3D Printed Metal Oxide-Polymer Composite Materials for Antifouling Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Filament Production
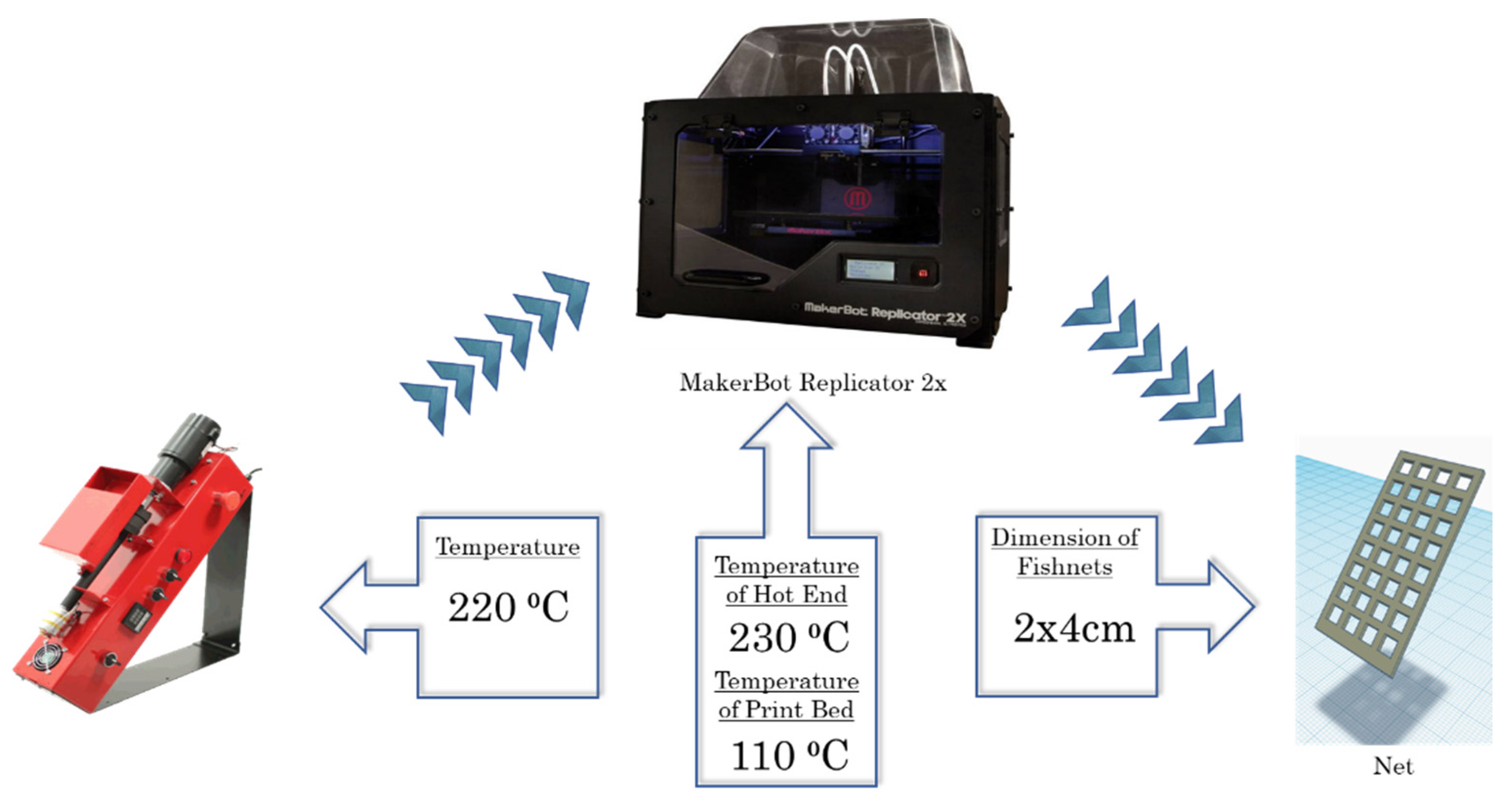
2.3. 3D Printing of “Fishnet-like” Grid Structures
2.4. Characterization Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD Characterization
3.2. SEM Characterization
3.3. Raman Characterization
3.4. Antifouling Properties
3.5. Properties of the Materials Following Exposure to Plankton
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United States. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. In The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020. In Brief; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United States: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bueno, N.; Marín, A. Ecological management of biomass and metal bioaccumulation in fish-cage nettings: Influence of antifouling paint and fiber manufacture. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yebra, D.M.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling Technology-Past, Present and Future Steps towards Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Antifouling Coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloecher, N.; Floerl, O. Efficacy testing of novel antifouling coatings for pen nets in aquaculture: How good are alternatives to traditional copper coatings? Aquaculture 2020, 519, 734936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Holmer, M.; Olsen, Y.; Soto, D.; Marbà, N.; Guiu, J.; Black, K.; Karakassis, I. Will the Oceans Help Feed Humanity? BioScience 2009, 59, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, R.A.; McEvoy, L.A. Marine Biofouling on Fish Farms and Its Remediation. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2004, 47, 215–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, R.A.; Carrascosa, M.C.C.; McEvoy, L.A. Biofouling of Salmon Cage Netting and the Efficacy of a Typical Copper-Based Antifoulant. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.P.; Seta, J.H.H.; Kuhnen, V.V.; Sanches, E.G. Antifouling alternatives for aquaculture in tropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claire Hellio, C.; Yebra, D. (Eds.) Advances in Marine Antifouling Coatings and Technologies, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 177–221. ISBN 9781845696313. [Google Scholar]
- Bloecher, N.; Olsen, Y.; Guenther, J. Variability of Biofouling Communities on Fish Cage Nets: A 1-Year Field Study at a Norwegian Salmon Farm. Aquaculture 2013, 416–417, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebert, P.; Lader, P.; Gansel, L.; Oppedal, F. Hydrodynamic Interactions on Net Panel and Aquaculture Fish Cages: A Review. Ocean. Eng. 2013, 58, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nys, R.; Guenther, J. The impact and control of biofouling in marine finfish aquaculture. In Advances in Marine Antifouling Coatings and Technologies; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2009; pp. 177–221. [Google Scholar]
- Bannister, J.; Sievers, M.; Bush, F.; Bloecher, N. Biofouling in Marine Aquaculture: A Review of Recent Research and Developments. Biofouling 2019, 35, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woods, C.M.C.; Floerl, O.; Hayden, B.J. Biofouling on GreenshellTM Mussel (Perna canaliculus) Farms: A Preliminary Assessment and Potential Implications for Sustainable Aquaculture Practices. Aquac. Int. 2012, 20, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, D.A.; Kelly, M. Settlement of Pomatoceros Triqueter (L.) in two Scottish lochs, and factors determining its abundance on mussels grown in suspended culture. J. Shellfish. Res. 2002, 21, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Pakrashi, V.; Ghosh, B. Fishing Net Health State Estimation Using Underwater Imaging. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitridge, I.; Dempster, T.; Guenther, J.; de Nys, R. The Impact and Control of Biofouling in Marine Aquaculture: A Review. Biofouling 2012, 28, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abioye, O.P.; Loto, C.A.; Fayomi, O.S.I. Evaluation of Anti-Biofouling Progresses in Marine Application. J. Bio-Tribo-Corros. 2019, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, J.P.; Hellio, C. Challenges for the Development of New Non-Toxic Antifouling Solutions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4623–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Archana, S.; Sundaramoorthy, B. Review on Biofouling Prevention Using Nanotechnology. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2019, 7, 640–648. [Google Scholar]
- Curtin, A.M.; Buckley, H.L. Biofouling Detection Methods That Are Widely Applicable and Useful across Disciplines: A Mini-Review. Biofouling 2021, 37, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.S.; El-Safty, S.A.; Shenashen, M.A.; Higazy, S.A.; Elmarakbi, A. Progress in Biomimetic Leverages for Marine Antifouling Using Nanocomposite Coatings. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3701–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yebra, D.M.; Kiil, S.; Weinell, C.E.; Dam-Johansen, K. Dissolution Rate Measurements of Sea Water Soluble Pigments for Antifouling Paints: ZnO. Prog. Org. Coat. 2006, 56, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobretsov, S.; Sathe, P.; Bora, T.; Barry, M.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Abri, M.A. Toxicity of Different Zinc Oxide Nanomaterials at 3 Trophic Levels: Implications for Development of Low-Toxicity Antifouling Agents. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathe, P.; Laxman, K.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Dobretsov, S.; Richter, J.; Dutta, J. Bioinspired Nanocoatings for Biofouling Prevention by Photocatalytic Redox Reactions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lithner, D.; Nordensvan, I.; Dave, G. Comparative acute toxicity of leachates from plastic products made of polypropylene, polyethylene, PVC, acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene, and epoxy to Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewiko, R.; Hakim, M.R.; Firdaus, A.N.; Alfaris, L.; Baswantara, A.; Wibowo, Y.A.; Krisnafi, Y. Use of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene and Polylactide Filaments as Basic Materials for Marine Technology Prototype. Int. J. Eng. Sci. (IJES) 2019, 8, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Rossini, P.; Napolano, L.; Matteucci, G. Biotoxicity and life cycle assessment of two commercial antifouling coatings in marine systems. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraflo, E. Mode of Failure 3-4 Thermal Expansion 3-5 Toxicity and Taint 3-5 Rigidity and Stiffness 3-5 Weathering 3-6 Abrasion Resistance 3-6 Chemical Resistance 3-7 Abs Material. Available online: http://xahax.com/subory/Spec_ABS.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Maniadi, A.; Vamvakaki, M.; Petousis, M.; Vidakis, N.; Suchea, M.; Sevastaki, M.; Viskadourakis, Z.; Kenanakis GKoudoumas, E. Effect of Zinc Oxide concentration on the dielectric properties of 3D Printed Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene nanocomposites. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Semiconductor Conference (CAS), Sinaia, Romania, 9–11 October 2019; pp. 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Vidakis, N.; Petousis, M.; Maniadi, A.; Koudoumas, E.; Kenanakis, G.; Romanitan, C.; Tutunaru, O.; Suchea, M.; Kechagias, J. The mechanical and physical properties of 3D-Printed materials composed of ABS-ZnO nanocomposites and ABS-ZnO microcomposites. Micromachines 2020, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrado, A.R.; Shemelya, C.M.; English, J.D.; Lin, Y.; Wicker, R.B.; Roberson, D.A. Characterizing the effect of additives to ABS on the mechanical property anisotropy of specimens fabricated by material extrusion 3D printing. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 6, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, Y.Y.; Yeoh, C.K.; Idris, M.A.; Teh, P.L.; Elyne, W.N.; Hamzah, K.A.; Sazali, S.A. Influence of filler precoating and printing parameter on mechanical properties of 3D printed acrylonitrile butadiene styrene/zinc oxide composite. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Mater. 2019, 58, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, Y.Y.; Yeoh, C.K.; Idris, M.A.; Teh, P.L.; Hamzah, K.A.; Sazali, S.A. Effect of printing parameters on tensile, dynamic mechanical, and thermoelectric properties of FDM 3D printed CABS/ZnO composites. Materials 2018, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, A.L. The Diffraction of X-Rays by Small Crystalline Particles. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikulčius, G.; Ignatjev, I.; Ručinskienė, A. Rapid method to determine suitability of ABS plastics for metallization. Trans. IMF 2014, 92, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, R.F.; Feng, H.T.; Liang, Q.; Liu, J.Z.; Chen, J.T.; Yan, D.; Feng, J.J.; Li, H.J.; Cheng, S.; Geng, B.S.; et al. Morphology-Controlled Synthesis, Growth Mechanism, Optical and Microwave Absorption Properties of ZnO Nanocombs. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 185405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.T.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mohammad, A.W.; Benamor, A.; Johnson, D.; Hilal, N. Development of polysulfone-nanohybrid membranes using ZnO-GO composite for enhanced antifouling and antibacterial control. Desalination 2017, 402, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotlhao, K.; Lawal, I.A.; Moutloali, R.M.; Klink, M.J. Antifouling properties of silver-zinc oxide polyamide thin film composite membrane and rejection of 2-chlorophenol and 2, 4-dichlorophenol. Membranes 2019, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.; Guan, Q.; Villalobos, L.F.; Peinemann, K.-V.; Pain, A.; Hong, P.-Y. Understanding the antifouling mechanisms related to copper oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 3467–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenten, I.G.; Syaifi, Y.S.; Saputra, F.A.; Zunita, M.; Aryanti, P.T.; Julian, H.; Khoiruddin, K. Preparation of antibacterial and antifouling PSF/ZnO/eugenol membrane for peat water ultrafiltration. Water Supply 2019, 19, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.S.; Yang, H.; Wang, F.Q.; Fatthallah, N.A.; Huang, Y.; Kuga, S. Silicone/ZnO nanorod composite coating as a marine antifouling surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Deng, J.C.; Deng, H.R.; Liu, Z.L.; Xin, L. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan/ZnO nanoparticle composite membranes. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiraman, T.; Kavitha, G.; Rengasamy, R.; Balasubramanian, S. Antifouling behavior of chitosan adorned zinc oxide nanorods. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 69206–69217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Vatanpour, V.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Zarrabi, H. Improvement in flux and antifouling properties of PVC ultrafiltration membranes by incorporation of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemi, N.; Daraei, P.; Astinchap, B. Influence of Nano-Zno Shape on Antifouling Properties of Polythersulfone Nanocomposite Membrane; Iran Membrane: Tehran, Iran, 1394. [Google Scholar]
- Hemalatha, J.; Kavitha, C.; Dasan, K.P. Nano ZnO/acrylic coating for antifouling applications. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2012, 19, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Årstøl, E.; Nymark, M.; Fages-Lartaud, M.; Mikkelsen, Ø. The Development of Polydimethysiloxane/ZnO–GO Antifouling Coatings. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 487, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooss, V.A.; Hamza, F.; Zinjarde, S.S.; Athawale, A.A. PANI-ZnO nanocomposites embedded polyurethane films for antifouling applications. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference and Expo on Ceramics and Composite Materials, London, UK, 3–4 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mooss, V.A.; Hamza, F.; Zinjarde, S.S.; Athawale, A.A. Polyurethane films modified with polyaniline-zinc oxide nanocomposites for biofouling mitigation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Jakaj, G.; Lin, H. Polymeric membranes incorporated with ZnO nanoparticles for membrane fouling mitigation: A brief review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yan, W.; Shi, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Improving permeability and antifouling performance of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of ZnO-DMF dispersion containing nano-ZnO and polyvinylpyrrolidone. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 478, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Qi, Y.H.; Sun, Q. Effect of Nano-ZnO on Properties of Anti-Fouling Coatings Based on FEVE Coploymer. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 496, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.E.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; Hyun, K.T.; Kim, S.J. Preparation of ZnO nanopaint for marine antifouling applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fori, M.; Dobretsov, S.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Dutta, J. Antifouling properties of zinc oxide nanorod coatings. Biofouling 2014, 30, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naamani, L.; Dobretsov, S.; Dutta, J.; Burgess, J.G. Chitosan-zinc oxide nanocomposite coatings for the prevention of marine biofouling. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Composition of Nanosized ZnO Containing Samples | Composition of Microsized ZnO Containing Samples | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | ZnO Nano | ABS | ZnO Micro |
| 80% | 20% | 80% | 20% |
| 90% | 10% | 90% | 10% |
| 95% | 5% | 95% | 5% |
| 97.5% | 2.5% | 97.5% | 2.5% |
| 99% | 1% | 99% | 1% |
| Sample | REF, τ (nm) | Navicula, τ (nm) | Chlorella, τ (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5% ZnO micro | 31.8 | 30.0 | 26.1 |
| 2.5% ZnO micro | 29.5 | 24.4 | 25.0 |
| 5% ZnO micro | 31.5 | 25.4 | 24.7 |
| 20% ZnO micro | 32.1 | 23.5 | 26.1 |
| 0.5% ZnO nano | 32.3 | 26.8 | 21.0 |
| 2.5% ZnO nano | 26.5 | 24.8 | 24.3 |
| 5% ZnO nano | 28.6 | 27.8 | 23.8 |
| 20% ZnO nano | 28.6 | 26.5 | 24.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bouranta, A.; Tudose, I.V.; Georgescu, L.; Karaiskou, A.; Vrithias, N.R.; Viskadourakis, Z.; Kenanakis, G.; Sfakaki, E.; Mitrizakis, N.; Strakantounas, G.; et al. 3D Printed Metal Oxide-Polymer Composite Materials for Antifouling Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060917
Bouranta A, Tudose IV, Georgescu L, Karaiskou A, Vrithias NR, Viskadourakis Z, Kenanakis G, Sfakaki E, Mitrizakis N, Strakantounas G, et al. 3D Printed Metal Oxide-Polymer Composite Materials for Antifouling Applications. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(6):917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060917
Chicago/Turabian StyleBouranta, Andrianna, Ioan Valentin Tudose, Luciana Georgescu, Anna Karaiskou, Nikolaos Rafail Vrithias, Zacharias Viskadourakis, George Kenanakis, Efsevia Sfakaki, Nikolaos Mitrizakis, George Strakantounas, and et al. 2022. "3D Printed Metal Oxide-Polymer Composite Materials for Antifouling Applications" Nanomaterials 12, no. 6: 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060917
APA StyleBouranta, A., Tudose, I. V., Georgescu, L., Karaiskou, A., Vrithias, N. R., Viskadourakis, Z., Kenanakis, G., Sfakaki, E., Mitrizakis, N., Strakantounas, G., Papandroulakis, N., Romanitan, C., Pachiu, C., Tutunaru, O., Barbu-Tudoran, L., Suchea, M. P., & Koudoumas, E. (2022). 3D Printed Metal Oxide-Polymer Composite Materials for Antifouling Applications. Nanomaterials, 12(6), 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060917













