Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor Based on PVDF/MXene Nanosheet/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites for Electronic Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials
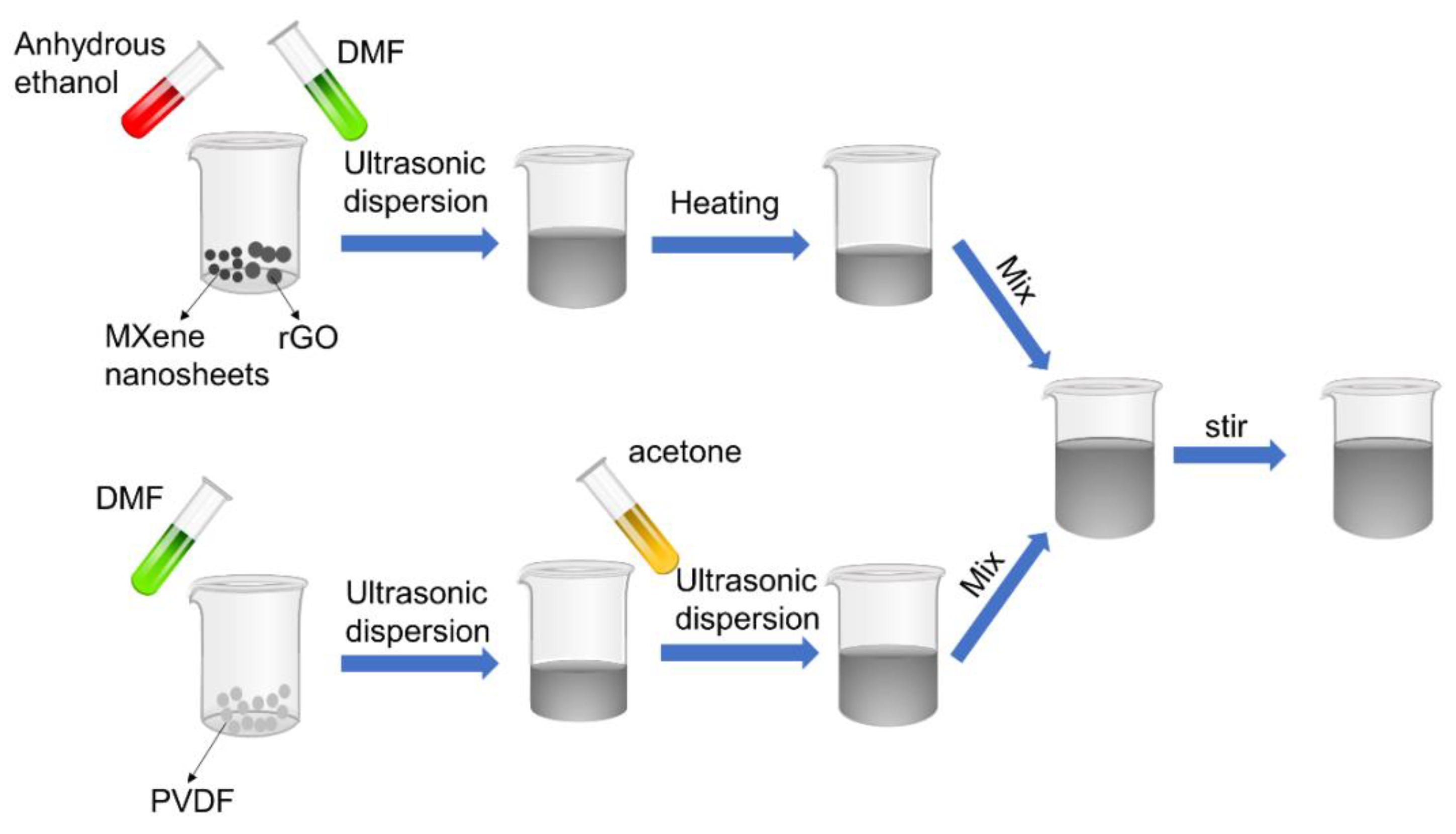
2.2. Preparation of PMR Mixed Printing Solution
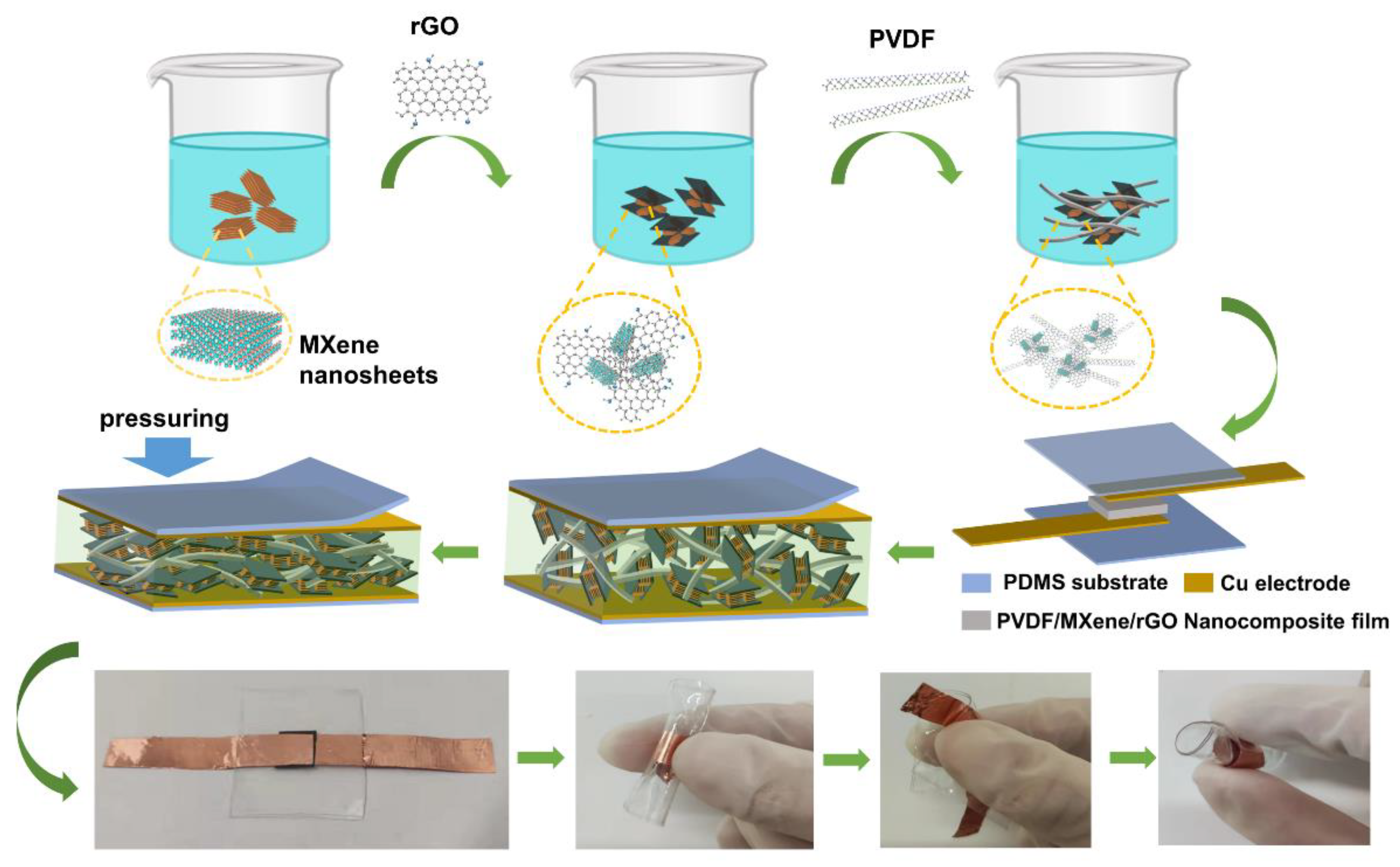
2.3. Preparation of PMR Nanocomposite Thin Films
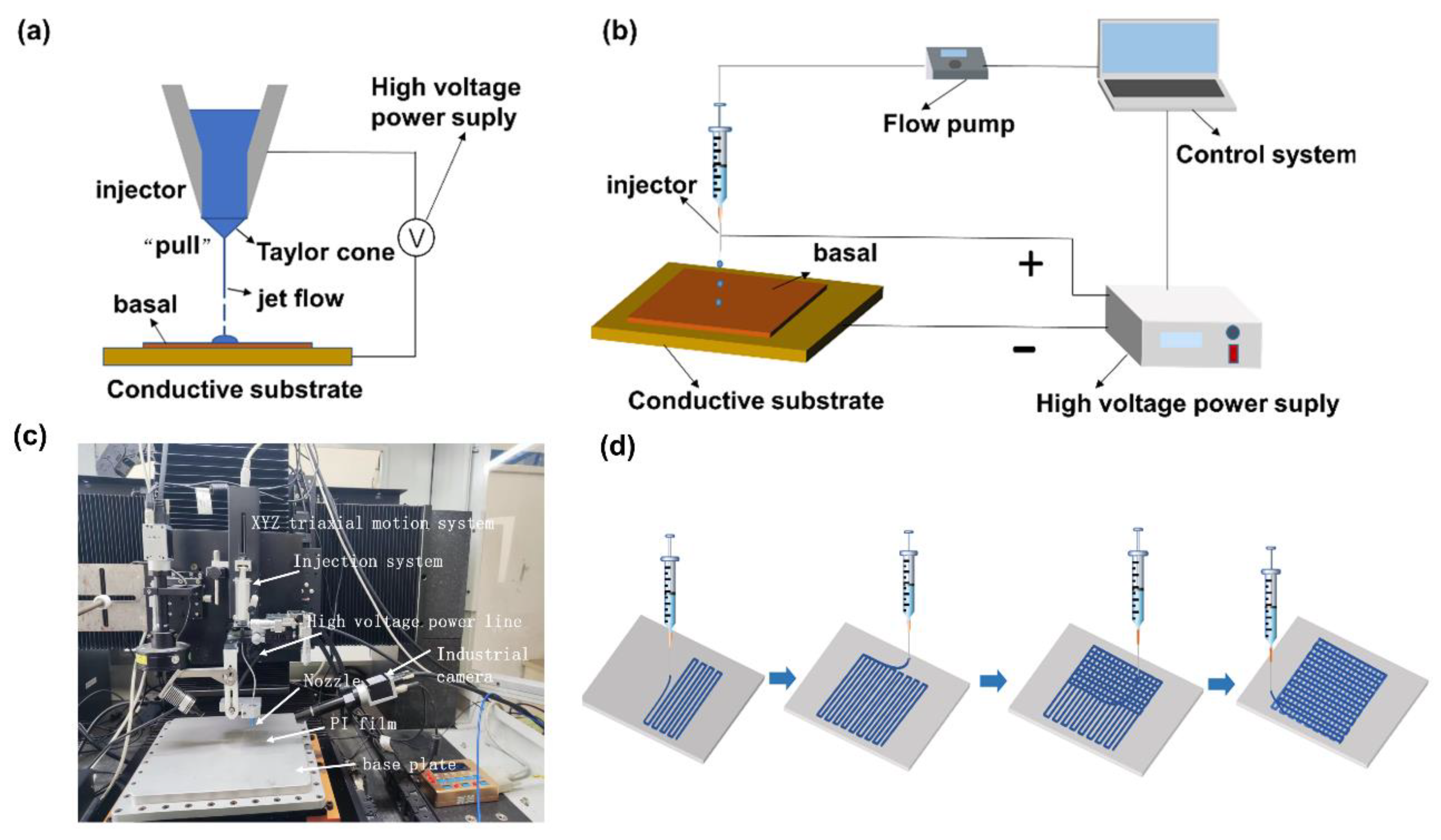
2.4. Fabrication of PMR Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor
2.5. Characterization and Measurement
3. Results and Discussions
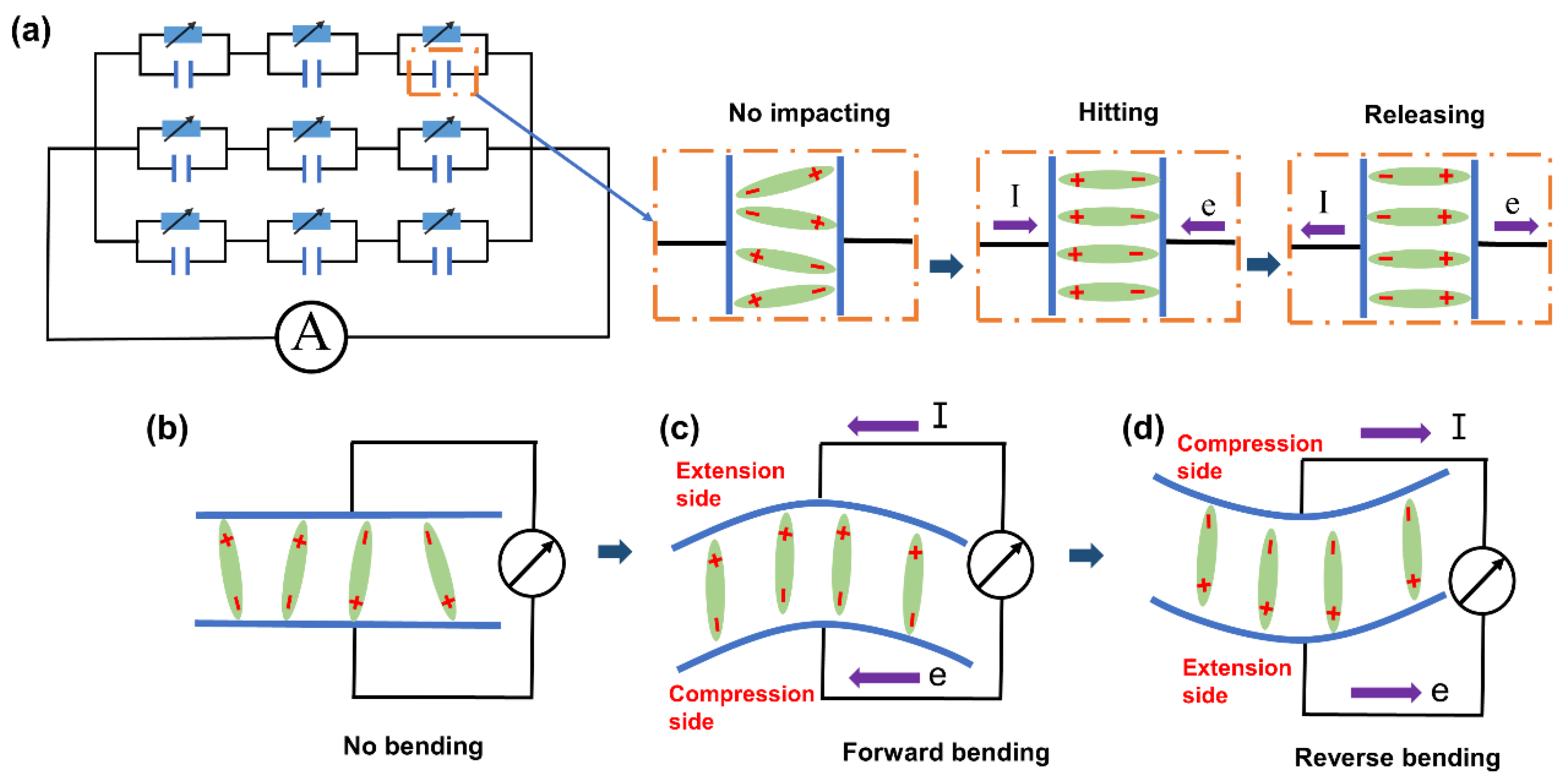
3.1. Sensing Mechanism of the PMR Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor
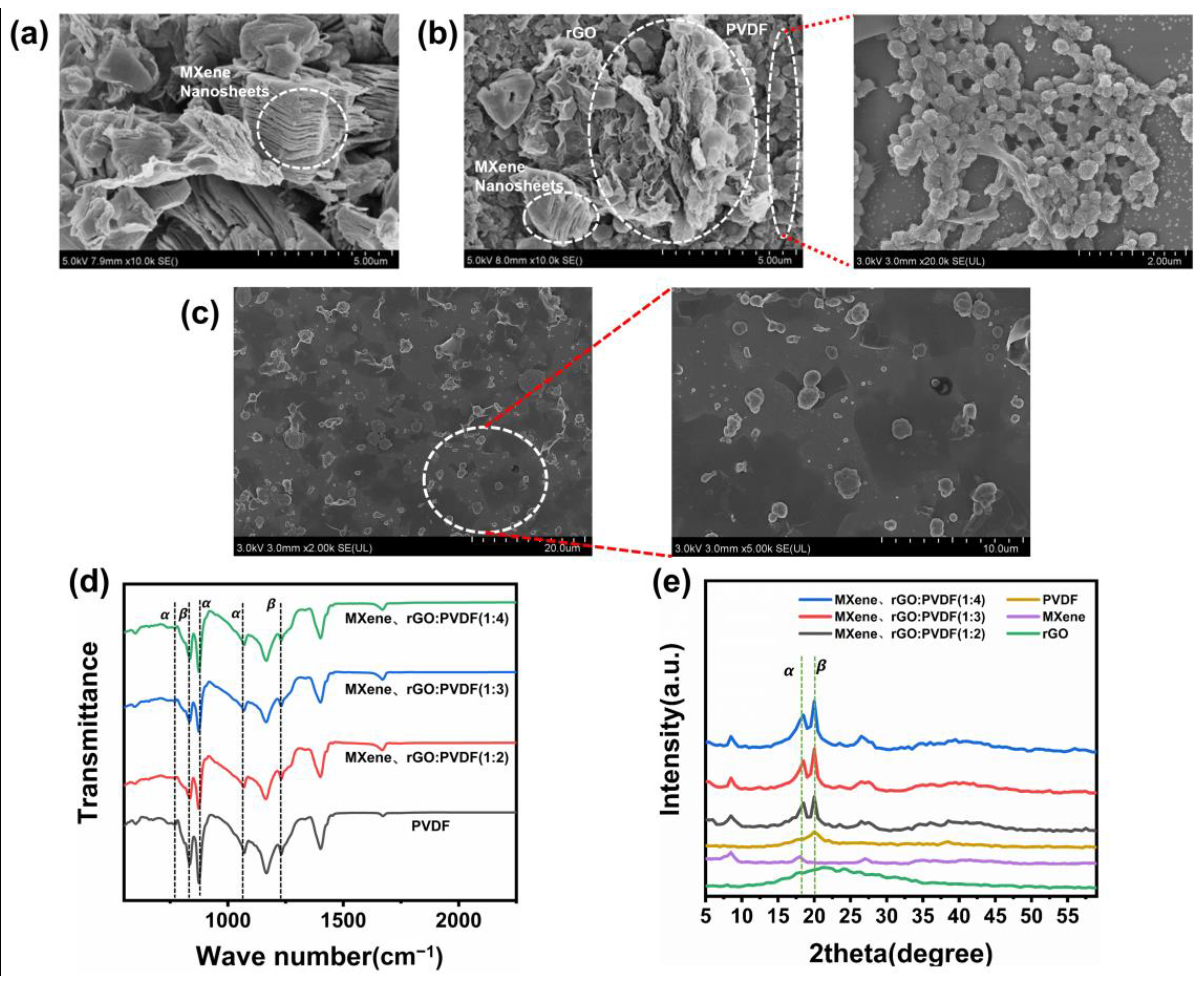
3.2. Characterization of the PMR Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor
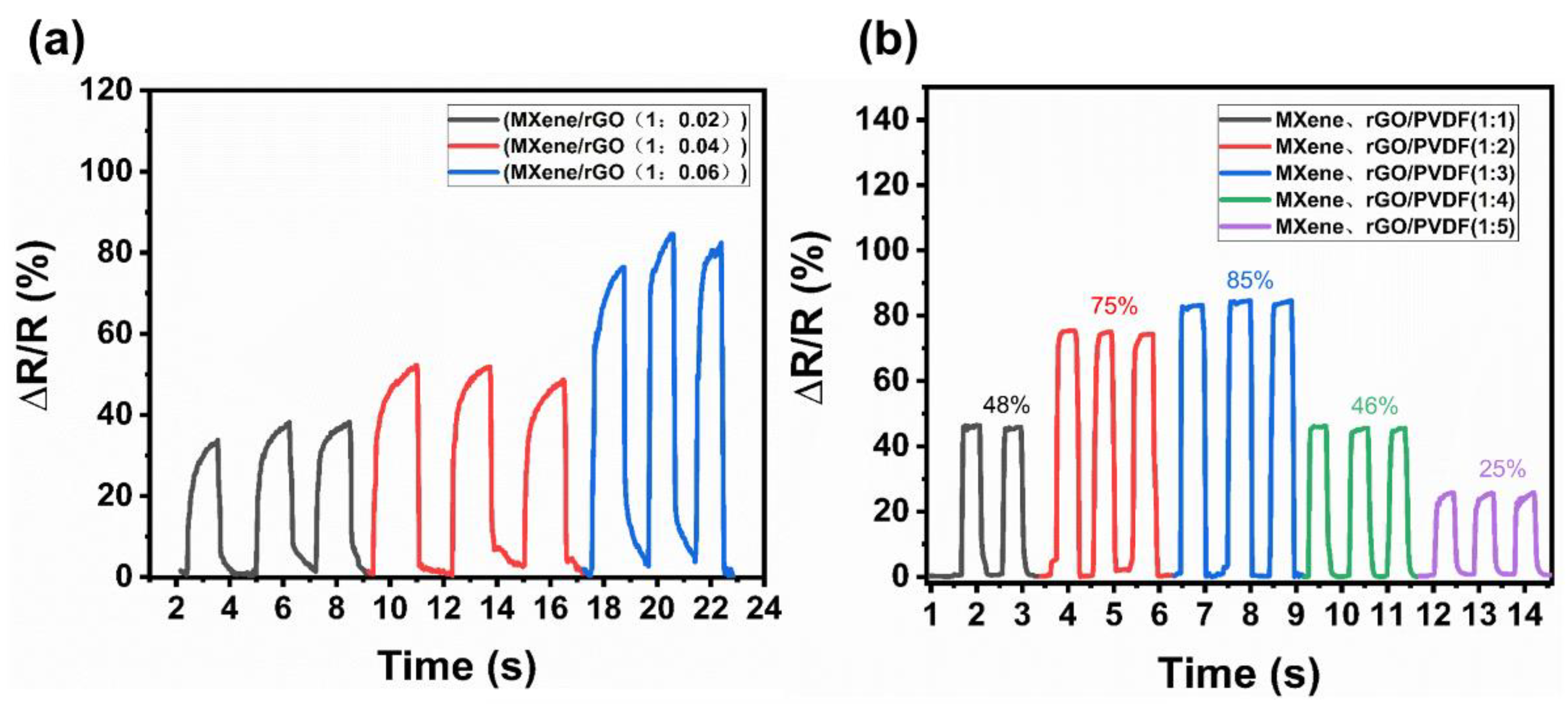
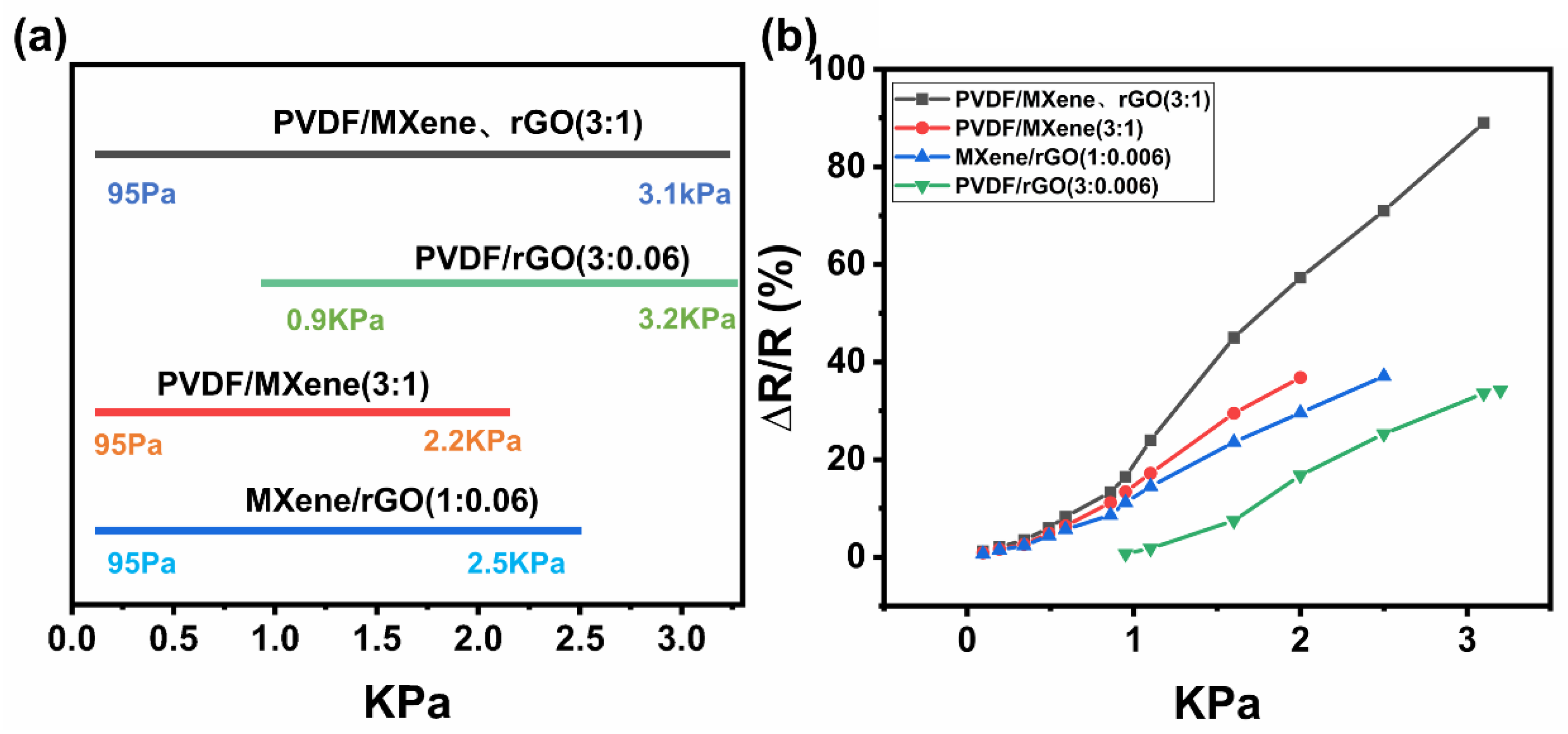
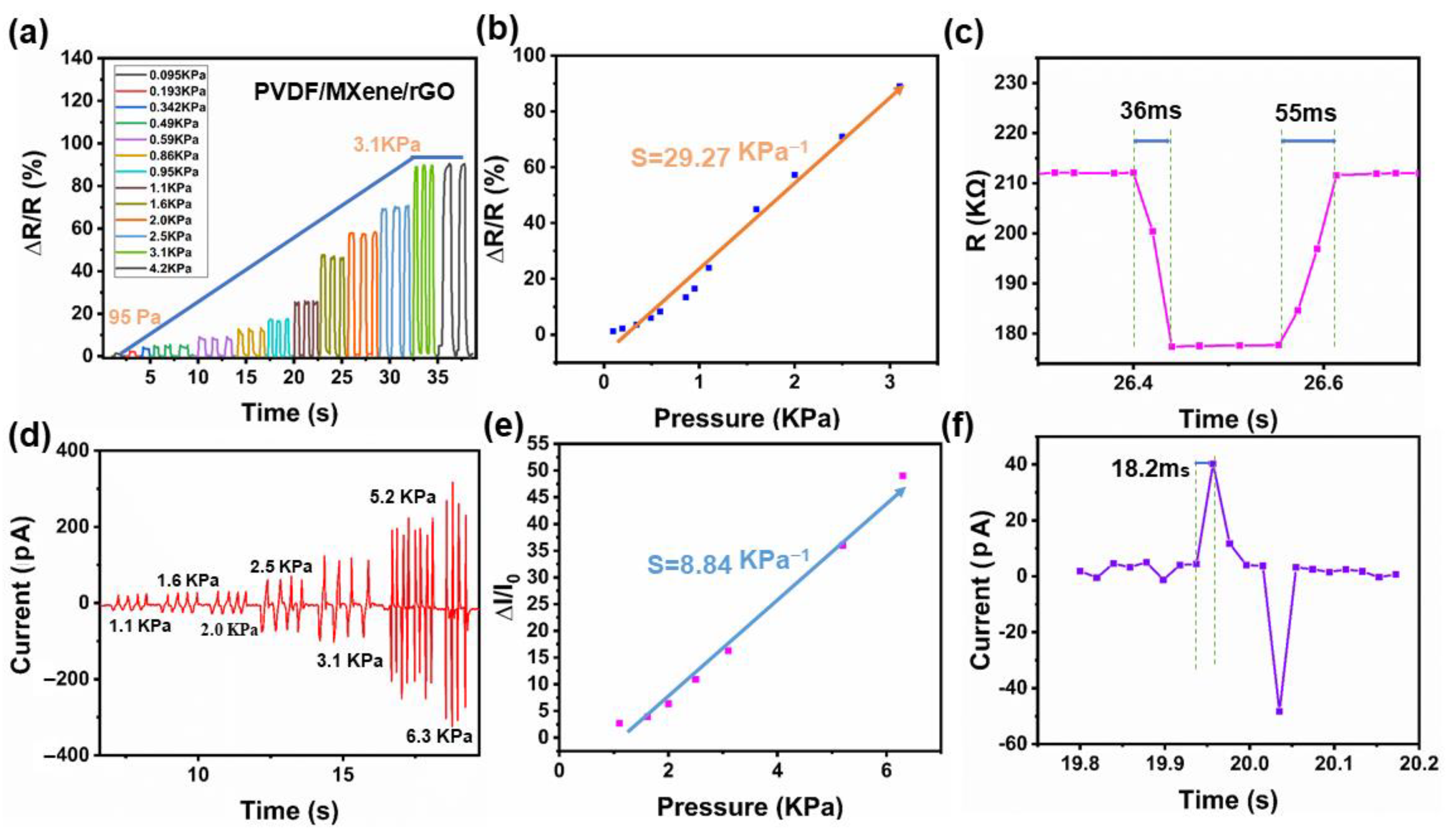
3.3. Sensing Properties of the PMR Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor
3.4. Practical Applications of PMR Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benight, S.J.; Wang, C.; Tok, J.B.H.; Bao, Z.A. Stretchable and self-healing polymers and devices for electronic skin. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1961–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chortos, A.; Bao, Z.N. Skin-inspired electronic devices. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Li, F.Y.; Han, C.P.; Cui, Z.M.; Xie, G.Y.; Zhang, A.Q. Highly sensitive and selective tryptophan colorimetric sensor based on 4, 4-bipyridine-functionalized silver nanoparticles. Sensor Actuat. B-Chem. 2010, 145, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.J.; Chortos, A.; Yu, G.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Isaacson, S.; Allen, R.; Shi, Y.; Dauskardt, R.; Bao, Z.N. An ultra-sensitive resistive pressure sensor based on hollow-sphere microstructure induced elasticity in conducting polymer film. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Wei, X.; Gao, S.; Yue, W.J.; Li, Y.; Shen, G.Z. Recent advances in carbon material-based multifunctional sensors and their applications in electronic skin systems. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 31, 2104288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavese, G.; Stassi, S.; Fallauto, C.; Corbellini, S.; Cauda, V.; Camarchia, V.; Pirola, M.; Pirri, C.F. Piezoresistive flexible composite for robotic tactile applications. Sensor Actuat. A-Phys. 2014, 208, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.C.; Ye, B.W.; Lu, C.F.; Chen, C.T.; Jao, M.H.; Su, W.F.; Hung, W.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Chen, Y.F. Extraordinarily sensitive and low-voltage operational cloth-based electronic skin for wearable sensing and multifunctional integration uses: A tactile-induced insulating-to-conducting transition. Adv. Funct. Mate. 2016, 26, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.L.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G.L. An ultra-sensitive and rapid response speed graphene pressure sensors for electronic skin and health monitoring. Nano Energy 2016, 23, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cu, Y.; Xiong, Z.P.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, T. Silk-molded flexible, ultrasensitive, and highly stable electronic skin for monitoring human physiological signals. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.C.; Shen, J.; Ge, G.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Jin, W.Q.; Huang, W.; Shao, J.J.; Yang, J.; Dong, X.C. Stretchable Ti3C2Tx MXene/carbon nanotube composite based strain sensor with ultrahigh sensitivity and tunable sensing range. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Liu, H.Z.; Chen, S.; Dong, X.C.; Wang, P.P.; Liu, S.Q.; Lin, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, L. Channel crack-designed gold@PU sponge for highly elastic piezoresistive sensor with excellent detectability. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 2098–20105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryafar, M.; Hamedi, M.; Ganjeh, M.M. A novel temperature compensated piezoresistive pressure sensor. Measurement 2015, 63, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, H.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Cheon, S.; Kim, H.; Koo, J.H.; Kim, T.R.; Lee, S.; Schwartz, G.; Chang, H. Stretchable energy-harvesting tactile electronic skin capable of differentiating multiple mechanical stimuli modes. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7324–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.Y.; Keplinger, C.; Whitesides, G.M.; Suo, Z.G. Ionic skin. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7608–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Kyung, K.U.; Park, I.; Sitti, M. Stretchable, skin-mountable, and wearable strain sensors and their potential applications: A review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1678–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Choi, E.; Sim, M.; Kang, M.; Choi, J.W.; Cha, S.; Kwon, H.J.; Kang, H.; Jang, J.E. Fundamental insights into the electrical signals of a piezoelectric sensor in a sliding condition. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, S.; Siponkoski, T.; Sarlin, E.; Mettanen, M.; Vuoriluoto, M.; Pammo, A.; Juuti, J.; Rojas, O.J.; Franssila, S.; Tuukkanen, S. Cellulose nanofibril film as a piezoelectric sensor material. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 15607–15614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kerpel, K.; De Schampheleire, S.; De Keulenaer, T.; De Paepe, M. Effect of the bend geometry on the two-phase frictional pressure drop and flow behaviour in the vicinity of the bend. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 104, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Sultana, A.; Garain, S.; Xie, M.; Bowen, C.R.; Henkel, K.; Schmeiβer, D.; Mandal, D. A Self-powered wearable pressure sensor and pyroelectric breathing sensor based on GO interfaced PVDF nanofibers. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pan, H.; Xie, G.Z.; Jiang, Y.D.; Chen, C.X.; Su, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Tai, H.L. Flexible piezoelectric pressure sensor based on polydopamine-modified BaTiO3/PVDF composite film for human motion monitoring. Sensor Actuat. A-Phys. 2019, 301, 11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.Q.; Zhang, L.B.; Wu, T.; Song, H.J.; Tang, C.L. Flexible piezoelectric pressure sensor with high sensitivity for electronic skin using near-field electrohydrodynamic direct-writing method. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2020, 48, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Ko, H. Fingertip skin–inspired microstructured ferroelectric skins discriminate static/dynamic pressure and temperature stimuli. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, 1500661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Shu, Y.; Wang, X.F.; Mohammad, M.A.; Bie, Z.; Xie, Q.Y.; Li, C.; Mi, W.T.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.L. A Graphene-based resistive pressure sensor with record-high sensitivity in a wide pressure range. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.Z.; Hu, M.J.; Li, X.; Yan, L.; Wu, X.G.; Liu, J.Z.; Gao, H.B.; Shan, G.G.; Huang, W. A highly sensitive piezoresistive sensor based on MXene and polyvinyl butyral with a wide detection limit and low power consumption. Nanoscale. Sep. 2020, 14, 32555857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Liu, H.L.; Yin, X.Y.; Wang, F.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X.N.; Cheng, T.L. Flexible Pressure Sensor Decorated with MXene and Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites for Motion Detection, Information Transmission, and Pressure Sensing Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 12, 36178119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.N.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, W.Q.; Rao, J.Y.; Luo, S.J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, X.L.; Liu, Z.; et al. 3D synergistical MXene/reduced graphene oxide aerogel for a piezoresistive sensor. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3209–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, Z.Y.; Zhong, M.J.; Wan, P.B.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhang, L.Q. A flexible wearable pressure sensor with bioinspired microcrack and interlocking for full-range human-machine interfacing. Small 2018, 14, 1803018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Sun, S.S.; Hu, J.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, A.P.; Cheng, H.Y.; Gao, W.Z.; Zhang, W.N.; et al. Bioinspired, multifunctional dual-mode pressure sensors as electronic skin for decoding complex loading processes and human motions. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Allnubaiai, M.; Holbrook, C.M.; Miao, J.S.; Pinto, T.; Wang, C.; Tan, X.B. Screen-printed soft capacitive sensors for spatial mapping of both positive and negative pressures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1809116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gui, J.H.; Luo, J.; Gao, J.S.; Zheng, C.D.; Xu, R.Q. Highly responsive screen-printed asymmetric pressure sensor based on laser-induced grapheme. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2022, 32, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamankar, N.; Khajavi, R.; Yousefi, A.A.; Rashidi, A.; Golestanifar, F. A flexible piezoelectric pressure sensor based on PVDF nanocomposite fibers doped with PZT particles for energy harvesting applications. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 19669–19681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, J.H.; Zhang, Z.M.; Bian, H.Q.; Sun, T.Y. g-C3N4 composited TiO2 nanofibers were prepared by high voltage electrostatic spinning to improve photocatalytic efficiency. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 2020, 31, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, V.; Stauffer, F.; Adagunodo, M.O.; Forro, C.; Larmagnac, A. Stretchable silver nanowire-elastomer composite microelectrodes with tailored electrical properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 13467–13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandala, B.S.P.K.; Zhang, G.Q.; Lcorriveau, C.; Paquin, M.; Chagnon, M.; Begun, D.; Shanov, V. Preliminary study on modelling, fabrication by photo-chemical etching and in vivo testing of biodegradable magnesium AZ31 stents. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Xin, B.J.; Chen, Z.M.; Liu, Y. Flexible and highly conductive Ag/G-coated cotton fabric based on graphene dipping and silver magnetron sputtering. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3691–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Cao, C.; Ao, J.P.; Bi, J.L.; Yao, L.Y.; Guo, J.J.; Sun, G.Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.F.; et al. Efficiency improvement of electrodeposition-processed Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cell with widen surface bandgap by spin-coating In2S3 thin film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 578, 152063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Dong, J.G. Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) Printing of molten metal ink for flexible and stretchable conductor with self-healing capability. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Zhang, H.M.; Chang, A.M.; Ma, X.H.; Rong, J.H.; Yang, L.Y. A novel core-shell structure NTC ceramic with high stability fabricating by an in-situ ink-jet printing method. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 41, 4167–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Chen, L.; Pan, H.H.; Zhang, D.M.; Hu, T.L.; Tyasi, T.L. Flexible Strain Sensor Based on 3D Electrospun Carbonized Sponge. CMC-Comput. Mater. Con. 2022, 73, 4971–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.; Gao, Y.Y.; Lo Verso, A.; Zhu, J.; Erdely, D.; Xue, C.L.; Lavelle, R.; Cheng, H.Y. Fabricating functional circuits on 3D freeform surfaces via intense pulsed light-induced zinc mass transfer. Mater Today 2021, 50, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.D.; Jia, S.Q.; Ding, S.A.; Liu, P.; Ma, J.R.; Xiao, X.T.; Qu, X.W.; Liu, H.C.; Yang, H.C.; Xu, B.; et al. Improved ink-jet-printed CdSe quantum dot light-emitting diodes with minimized hole transport layer erosion. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 3005–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.Q.; Zhang, L.B.; Wu, T.; Song, H.J.; Tang, C.L.; Huang, F.L.; Zuo, C.C. Flexible electronic skin with high performance pressure sensing based on PVDF/rGO/BaTiO3 composite thin film. Org. Electron. 2021, 98, 106296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; Wu, T.; Zhang, L.B.; Feng, X.W.; Mao, Z.P. Fabrication of flexible organic electronic microcircuit pattern using near-field electrohydrodynamic direct-writing method. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. El. 2019, 30, 17863–17871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.F.; Zhang, L.B.; Wu, T.; Song, H.J.; Luo, J.Q.; Huang, F.L.; Zuo, C.C. Flexible pressure sensor with high sensitivity and fast response for electronic skin using near-field electrohydrodynamic direct writing. Org. Electron. 2021, 89, 106044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.Y.; Wang, L.L.; Lou, Z.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L.J.; Han, W.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G.Z. Biomimetic, biocompatible and robust silk Fibroin-MXene film with stable 3D cross-link structure for flexible pressure sensors. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.F.; Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.M.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G. All rGO-on-PVDF-nanofibers based self-powered electronic skins. Nano Energy 2017, 35, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Meena, D.; Bhatnagar, M.C. Synthesis and characterization of flexible PVDF/Bi2Al4O9/RGO based piezoelectric materials for nanogenerator application. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 843, 156019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsouras, I.; Asadi, K.; Li, M.; Driel, T.; Kjaer, K.S.; Dong, Z.; Lenz, T.; Yun, G.; Blom, P.; Damjanovic, D. The negative piezoelectric effect of the ferroelectric polymer poly(vinylidene fluoride). Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.Z.; Tan, C.X.; Shi, K.M.; Li, J.W.; Wang, X.X.; Sun, B.; Huang, X.Y.; Long, Y.Z.; Jiang, P.K. Wireless piezoelectric device based on electrospun PVDF/BaTiO3 NW nanocomposite fibers for human motion monitoring. Nanoscale 2018, 37, 17751–17760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Deng, W.L.; Xiong, D.; Yang, T.; Zhang, B.B.; Ren, X.R.; Lan, B.L.; Zhong, S.; Jin, L.; Zhang, H.R.; et al. Dielectric micro-capacitance for enhancing piezoelectricity via aligning MXene sheets in composites. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chhetry, A.; Sharifuzzaman, M.; Yoon, H.; Park, J.Y. Wearable Capacitive Pressure Sensor Based on MXene Composite Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Reliable Human Physiological Signal Acquisition. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2020, 12, 22212–22224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.H.; Hu, Y.J.; Zhuo, H.X.; Liu, L.X.; Jing, S.S.; Zhong, L.X.; Peng, X.W.; Sun, R.C. Compressible, elastic, and pressure-sensitive carbon aerogels derived from 2D titanium carbide nanosheets and bacterial cellulose for wearable sensors. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 3301–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; Sun, M.Y.; Han, S.W.; Zhang, R.T.; Liang, N.; Sun, D.H.; Liu, H. Energy-efficient, fully flexible, high-performance tactile sensor based on piezotronic effect: Piezoelectric signal amplified with organic field-effect transistors. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 2211–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.Y.; Joe, D.J.; Kim, D.H.; Park, H.; Han, J.H.; Jeong, C.K.; Jeong, C.K.; Park, H.; Park, J.G.; Joung, B.; et al. Self-Powered Real-Time Arterial Pulse Monitoring Using Ultrathin Epidermal Piezoelectric Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Dong, Y.C.; Hossain, M.M.; Gorman, S.; Towfeeq, I.; Gajula, D.; Childress, A.; Rao, A.M.; Koley, G. Piezoresistive graphene/P(VDF-TrFE) heterostructure based highly sensitive and flexible pressure sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 16006–16017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, S.; Schwalb, W.; Wang, Y.W.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Si, J.; Shirinzadeh, B.; Cheng, W.L. A wearable and highly sensitive pressure sensor with ultrathin gold nanowires. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Mode | Materials | Sensitivity | Responsiveness | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piezoresistive | PVDF/MXene/rGO | 29.27 kPa−1 | 36/55 ms | This work |
| MXene/rGO | 22.56 kPa−1 | 245/212 msk. | [26] | |
| SF@MXene Ti3C2Tx | 25.5 kPa−1 | 40/35 ms | [45] | |
| MXene/PVDF-TrFE | 0.51 kPa−1 | 150/150 ms | [51] | |
| MXene/bacterial | 12.5 kPa−1 | 167/121 ms | [52] | |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO | 14.5 kPa−1 | ----------- | [28] | |
| Piezoelectricity | PVDF/MXene/rGO | 8.84 kPa−1 | 18.2 ms | This work |
| PVDF nanorod | 5.17 kPa−1 | 150 ms | [53] | |
| PET-Self-Powered | 0.018 kPa−1 | 60 ms | [54] | |
| Graphene/P(VDF-TrFE) | 0.76 kPa−1 | <100 ms | [55] | |
| AuNW | >1.14 kPa−1 | <17 ms | [56] | |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/rGO | 1.62 V/kPa | ----------- | [28] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, T.; Song, H.; Tang, C. Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor Based on PVDF/MXene Nanosheet/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites for Electronic Skin. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13010102
Liang H, Zhang L, Wu T, Song H, Tang C. Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor Based on PVDF/MXene Nanosheet/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites for Electronic Skin. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Hu, Libing Zhang, Ting Wu, Haijun Song, and Chengli Tang. 2023. "Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor Based on PVDF/MXene Nanosheet/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites for Electronic Skin" Nanomaterials 13, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13010102
APA StyleLiang, H., Zhang, L., Wu, T., Song, H., & Tang, C. (2023). Dual-Mode Flexible Sensor Based on PVDF/MXene Nanosheet/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites for Electronic Skin. Nanomaterials, 13(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13010102






