A Review of the Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Utilising Southern African Indigenous Medicinal Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
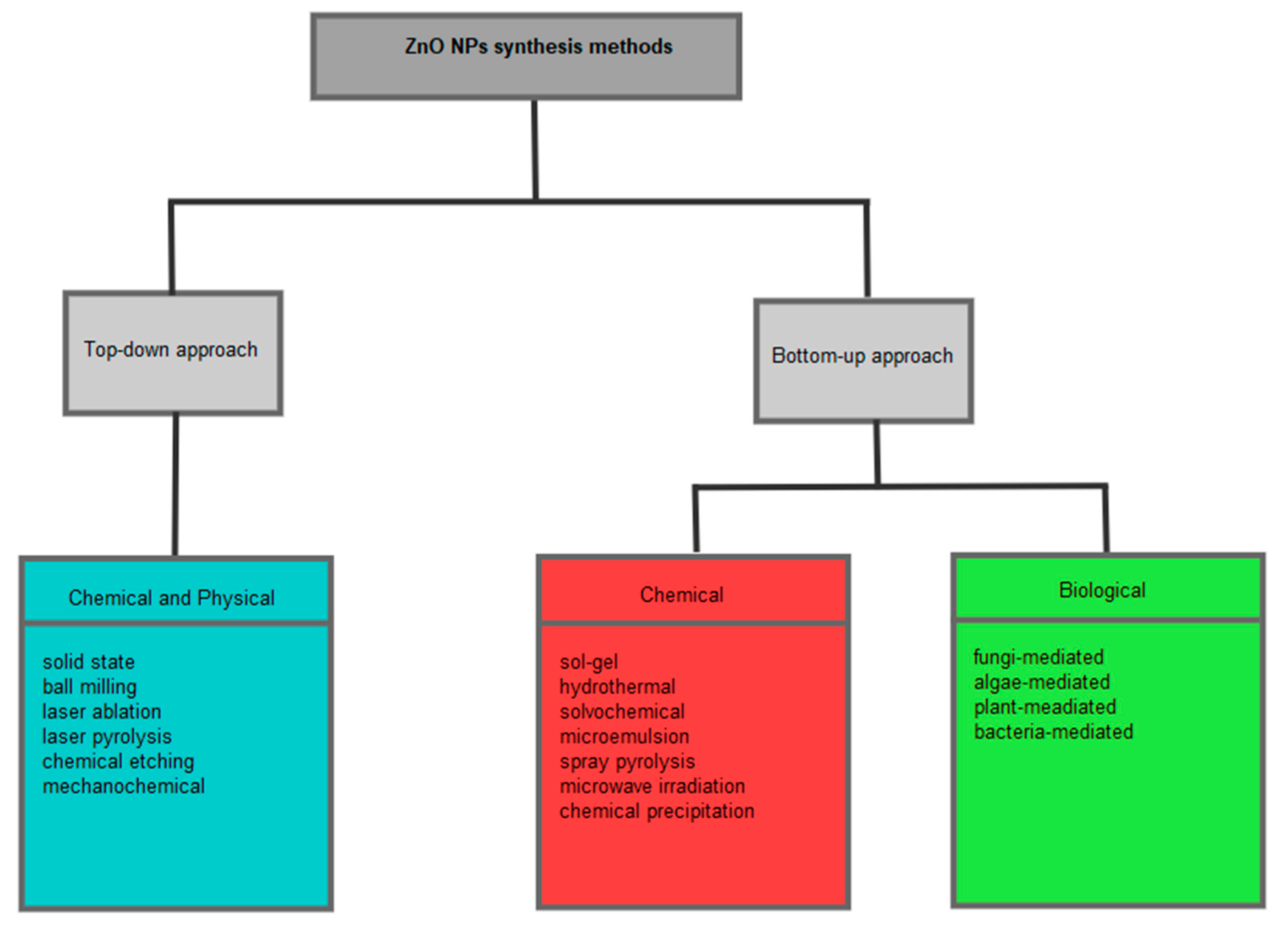
2. Properties and Synthesis of ZnO NPs
2.1. Properties of ZnO NPs
2.2. Synthesis of ZnO NPs
2.3. Green Synthesis
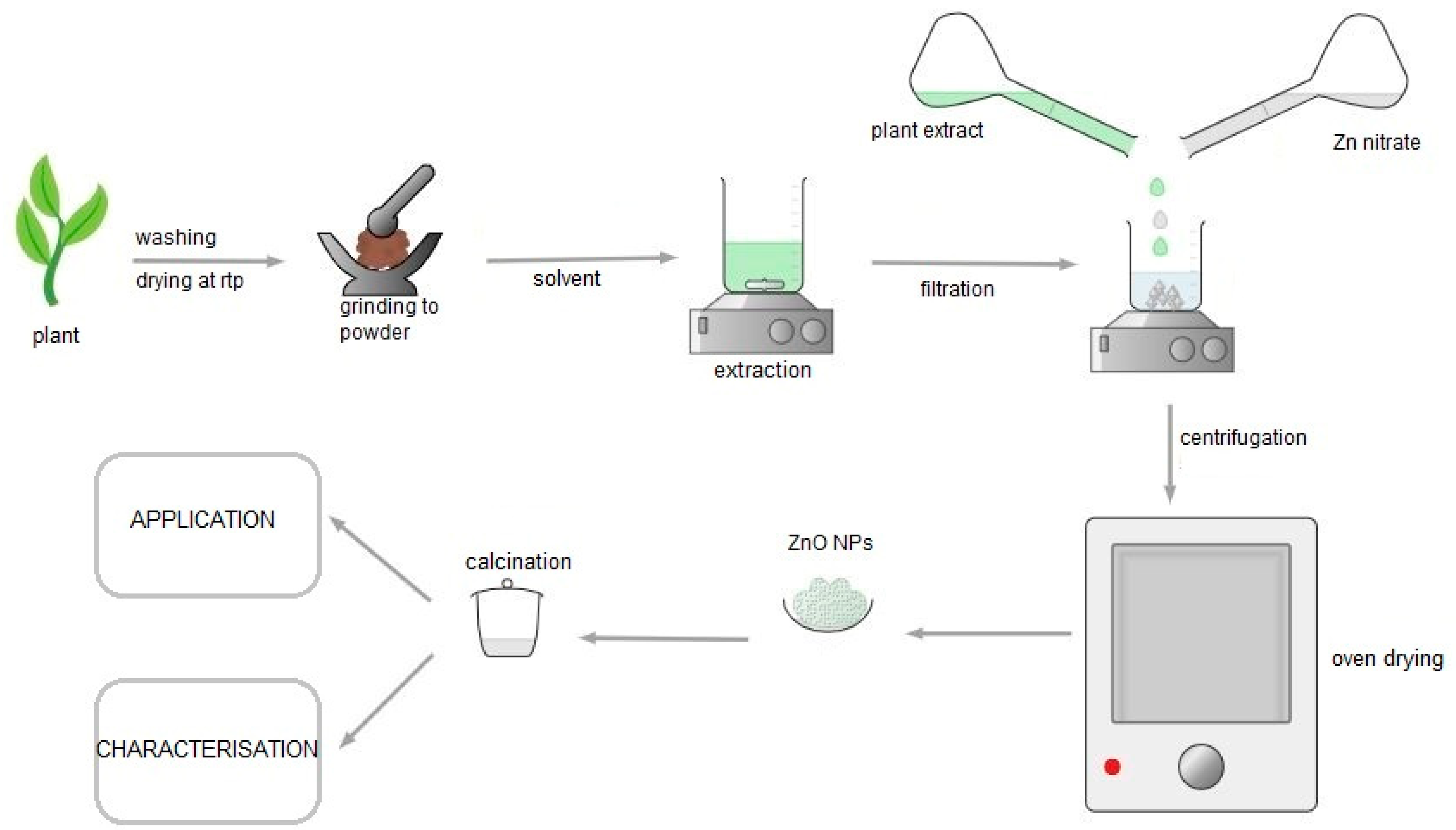
2.3.1. Plant-Mediated Synthesis
2.3.2. Plant-Mediated Synthesis of ZnO NPs Procedure
2.3.3. Factors Affecting Synthesis of Plant-Mediated ZnO NPs
3. Green Synthesis of ZnO NPs Using Some Indigenous Plant of Southern Africa
3.1. Indigenous Medicinal Plants of Southern Africa
3.2. Plant-Mediated Synthesis of ZnO NPs Using Some Indigenous Medical Plant Extract of Southern Africa and Their Applications
3.2.1. Agathosma betulina
3.2.2. Plumbago auriculata
3.2.3. Monsomia burkeana
3.2.4. Lessertia montana
3.2.5. Lessertia frutescens
3.2.6. Tulbaghia violacea
3.2.7. Aspalathus linearis
3.2.8. Dovyalis caffra
3.2.9. Athrixia phylicoides DC
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ntozakhe, L.; Tichaona Taziwa, R. Pyrolysis of Carbon-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for Solar Cell Application. In Zinc Oxide Based Nano Materials and Devices; Intechopen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mungondori, H.H.; Ramujana, S.; Katwire, D.M.; Taziwa, R.T. Synthesis of a Novel Visible Light Responsive γ-Fe2O3/SiO2/C-TiO2 Magnetic Nanocomposite for Water Treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauricio, M.D.; Guerra-Ojeda, S.; Marchio, P.; Valles, S.L.; Aldasoro, M.; Escribano-Lopez, I.; Herance, J.R.; Rocha, M.; Vila, J.M.; Victor, V.M. Nanoparticles in Medicine: A Focus on Vascular Oxidative Stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rastogi, A.; Tripathi, D.K.; Yadav, S.; Chauhan, D.K.; Živčák, M.; Ghorbanpour, M.; El-Sheery, N.I.; Brestic, M. Application of Silicon Nanoparticles in Agriculture. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamkhande, P.G.; Ghule, N.W.; Bamer, A.H.; Kalaskar, M.G. Metal Nanoparticles Synthesis: An Overview on Methods of Preparation, Advantages and Disadvantages, and Applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J. Lipid Nanoparticles Based Cosmetics with Potential Application in Alleviating Skin Disorders. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freynman, R.P. There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom. Eng. Sci. 1960, 23, 22–36. [Google Scholar]
- Janaki, A.C.; Sailatha, E.; Gunasekaran, S. Synthesis, Characteristics and Antimicrobial Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 144, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, T.A. Nanomaterials: Classification, Properties, and Environmental Toxicities. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, Applications and Toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Venkat Kumar, S.; Rajeshkumar, S. A Review on Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles—An Eco-Friendly Approach. Resour. Effic. Technol. 2017, 3, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldegebrieal, G.K. Synthesis Method, Antibacterial and Photocatalytic Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles for Azo Dyes in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 120, 108140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Abbes, N.; Jing, X.; Zhang, L. A Review of the Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts and Their Prospects for Application in Antibacterial Textiles. J. Eng. Fiber Fabr. 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintelu, S.A.; Folorunso, A.S. A Review on Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts and Its Biomedical Applications. Bionanoscience 2020, 10, 848–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummer, S.; Madzimbamuto, T.; Chowdhury, M. Green Synthesis of Transition-Metal Nanoparticles and Their Oxides: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, D.; Nethravathi, P.C.; Rajanaika, H.; Nagabhushana, H.; Sharma, S.C. Green Synthesis of Multifunctional Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles Using Cassia Fistula Plant Extract and Their Photodegradative, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 31, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Kalra, D. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Anti Microbial Activities of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Euphorbia Hirta Leaf Extract. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 2358–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Lawerence, R. Green Synthesis and Charcterization of ZnO Nanoparticles from Leafs Extracts of Rosa Indica and Its Antibacterial Activity. Rasayan J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, J.; Pradheesh, G.; Alexramani, V.; Sundrarajan, M.; Hong, S.I. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Using Insulin Plant (Costus Pictus D. Don) and Investigation of Its Antimicrobial as Well as Anticancer Activities. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, M.; Anbuvannan, M.; Viruthagiri, G. Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Solanum Nigrum Leaf Extract and Their Antibacterial Activity. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 136, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuuren, S.F. Antimicrobial Activity of South African Medicinal Plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thema, F.T.; Manikandan, E.; Dhlamini, M.S.; Maaza, M. Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles via Agathosma Betulina Natural Extract. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melk, M.M.; El-Hawary, S.S.; Melek, F.R.; Saleh, D.O.; Ali, O.M.; el Raey, M.A.; Selim, N.M. Nano Zinc Oxide Green-Synthesized from Plumbago Auriculata Lam. Alcoholic Extract. Plants 2021, 10, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoepe, N.M.; Mbita, Z.; Mathipa, M.; Mketo, N.; Ntsendwana, B.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Biogenic Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Monsonia Burkeana for Use in Photocatalytic, Antibacterial and Anticancer Applications. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16999–17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, F.O.; Ashafa, A.O.T. Potentials of Synthesised Lessertia Montana Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Free Radicals-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Carbohydrate- Hydrolysing Enzymes. Acta Biol. Szeged. 2021, 64, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlaule-Glory, L.M.; Mbita, Z.; Ntsendwana, B.; Mathipa, M.M.; Mketo, N.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. ZnO Nanoparticles via Sutherlandia Frutescens Plant Extract: Physical and Biological Properties. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 085006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbenga, Y.; Mthiyane, M.N.; Botha, T.L.; Horn, S.; Pieters, R.; Wepener, V.; Onwudiwe, D.C. Nanoarchitectonics of ZnO Nanoparticles Mediated by Extract of Tulbaghia Violacea and Their Cytotoxicity Evaluation. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 3249–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, A.; Ngom, B.D.; Park, E.; Maaza, M. Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles by Aspalathus Linearis: Structural & Optical Properties. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 646, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, J.O.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Oyedeji, A.O. Biogenic Synthesis of CuO, ZnO, and CuO–ZnO Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extracts of Dovyalis Caffra and Their Biological Properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, J.O.; Elemike, E.E.; Onwudiwe, D.C. ZnO Nanoparticles Mediated by Aqueous Extracts of Dovyalis Caffra Fruits and the Photocatalytic Evaluations. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaningini, A.G.; Azizi, S.; Sintwa, N.; Mokalane, K.; Mohale, K.C.; Mudau, F.N.; Maaza, M. Effect of Optimized Precursor Concentration, Temperature, and Doping on Optical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized via a Green Route Using Bush Tea ( Athrixia Phylicoides DC.) Leaf Extracts. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 31658–31666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uikey, P.; Vishwakarma, K. Review of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles Applications and Properties. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. Sci. Electron. (IJETCSE) 2016, 21, 976–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Parihar, V.; Raja, M.; Paulose, R. A Brief Review of Structural, Electrical and Electrochemical Properties of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagadevan, S.; Raj, K.P.; Aziz, F.A.; Chowdhury, Z.Z.; bin Johan, M.R.; Podder, J. Structure, Properties, Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activity and Applications of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles-An Overview. J. Bionanoscience 2018, 12, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.Y.; Pang, Y.L.; Lim, S.; Chong, W.C. Facile Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Natural-Based Materials: Properties, Mechanism, Surface Modification and Application. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, P.; Inakhunbi Chanu, T.; Samanta, D.; Chatterjee, S. A Review on Bio-Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts as Reductants and Stabilizing Agents. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 183, 201–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, N.; Khan, A.M.; Shujait, S.; Chaudhary, K.; Ikram, M.; Imran, M.; Haider, J.; Khan, M.; Khan, Q.; Maqbool, M. Synthesis of Nanomaterials Using Various Top-down and Bottom-up Approaches, Influencing Factors, Advantages, and Disadvantages: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 300, 102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, G.; Thirumarimurugan, M.; Muthukumaran, C. Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Tecoma Castanifolia Leaf Extract: Characterization and Evaluation of Its Antioxidant, Bactericidal and Anticancer Activities. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Ishak, N.A.I.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Timmiati, S.N. Green Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles via Plant Extracts: An Overview. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suba, S.; Vijayakumar, S.; Vidhya, E.; Punitha, V.N.; Nilavukkarasi, M. Microbial Mediated Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Derived from Lactobacillus Spp: Characterizations, Antimicrobial and Biocompatibility Efficiencies. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefny, M.E.; El-Zamek, F.I.; Abd El-Fattah, H.; Mahgoub, S. Biosynthesis of Zinc Nanoparticles Using Culture Filtrates of Aspergillus, Fusarium and Penicillium Fungal Species and Their Antibacterial Properties against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Biotechnol. Res. 2019, 46, 2009–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, P.K.; Jain, V.K.; Sharma, S.; Shrivastav, A.K.; Sharma, R. Green and Chemically Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles: A Comparative Study. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 798, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunalan, S.; Sivaraj, R.; Rajendran, V. Green Synthesized ZnO Nanoparticles against Bacterial and Fungal Pathogens. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 22, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, T.; Mishra, K.; Khanuja, M.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Azadirachta Indica for Antibacterial and Photocatalytic Applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 32, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, A.; Railean-Plugaru, V.; Pomastowski, P.; Buszewski, B. Phytochemical Investigation of Medicago Sativa L. Extract and Its Potential as a Safe Source for the Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles: The Proposed Mechanism of Formation and Antimicrobial Activity. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 31, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayachandran, A.; Aswathy, T.R.; Nair, A.S. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Cayratia Pedata Leaf Extract. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 100995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism. Nanomicro. Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Padalia, H.; Baluja, S.; Chanda, S. Effect of PH on Size and Antibacterial Activity of Salvadora Oleoides Leaf Extract-Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Bionanoscience 2017, 7, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umamaheswari, A.; Prabu, S.L.; John, S.A.; Puratchikody, A. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extracts of Raphanus Sativus Var. Longipinnatus and Evaluation of Their Anticancer Property in A549 Cell Lines. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagier, M.A. Plant-Mediated Biosynthesis and Photocatalysis Activities of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Prospect towards Dyes Mineralization. J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, Y.N.; Torres, E.; Blázquez, M.L.; Ballester, A.; González, F.; Muñoz, J.A. Gold(III) Biosorption and Bioreduction with the Brown Alga Fucus Vesiculosus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukri, S.N.A.M.; Isa, E.D.M.; Shameli, K. Photocatalytic Degradation of Malachite Green Dye by Plant-Mediated Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 808, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.M.; Ghasemi, N. Influence of Temperature and Concentration on Biosynthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Cherry Extract. J. Nanostructure. Chem. 2018, 8, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahomoodally, M.F. Traditional Medicines in Africa: An Appraisal of Ten Potent African Medicinal Plants. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 617459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Wyk, B.E. The Potential of South African Plants in the Development of New Medicinal Products. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2011, 77, 812–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aboyewa, J.A.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Meyer, M.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications. Plants 2021, 10, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavimbela, T.; Viljoen, A.; Vermaak, I. Differentiating between Agathosma Betulina and Agathosma Crenulata—A Quality Control Perspective. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2014, 1, e8–e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendler, T.; Abdel-Tawab, M. Buchu (Agathosma Betulina and A. Crenulata): Rightfully Forgotten or Underutilized? Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 813142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolla, A.; van Vuuren, S.F.; van Zyl, R.L.; Viljoen, A.M. Biological Activity and Toxicity Profile of 17 Agathosma (Rutaceae) Species. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2007, 73, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thema, F.T.; Beukes, P.; Gurib-Fakim, A.; Maaza, M. Green Synthesis of Monteponite CdO Nanoparticles by Agathosma Betulina Natural Extract. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 646, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thema, F.T.; Manikandan, E.; Gurib-Fakim, A.; Maaza, M. Single Phase Bunsenite NiO Nanoparticles Green Synthesis by Agathosma Betulina Natural Extract. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 657, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thema, F.T.; Letsholathebe, D.; Mphale, K. Enhanced Antibacterial Properties of Green Synthesized Nano Ceria via Agathosma Betulina Natural Extract. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 36, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Naidoo, Y.; Baijnath, H. A Comprehensive Review on the Genus Plumbago with Focus on Plumbago Auriculata (Plumbaginaceae). Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 15, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Naidoo, Y.; Bharuth, V.; Baijnath, H. Micromorphology and Histochemistry of the Secretory Apparatus of Plumbago Auriculata Lam. South Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 121, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, G.; Bupesh, G.; Vignesh, A.; Sathiyaseelan, A.; Murugesan, K. Micropropagation and Anticancer Activity of Methanolic Extract of Plumbago Auriculata Lam. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res. (IJBR) 2016, 7, 2001–2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tharmaraj, R.J.J.M.; Antonysamy, J.M. Studies on Inter-Specific Variation in the Genus Plumbago (Plumbaginaceae) from South India Using Phytochemical Analysis. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 2013, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelbaky, A.S.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Babalghith, A.O.; Selim, S.; Mohamed, A.M.H.A. Green Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Pelargonium Odoratissimum (L.) Aqueous Leaf Extract and Their Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, L.; Anbazhagan, S.; Altemimi, A.B.; Lakshminarayanan, K.; Kuppan, S.; Pratap-Singh, A.; Kandasamy, M. Efficacy of Antimicrobial and Larvicidal Activities of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Plumbago Auriculata Lam. Plants 2020, 9, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamphiswana, N.D.; Mashela, P.W.; Mdee, L.K. Distribution of Total Phenolics and Antioxidant Activity in Fruit, Leaf, Stem and Root of Monsonia Burkeana. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 2570–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnzeru, L.R.; Ntushelo, K.; Mudau, F.N. Prevalence of Bacillus in the Interior Tissues of Monsonia Burkeana and Other Medicinal Plants in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 113, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tshivhandekano, I.; Ntushelo, K.; Ngezimana, W.; Tshikalange, T.E.; Mudau, F.N. Chemical Compositions and Antimicrobial Activities of Athrixia Phylicoides DC. (Bush Tea), Monsonia Burkeana (Special Tea) and Synergistic Effects of Both Combined Herbal Teas. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, S448–S453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronald Nnzeru, L.; Ntushelo, K.; Nixwell Mudau, F. Physical Appraisal and Attributes of Monsonia Burkeana (Special Tea): The Perspective of Tea Users. Afr. J. Indig. Knowl. Syst. 2016, 15, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ngoepe, N.M.; Mathipa, M.M.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Biosynthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles for the Photodegradation of Dyes and Removal of Bacteria. Opt. Int. J. Light Electron. 2020, 224, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahsay, M.H. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Becium Grandiflorum for Antimicrobial Activity and Adsorption of Methylene Blue. Appl. Water. Sci. 2021, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Jan, H.; Shah, S.A.; Shah, S.; Khan, A.; Akbar, M.T.; Rizwan, M.; Jan, F.; Wajidullah; Akhtar, N.; et al. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Fruit Extracts of Myristica Fragrans: Their Characterizations and Biological and Environmental Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9709–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ware, P.; Shimpi, N. Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Using Peels of Passiflora Foetida and Study of Its Activity as an Efficient Catalyst for the Degradation of Hazardous Organic Dye. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kganyago, P.; Mahlaule-Glory, L.M.; Mathipa, M.M.; Ntsendwana, B.; Mketo, N.; Mbita, Z.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Synthesis of NiO Nanoparticles via a Green Route Using Monsonia Burkeana: The Physical and Biological Properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 182, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashafa, A.O.T.; Balogun, F.O.; Adegbegi, A.J. Inhibitory Potentials and Kinetics of the Inhibition of Carbohydratehydrolysing Enzymes by the Pod and Seed Extracts of Lessertia Montana (Fabaceae) E. Phillips & R.A. Dyer. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alimi, A.A.; Ashafa, A.O.T. An in Vitro Evaluation of the Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Potential of Sutherlandia Montana E. Phillips & R.A. Dyer Leaf Extracts. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xaba, P. The cancer bush, a timeless remedy: Gardening with traditionally useful plants. Veld Flora 2007, 93, 234–236. [Google Scholar]
- van Wyk, B.E.; Albrecht, C. A Review of the Taxonomy, Ethnobotany, Chemistry and Pharmacology of Sutherlandia Frutescens (Fabaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wyk, B.E. A Broad Review of Commercially Important Southern African Medicinal Plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboyade, O.M.; Styger, G.; Gibson, D.; Hughes, G. Sutherlandia Frutescens: The Meeting of Science and Traditional Knowledge. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2014, 20, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Motene, K.; Mahlaule-Glory, L.M.; Ngoepe, N.M.; Mathipa, M.M.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Photocatalytic Degradation of Dyes and Removal of Bacteria Using Biosynthesised Flowerlike NiO Nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlaule-Glory, L.M.; Mbita, Z.; Mathipa, M.M.; Tetana, Z.N.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Biological Therapeutics of AgO Nanoparticles against Pathogenic Bacteria and A549 Lung Cancer Cells. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyai, S.; Mahlaule-Glory, L.M.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Green Synthesis of Zinc Sulphide (ZnS) Nanostructures Using S. Frutescences Plant Extract for Photocatalytic Degradation of Dyes and Antibiotics. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyai, S.; Tetana, Z.N.; Mathipa, M.M.; Ntsendwana, B.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Green Synthesis of Cadmium Sulphide Nanoparticles for the Photodegradation of Malachite Green Dye, Sulfisoxazole and Removal of Bacteria. Opt. (Stuttg) 2021, 247, 167851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlaule-Glory, L.M.; Mathobela, S.; Hintsho-Mbita, N.C. Biosynthesized Bimetallic (ZnOSnO2) Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes and Pharmaceutical Pollutants. Catalysts 2022, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, P.; Meyer, S.; Madiehe, A.; Meyer, M. Antibacterial Activity of Biogenic Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized from Salvia Africana-Lutea and Sutherlandia Frutescens. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 505607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackraj, I.; Ramesar, S.; Singh, M.; Govender, T.; Baijnath, H.; Singh, R.; Gathiram, P. The in Vivo Effects of Tulbhagia Violacea on Blood Pressure in a Salt-Sensitive Rat Model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moodley, K.; Mackraj, I. Metabolic Effects of Tulbaghia Violacea Harv. In a Diabetic Model. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 13, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takaidza, S.; Pillay, M.; Mtunzi, F.M. Biological Activities of Species in the Genus Tulbaghia: A Review. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 3037–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takaidza, S.; Mtunzi, F.; Pillay, M. Analysis of the Phytochemical Contents and Antioxidant Activities of Crude Extracts from Tulbaghia Species. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 38, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madike, L.N.; Takaidza, S.; Pillay, M. Preliminary Phytochemical Screening of Crude Extracts from the Leaves, Stems, and Roots of Tulbaghia Violacea. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2017, 9, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreb, N.; O’Dwyer, C.; Jaiswal, S.; Jaiswal, A.K. Pepper. In Nutritional Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Fruits and Vegetables; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 223–238. [Google Scholar]
- Diallo, A.; Beye, A.C.; Doyle, T.B.; Park, E.; Maaza, M. Green Synthesis of Co3O4 Nanoparticles via Aspalathus Linearis: Physical Properties. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2015, 8, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasile, O.R.; Serdaru, I.; Andronescu, E.; Trusca, R.; Surdu, V.A.; Oprea, O.; Ilie, A.; Vasile, B.Ş. Influence of the Size and the Morphology of ZnO Nanoparticles on Cell Viability. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2015, 18, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom van Staden, A.; Kovacs, D.; Cardinali, G.; Picardo, M.; Lebeko, M.; Khumalo, N.C.; Ray, S.S.; Lall, N. Synthesis and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles Biosynthesised from Aspalathus Linearis (Burm.f.) R.Dahlgren for Progressive Macular Hypomelanosis. J. Herb. Med. 2021, 29, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, E.; Gelderblom, W.C.A.; Louw, A.; de Beer, D. South African Herbal Teas: Aspalathus Linearis, Cyclopia spp. and Athrixia Phylicoides-A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 119, 376–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, A.; Mothudi, B.M.; Manikandan, E.; Maaza, M. Luminescent Eu2O3 Nanocrystals by Aspalathus Linearis’ Extract: Structural and Optical Properties. J. Nanophotonics. 2016, 10, 026010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinfenwa, A.O.; Abdul, N.S.; Docrat, F.T.; Marnewick, J.L.; Luckay, R.C.; Hussein, A.A. Cytotoxic Effects of Phytomediated Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Synthesised from Rooibos (Aspalathus Linearis), and Aspalathin. Plants 2021, 10, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; Khenfouch, M.; Dhlamini, M.; Dube, S.; Maaza, M. Green Palladium and Palladium Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized via Aspalathus Linearis Natural Extract. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 695, 3632–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; Kenfouch, M.; Dhlamini, M.; Dube, S.; Maaza, M. Green Biosynthesis of Rhodium Nanoparticles via Aspalathus Linearis Natural Extract. J. Nanomater. Mol. Nanotechnol. 2017, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; Diallo, A.; Khenfouch, M.; Dhlamini, S.M.; Maaza, M. RuO2 Nanoparticles by a Novel Green Process via Aspalathus Linearis Natural Extract & Their Water Splitting Response. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 662, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, A.; Manikandan, E.; Rajendran, V.; Maaza, M. Physical & Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties of Green Synthesized SnO2 Nanoparticles via Aspalathus Linearis. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 681, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayedwa, N.; Mongwaketsi, N.; Khamlich, S.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Matinise, N.; Maaza, M. Green Synthesis of Nickel Oxide, Palladium and Palladium Oxide Synthesized via Aspalathus Linearis Natural Extracts: Physical Properties & Mechanism of Formation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 446, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroyi, A. Traditional Uses, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Properties of Dovyalis Caffra. J. Pharm. Nutr. Sci. 2018, 8, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aremu, A.O.; Ncama, K.; Omotayo, A.O. Ethnobotanical Uses, Biological Activities and Chemical Properties of Kei-Apple [Dovyalis Caffra (Hook.f. & Harv.) Sim]: An Indigenous Fruit Tree of Southern Africa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 241, 111963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qanash, H.; Yahya, R.; Bakri, M.M.; Bazaid, A.S.; Qanash, S.; Shater, A.F.; Abdelghany, T.M. Anticancer, Antioxidant, Antiviral and Antimicrobial Activities of Kei Apple (Dovyalis Caffra) Fruit. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan, M.; Popa, A.; Toloman, D.; Silipas, T.D.; Vodnar, D.C. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Extracts of Allium Sativum, Rosmarinus Officinalis and Ocimum Basilicum. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2016, 29, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lerotholi, L.; Chaudhary, S.K.; Combrinck, S.; Viljoen, A. Bush Tea (Athrixia Phylicoides): A Review of the Traditional Uses, Bioactivity and Phytochemistry. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 110, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichelt, K.V.; Hoffmann-Lücke, P.; Hartmann, B.; Weber, B.; Ley, J.P.; Krammer, G.E.; Swanepoel, K.M.; Engel, K.H. Phytochemical Characterization of South African Bush Tea (Athrixia Phylicoides DC.). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2012, 83, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandra, H.; Patel, D.; Kumari, P.; Jangwan, J.S.; Yadav, S. Phyto-Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles of Berberis Aristata: Characterization, Antioxidant Activity and Antibacterial Activity with Special Reference to Urinary Tract Pathogens. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



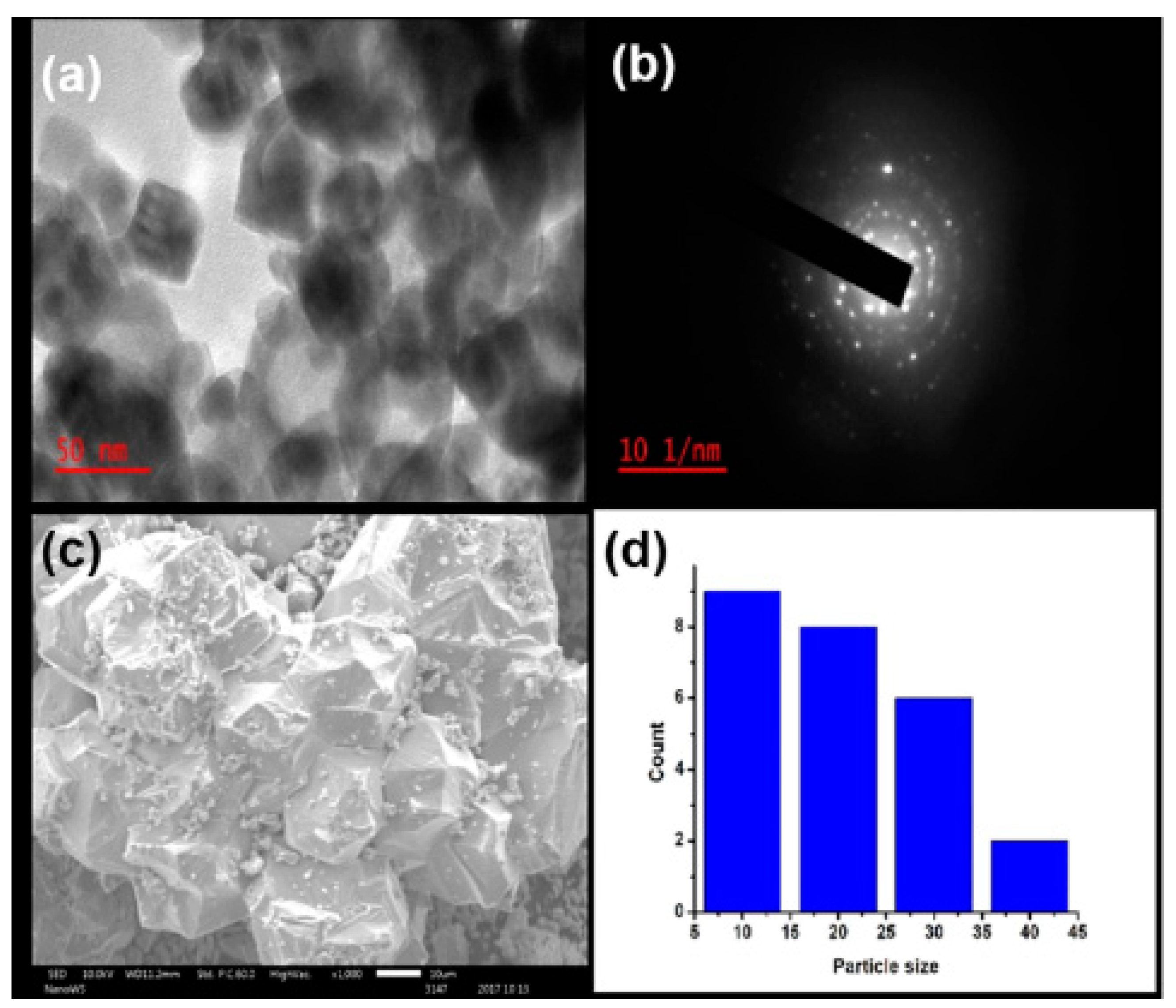
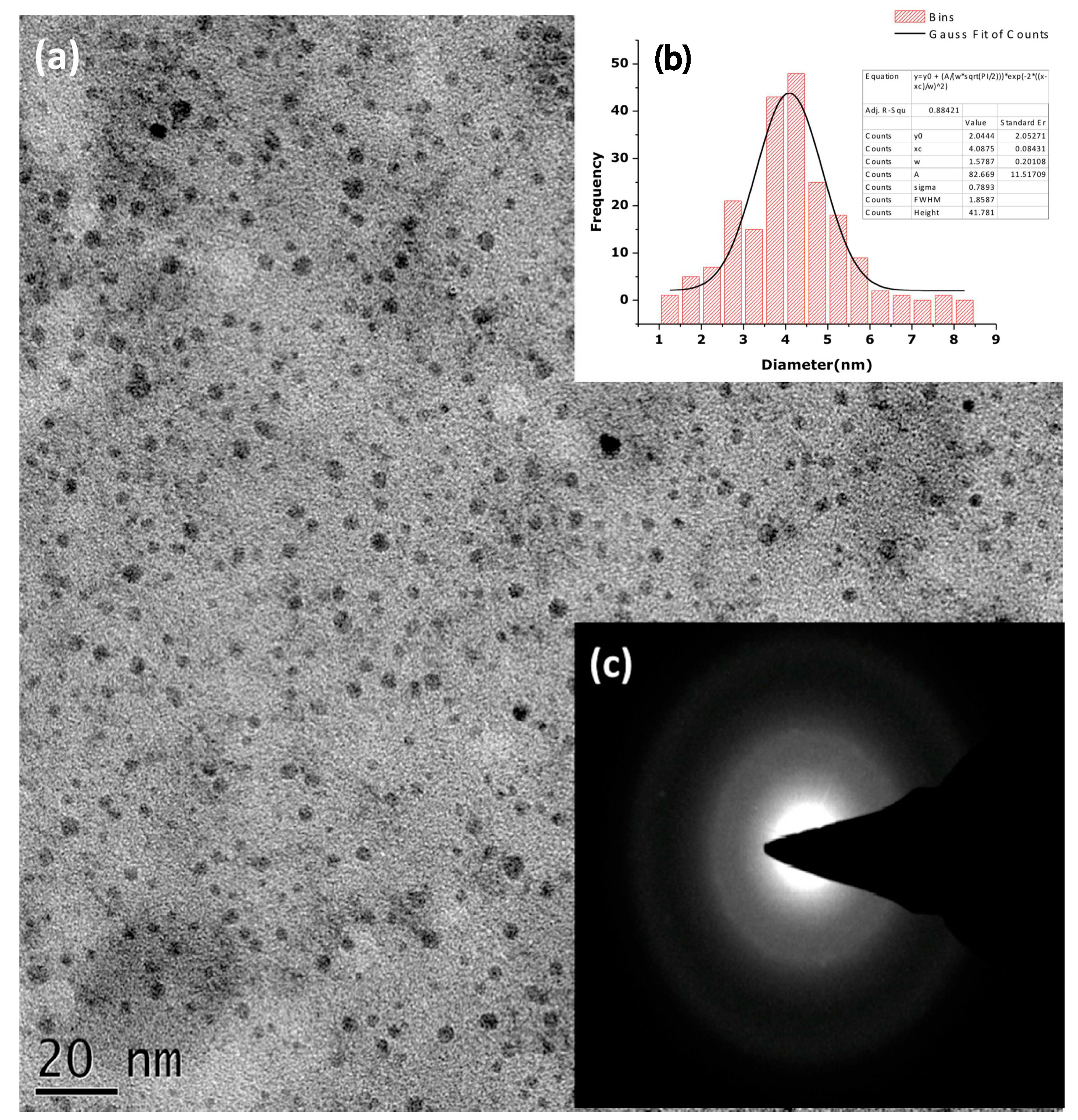
| Plant and Plant Part | Extraction of Phytochemicals | Zn Salt Precursor | Synthesis Conditions | Average Particle Size | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agathosma betulina Leaf | Deionised water as solvent, ~100 °C for 1 h, pH 5 | Zn(NO3)2·6H2O | 100 °C for 2 h, dried at 100 °C, calcined from 100 to 500 °C with 500 °C as optimal | 15.8 nm | [22] |
| Plumbago auriculata Aerial parts | Ethanol as solvent, evaporation under reduced pressure using Buchi rotary evaporator | Zn(CH3COO)2·2H2O | Heated in boiling water bath for 20 min, pH 12, freeze drying | 38.3 nm | [23] |
| Monsomia burkeana plant | Deionised water as solvent, 80 °C for 1 h | ZnCl2·6H2O | 80 °C for 1 h, dried at 100 °C, calcined at 700 °C for 1 h | 5–15 nm | [24] |
| Lessertia montana Leaf | Distilled water as solvent, 65 °C for 4 h | ZnO | 70 °C for 4 h, dried at 50 °C, −80 °C until characterisation | 13.8 nm | [25] |
| Lessertia frutescens Leaf | Deionised water as solvent, 80 °C for 15 min | Zn(NO)3·6H2O | Boiled for 1 h, dried at 80 °C overnight, calcined at 700 °C | 13.3 nm | [26] |
| Tulbaghia violacea Bulb | Distilled water as solvent, 80 °C for 1 h | Zn(CH3COO)2·2H2O | 80 °C until precipitate formed, pH 12, dried at 50 °C for 3 h, calcined at 350 °C | 45.26 nm | [27] |
| Aspalathus linearis Leaf | Deionised water as solvent, 25 °C for 48 h | Zn(NO3)2·6H2O | Room temperature, dried at 80 °C for 2 h, calcined at 300 °C | 12.5 nm | [28] |
| Dovyalis caffra Leaf | Deionised water as solvent, 80 °C for 2 h | Zn(CH3CO2)2·2H₂O | 85 °C for 1 h, pH 10, dried at 50 °C, calcined at 400 °C for 2 h | 25.29 nm | [29] |
| Dovyalis caffra Fruit | Distilled water as solvent, boiled for 20 min | Zn(CH3CO2)2 | 85 °C for 1 h, calcined at 300 °C for 2 h | 34.1 nm * 10.4 nm ** | [30] |
| Athrixia phylicoides DC Leaf | Deionised water as solvent, 60 °C until water turned dark green in colour | Zn(NO3)2·6H2O | ~80 °C until dark paste formed, calcined at 600 °C and 800 °C | 24.5 nm | [31] |
| Flavonoid Subgroup | Compound |
|---|---|
| Flavones | orientin, isoorientin, vitexin, isovitexin, luteolin, and chrysoeriol |
| Flavanones | dihydro-orientin, dihydro-isoorientin, and hemiphlorin |
| Flavonols | quercetin, hyperoside, isoquerci-trin, and rutin |
| Dihydrochalcone | Aspalathin |
| Cyclic dihydrochalcone | Aspalalinin |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mutukwa, D.; Taziwa, R.; Khotseng, L.E. A Review of the Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Utilising Southern African Indigenous Medicinal Plants. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3456. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193456
Mutukwa D, Taziwa R, Khotseng LE. A Review of the Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Utilising Southern African Indigenous Medicinal Plants. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(19):3456. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193456
Chicago/Turabian StyleMutukwa, Dorcas, Raymond Taziwa, and Lindiwe Eudora Khotseng. 2022. "A Review of the Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Utilising Southern African Indigenous Medicinal Plants" Nanomaterials 12, no. 19: 3456. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193456
APA StyleMutukwa, D., Taziwa, R., & Khotseng, L. E. (2022). A Review of the Green Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Utilising Southern African Indigenous Medicinal Plants. Nanomaterials, 12(19), 3456. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193456







