Screening of the Toxicity of Polystyrene Nano- and Microplastics Alone and in Combination with Benzo(a)pyrene in Brine Shrimp Larvae and Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Plastic Particles
2.2. Preparation and Analysis of Exposure Media
2.3. Acute Toxicity Assays
2.3.1. Brine Shrimp Cultures and Immobilization Test
2.3.2. Zebrafish Maintenance, Egg Production, and Embryo Toxicity Test
2.4. Analysis of Bioavailability of Plastic Particles and B(a)P
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the B(a)P Exposure Media
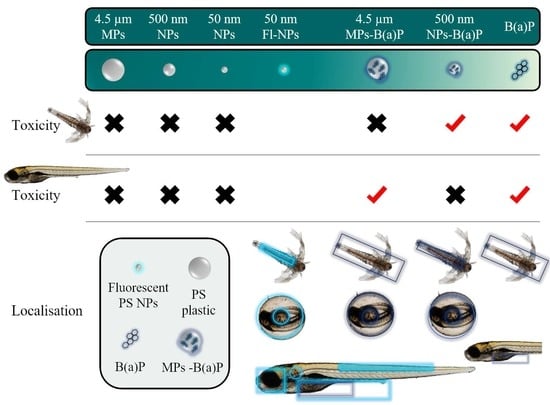
3.2. Toxicity Assays in Brine Shrimp Larvae
3.3. Toxicity Assays in Zebrafish Embryos
3.4. Bioavailability of Plastic Particles and B(a)P
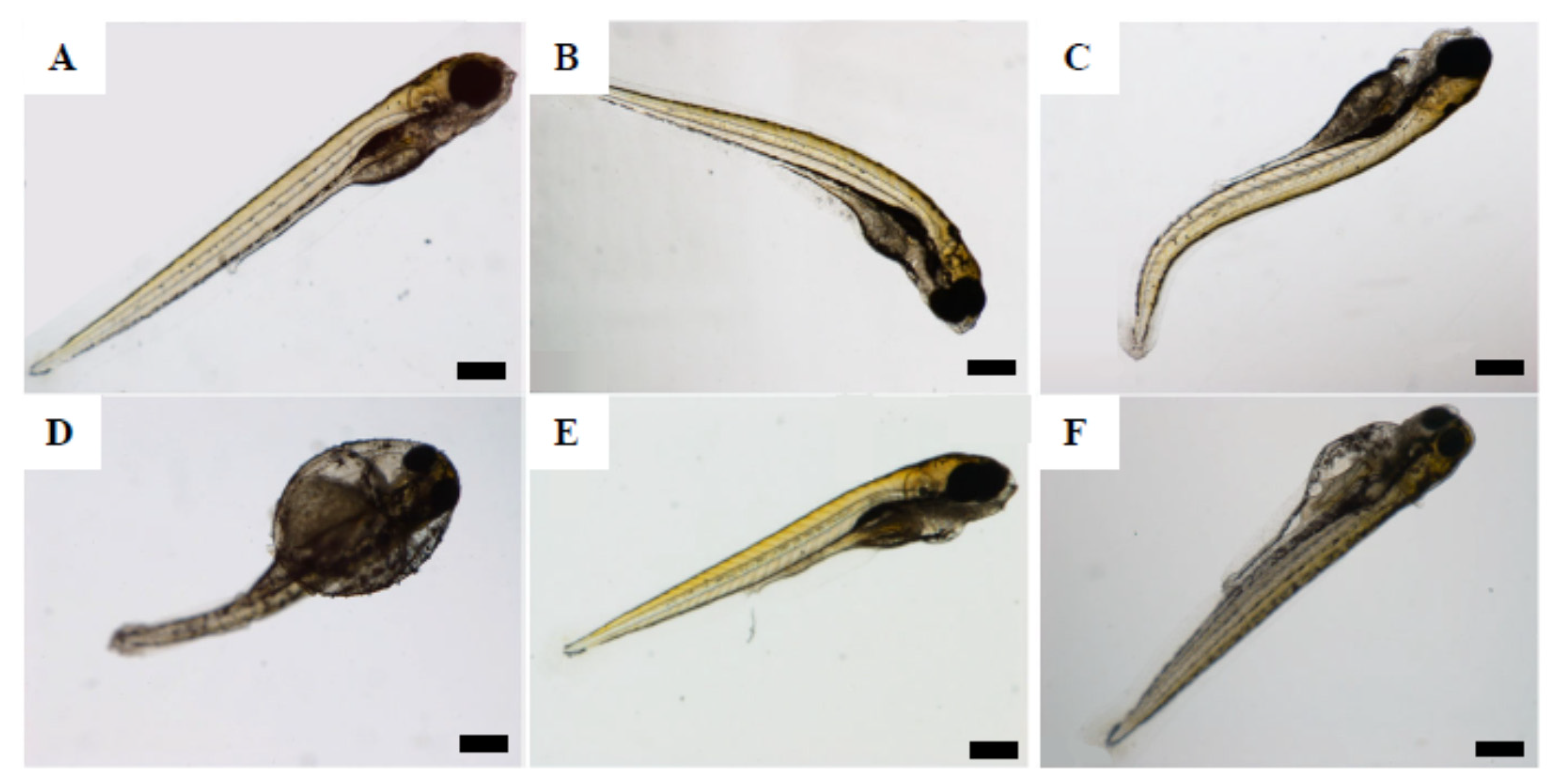
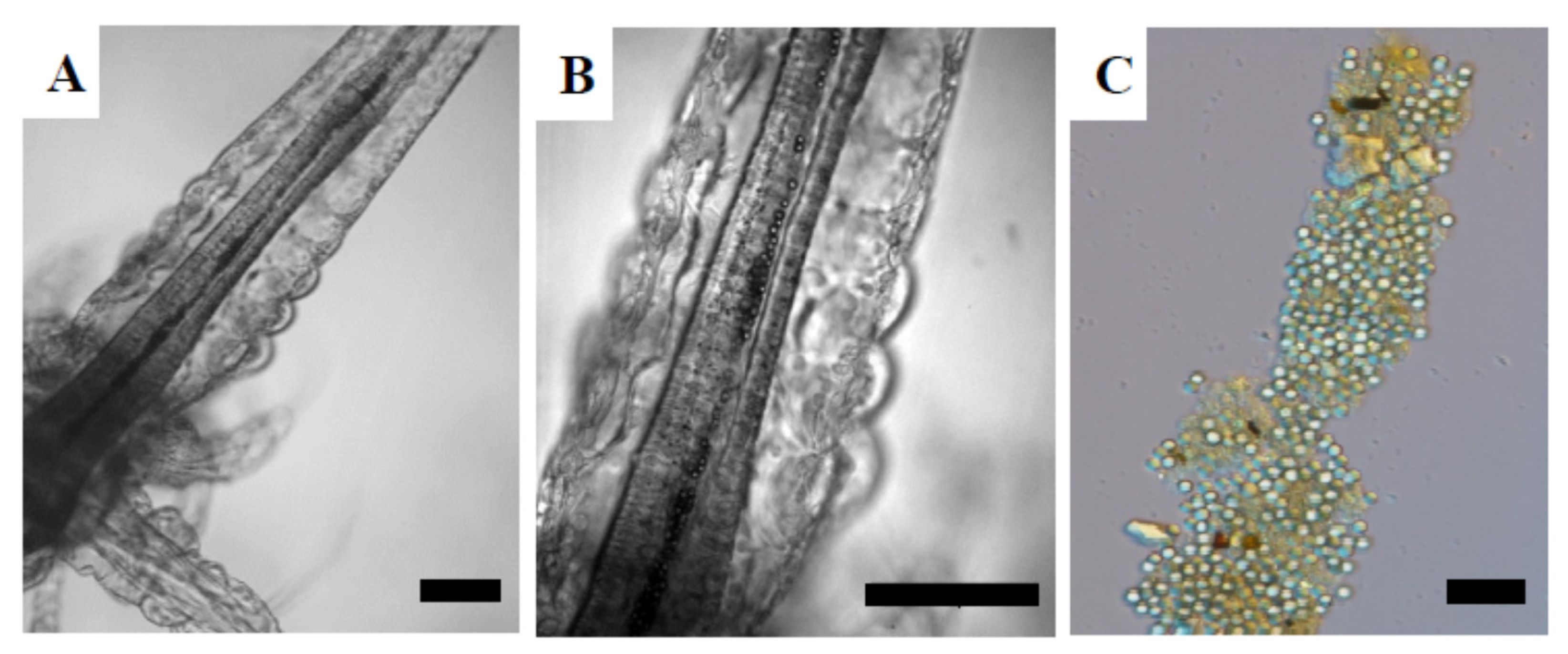
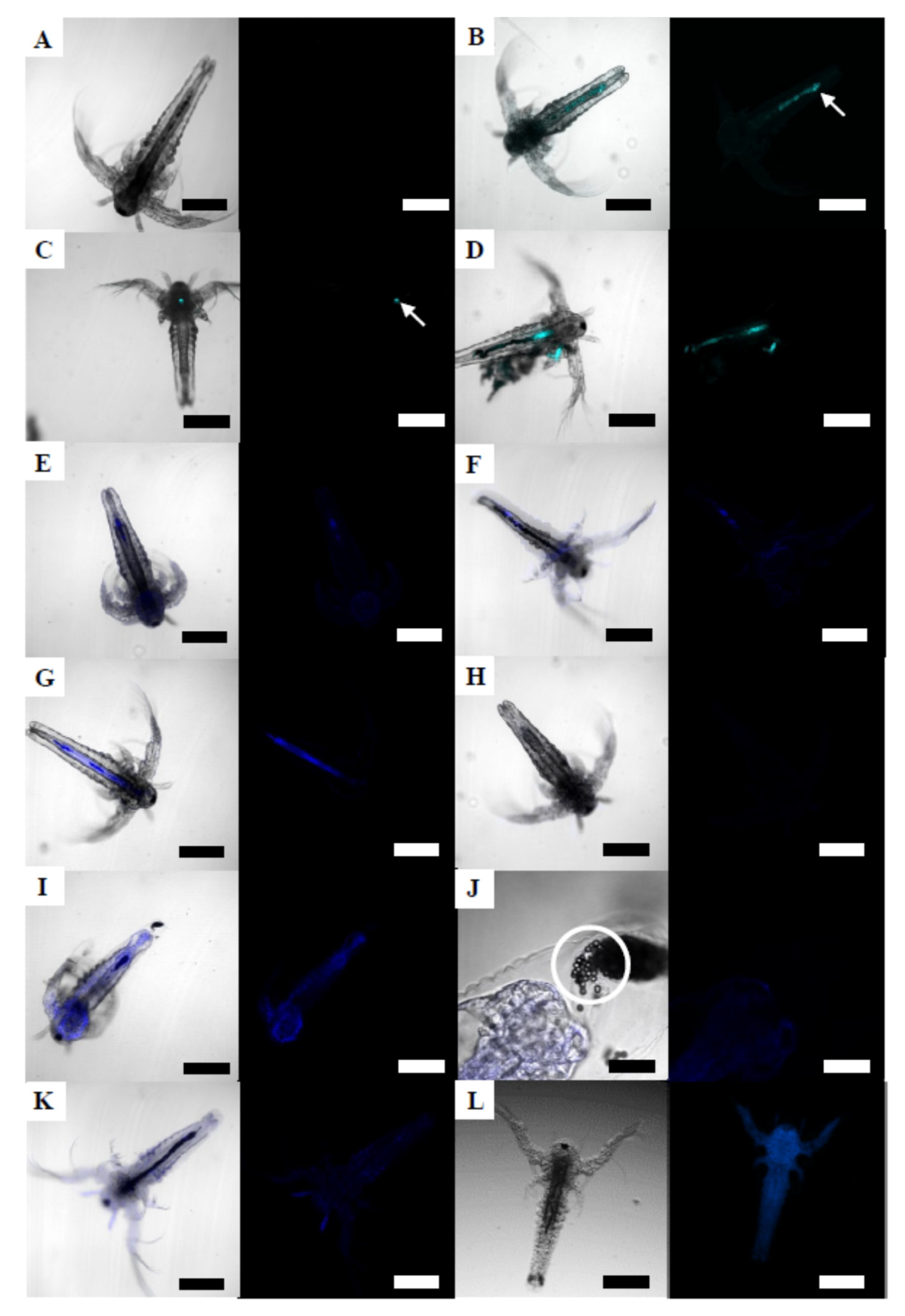
3.4.1. Brine Shrimp Larvae
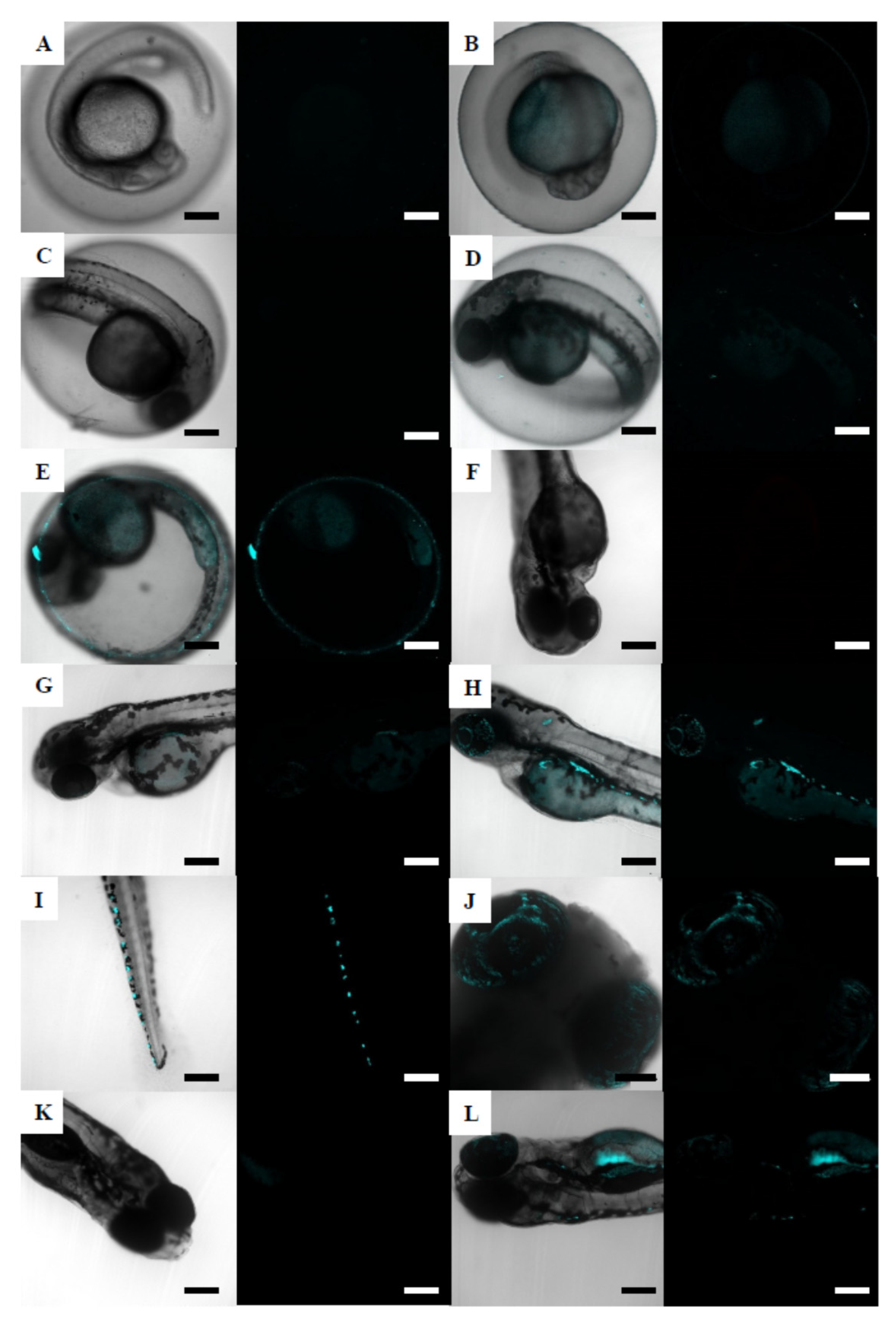
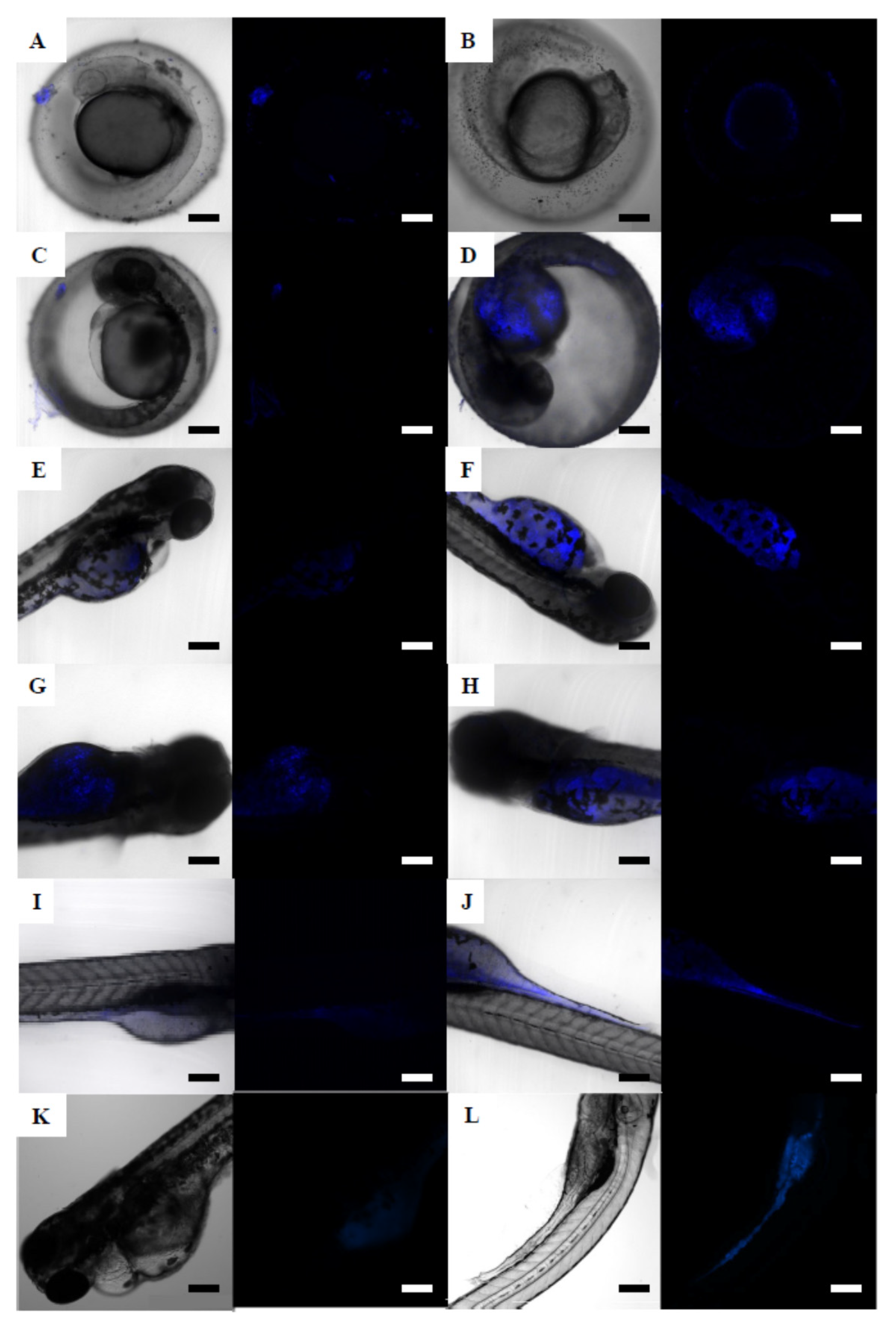
3.4.2. Zebrafish Embryos
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arp, H.P.H.; Kühnel, D.; Rummel, C.; MacLeod, M.; Potthoff, A.; Reichelt, S.; Rojo-Nieto, E.; Schmitt-Jansen, M.; Sonnenberg, J.; Toorman, E.; et al. Weathering plastics as a planetary boundary threat: Exposure, fate, and hazards. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 7246–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Chen, H.; Quan, G.; Yan, J.; Li, T.; et al. Environmental occurrences, fate, and impacts of microplastics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erni-Cassola, G.; Zadjelovic, V.; Gibson, M.I.; Christie-Oleza, J.A. Distribution of plastic polymer types in the marine environment: A meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kögel, T.; Bjorøy, Ø.; Toto, B.; Bienfait, A.M.; Sanden, M. Micro- and nanoplastic toxicity on aquatic life: Determining factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botterell, Z.L.R.; Beaumont, N.; Dorrington, T.; Steinke, M.; Thompson, R.C.; Lindeque, P.K. Bioavailability and effects of mi-croplastics on marine zooplankton: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libralato, G. The case of Artemia spp. in nanoecotoxicology. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 101, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO/TS 20787. Nanotechnologies—Aquatic Toxicity Assessment of Manufactured Nanomaterials in Saltwater Lakes Using Artemia sp. Nauplii; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Bergami, E.; Bocci, E.; Vannuccini, M.L.; Monopoli, M.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A.; Corsi, I. Nano-sized polystyrene affects feeding, behaviour and physiology of brine shrimp Artemia franciscana larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 123, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Mu, J.; Ding, G.; Mao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Jin, F.; Cong, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Effects of ingested polystyrene microplastics on brine shrimp, Artemia parthenogenetica. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendra, M.; Sparaventi, E.; Blasco, J.; Moreno-Garrido, I.; Araujo, C.V.M. Ingestion and bioaccumulation of polystyrene nano-plastics and their effects on the microalgal feeding of Artemia franciscana. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyavani, J.; Sibiya, A.; Bhavaniramya, S.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Nisa, Z.U.; Riaz, M.N.; Nicoletti, M.; Govindarajan, M.; Vaseeharan, B. Toxicity evaluation of polypropylene microplastic on marine microcrustacean Artemia salina: An analysis of im-plications and vulnerability. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambardella, C.; Morgana, S.; Ferrando, S.; Bramini, M.; Piazza, V.; Costa, E.; Garaventa, F.; Faimali, M. Effects of polystyrene microbeads in marine planktonic crustaceans. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ding, G.; Sun, J.; Du, M.; Liu, Q.; Cong, Y.; Jin, F.; Zhang, W.; et al. The uptake and elimination of polystyrene microplastics by the brine shrimp, Artemia parthenogenetica, and its impact on its feeding behavior and intestinal histology. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendel, A.J.; Bessa, F.; Alves, V.E.N.; Amorim, A.L.A.; Patrício, J.; Palma, A.R.T. Widespread microplastic ingestion by fish assemblages in tropical estuaries subjected to anthropogenic pressures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, B. Ingestion of microplastics by fish and its potential consequences from a physical perspective. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barría, C.; Brandts, I.; Tort, L.; Oliveira, M.; Teles, M. Effect of nanoplastics on fish health and performance: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammer, E.; Carr, G.J.; Wendler, K.; Rawlings, J.M.; Belanger, S.E.; Braunbeck, T. Is the fish embryo toxicity test (FET) with the zebrafish (Danio rerio) a potential alternative for the fish acute toxicity test? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 149C, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, E.; Ward, A.C. Zebrafish as a model to evaluate nanoparticle toxicity. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiang, L.; Cheng, J. Exposure to microplastics decreases swimming competence in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gundlach, M.; Yang, S.; Jiang, J.; Velki, M.; Yin, D.; Hollert, H. Quantitative investigation of the mechanisms of mi-croplastics and nanoplastics toward zebrafish larvae locomotor activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Groman, D.B.; Wilson, S.P.; Ismail, P.; Neela, V.K. Biomarker responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae exposed to pristine low-density polyethylene fragments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, N.R.; Koch, B.E.V.; Varela, M.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Spaink, H.P.; Vijver, M.G. Nanoparticles induce dermal and intestinal innate immune system responses in zebrafish embryos. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.A.; Kozal, J.S.; Jayasundara, N.; Massarsky, A.; Trevisan, R.; Geitner, N.; Wiesner, M.; Levin, E.D.; Di Giulio, R.T. Uptake, tissue distribution, and toxicity of polystyrene nanoparticles in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, A.F.; Meyer, D.N.; Petriv, A.-M.V.; Soto, A.L.; Shields, J.N.; Akemann, C.; Baker, B.B.; Tsou, W.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Baker, T.R. Nanoplastics impact the zebrafish (Danio rerio) transcriptome: Associated developmental and neurobehavioral consequences. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic resin pellets as a transport medium for toxic chemicals in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuten, E.L.; Rowland, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Potential for plastics to transport hydrophobic contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 7759–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, M.S.; Sandrini-Neto, L.; Neto, F.F.; Ribeiro, C.A.O.; Di Domenico, M.; Prodocimo, M.M. Biomarker responses in fish exposed to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, T.K.; Anulacion, B.F.; Arkoosh, M.R.; Dietrich, J.P.; Incardona, J.P.; Johnson, L.L.; Ylitalo, G.M.; Myers, M.S. Effects on Fish of Polycyclic Aromatic HydrocarbonS (PAHS) and Naphthenic Acid Exposures. In Organic Chemical Toxicology of Fishes; Tierney, K.B., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 195–255. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, A.; Cao, S.; Sun, F.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Ji, R. Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Rist, S.; Bodin, J.; Jensen, L.H.S.; Schmidt, S.N.; Mayer, P.; Meibom, A.; Baun, A. Microplastics as vectors for environmental contaminants: Exploring sorption, desorption, and transfer to biota. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, W.; Jiang, R.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, F.; Ouyang, G. Quantification of the combined toxic effect of poly-chlorinated biphenyls and nano-sized polystyrene on Daphnia magna. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannetier, P.; Morin, B.; Clérandeau, C.; Laurent, J.; Chapelle, C.; Cachot, J. Toxicity assessment of pollutants sorbed on environmental microplastics collected on beaches: Part II—Adverse effects on Japanese Medaka early life stage. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, V.A.; Bakir, A.; Thompson, R.C.; Henry, T.B. Assessment of micropalstic-sorbed contaminant bioavailability through analysis of biomarker gene expression in larval zebrafish. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 116, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Goss, G.G. Potentiation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon uptake in zebrafish embryos by nanoplastics. Environ. Sci. Nano 2020, 7, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, R.; Uzochukwu, D.; Di Giulio, R.T. PAH sorption to nanoplastics and the Trojan horse effect as drivers of mitochondrial toxicity and PAH localization in zebrafish. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacave, J.M.; Fanjul, A.; Bilbao, E.; Gutiérrez, N.; Barrio, I.; Arostegui, I.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Orbea, A. Acute toxicity, bioaccu-mulation and effects of dietary transfer of silver from brine shrimp exposed to PVP/PEI-coated silver nanoparticles to zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 199, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, M.; Granato, M.; Nüsslein-Volhard, C. Chapter 1: Keeping and raising zebrafish. In Zebrafish: A Practical Approach; Nusslein-Volhard, C., Dahm, R., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 7–37. [Google Scholar]
- OECD TG236. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Section 2: Effects on Biotic Systems Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD): Paris, France, 2013; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Fako, V.E.; Furgeson, D.Y. Zebrafish as a correlative and predictive model for assessing biomaterial nanotoxicity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orbea, A.; Gonzalez, N.; Lacave, J.M.; Barrio, I.; Cajaraville, M.P. Developmental and reproductive toxicity of PVP/PEI-coated silver nanoparticles to zebrafish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 199, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Ruiz, M.; De la Vieja, A.; de Alba Gonzalez, M.; Esteban, M.; Castaño, A.; Cañas, A.I. Toxicity of nanoplastics for zebrafish embryos, what we know and where to go next. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duis, K.; Coors, A. Microplastics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment: Sources (with a specific focus on personal care products), fate and effects. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Busquets, R.; Campos, L.C. Assessment of microplastics in freshwater systems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudrimont, M.; Arini, A.; Guégan, C.; Venel, Z.; Gigault, J.; Pedrono, B.; Prunier, J.; Maurice, L.; Ter Halle, A.; Feurtet-Mazel, A. Ecotoxicity of polyethylene nanoplastics from the North Atlantic oceanic gyre on freshwater and marine organisms (microalgae and filter-feeding bivalves). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 3746–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, D.; Amorim, J.; Pinheiro, C.; Oliva-Teles, L.; Varó, I.; Rocha, R.M.; Vieira, M.N. Uptake and effects of different concentrations of spherical polymer microparticles on Artemia franciscana. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, T.Y.; Jia, P.-P.; Li, W.-G.; Junaid, M.; Xin, G.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Pei, D.-S. Acute and chronic effects of polystyrene microplastics on brine shrimp: First evidence highlighting the molecular mechanism through transcriptome analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Wu, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, Z.; Shi, H.; Raley-Susman, K.M.; He, D. Microplastic particles cause intestinal damage and other adverse effects in zebrafish Danio rerio and nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 619–620, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurchaba, N.; Cassone, B.J.; Northam, C.; Ardelli, B.F.; LeMoine, C.M.R. Effects of MP polyethylene microparticles on micro-biome and inflammatory response of larval zebrafish. Toxics 2020, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Vijver, M.G.; Lahive, E.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Svendsen, C.; Heutink, R.; van Bodegom, P.M.; Baas, J. Acute toxicity of organic pesticides to Daphnia magna is unchanged by co-exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Enhanced desorption of persistent organic pollutants from microplastics under simulated physiological conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormier, B.; Batel, A.; Cachot, J.; Bégout, M.-L.; Braunbeck, T.; Cousin, X.; Keiter, S.H. Multi-laboratory hazard assessment of contaminated microplastic particles by means of enhanced fish embryo test with the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Incardona, J.P.; Swarts, T.L.; Edmunds, R.C.; Linbo, T.L.; Aquilina-Beck, A.; Sloan, C.A.; Gardner, L.D.; Block, B.A.; Scholz, N.L. Exxon Valdez to Deepwater Horizon: Comparable toxicity of both crude oils to fish early life stages. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142–143, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, W.M.; Hooven, L.A.; Mahadevan, B. Carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-DNA adducts and mechanism of action. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2005, 45, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F. Comparative acute toxicity of organic pollutants and reference values for crustaceans. I. Branchiopoda, Cope-poda and Ostracoda. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 385–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenaka, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Nagata, T.; Takahashi, H.; Miyabara, Y.; Hanazato, T.; Ishizuka, M.; Isobe, T.; Kim, J.-W.; Chang, K.-H. Effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) on an aquatic ecosystem: Acute toxicity and community-level toxic impact tests of benzo[a]pyrene using lake zooplankton community. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 38, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weigt, S.; Huebler, N.; Strecker, R.; Braunbeck, T.; Broschard, T.H. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos as a model for testing proteratogens. Toxicology 2011, 281, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogbanmu, T.O.; Nagy, E.; Philips, D.H.; Arlt, V.M.; Otitoloju, A.A.; Bury, N.R. Lagos lagoon sediment organic extracts and pol-ycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons induce embryotoxic, teratogenic and genotoxic effects in Danio rerio (zebrafish) embryos. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 14489–14501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knecht, A.L.; Truong, L.; Simonich, M.T.; Tanguay, R.L. Developmental benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) exposure impacts larval behavior and impairs adult learning in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 59, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarrick, S.; Cunha, V.; Zapletal, O.; Vondráček, J.; Dreji, K. In vitro and in vivo genotoxicity of oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, M.; Suzuki, N. Toxicities of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons for aquatic animals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, W.E.; Wasik, S.P.; Miller, M.M.; Tewari, Y.B.; Brown-Thomas, J.M.; Goldberg, R.N. Solution thermodynamics of some slightly soluble hydrocarbons in water. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1983, 28, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Ferreira, M.; Rey-Salgueiro, L.; Reis-Henriques, M.A. Comparision of the waterborne and dietary routes of exposure on the effects of benzo(a)pyrene on biotransformation pathways in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Luo, K.; Fan, Z.; Huang, C.; Hu, J. Modulation of benzo[a]pyrene-induced toxic effects in Japanese Medaka (Oryzias latipes) by 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13068–13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebowski, A.C.; Tanguay, R.L.; Simonich, S.L.M. Quantitation and prediction of sorptive losses during toxicity testing of pol-ycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) and nitrated PAH (NPAH) using polystyrene 96-well plates. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2016, 57, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, F.C.; Cirpka, O.A.; Goss, K.-U.; Henneberger, L.; Escher, B.I. Application of experimental polystyrene partition constants and diffusion coefficients to predict the sorption of neutral organic chemicals to multiwell plates in vivo and in vitro bioassays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13511–13522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setälä, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Gong, Z.; Wang, L. Barrier function of zebrafish embryonic chorions against microplastics and nanoplastics and its impact on embryo development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Pomeren, M.; Brun, N.R.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Vijver, M.G. Exploring uptake and biodistribution of polystyrene (nano)particles in zebrafish embryos at different developmental stages. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacave, J.M.; Retuerto, A.; Vicario-Parés, U.; Gilliland, D.; Oron, M.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Orbea, A. Effects of metal-bearing nano-particles (Ag, Au, CdS, ZnO, SiO2) on developing zebrafish embryos. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 325102–325116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Silic, M.R.; Schaber, A.; Wasel, O.; Freeman, J.L.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Exposure route affects the distribution and toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics in zebrafish. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evensen, L.; Johansen, P.L.; Koster, G.; Zhu, K.; Herfindal, L.; Speth, M.; Fenaroli, F.; Hildahl, J.; Bagherifam, S.; Tulotta, C.; et al. Zebrafish as a model system for characterization of nano-particles against cancer. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 862–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; He, C.; Jin, Y.; Fu, Z. Polystyrene nanoparticles trigger the activation of p38 MAPK and apoptosis via inducing oxidative stress in zebrafish and macrophage cells. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batel, A.; Linti, F.; Scherer, M.; Erdinger, L.; Braunbeck, T. Transfer of benzo[a]pyrene from microplastics to Artemia nauplii and further to zebrafish via a trophic food web experiment: CYP1A induction and visual tracking of persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| 50 nm NPs | 500 nm NPs | 4.5 µm MPs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particles/mL | mg/L | Particles/mL | mg/L | Particles/mL | mg/L |
| 106 | 0.000069 | ||||
| 5 × 103 | 0.00034 | ||||
| 107 | 0.00069 | 0.00069 | |||
| 5 × 102 | 0.025 | ||||
| 109 | 0.069 | 106 | 0.069 | 103 | 0.069 |
| 1010 | 0.687 | 107 | 0.687 | 107 | 0.687 |
| 1011 | 6.87 | 108 | 6.87 | 108 | 6.87 |
| 106 | 50.1 | ||||
| Nominal Concentration | Measured Concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 24 h | 48 h | 120 h | |
| 0.1 | 0.029 ± 0.005 | 0.029 ± 0.006 (100%) | 0.022 ± 0.002 (75.9%) | 0.014 ± 0.001 (48.3%) |
| 0.5 | 0.315 ± 0.142 | 0.432 ± 0.084 (137.1%) | 0.2578 ± 0.011 (81.8%) | 0.282 ± 0.012 (89.5%) |
| 1 | 0.496 ± 0.111 | 0.503 ± 0.006 (101.4%) | 0.301 ± 0.001 (60.7%) | 0.265 ± 0.025 (53.4%) |
| 5 | 1.496 ± 0.707 | 1.173 ± 0.505 (78.4%) | 0.738 ± 0.299 (49.3%) | 1.118 ± 0.053 (74.7%) |
| 10 | 4.922 ± 1.995 | 5.023 ± 0.397 (102.1%) | 4.927 ± 0.283 (100.1%) | 5.269 ± 1.095 (107%) |
| Concentration (mg/L) | 24 hph Larvae | 48 hph Larvae | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | 48 h | 24 h | 48 h | ||
| 50 nm NPs | 0 | 100.0 | 96.8 | 93.8 | 100.0 |
| 0.000069 | 93.3 | 90.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 0.00069 | 97.0 | 97.0 | 96.8 | 93.3 | |
| 0.069 | 96.9 | 96.9 | 93.3 | 100.0 | |
| 0.687 | 96.7 | 90.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 6.87 | 93.1 | 89.7 | 100.0 | 93.3 | |
| 500 nm NPs | 0 | 96.8 | 93.5 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 0.00034 | 93.5 | 96.8 | 100.0 | 96.8 | |
| 0.00069 | 93.3 | 93.3 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| 0.069 | 96.8 | 87.1 | 100.0 | 91.2 | |
| 0.687 | 90.9 | 87.9 | 100.0 | 97.0 | |
| 6.87 | 97.1 | 94.3 | 100.0 | 96.9 | |
| 4.5 µm MPs | 0 | 100.0 | 96.8 | 100.0 | 93.3 |
| 0.0251 | 100.0 | 96.8 | 100.0 | 96.8 | |
| 0.0501 | 96.8 | 93.5 | 100.0 | 80.0 | |
| 0.501 | 100.0 | 93.3 | 96.9 | 93.8 | |
| 5.01 | 96.7 | 93.3 | 96.7 | 87.1 | |
| 50.1 | 100.0 | 96.7 | 100.0 | 75.0 | |
| 500 nm NPs-B(a)P | 0 | 96.7 | 86.7 | 100.0 | 80.0 |
| 0.00034 | 93.3 | 80.0 * | 93.3 | 53.3 *$ | |
| 0.00069 | 100.0 | 60.0 *$ | 100.0 | 60.0 | |
| 0.069 | 96.7 | 83.3 | 100.0 | 56.7 | |
| 0.687 | 100.0 | 73.3 | 100.0 | 56.7 $# | |
| 6.87 | 93.3 | 36.7 *$# | 100.0 | 60.0 $# | |
| 4.5 µm MPs-B(a)P | 0 | 96.7 | 76.7 | 93.3 | 80.0 |
| 0.0251 | 90.0 | 60.0 $ | 96.7 | 90.0 | |
| 0.0501 | 100.0 | 83.3 | 100.0 | 86.7 | |
| 0.501 | 86.7 | 56.7 $ | 100.0 | 90.0 | |
| 5.01 | 90.0 | 70.0 | 100.0 | 70.0 | |
| 50.1 | 100.0 | 63.3 $ | 93.3 | 90.0 | |
| B(a)P | 0 | 97.2 | 91.7 | 93.3 | 80.0 |
| 0.1 | 100.0 | 65.6 * | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 0.5 | 94.3 | 51.4 * | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 1 | 97.0 | 57.6 * | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 5 | 87.9 | 45.5 * | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| 10 | 90.6 | 59.4 * | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Exposure Conc. (mg/L) | Surv. (%) | Hatching Time (h) | Malform. (%) | Type of Malform. (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | PE | YE | EA | |||||
| 50 nm NPs | 0 | 97.2 | 72 | 11.4 | 11.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.000069 | 96.7 | 72 | 20.7 | 20.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.00069 | 100 | 72 | 6.7 | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.069 | 93.3 | 72 | 7.1 | 3.6 | 3.6 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.687 | 96.7 | 72 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6.87 | 90 | 72 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 500 nm NPs | 0 | 94.4 | 72 | 8.8 | 8.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.00034 | 93.3 | 72 | 10.7 | 10.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.00069 | 90 | 71.1 ± 4.6 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.069 | 96.7 | 72 | 17.2 | 17.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.687 | 96.7 | 72 | 20.7 | 20.7 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | |
| 6.87 | 93.3 | 72 | 21.4 | 14.3 | 10.7 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4.5 µm MPs | 0 | 94.4 | 71.3 ± 4.1 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.0251 | 96.7 | 72 | 10.3 | 6.9 | 3.4 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.0501 | 100 | 72 | 16.7 | 10 | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.501 | 93.3 | 70.3 ± 6.3 | 7.1 | 7.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5.01 | 100 | 72 | 16.7 | 13.3 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 50.1 | 100 | 70.4 ± 6.1 | 20 | 16.6 | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | |
| 500 nm NPs-B(a)P | 0 | 94.4 | 58.6 ± 12.1 | 16.7 | 13.9 | 2.8 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.00034 | 93.3 | 55.7 ± 11.4 | 16.7 | 10 | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.00069 | 90 | 54.2 ± 10.7 | 26.7 | 26.7 | 6.6 | 3.3 | 0 | |
| 0.069 | 96.7 | 57.1 ± 11.9 | 16.7 | 13.3 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.687 | 96.7 | 55.4 ± 11.3 | 16.7 | 10 | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6.87 | 93.3 | 56.6 ± 12.0 | 10 | 6.7 | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4.5 µm MPs-B(a)P | 0 | 100 | 71.3 ± 4 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.0251 | 100 | 72 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.0501 | 100 | 72.0 | 16.7 | 16.7 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.501 | 100 | 70.4 ± 6.1 | 13.3 | 10 | 3.3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5.01 | 100 | 72 | 26.7 | 20 | 10 | 3.3 | 0 | |
| 50.1 | 100 | 70.4 ± 6.1 | 56.7 *$ | 36.7 | 30 | 6.7 | 0 | |
| B(a)P | 0 | 97.2 | 67.2 ± 9.7 | 11.6 | 8.6 | 2.9 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.1 | 96.7 | 69.5 ± 8.3 | 13.8 | 13.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.5 | 86.7 | 69.6 ± 7.8 | 24.1 | 23.1 | 7.7 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 | 86.7 | 69.2 ± 7.8 | 26.9 | 23.1 | 7.7 | 3.8 | 0 | |
| 5 | 96.7 | 70.3 ± 6.2 | 50 * | 27.5 | 20.6 | 3.4 | 0 | |
| 10 | 96.7 | 70.3 ± 6.2 | 58.6 * | 44.8 | 24.1 | 0 | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Álvarez, I.; Le Menach, K.; Devier, M.-H.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Budzinski, H.; Orbea, A. Screening of the Toxicity of Polystyrene Nano- and Microplastics Alone and in Combination with Benzo(a)pyrene in Brine Shrimp Larvae and Zebrafish Embryos. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060941
Martínez-Álvarez I, Le Menach K, Devier M-H, Cajaraville MP, Budzinski H, Orbea A. Screening of the Toxicity of Polystyrene Nano- and Microplastics Alone and in Combination with Benzo(a)pyrene in Brine Shrimp Larvae and Zebrafish Embryos. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(6):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060941
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Álvarez, Ignacio, Karyn Le Menach, Marie-Hélène Devier, Miren P. Cajaraville, Hélène Budzinski, and Amaia Orbea. 2022. "Screening of the Toxicity of Polystyrene Nano- and Microplastics Alone and in Combination with Benzo(a)pyrene in Brine Shrimp Larvae and Zebrafish Embryos" Nanomaterials 12, no. 6: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060941
APA StyleMartínez-Álvarez, I., Le Menach, K., Devier, M. -H., Cajaraville, M. P., Budzinski, H., & Orbea, A. (2022). Screening of the Toxicity of Polystyrene Nano- and Microplastics Alone and in Combination with Benzo(a)pyrene in Brine Shrimp Larvae and Zebrafish Embryos. Nanomaterials, 12(6), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12060941