Polyol-Mediated Synthesis of V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalysts for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
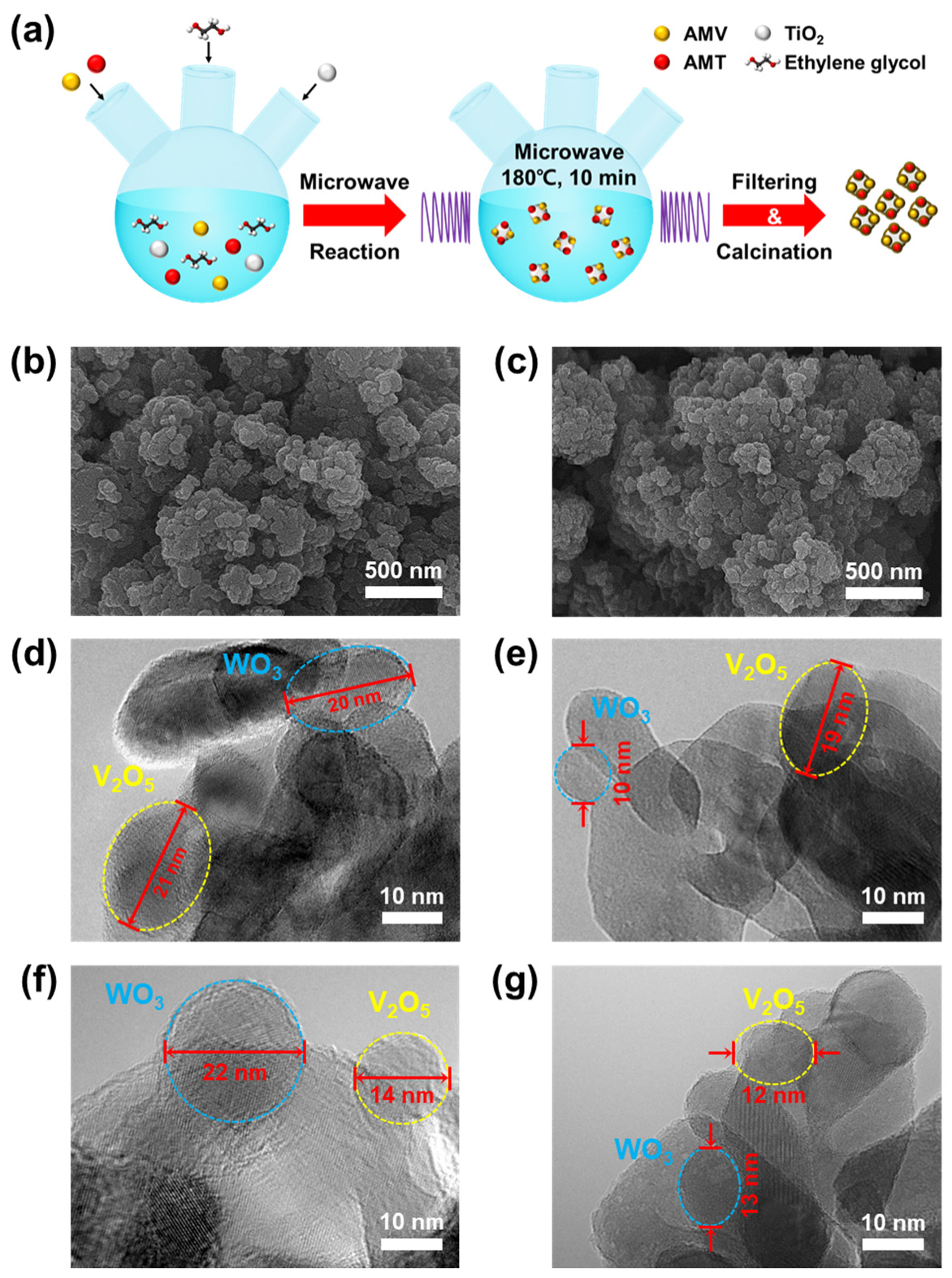
2.2. Preparation of V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalysts
2.3. Catalyst Characterization
2.4. Catalytic Activity Evaluation
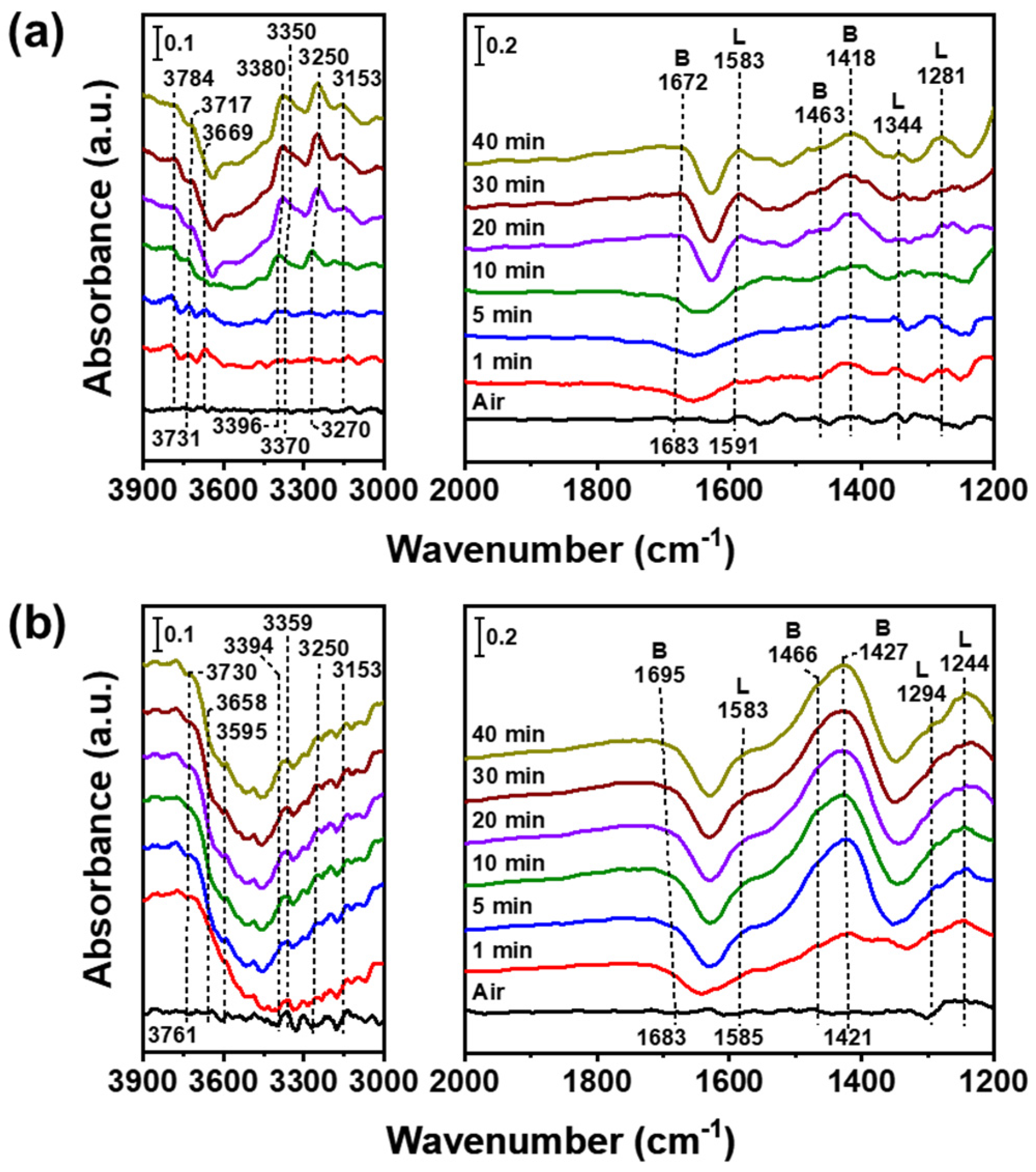
2.5. In Situ FTIR Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
3.2. Evaluation of Catalytic Activity
3.3. NH3-TPD and H2-TPR Analyses
3.4. In Situ FTIR Measurement
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernando, S.; Hall, C.; Jha, S. NOx Reduction from biodiesel fuels. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, M.; Ye, B.; Jeong, B.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, H. Enhanced NOx removal efficiency for SCR catalyst of well-dispersed Mn-Ce nanoparticles on hexagonal boron nitride. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 36107–36116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Li, C.; Lu, P.; Qu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, M.; Fang, Y. A review on selective catalytic reduction of NOx by supported catalysts at 100–300 °C—Catalysts, mechanism, kinetics. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Lee, M.; Jeong, B.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.H.; Baik, J.M.; Kim, H.-D. Partially reduced graphene oxide as a support of Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Today 2019, 328, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boningari, T.; Smirniotis, P.G. Impact of nitrogen oxides on the environment and human health: Mn-based materials for the NOx abatement. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Krishnan, R.M.; Beelen, R.; Peters, A.; Ostro, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Kaufman, J.D. Long-term air pollution exposure and cardio-respiratory mortality: A review. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeshan, M.; Bhatti, I.A.; Mohsin, M.; Iqbal, M.; Amjed, N.; Nisar, J.; AlMasoud, N.; Alomar, T.S. Remediation of pesticides using TiO2 based photocatalytic strategies: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafi, M.A.E.; Ahmed, M.A.; Abdel-Samad, H.S.; Medien, H.A.A. Exceptional removal of methylene blue and p-aminophenol dye over novel TiO2/RGO nanocomposites by tandem adsorption-photocatalytic processes. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2022, 5, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balayeva, N.O.; Mamiyev, Z. Chapter 5—Integrated processes involving adsorption, photolysis, and photocatalysis. In Hybrid and Combined Processes for Air Pollution Control; Assadi, A., Amrane, A., Nguyen, T.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 117–153. [Google Scholar]
- Khanal, V.; Balayeva, N.O.; Günnemann, C.; Mamiyev, Z.; Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Subramanian, V. Photocatalytic NOx removal using tantalum oxide nanoparticles: A benign pathway. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 291, 119974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balayeva, N.O.; Fleisch, M.; Bahnemann, D.W. Surface-grafted WO3/TiO2 photocatalysts: Enhanced visible-light activity towards indoor air purification. Catal. Today 2018, 313, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.-T.; Han, J.-K.; Gain, A.K.; Lee, K.-H.; Saito, F. TEM microstructure characterization of nano TiO2 coated on nano ZrO2 powders and their photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 2101–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Kim, S.I.; Jeong, B.; Park, J.W.; Kim, T.; Lee, J.W.; Kwon, G.; Lee, D.H. Ammonium ion enhanced V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction with ammonia. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radojevic, M. Reduction of nitrogen oxides in flue gases. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Ye, B.; Kim, E.-S.; Kim, H.-D. Characteristics of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalyst adding graphene-tungsten nanocomposite. Catal. Commun. 2017, 93, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Zhan, W.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, G. A highly effective catalyst of Sm-MnOx for the NH3-SCR of NOx at low temperature: Promotional role of Sm and its catalytic performance. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5973–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Tran, D.; Burton, S.D.; Szanyi, J.; Lee, J.H.; Peden, C.H.F. Effects of hydrothermal aging on NH3-SCR reaction over Cu/zeolites. J. Catal. 2012, 287, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, M.J.; Ye, B.; Kim, T.; Kim, H.D.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, D.H. Effect of catalyst crystallinity on V-based selective catalytic reduction with ammonia. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Hegde, M.S.; Madras, G. Catalysis for NOx abatement. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Lietti, L.; Ramis, G.; Berti, F. Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NO by ammonia over oxide catalysts: A Review. Appl. Catal. B 1998, 18, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, A.; Andersson, C.; Myringer, A.; Eskilsson, D.; Järås, S.G. Alkali deactivation of high-dust SCR catalysts used for NOx reduction exposed to flue gas from 100MW-scale biofuel and peat fired boilers: Influence of flue gas composition. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 69, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chang, H.; Ma, L.; Hao, J.; Yang, R.T. Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over metal oxide and zeolite catalysts—A review. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, J.-W.; Gao, C.; Niu, C. Manganese oxide-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: A review. Appl. Catal. A 2016, 522, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, H.; Dong, L. Ceria-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Liu, F.; He, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, C. A superior Ce-W-Ti mixed oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Appl. Catal. B 2012, 115–116, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenović, M.; Paprika, M.; Marinković, A. Denitrification techniques for biomass combustion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3350–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. New insight into the promotion effect of Cu doped V2O5/WO3–TiO2 for low temperature NH3-SCR performance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 35155–35165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Tan, P.; Zhou, A.; Fang, Q.; Chen, G. Ho-modified Mn-Ce/TiO2 for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3: Evaluation and characterization. Chin. J. Catal. 2018, 39, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, H.; Jiang, H.; Liu, L. The promotional role of Nd on Mn/TiO2 catalyst for the low-temperature NH3-SCR of NOx. Catal. Today 2019, 332, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Guo, R.-T.; Liu, S.-M.; Wang, S.-X.; Pan, W.-G.; Li, M.-Y. The enhanced performance of MnOx catalyst for NH3-SCR reaction by the modification with Eu. Appl. Catal. A 2017, 531, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Xie, J.L.; Fang, D.; He, F. Study of Co-Mn/TiO2 SCR catalyst at low temperature. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1102, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; He, H.; Yu, Y. Deactivation of a Ce/TiO2 Catalyst by SO2 in the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4426–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Gao, M.; Hasegawa, J.-Y.; Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. SO2-tolerant selective catalytic reduction of NOx over meso-TiO2@ Fe2O3@ Al2O3 metal-based monolith catalysts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6462–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, W. Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite–metal oxide hybrid catalysts with enhanced SO2-tolerance in the NH3-SCR of NOx. Appl. Catal. B 2020, 269, 118825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Ge, M. DRIFT study on cerium-tungsten/titania catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9590–9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. The activity and characterization of CeO2-TiO2 Catalysts prepared by the sol-gel method for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purbia, R.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Ye, B.; Jeong, B.; Lee, D.H.; Park, H.; Kim, H.-D.; Baik, J.M. Cu- and Ce-promoted nano-heterostructures on vanadate catalysts for low-temperature NH3–SCR activity with improved SO2 and water resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Kim, J.; Lee, M.-J.; Chun, S.-Y.; Jeong, B.; Kim, T.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, H.-D. Mn-Ce oxide nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide as low-temperature catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 310, 110588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.K.; Kim, T.-W.; Kim, J.-R.; Kim, Y.; Ha, K.-S.; Chae, H.-J. Enhanced SO2 tolerance of V2O5-Sb2O3/TiO2 Catalyst for NO reduction with Co-use of ammonia and liquid ammonium nitrate. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 96, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Rajic, L.; Meng, X.; Nazari, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Qin, Y.; Alshawabkeh, A.N. Efficient H2O2 Electrogeneration at Graphite Felt Modified via Electrode Polarity Reversal: Utilization for Organic Pollutants Degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, M.S.; Pullur, A.K.; Ha, H.P. Novel sulfation effect on low-temperature activity enhancement of CeO2-added Sb-V2O5/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 152–153, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiévet, F.; Ammar-Merah, S.; Brayner, R.; Chau, F.; Giraud, M.; Mammeri, F.; Peron, J.; Piquemal, J.Y.; Sicard, L.; Viau, G. The polyol process: A unique method for easy access to metal nanoparticles with tailored sizes, shapes and compositions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5187–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohra, B.; Candy, L.; Blanco, J.-F.; Guerin, C.; Raoul, Y.; Mouloungui, Z. From petrochemical polyurethanes to biobased polyhydroxyurethanes. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 3771–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bak, S.J.; Kim, S.I.; Lim, S.Y.; Kim, T.; Kwon, S.H.; Lee, D.H. Small reduced graphene oxides for highly efficient oxygen reduction catalysts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, P.D.; Patil, B.S.; Zhu, H.; Bravo-Suárez, J.J. Application of modulation excitation-phase sensitive detection-DRIFTS for in situ/operando characterization of heterogeneous catalysts. React. Chem. Eng. 2019, 4, 862–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Ge, M. Promotional effect of Ce-doped V2O5-WO3/TiO2 with low vanadium loadings for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 21177–21184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-K.; Wachs, I.E. A perspective on the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 by supported V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6537–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cai, S.; Gao, M.; Hasegawa, J.-Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 by using novel catalysts: State of the art and future prospects. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10916–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Cheng, Y.; Cavataio, G.; McCabe, R.W.; Fu, L.; Li, J. In situ DRIFTS and temperature-programmed technology study on NH3-SCR of NOx over Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts. J. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 156, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezcano-Gonzalez, I.; Deka, U.; Arstad, B.; Van Yperen-De Deyne, A.; Hemelsoet, K.; Waroquier, M.; Van Speybroeck, V.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Beale, A.M. Determining the storage, availability and reactivity of NH3 within Cu-chabazite-based ammonia selective catalytic reduction systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | TiO2 | V2O5 | WO3 | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V2O5(IM)–WO3(IM) | 92.33 | 1.93 | 5.02 | 0.72 |
| V2O5(IM)–WO3(P) | 92.43 | 2.02 | 4.89 | 0.66 |
| V2O5(P)–WO3(IM) | 92.29 | 1.91 | 5.08 | 0.72 |
| V2O5(P)–WO3(P) | 92.44 | 1.88 | 4.97 | 0.71 |
| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| V2O5(IM)–WO3(IM) | 71.33 | 0.22 | 11.01 |
| V2O5(IM)–WO3(P) | 74.23 | 0.28 | 14.77 |
| V2O5(P)–WO3(IM) | 75.67 | 0.22 | 11.68 |
| V2O5(P)–WO3(P) | 75.83 | 0.28 | 14.90 |
| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|
| V2O5(IM)–WO3(IM) | 71.33 | 0.22 |
| V2O5(IM)–WO3(P) | 74.23 | 0.28 |
| V2O5(P)–WO3(IM) | 75.67 | 0.22 |
| V2O5(P)–WO3(P) | 75.83 | 0.28 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Bak, S.-J.; Son, M.; Shin, J.; Lee, D.H. Polyol-Mediated Synthesis of V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalysts for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3644. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203644
Lee MS, Choi YJ, Bak S-J, Son M, Shin J, Lee DH. Polyol-Mediated Synthesis of V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalysts for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(20):3644. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203644
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Min Seong, Yeong Jun Choi, Su-Jeong Bak, Mingyu Son, Jeehoon Shin, and Duck Hyun Lee. 2022. "Polyol-Mediated Synthesis of V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalysts for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia" Nanomaterials 12, no. 20: 3644. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203644
APA StyleLee, M. S., Choi, Y. J., Bak, S.-J., Son, M., Shin, J., & Lee, D. H. (2022). Polyol-Mediated Synthesis of V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalysts for Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia. Nanomaterials, 12(20), 3644. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12203644






