |
|---|---|---|
| LX2 | p = 0.1 ns | p = 0.11 ns |
| SD24 = 0.021 | SD24 = 1.237 | |
| SD48 = 0.361 | SD48 = 0.099 | |
| SK-HEP-1 | p = 0.006 ** | p = 0.007 ** |
| SD24 = 0.382 | SD24 = 0.290 | |
| SD48 = 0.002 | SD48 = 0.205 | |
| HepG2 | p = 0.154 (ns) | p = 0.017 * |
| SD24 = 1.252 | SD24 = 0.212 | |
| SD48 = 0.033 | SD48 = 0.262 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartos, A.; Iancu, I.; Ciobanu, L.; Onaciu, A.; Moldovan, C.; Moldovan, A.; Moldovan, R.C.; Tigu, A.B.; Stiufiuc, G.F.; Toma, V.; et al. Hybrid Lipid Nanoformulations for Hepatoma Therapy: Sorafenib Loaded Nanoliposomes—A Preliminary Study. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2833. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162833
Bartos A, Iancu I, Ciobanu L, Onaciu A, Moldovan C, Moldovan A, Moldovan RC, Tigu AB, Stiufiuc GF, Toma V, et al. Hybrid Lipid Nanoformulations for Hepatoma Therapy: Sorafenib Loaded Nanoliposomes—A Preliminary Study. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(16):2833. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162833
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartos, Adrian, Ioana Iancu, Lidia Ciobanu, Anca Onaciu, Cristian Moldovan, Alin Moldovan, Radu Cristian Moldovan, Adrian Bogdan Tigu, Gabriela Fabiola Stiufiuc, Valentin Toma, and et al. 2022. "Hybrid Lipid Nanoformulations for Hepatoma Therapy: Sorafenib Loaded Nanoliposomes—A Preliminary Study" Nanomaterials 12, no. 16: 2833. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162833
APA StyleBartos, A., Iancu, I., Ciobanu, L., Onaciu, A., Moldovan, C., Moldovan, A., Moldovan, R. C., Tigu, A. B., Stiufiuc, G. F., Toma, V., Iancu, C., Al Hajjar, N., & Stiufiuc, R. I. (2022). Hybrid Lipid Nanoformulations for Hepatoma Therapy: Sorafenib Loaded Nanoliposomes—A Preliminary Study. Nanomaterials, 12(16), 2833. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162833








