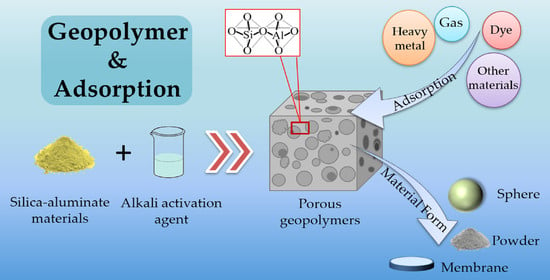
Research and Application Progress of Geopolymers in Adsorption: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geopolymer Reaction Mechanism and Research Status
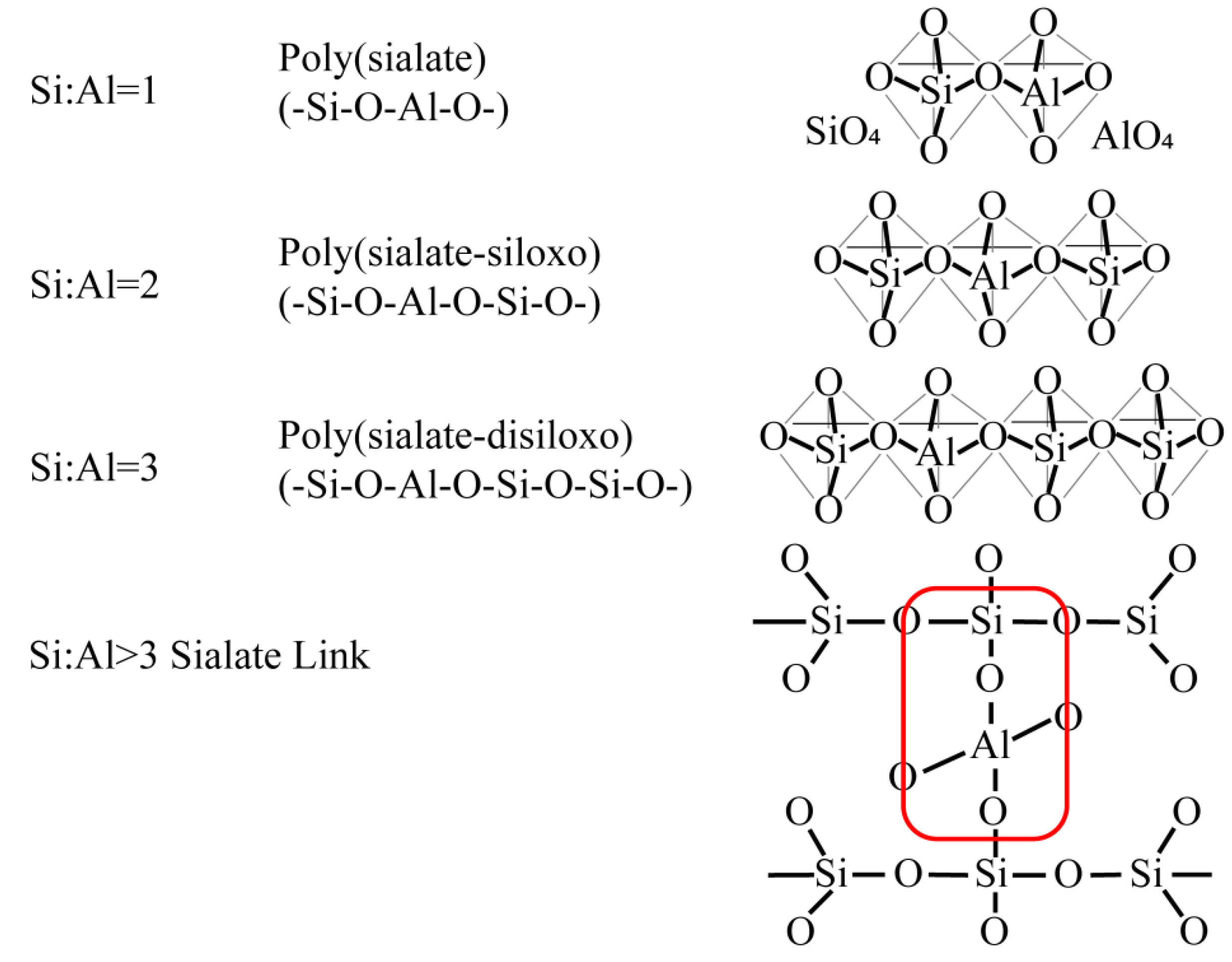
2.1. Geopolymer Reaction Mechanism
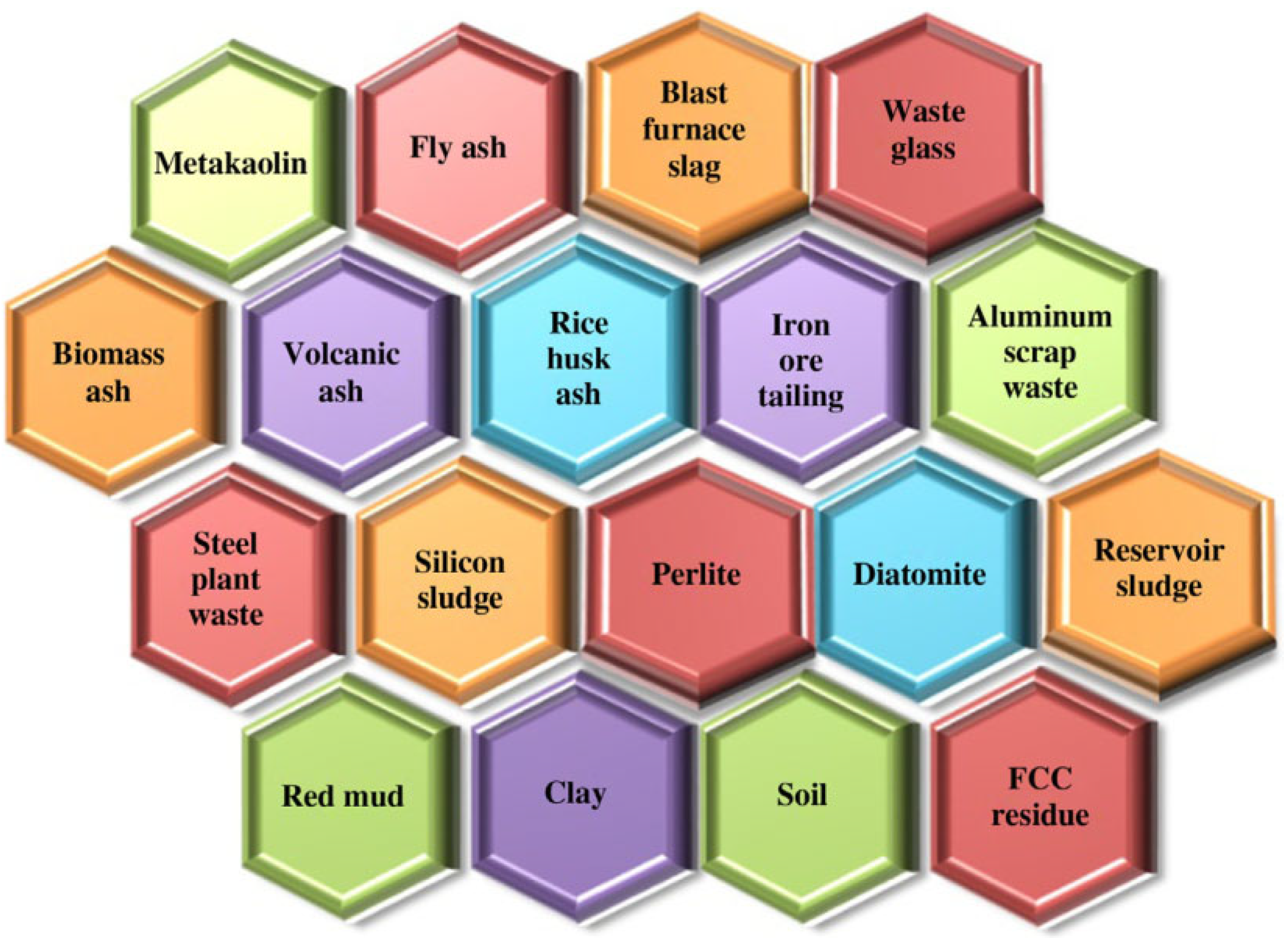
2.2. Status of Geopolymer Research
2.3. Application of Geopolymers
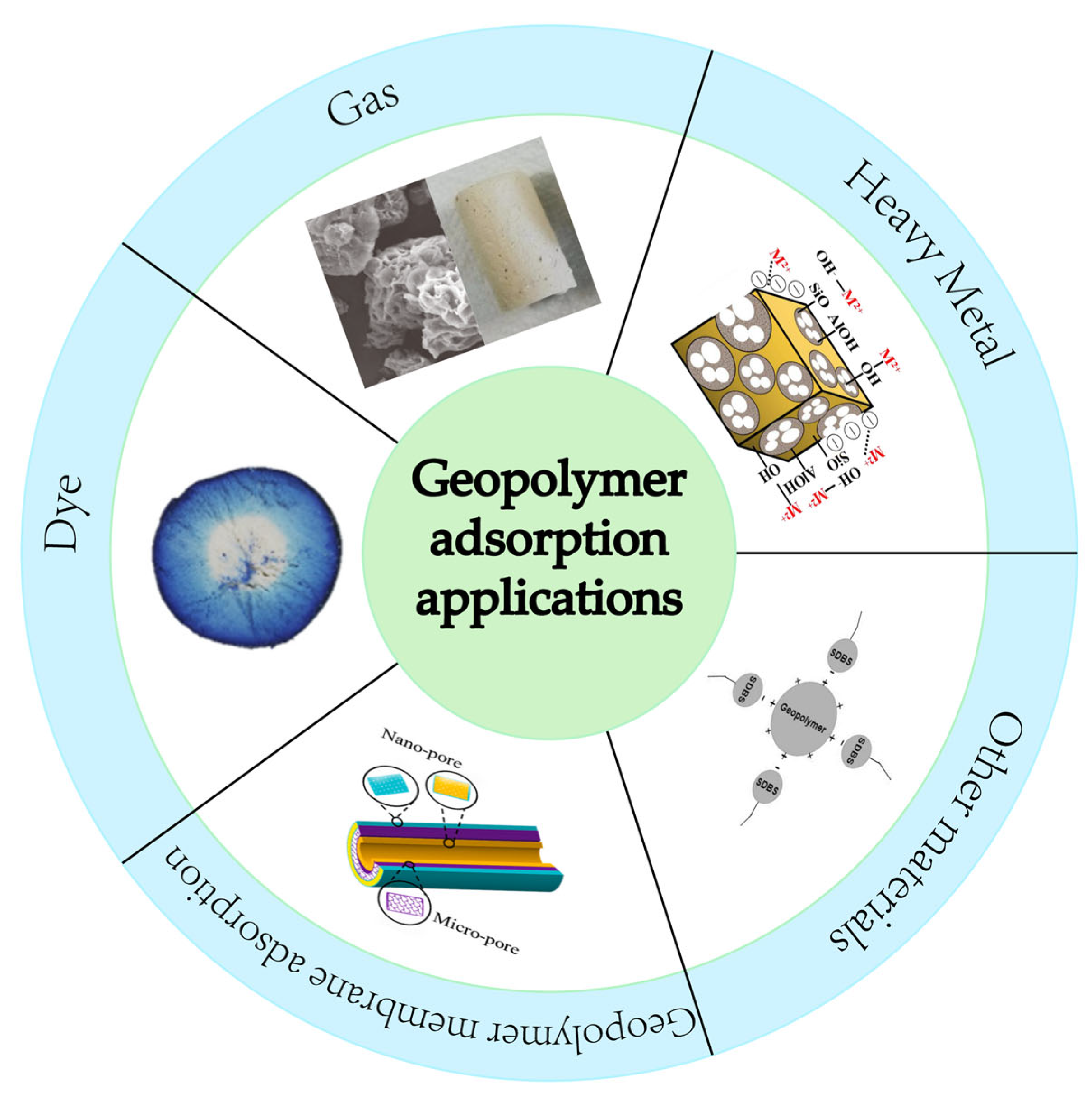
3. Application of Geopolymers in Adsorption
3.1. Heavy Metal
3.2. Other Ions
3.3. Dyes
3.4. Other Adsorption Applications
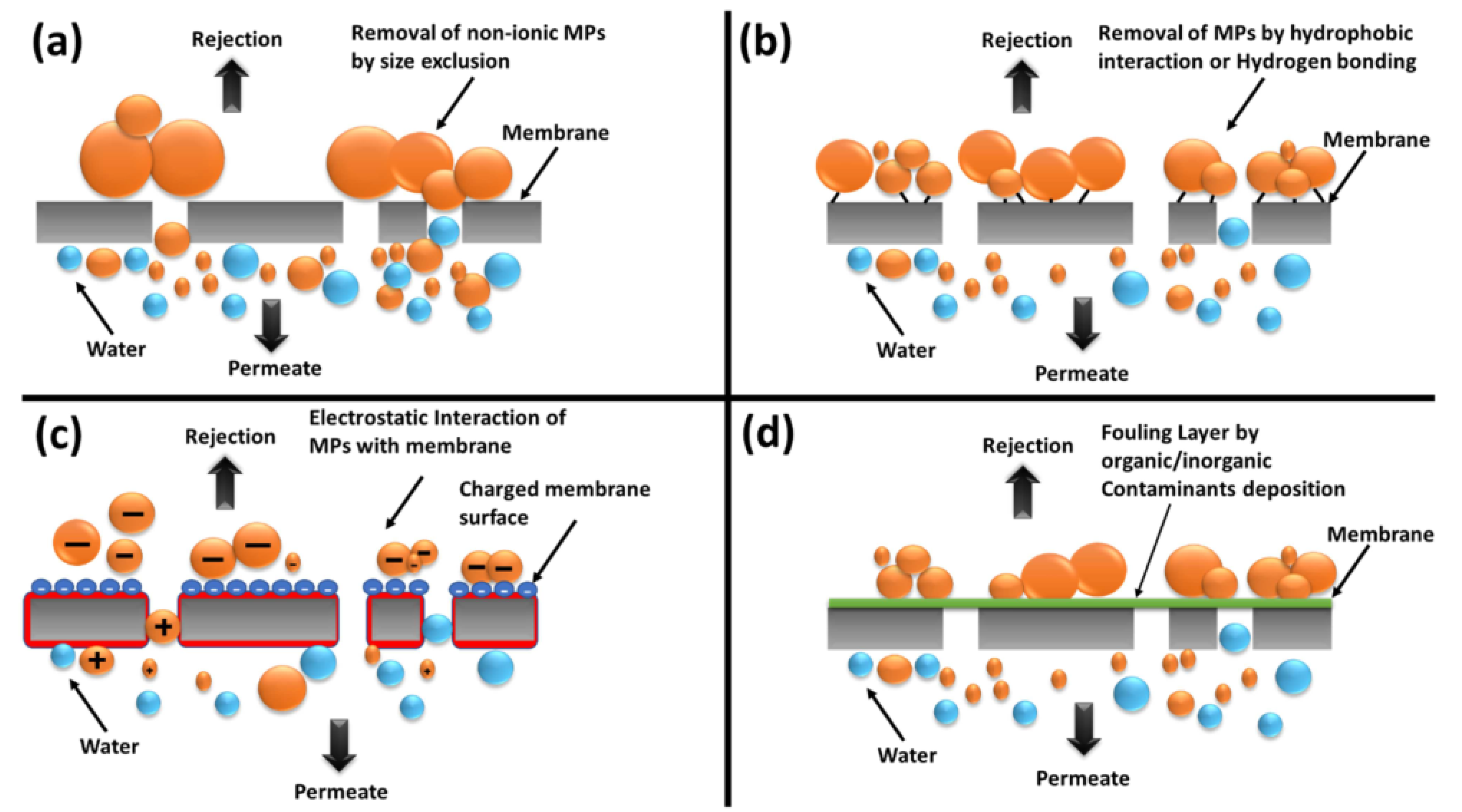
3.5. Application of Geopolymer Membranes in Adsorption
4. Conclusions
- The components of geopolymers have a significant impact on the material properties, and further innovative development of composite geopolymer materials while improving the performance of existing geopolymer materials.
- Geopolymers are strongly influenced by various factors, and the mechanisms should be explored in depth. For example, how does the ratio of raw materials affect the final formation of geopolymers? How do the coupling agents, K+, Na+ and other added substances affect the performance of geopolymers? By studying the mechanism of each step in depth, a complete and comprehensive theoretical system should be established to turn the uncontrollable process in the experiment into one that is controllable.
- The raw materials for the present preparation of geopolymers are mainly natural minerals, and the use of pure chemicals for their preparation may be explored. Try to apply geopolymers in other neighborhoods such as fine chemicals, chemical separation, microelectronics, electrical, etc.
- Geopolymer and zeolite have similar structures. There are few studies on the selectivity of zeolite-based adsorbents, and the selective adsorption of geopolymers should be further studied.
- For industrial applications, geopolymers could be prepared as flat membranes, tubular membranes, multi-channel membranes, and single or multiple geopolymer membranes assembled into membrane assemblies. Complete membrane units are more conducive to industrial production and laboratory research.
- Finally, the basic research on geopolymers and their practical application still has enormous research space, from many aspects such as performance, cost, emission and use, to transfer the innovation of geopolymers to practical application based on theoretical knowledge.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers and geopolymeric materials. J. Therm. Anal. 1989, 35, 429–441. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers: Man-made rock geosynthesis and the resulting development of very early high Strength Cement. J. Mater. Educ. 1994, 16, 91–139. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovits, J. Recent progresses in concretes for nuclear waste and uranium waste containment. Concr. Int. 1994, 16, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.; Colombo, P. Processing, properties and applications of highly porous geopolymers: A review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16103–16118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Jia, Y. Preparation of geopolymer composites based on alkali excitation. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 600. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Bai, C.Y.; Qiao, Y.J.; Wang, X.D.; Jia, D.C.; Li, H.Q.; Colombo, P. Porous geopolymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 150, 106629. [Google Scholar]
- Amran, M.; Debbarma, S.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Fly ash-based eco-friendly geopolymer concrete: A critical review of the long-term durability properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 270, 121857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komnitsas, K.; Zaharaki, D. Geopolymerisation: A review and prospects for the minerals industry. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Lahoti, M.; Tan, K.H.; Yang, E.H. A critical review of geopolymer properties for structural fire-resistance applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 514–526. [Google Scholar]
- Luhar, S.; Nicolaides, D.; Luhar, I. Fire resistance behaviour of geopolymer concrete: An overview. Buildings 2021, 11, 82. [Google Scholar]
- Mesgari, S.; Akbarnezhad, A.; Xiao, J.Z. Recycled geopolymer aggregates as coarse aggregates for Portland cement concrete and geopolymer concrete: Effects on mechanical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 236, 117571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A. Protocols for synthesis of nanomaterials, polymers, and green materials as adsorbents for water treatment technologies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N. Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 17, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.B.; Vakili, M.; Horri, B.A.; Poh, P.E.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Salamatinia, B. Adsorption of dyes by nanomaterials: Recent developments and adsorption mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Samadder, S.R. Removal of arsenic from water using nano adsorbents and challenges: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar]
- Awual, M.R.; Rahman, I.M.M.; Yaita, T.; Khaleque, M.A.; Ferdows, M. pH dependent Cu(II) and Pd(II) ions detection and removal from aqueous media by an efficient mesoporous adsorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R. A novel facial composite adsorbent for enhanced copper(II) detection and removal from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.H.K.; Yun, Y.S. Spinel ferrite magnetic adsorbents: Alternative future materials for water purification? Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 315, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.H.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z. A review on agro-industrial waste (AIW) derived adsorbents for water and wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 227, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, V.D.; Tran, T.K.N.; Nguyen, A.T.; Tran, V.A.; Nguyen, T.D.; Le, V.T. Comparative study on adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes by nanomagnetite supported on biochar derived from Eichhornia crassipes and Phragmites australis stems. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100569. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.B.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.D. Recent advances for dyes removal using novel adsorbents: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tran, V.A.; Kadam, A.N.; Lee, S.W. Adsorption-assisted photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye by zeolite-imidazole-framework-derived nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 835, 155414. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, V.A.; Phung, T.K.; Le, V.T.; Vo, T.K.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, T.A.N.; Viet, D.Q.; Hieu, V.Q.; Vo, T.T.T. Solar-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye over Co3O4-ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2021, 284, 128902. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Tajsabreen, B.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Reshma, B. Effective water/wastewater treatment methodologies for toxic pollutants removal: Processes and applications towards sustainable development. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130595. [Google Scholar]
- Crini, G. Recent developments in polysaccharide-based materials used as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 38–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Asim, M.; Khan, T.A. Low cost adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 170–183. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Basheer, A.A.; Mbianda, X.Y.; Burakov, A.; Galunin, E.; Burakova, I.; Mkrtchyan, E.; Tkachev, A.; Grachev, V. Graphene based adsorbents for remediation of noxious pollutants from wastewater. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 160–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, W.S.; Cheun, J.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; Mubashir, M.; Majeed, Z.; Banat, F.; Ho, S.H.; Show, P.L. A review on conventional and novel materials towards heavy metal adsorption in wastewater treatment application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126589. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Shang, R.; Heijman, S.G.J.; Rietveld, L.C. High-silica zeolites for adsorption of organic micro-pollutants in water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2018, 144, 145–161. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovits, J. Geopolymers: Inorganic polymeric new materials. J. Therm. Anal. 1991, 37, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Criado, M.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Alkali activation of fly ash. Part III: Effect of curing conditions on reaction and its graphical description. Fuel 2010, 89, 3185–3192. [Google Scholar]
- Criado, M.; Palomo, A.; Fernandezjimenez, A. Alkali activation of fly ashes. Part 1: Effect of curing conditions on the carbonation of the reaction products. Fuel 2005, 84, 2048–2054. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A.; Criado, M. Microstructure development of alkali-activated fly ash cement: A descriptive model. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Van Jaarsveld, J.G.S.; van Deventer, J.S.J.; Lukey, G.C. The characterisation of source materials in fly ash-based geopolymers. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Provis, J.L. Geopolymers and other alkali activated materials: Why, how, and what? Mater. Struct. 2013, 47, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Duxson, P.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Mallicoat, S.W.; Kriven, W.M.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Understanding the relationship between geopolymer composition, microstructure and mechanical properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 269, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Ming, L.Y.; Yong, H.C.; Tahir, M.F.M. Clay-based materials in geopolymer technology. In Cement Based Materials; Saleh, H.M., Abdel Rahman, R.O., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 239–264. [Google Scholar]
- Duxson, P.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Provis, J.L.; Lukey, G.C.; Palomo, A.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Geopolymer technology: The current state of the art. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 42, 2917–2933. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Ishwarya, G.; Gupta, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.K. Geopolymer concrete: A review of some recent developments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 85, 78–90. [Google Scholar]
- Perumal, P.; Luukkonen, T.; Sreenivasan, H.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. Porous alkali-activated materials. In New Materials in Civil Engineering; Samui, P., Kim, D., Iyer, N.R., Chaudhary, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 529–563. [Google Scholar]
- Criado, M.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; de la Torre, A.G.; Aranda, M.A.G.; Palomo, A. An XRD study of the effect of the SiO2/Na2O ratio on the alkali activation of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 671–679. [Google Scholar]
- Okoye, F.N.; Durgaprasad, J.; Singh, N.B. Effect of silica fume on the mechanical properties of fly ash based-geopolymer concrete. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 3000–3006. [Google Scholar]
- Panias, D.; Giannopoulou, I.P.; Perraki, T. Effect of synthesis parameters on the mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 301, 246–254. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.S.; Dai, J.G.; Ding, Z.; Xu, W.T. Phosphate-based geopolymer: Formation mechanism and thermal stability. Mater. Lett. 2017, 190, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Tummala, S.; Ramesh, V.; Srikanth, D.K.; Kosaraju, S.; Bobba, P.; Singh, S. Mechanical properties and mix design of geopolymer concrete—A review. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 184, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Tchakouté, H.K.; Rüscher, C.H.; Kamseu, E.; Andreola, F.; Leonelli, C. Influence of the molar concentration of phosphoric acid solution on the properties of metakaolin-phosphate-based geopolymer cements. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 147, 184–194. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolov, A.; Nugteren, H.; Rostovsky, I. Optimization of geopolymers based on natural zeolite clinoptilolite by calcination and use of aluminate activators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 243, 118257. [Google Scholar]
- Görhan, G.; Kürklü, G. The influence of the NaOH solution on the properties of the fly ash-based geopolymer mortar cured at different temperatures. Compos. B Eng. 2014, 58, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Van Jaarsveld, J.G.S.; van Deventer, J.S.J.; Lukey, G.C. The effect of composition and temperature on the properties of fly ash- and kaolinite-based geopolymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 89, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Pu, Z.; Khan, K.A.; Ahmad, I.; Shaukat, A.J.; Hao, Z.; Khan, I. A Review on the effect of silica to alumina ratio, alkaline solution to binder ratio, calcium Oxide + Ferric oxide, molar concentration of sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate to sodium hydroxide ratio on the compressive strength of geopolymer concrete. Silicon 2021, 14, 3147–3162. [Google Scholar]
- Khale, D.; Chaudhary, R. Mechanism of geopolymerization and factors influencing its development: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 729–746. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, M.S.; Dinakar, P.; Rao, B.H. A review of the influence of source material’s oxide composition on the compressive strength of geopolymer concrete. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 234, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, B.C.; Williams, R.P.; Lay, J.; van Riessen, A.; Corder, G.D. Costs and carbon emissions for geopolymer pastes in comparison to ordinary portland cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 1080–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.K.; Collins, F.G. Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-e) emissions: A comparison between geopolymer and OPC cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.H.; Song, J.K.; Song, K.I. Assessment of CO2 reduction of alkali-activated concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 39, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albitar, M.; Mohamed Ali, M.S.; Visintin, P. Evaluation of tension-stiffening, crack spacing and crack width of geopolymer concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albitar, M.; Mohamed Ali, M.S.; Visintin, P.; Drechsler, M. Durability evaluation of geopolymer and conventional concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, P.H.; Paixao, R. Tension stiffening and cracking of concrete reinforced with glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) bars. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2004, 31, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, T.; Ramaswamy, A. A review on fly ash characteristics—Towards promoting high volume utilization in developing sustainable concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, N.; Sayed, E.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Recent progress in environmentally friendly geopolymers: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandoman, M.; Kokabi, M. Sound barrier properties of sustainable waste rubber/geopolymer concretes. Iran. Polym. J. 2015, 24, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, D. Multifunctional structural supercapacitor based on graphene and geopolymer. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 224, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.H.; Wang, A.Y.; Bao, X.F.; Ni, T.Y.; Ling, J. A review on geopolymer in potential coating application: Materials, preparation and basic properties. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 32, 101734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.H.; Mo, K.H.; Ling, T.C.; Lai, S.H. Current development of geopolymer as alternative adsorbent for heavy metal removal. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazama, P.; Bortnovsky, O.; Dědeček, J.; Tvarůžková, Z.; Sobalík, Z. Geopolymer based catalysts—New group of catalytic materials. Catal. Today 2011, 164, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; He, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Cui, X.M. Study on the immobilization of carbonic anhydrases on geopolymer microspheres for CO2 capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 316, 128163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.H.; Zhao, B.Y.; Wu, W.P.; Yang, H.Y.; Ning, Y.S.; Lai, Y.J.; Bradley, R. Low cost, robust, environmentally friendly geopolymer-mesoporous carbon composites for efficient solar powered steam generation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobello, F.; Ielo, I.; Belhamdi, H.; Plutino, M.R. Geopolymers and functionalization strategies for the development of sustainable materials in construction industry and cultural heritage applications: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parathi, S.; Nagarajan, P.; Pallikkara, S.A. Ecofriendly geopolymer concrete: A comprehensive review. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 1701–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.G.; Lu, B.W.; Bai, T.; Wang, H.; Du, F.P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Cai, L.; Jiang, C.; Wang, W.J. Geopolymer, green alkali activated cementitious material: Synthesis, applications and challenges. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 930–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, H.; El-Korchi, T.; Zhang, G.P.; Tao, M.J. Experimental feasibility study of geopolymer as the next-generation soil stabilizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glad, B.E.; Kriven, W.M.; Colombo, P. Highly porous geopolymers through templating and surface interactions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 98, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glad, B.E.; Kriven, W.M.; Scherer, G. Optimization of Gas Adsorption Porosimetry for Geopolymer Analysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 3643–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Rabat, N.E.; Zulfiqar, M.; Man, Z.; Low, A. Fly ash based geopolymer for the adsorption of anionic surfactant from aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
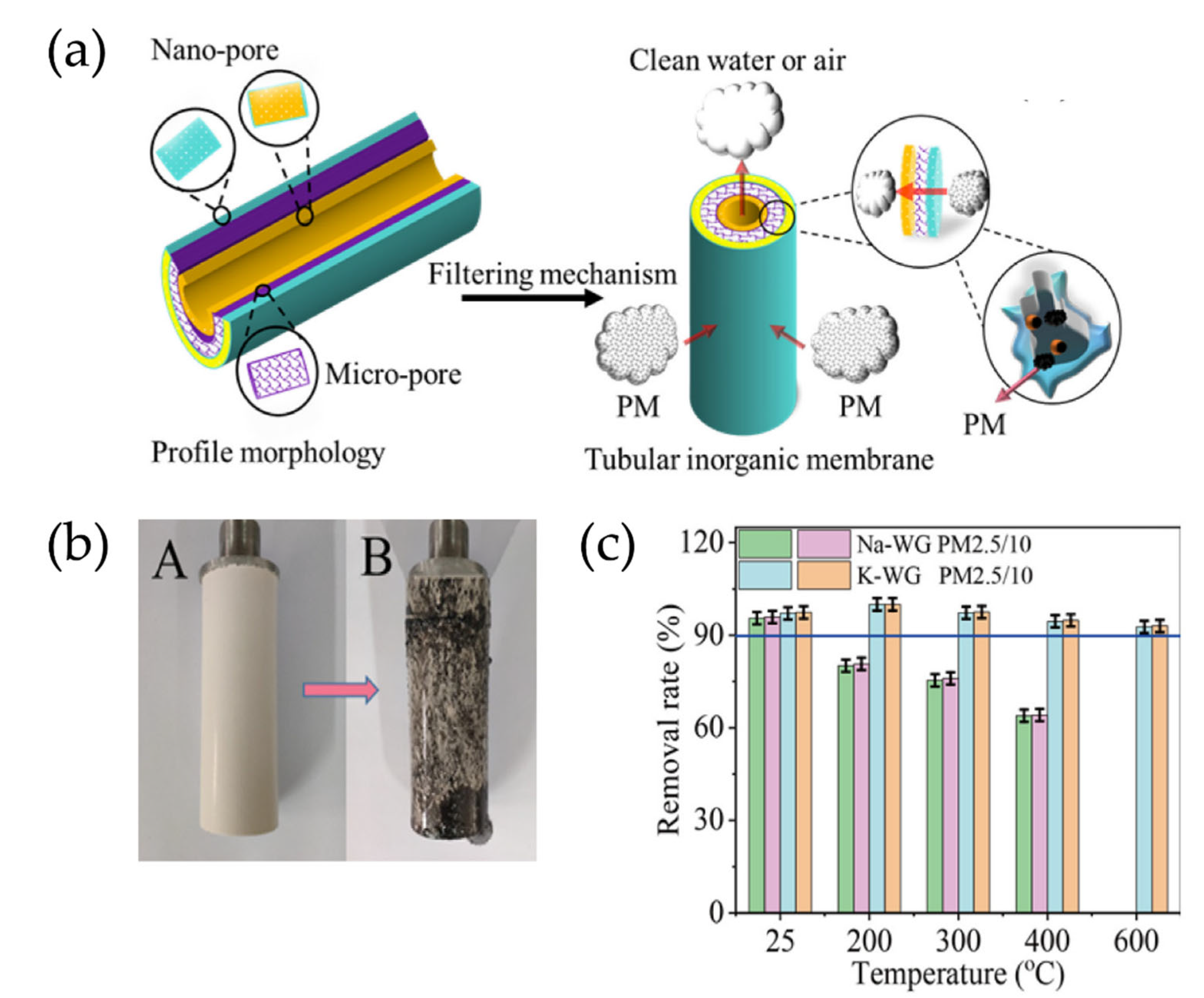
- Zhang, Z.W.; Yu, H.Y.; Xu, M.X.; Cui, X.M. Preparation, characterization and application of geopolymer-based tubular inorganic membrane. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 203, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, E.; Mor, M.; Natali Murri, A.; Landi, E.; Medri, V. Ice-templated geopolymer beads for dye removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 572, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, E.; Medri, V.; Paillard, C.; Contri, B.; Natali Murri, A.; Vaccari, A.; Landi, E. Geopolymer-hydrotalcite composites for CO2 capture. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, F.Y.; Wang, L.; Rong, Y.D.; He, P.G.; Jia, D.C.; Yang, J.L. A green and low-cost hollow gangue microsphere/geopolymer adsorbent for the effective removal of heavy metals from wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, S.J.; MacKenzie, K.J.D.; Smith, M.E.; Hanna, J.V. Ion exchange in the charge-balancing sites of aluminosilicate inorganic polymers. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 10234–10240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorina, T. Ion exchange in amorphous alkali-activated aluminosilicates: Potassium based geopolymers. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 87, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W.; Ren, D. Development of fly ash and iron ore tailing based porous geopolymer for removal of Cu(II) from wastewater. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 13507–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, I.; Tunc, D.; Sayin, F.; Akar, S.T. Study on the performance of metakaolin based geopolymer for Mn(II) and Co(II) removal. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, C.J.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, H.Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, W. A comparative study on fly ash, geopolymer and faujasite block for Pb removal from aqueous solution. Fuel 2016, 185, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Li, P.F.; Rehman, F.U.; Li, X.L.; Yang, W.; Guo, S.W. Efficient adsorption of Cd2+ from aqueous solution using metakaolin geopolymers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33555–33567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, İ.; Yilmazer, D.; Akar, S.T. Metakaolin based geopolymer as an effective adsorbent for adsorption of zinc(II) and nickel(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 139, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.J.; Guo, L.; Ren, D.M.; Duan, P. Novel composites based on geopolymer for removal of Pb(II). Mater. Lett. 2019, 239, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Abou El-Reash, Y.G.; Youssef, H.M.; Kotp, Y.H.; Hegazey, R.M. Utilization of rice husk and waste aluminum cans for the synthesis of some nanosized zeolite, zeolite/zeolite, and geopolymer/zeolite products for the efficient removal of Co(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) ions from aqueous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Věžníková, K.; Tolonen, E.-T.; Runtti, H.; Yliniemi, J.; Hu, T.; Kemppainen, K.; Lassi, U. Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater with powdered and granulated metakaolin geopolymer. Environ. Technol. 2017, 39, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luukkonen, T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Metakaolin geopolymer characterization and application for ammonium removal from model solutions and landfill leachate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguanpak, S.; Wannagon, A.; Saengam, C.; Chiemchaisri, W.; Chiemchaisri, C. Porous metakaolin-based geopolymer granules for removal of ammonium in aqueous solution and anaerobically pretreated piggery wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runtti, H.; Luukkonen, T.; Niskanen, M.; Tuomikoski, S.; Kangas, T.; Tynjälä, P.; Tolonena, E.T.; Sarkkinen, M.; Kemppainen, K.; Rämö, J.; et al. Sulphate removal over barium-modified blast-furnace-slag geopolymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.W.; Lee, M.L.; Ko, M.S.; Ueng, T.H.; Yang, S.F. The heavy metal adsorption characteristics on metakaolin-based geopolymer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 56, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Carvalheiras, J.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Pullar, R.C.; Labrincha, J.A. Synthesis of porous biomass fly ash-based geopolymer spheres for efficient removal of methylene blue from wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Mohammad, M.; Emdadi, Z.; Asim, N.; Azizi, M.; Safaei, J. Adsorbent materials based on a geopolymer paste for dye removal from aqueous solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 3017–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; He, P.G.; Jia, D.C.; Wang, Q.G.; Liu, J.J.; Yang, J.L.; Huang, Y. Synthesis of novel low-cost porous gangue microsphere/geopolymer composites and their adsorption properties for dyes. Int. J. Appl. Geram. Technol. 2018, 15, 1602–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z. Geopolymeric adsorbents from fly ash for dye removal from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 300, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, P.; Sellaoui, L.; Franco, D.; Netto, M.S.; Luiz Dotto, G.; Bajahzar, A.; Belmabrouk, H.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Li, Z. Adsorption of acid green and procion red on a magnetic geopolymer based adsorbent: Experiments, characterization and theoretical treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açışlı, Ö.; Acar, İ.; Khataee, A. Preparation of a surface modified fly ash-based geopolymer for removal of an anionic dye: Parameters and adsorption mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, T.R.; Foletto, E.L.; Dotto, G.L.; Jahn, S.L. Preparation of mesoporous geopolymer using metakaolin and rice husk ash as synthesis precursors and its use as potential adsorbent to remove organic dye from aqueous solutions. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.F.; Montao, A.M.; González, C.; Barón, G. Removal of rhodamine B in wastewater from the textile industry using geopolymeric material. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1386, 012040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumba, G.; Essomba, J.S.; Tagne, G.M.; Nsami, J.N.; Mbadcam, J.K. Equilibrium and kinetic adsorption studies of methyl orange from aqueous solutions using kaolinite, metakaolinite and activated geopolymer as low cost adsorbents. J. Acad. Ind. Res. 2014, 3, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Medri, V.; Papa, E.; Mor, M.; Vaccari, A.; Natali Murri, A.; Piotte, L.; Melandri, C.; Landi, E. Mechanical strength and cationic dye adsorption ability of metakaolin-based geopolymer spheres. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 193, 105678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.K.; Chang, Q.B.; Li, C.X. Rapid removal of methylene blue and nickel ions and adsorption/desorption mechanism based on geopolymer adsorbent. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 45, 100551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmapriya, M.; Ramesh, S.T.; Biju, V.M. Synthesis of seawater based geopolymer: Characterization and adsorption capacity of methylene blue from wastewater. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 51, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossatto, D.L.; Netto, M.S.; Jahn, S.L.; Mallmann, E.S.; Dotto, G.L.; Foletto, E.L. Highly efficient adsorption performance of a novel magnetic geopolymer/Fe3O4 composite towards removal of aqueous acid green 16 dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadeck Netto, M.; Leindcker Rossatto, D.; Jahn, S.L.; Stoffels Mallmann, E.; Luiz Dotto, G.; Luiz Foletto, E. Preparation of a novel magnetic geopolymer/zero–valent iron composite with remarkable adsorption performance towards aqueous Acid Red 97. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2019, 207, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, K.G.; Botti, R.; Kavun, V.; Gafiullina, A.; Franchin, G.; Repo, E.; Colombo, P. Geopolymer beads and 3D printed lattices containing activated carbon and hydrotalcite for anionic dye removal. Catal. Today 2022, 390–391, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tome, S.; Hermann, D.T.; Shikuku, V.O.; Otieno, S. Synthesis, characterization and application of acid and alkaline activated volcanic ash-based geopolymers for adsorptive remotion of cationic and anionic dyes from water. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 20965–20973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, A.A.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Khan, M.I.; Rabat, N.E.; Zulfiqar, M.; Man, Z.; Siame, J.; Azizli, K.A. A review on geopolymers as emerging materials for the adsorption of heavy metals and dyes. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscherini, M.; Miccio, F.; Papa, E.; Medri, V.; Landi, E.; Doghieri, F.; Minelli, M. The relevance of thermal effects during CO2 adsorption and regeneration in a geopolymer-zeolite composite: Experimental and modelling insights. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, M.; Medri, V.; Papa, E.; Miccio, F.; Landi, E.; Doghieri, F. Geopolymers as solid adsorbent for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 148, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minelli, M.; Papa, E.; Medri, V.; Miccio, F.; Benito, P.; Doghieri, F.; Landi, E. Characterization of novel geopolymer—Zeolite composites as solid adsorbents for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 341, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candamano, S.; Policicchio, A.; Macario, A.; Conte, G.; Agostino, R.G.; Frontera, P.; Crea, F. CO2 Adsorption Investigation on an Innovative Nanocomposite Material with Hierarchical Porosity. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 3223–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikova, L.A.; Bogdanov, D.S.; Belchinskaya, L.I.; Kolousek, D.; Doushova, B.; Lhotka, M.; Petukhova, G.A. Adsorption of formaldehyde from aqueous solutions using metakaolin-based geopolymer sorbents. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2019, 55, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Vedachalam, S.; Dalai, A.K. Performance of geopolymer as adsorbent on desulphurization of heavy gas oil. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 99, 2355–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rocca, D.G.; Peralta, R.M.; Peralta, R.A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Moreira, R.D.P.M. Adding value to aluminosilicate solid wastes to produce adsorbents, catalysts and filtration membranes for water and wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 56, 1039–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzada, N.K.; Farid, M.U.; Kharraz, J.A.; Choi, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Nghiem, L.D.; Jang, A.; An, A.K. Removal of organic micropollutants using advanced membrane-based water and wastewater treatment: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 598, 117672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Ascensão, G.; Tobaldi, D.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Biomass fly ash geopolymer monoliths for effective methylene blue removal from wastewaters. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, K.T.; He, Y.; Cui, X.M. Preparation of geopolymer-based inorganic membrane for removing Ni2+ from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Ge, Y.Y.; He, Y.; Xu, M.X.; Cui, X.M. A porous gradient geopolymer-based tube membrane with high PM removal rate for air pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, F.A.; Della-Rocca, D.; de Amorim, S.M.; Salla, J.D.; Peralta, R.A.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Moreira, R.F.P.M. Development of Membranes Based on Alkali-Activated Phosphate Mine Tailings for Humic Acid and Copper Removal from Water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.X.; He, Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Tong, Z.F.; Cui, X.M. Preparation of geopolymer inorganic membrane and purification of pulp-papermaking green liquor. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Ding, S.Y.; Ge, Y.Y.; Li, Z.L. Enhanced removal of crystal violet in water using a facile-fabricated and environmental-friendly laccase immobilized composite membrane. Process Biochem. 2020, 98, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.N.; Tang, S.Q.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.T. Defective analcime/geopolymer composite membrane derived from fly ash for ultrafast and highly efficient filtration of organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.B.; Ge, Y.Y.; Li, Z.L.; Wang, Y.P. Facile fabrication of a low-cost and environmentally friendly inorganic-organic composite membrane for aquatic dye removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 256, 109969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luukkonen, T.; Heponiemi, A.; Runtti, H.; Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Lassi, U. Application of alkali-activated materials for water and wastewater treatment: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 271–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



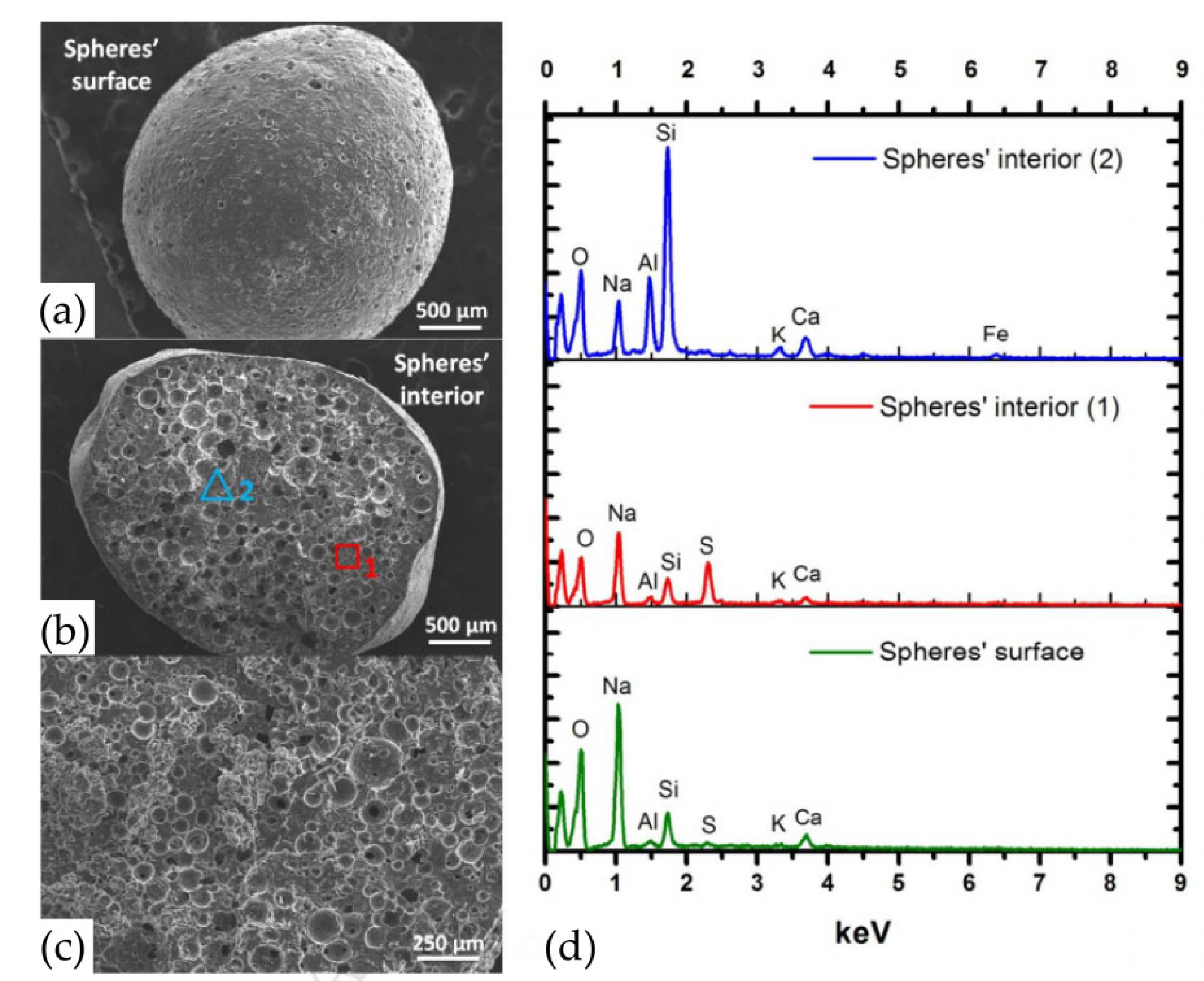
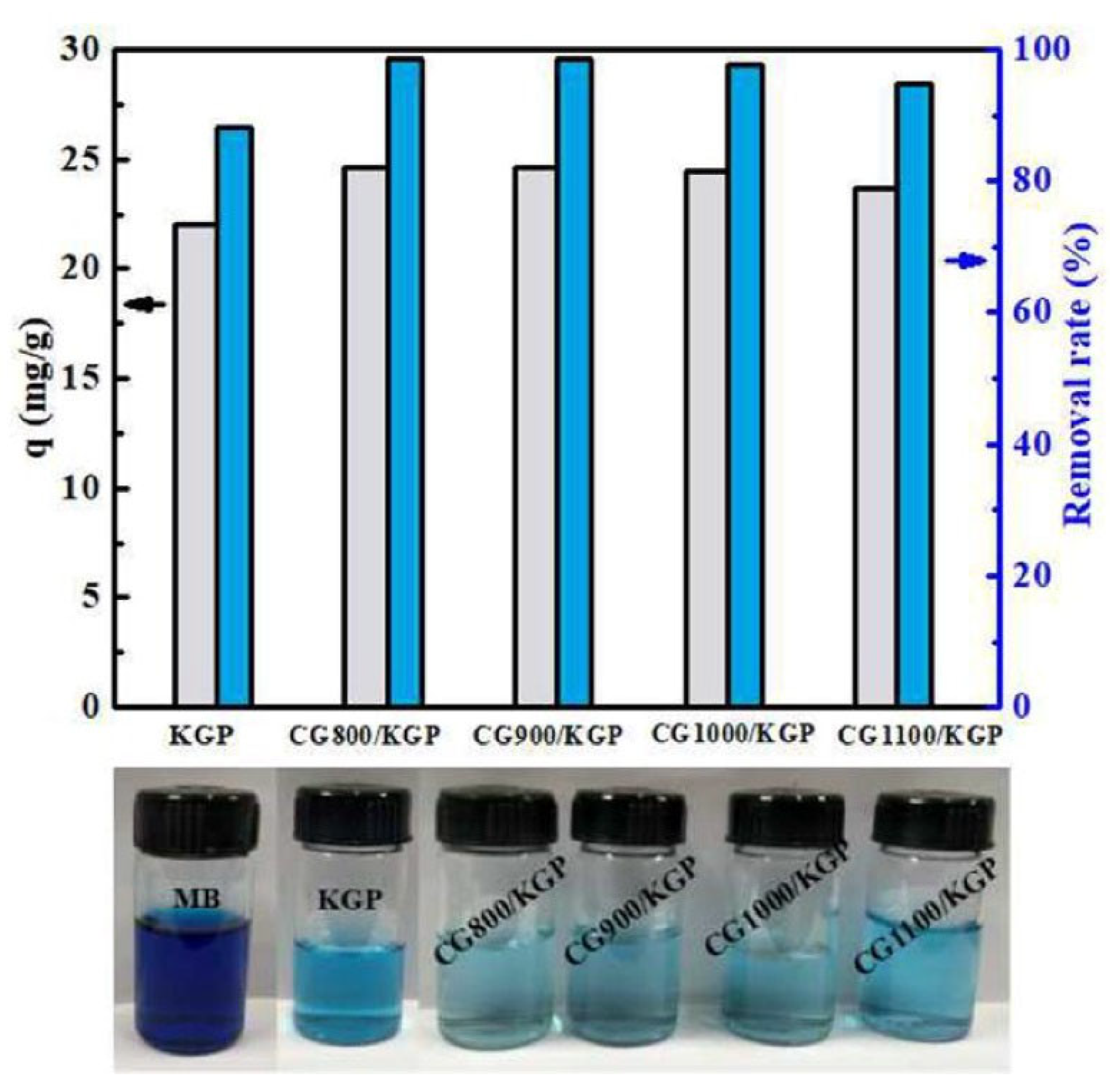
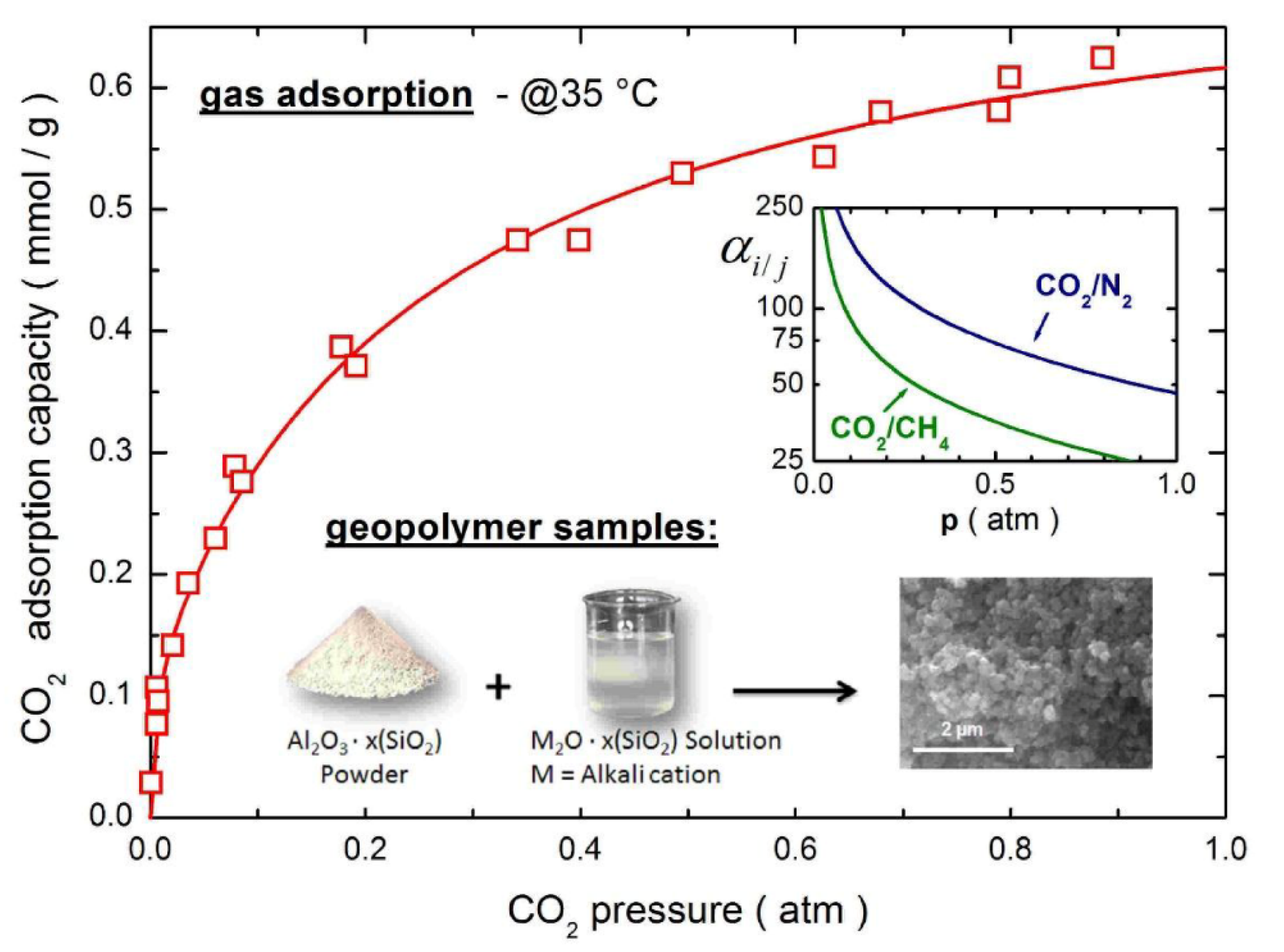
| Geopolymer | Dye | Co (ppm) | qmax (mg/g) | R (%) | SSA (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (mm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G13A-20TiO2 geopolymer | MB | 50 | 42 | 82 | 20 | 714 | 110 | [103] |
| Synthesized geopolymer paste | MB | 32 | n.r. 1 | 85.6 | 5.8 | n.r. | 1300 | [95] |
| CG900/KGP porous particles | MB | 100 | n.r. | 98.5 | 37.3 | 352 | 37.8 | [96] |
| Metakaolin-based geopolymer | MB | 60 | 2.7 | 81.5 | 26.4 | n.r. | 30.3 | [104] |
| G-70-P geopolymer | MB | 50 | 5.1 | 99 | 21 | 1252 | 320 | [77] |
| Seawater-based geopolymer | MB | n.r. | 59.5 | 81.4 | 11.9 | 25 | 25 | [105] |
| CTAB-modified fly ash-based powder | AB 185 | 30 | 0.2 | 96.8 | 34.9 | 138 | 11.7 | [99] |
| Magnetic geopolymer | AG | n.r. | n.r. | n.r. | 19.5 | 45.3 | 10.4 | [98] |
| Magnetic geopolymer | PR | n.r. | n.r. | n.r. | 19.5 | 45.3 | 10.4 | [98] |
| Magnetic geopolymer | AG 16 | 50 | 400 | 85.9 | 53.4 | 190 | 14.1 | [106] |
| Magnetic geopolymer | Acid Red 97 | 100 | 1814.3 | 97 | 42.9 | 52.3 | 4.9 | [107] |
| MGP geopolymer | MV10B | 50 | 21.6 | 73.8 | 62 | 360 | 14.3 | [100] |
| Geopolymer lattice with activated carbon (3D Printing) | Orange II | 400 | 66.5 | n.r. | 185.6 | n.r. | n.r. | [108] |
| Alkaline-activated geopolymer | Eriochrome Black T | 40 | 251 | 98 | 74.5 | 60 | 3.2 | [109] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, D.; Zhong, G.; Sun, Y.; Hu, X.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, M.; et al. Research and Application Progress of Geopolymers in Adsorption: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12173002
Xu J, Li M, Zhao D, Zhong G, Sun Y, Hu X, Sun J, Li X, Zhu W, Li M, et al. Research and Application Progress of Geopolymers in Adsorption: A Review. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(17):3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12173002
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jinyun, Minjing Li, Di Zhao, Guoqiang Zhong, Yu Sun, Xudong Hu, Jiefang Sun, Xiaoyun Li, Wenju Zhu, Ming Li, and et al. 2022. "Research and Application Progress of Geopolymers in Adsorption: A Review" Nanomaterials 12, no. 17: 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12173002
APA StyleXu, J., Li, M., Zhao, D., Zhong, G., Sun, Y., Hu, X., Sun, J., Li, X., Zhu, W., Li, M., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhao, L., Zheng, C., & Sun, X. (2022). Research and Application Progress of Geopolymers in Adsorption: A Review. Nanomaterials, 12(17), 3002. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12173002