Ferrimagnetic Large Single Domain Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles
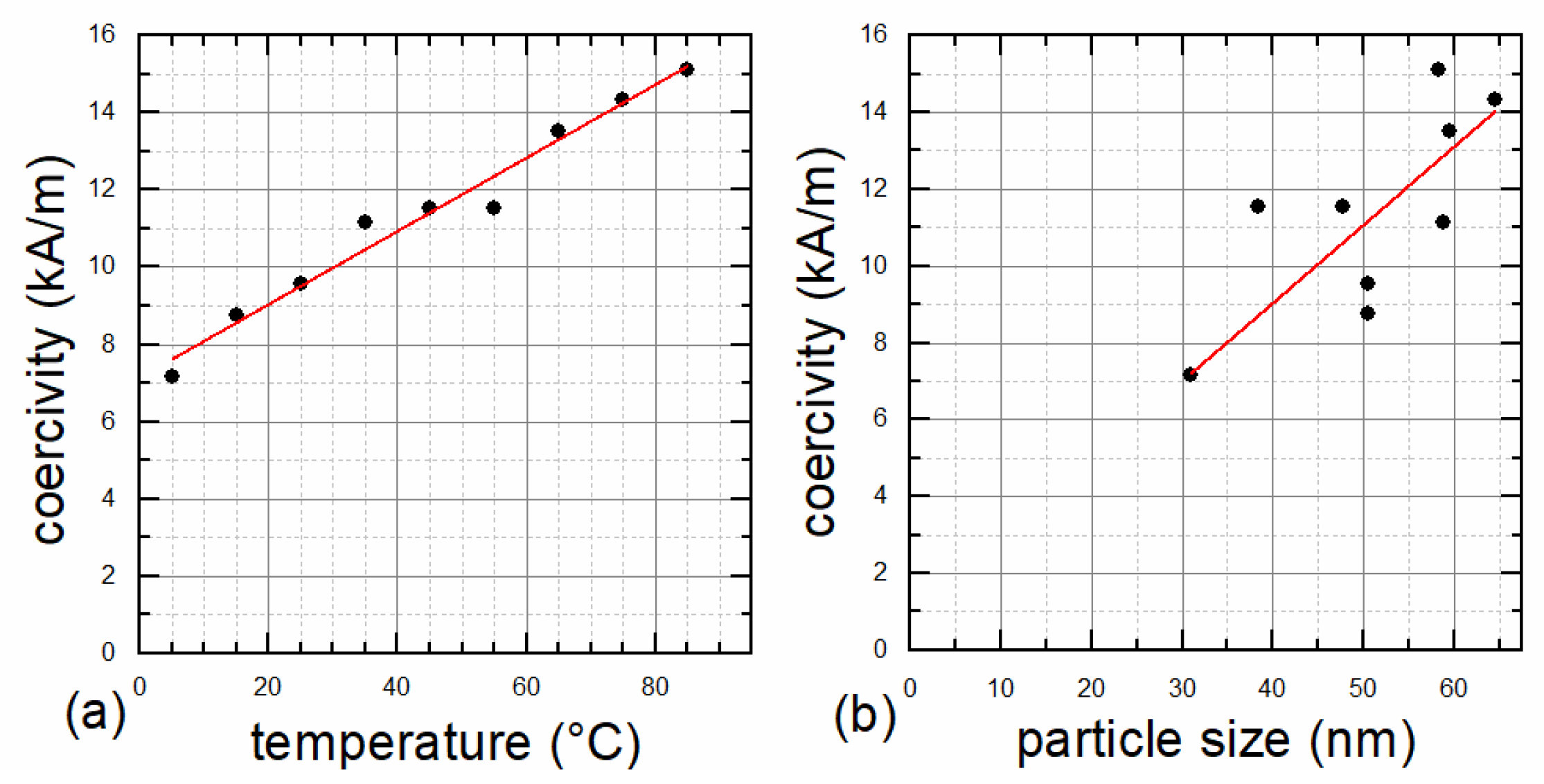
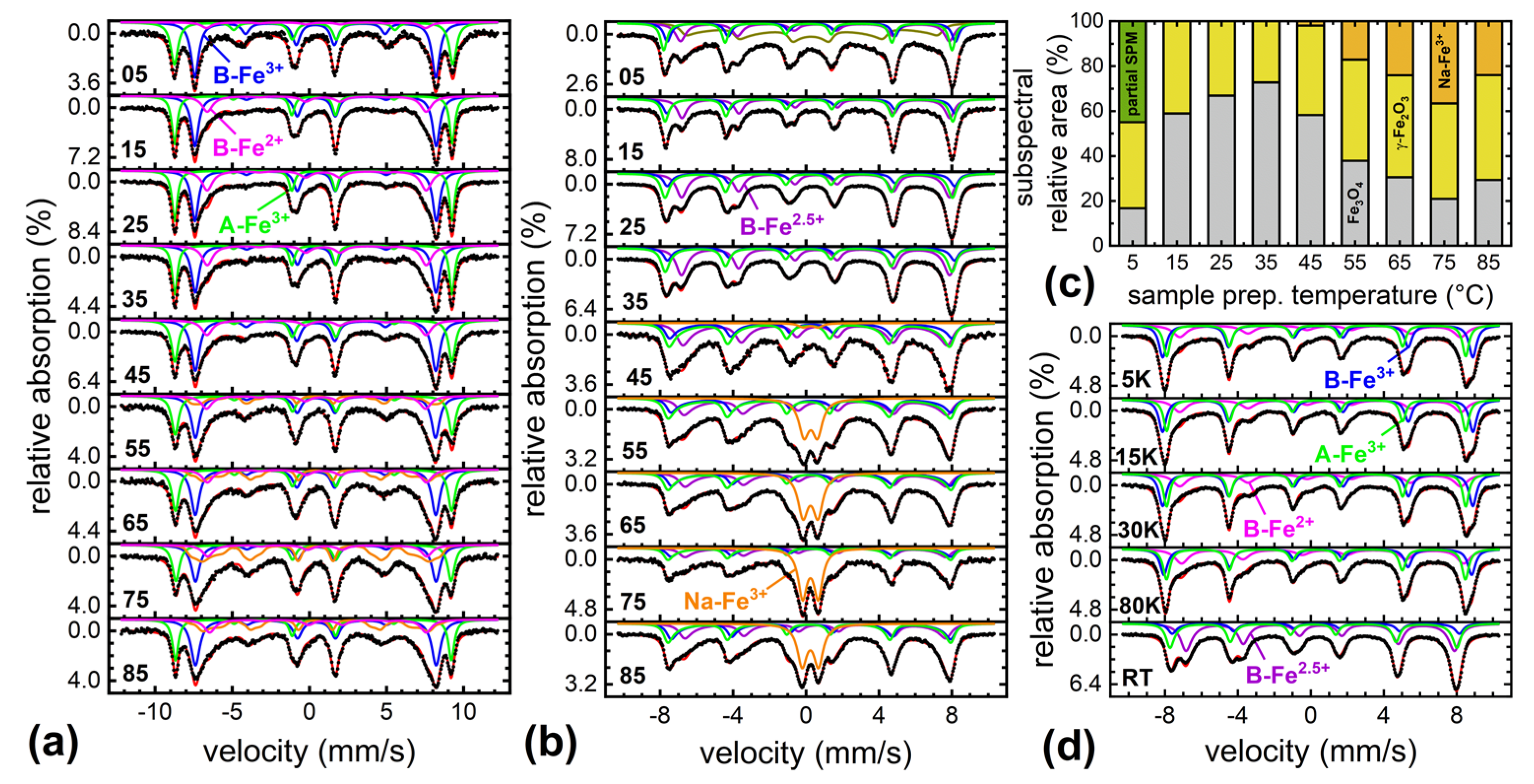
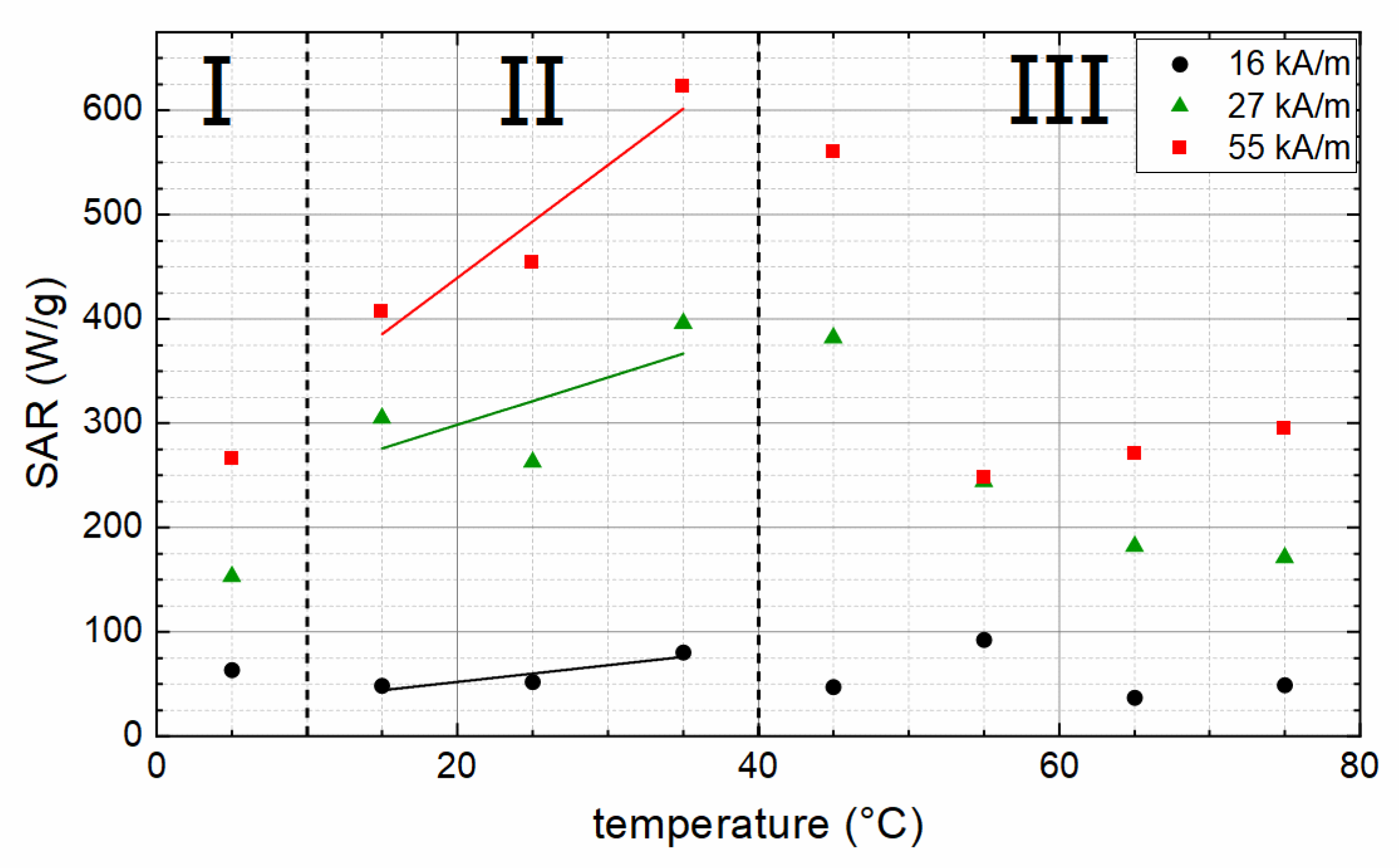
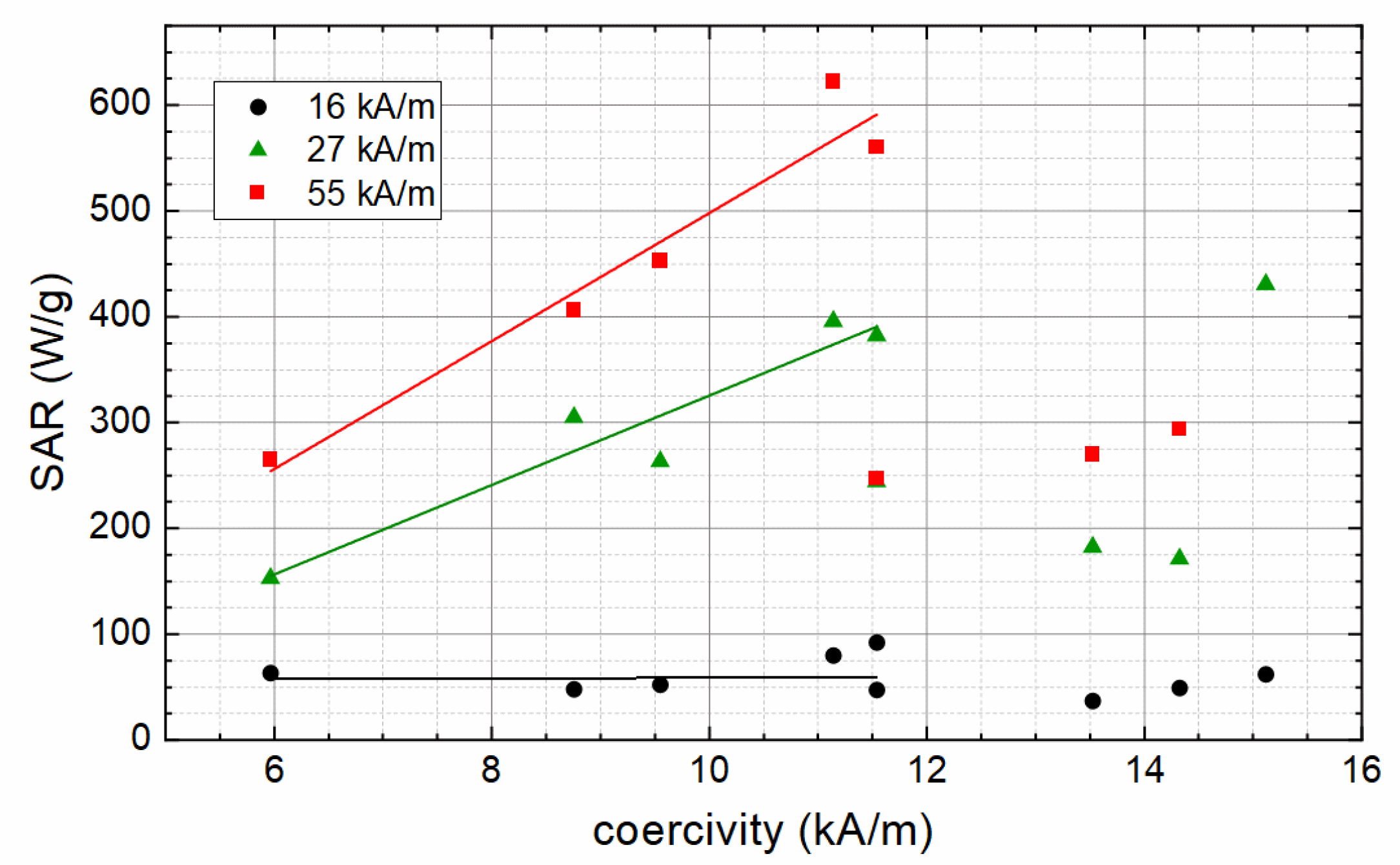
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gordon, R.T.; Hines, J.R.; Gordon, D. Intracellular hyperthermia. A biophysical approach to cancer treatment via intracellular temperature and biophysical alterations. Med. Hypotheses 1979, 5, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Hergt, R. Magnetic particle hyperthermia–a promising tumour therapy? Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 452001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Colombo, M.; Prosperi, D. Recent advances in magnetic fluid hyperthermia for cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, H.; Slimani, N.; Pawar, M.; Kumon, R.E.; Vaishnava, P.; Besirli, C.G. Magnetic hyperthermia in Y79 retinoblastoma and ARPE-19 retinal epithelial cells: Tumor selective apoptotic activity of iron oxide nanoparticle. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habra, K.; McArdle, S.E.B.; Morris, R.H.; Cave, G.W.V. Synthesis and Functionalisation of Superparamagnetic Nano-Rods towards the Treatment of Glioblastoma Brain Tumours. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergt, R.; Dutz, S. Magnetic Particle Hyperthermia–Biophysical Limitations of a Visionary Tumour Therapy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 311, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S. Nanopartikel in der Medizin-Magnetische Eisenoxid-Nanopartikel für Intrakorporale Erwärmungsanwendungen; Verlag Dr. Kovač: Hamburg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Caizer, C. Optimization Study on Specific Loss Power in Superparamagnetic Hyperthermia with Magnetite Nanoparticles for High Efficiency in Alternative Cancer Therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.M. Electromagnetic activation of shape memory polymer networks containing magnetic nanoparticles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakacki, C.M.; Satarkar, N.S.; Gall, K.; Likos, R.; Hilt, J.Z. Shape-memory polymer networks with Fe3O4nanoparticles for remote activation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 3166–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Leung, V.; Yuqin Wan, L.; Dutz, S.; Ko, F.K.; Häfeli, U.O. Electrospun magnetic nanofibre mats–A new bondable biomaterial using remotely activated magnetic heating. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 380, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.M.; Khandhar, A.P.; Arami, H.; Hua, L.; Hovorka, O.; Krishnan, K.M. Tailoring the magnetic and pharmacokinetic properties of iron oxide magnetic particle imaging tracers. Biomed. Technik. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 58, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, R.M.; Khandhar, A.P.; Krishnan, K.M. Tracer design for magnetic particle imaging (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07B318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tachiki, M. Origin of the Magnetic Anisotropy Energy of Cobalt Ferrite. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1960, 23, 1055–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kita, E.; Oda, T.; Kayano, T.; Sato, S.; Minagawa, M.; Yanagihara, H.; Kishimoto, M.; Mitsumata, C.; Hashimoto, S.; Yamada, K.; et al. Ferromagnetic nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia and thermoablation therapy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 474011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Buske, N.; Landers, J.; Gräfe, C.; Wende, H.; Clement, J.H. Biocompatible Magnetic Fluids of Co-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Tunable Magnetic Properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathya, A.; Guardia, P.; Brescia, R.; Silyestri, N.; Pugliese, G.; Nitti, S.; Manna, L.; Pellegrino, T. CoxFe3-xO4 Nanocubes for Theranostic Applications: Effect of Cobalt Content and Particle Size. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.S.A.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Ryu, C.; Young Lee, J.; Yoon, J. Engineering Core-Shell Structures of Magnetic Ferrite Nanoparticles for High Hyperthermia Performance. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Wilhelm, C.; Siaugue, J.M.; Horner, O.; Bacri, J.C.; Gazeau, F. Magnetically induced hyperthermia: Size-dependent heating power of gamma-Fe(2)O(3) nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 204133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kartikowati, C.W.; Horie, S.; Ogi, T.; Iwaki, T.; Okuyama, K. Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, Z.; Alonso, J.; Rodrigo, I.; Das, R.; Garaio, E.; Garcia, J.A.; Orue, I.; Phan, M.H.; Srikanth, H. Improving the heating efficiency of iron oxide nanoparticles by tuning their shape and size. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 2367–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, S.H.; Na, W.; Jang, J.T.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, E.J.; Moon, S.H.; Lim, Y.; Shin, J.S.; Cheon, J. Nanoscale magnetism control via surface and exchange anisotropy for optimized ferrimagnetic hysteresis. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3716–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Lv, Y.B.; Herng, T.S.; Xu, X.H.; Xia, W.X.; Zhang, T.S.; Fang, J.; Xiao, W.; Ding, J. Orientation Mediated Enhancement on Magnetic Hyperthermia of Fe3O4 Nanodisc. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Ortega, F.; Delgado, A.V.; Iglesias, G.R. Modulation of the magnetic hyperthermia response using different superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle morphologies. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch, F. Zur Theorie des Ferromagnetismus. Z. Phys. 1930, 61, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung Lee, J.; Myung Cha, J.; Young Yoon, H.; Lee, J.K.; Keun Kim, Y. Magnetic multi-granule nanoclusters: A model system that exhibits universal size effect of magnetic coercivity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Hergt, R. Magnetic nanoparticle heating and heat transfer on a microscale: Basic principles, realities and physical limitations of hyperthermia for tumour therapy. Int. J. Hyperth. 2013, 29, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N. Size dependence of specific power absorption of Fe3O4 particles in AC magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 268, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Hergt, R.; Mürbe, J.; Müller, R.; Zeisberger, M.; Andrä, W.; Töpfer, J.; Bellemann, M.E. Hysteresis losses of magnetic nanoparticle powders in the single domain size range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Quinto, C.A.; Zhang, L.; Mohindra, P.; Bao, G. Size-Dependent Heating of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6808–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, K.; Ikeda, M.; Gokon, N.; Tsubouchi, S.; Narimatsu, H.; Mochizuki, Y.; Sakamoto, S.; Sandhu, A.; Abe, M.; Handa, H. Preparation of size-controlled (30–100nm) magnetite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, 2408–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kawashita, M.; Araki, N.; Mitsumori, M.; Hiraoka, M. Preparation of size-controlled magnetite nanoparticles for hyperthermia of cancer. Trans. Mater. Res. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 34, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, P.; Zhuang, L.; Liang, R.; Xu, Y.; Shen, H. Nucleation Features of the Magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles with the size of 30–40 nm for the hyperthermia applications. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 287–290, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Dutz, S.; Neeb, A.; Cato, A.C.B.; Zeisberger, M. Magnetic heating effect of nanoparticles with different sizes and size distributions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 328, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Kettering, M.; Hilger, I.; Müller, R.; Zeisberger, M. Magnetic multicore nanoparticles for hyperthermia–influence of particle immobilization in tumour tissue on magnetic properties. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 265102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Müller, R.; Eberbeck, D.; Hilger, I.; Zeisberger, M. Magnetic nanoparticles adapted for specific biomedical applications. Biomed. Technik. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 60, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutz, S.; Hergt, R.; Mürbe, J.; Töpfer, J.; Müller, R.; Zeisberger, M.; Andrä, W.; Bellemann, M.E. Magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical heating applications. Z. Phys. Chem. 2006, 220, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Landers, J.; Stromberg, F.; Darbandi, M.; Schoppner, C.; Keune, W.; Wende, H. Correlation of superparamagnetic relaxation with magnetic dipole interaction in capped iron-oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2015, 27, 026002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebodos, R.; Vikesland, P. Effects of Oxidation on the Magnetization of Nanoparticulate Magnetite. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2010, 26, 16745–16753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddis, D.; Yaacoub, N.; Ferretti, M.; Martinelli, A.; Piccaluga, G.; Musinu, A.; Cannas, C.; Navarra, G.; Greneche, J.M.; Fiorani, D. Cationic distribution and spin canting in CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2011, 23, 426004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, J.; Hansen, M.F.; Frandsen, C.; Mørup, S. On the interpretation of Mössbauer spectra of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 445, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mørup, S.; Topsøe, H. Magnetic and electronic properties of microcrystals of Fe3O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1983, 31–34, 953–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
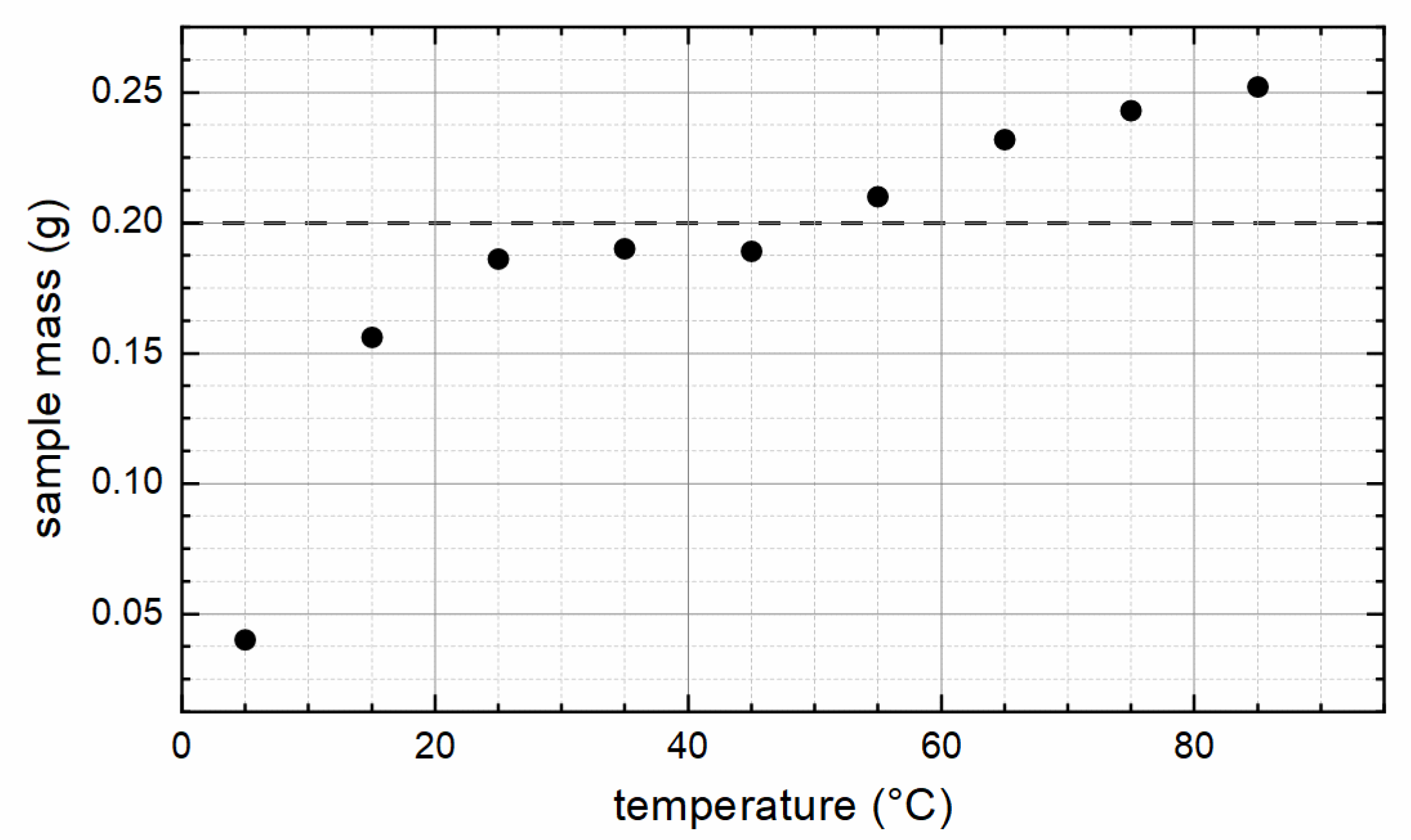
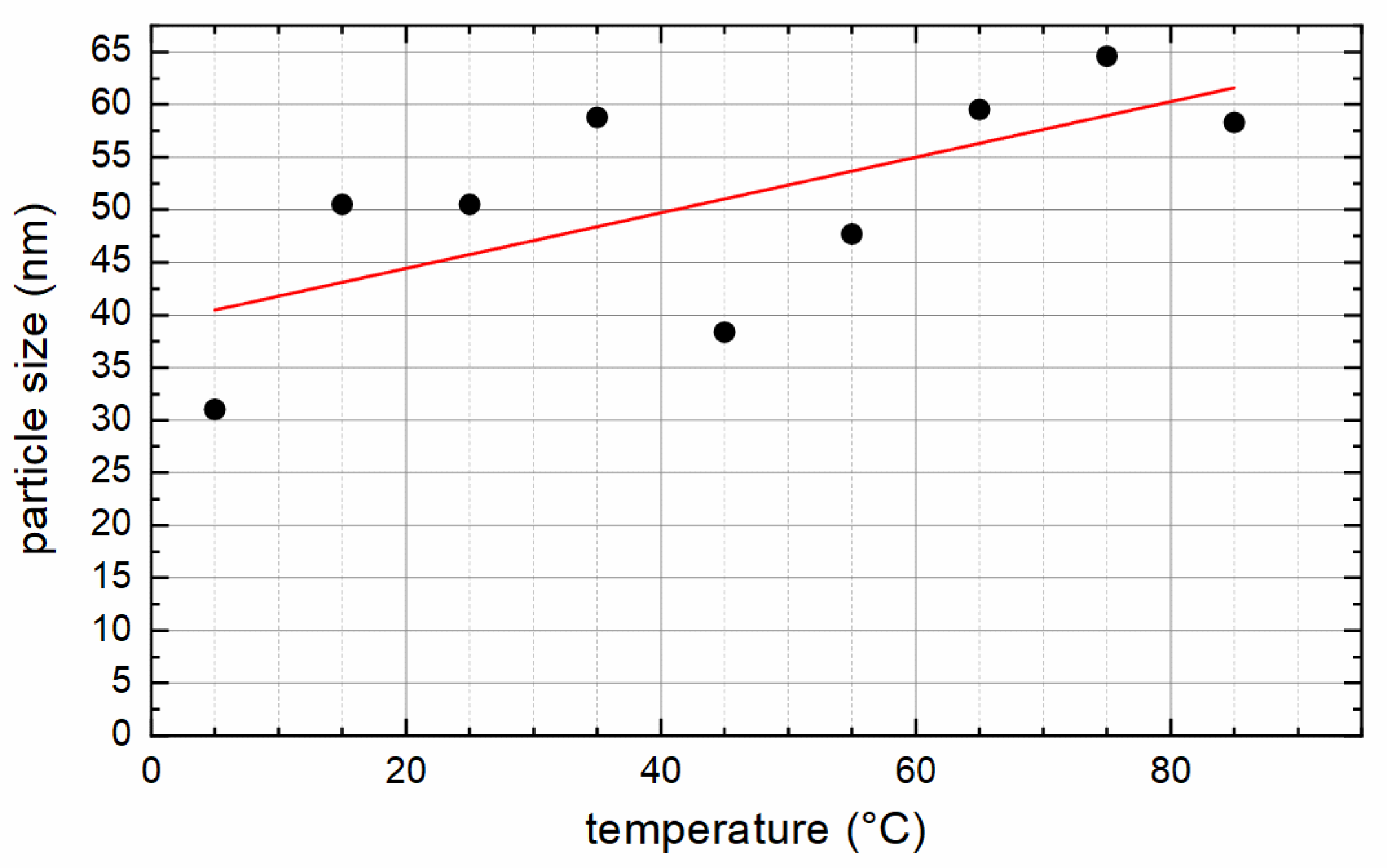
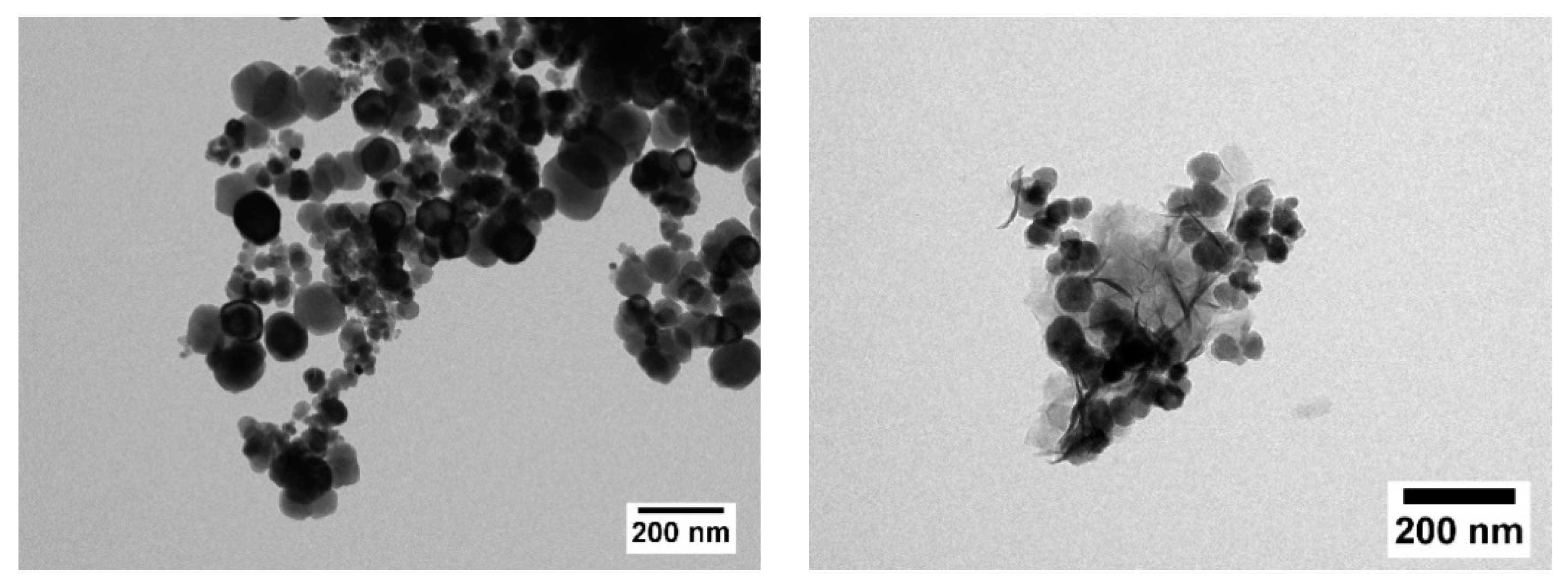
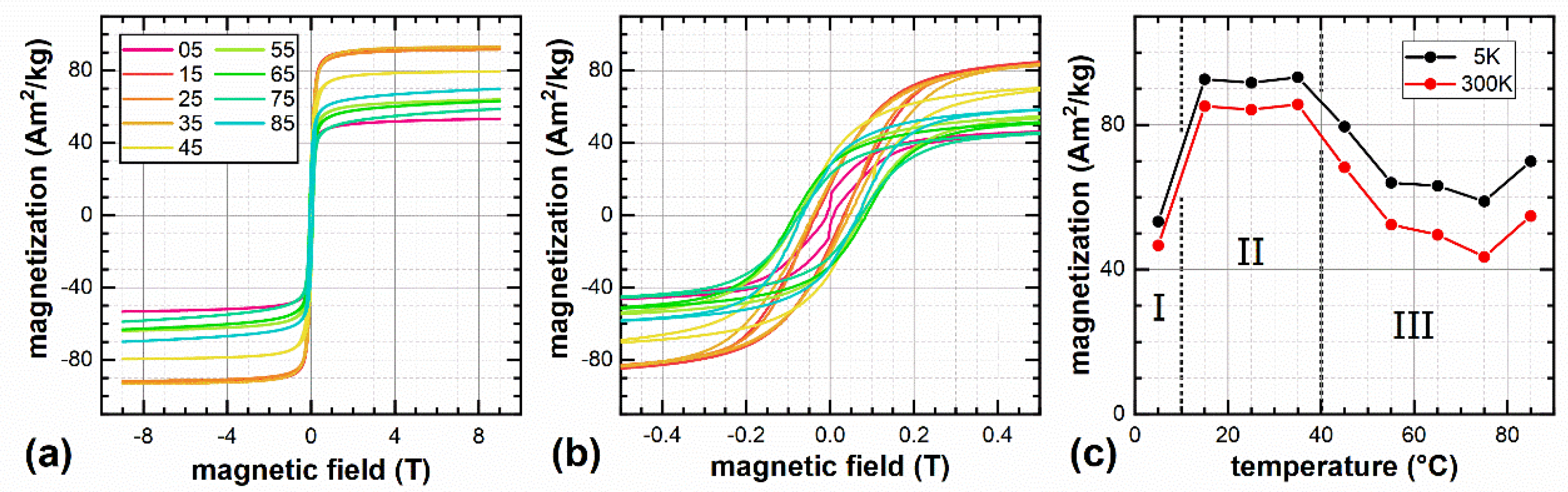
| Sample | XRD | VSM at 300 K/9 T | VSM at 5 K/9 T | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T | D | 2theta | Ms | Hc | Mr/Ms | Ms | Hc | Mr/Ms |
| (°C) | (nm) | (°) | (Am²/kg) | (kA/m) | (Am²/kg) | (kA/m) | ||
| 05 | 31.0 | 62.43 | 46.7 | 6.0 | 0.08 | 53.3 | 7.2 | 0.12 |
| 15 | 50.5 | 62.53 | 85.2 | 8.8 | 0.08 | 92.6 | 26.3 | 0.18 |
| 25 | 50.5 | 62.51 | 84.2 | 9.6 | 0.10 | 91.7 | 29.4 | 0.19 |
| 35 | 58.8 | 62.50 | 85.7 | 11.1 | 0.11 | 93.2 | 39.8 | 0.29 |
| 45 | 38.4 | 62.49 | 68.3 | 11.5 | 0.13 | 79.5 | 53.3 | 0.40 |
| 55 | 47.7 | 62.48 | 52.5 | 11.5 | 0.15 | 64.0 | 60.5 | 0.44 |
| 65 | 59.5 | 62.50 | 49.6 | 13.5 | 0.16 | 63.2 | 67.6 | 0.44 |
| 75 | 64.6 | 62.55 | 43.5 | 14.3 | 0.16 | 58.9 | 58.1 | 0.39 |
| 85 | 58.3 | 62.56 | 54.8 | 15.1 | 0.20 | 69.9 | 52.5 | 0.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zahn, D.; Landers, J.; Buchwald, J.; Diegel, M.; Salamon, S.; Müller, R.; Köhler, M.; Ecke, G.; Wende, H.; Dutz, S. Ferrimagnetic Large Single Domain Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030343
Zahn D, Landers J, Buchwald J, Diegel M, Salamon S, Müller R, Köhler M, Ecke G, Wende H, Dutz S. Ferrimagnetic Large Single Domain Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(3):343. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030343
Chicago/Turabian StyleZahn, Diana, Joachim Landers, Juliana Buchwald, Marco Diegel, Soma Salamon, Robert Müller, Moritz Köhler, Gernot Ecke, Heiko Wende, and Silvio Dutz. 2022. "Ferrimagnetic Large Single Domain Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Applications" Nanomaterials 12, no. 3: 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030343
APA StyleZahn, D., Landers, J., Buchwald, J., Diegel, M., Salamon, S., Müller, R., Köhler, M., Ecke, G., Wende, H., & Dutz, S. (2022). Ferrimagnetic Large Single Domain Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials, 12(3), 343. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12030343






