Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Epoxy Hybrid System Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Exceptional mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties such as high elastic modulus, tensile strength, thermal, and electrical conductivity.
- A high specific surface area and aspect-to-diameter ratio, which enable the formation of a three-dimensional conductive network in the matrix at low filler loads.
- A nanometric structure that can be modified to improve the compatibility and dispersion in the epoxy matrix.
- Biocompatibility, facilitating biological and medical applications.
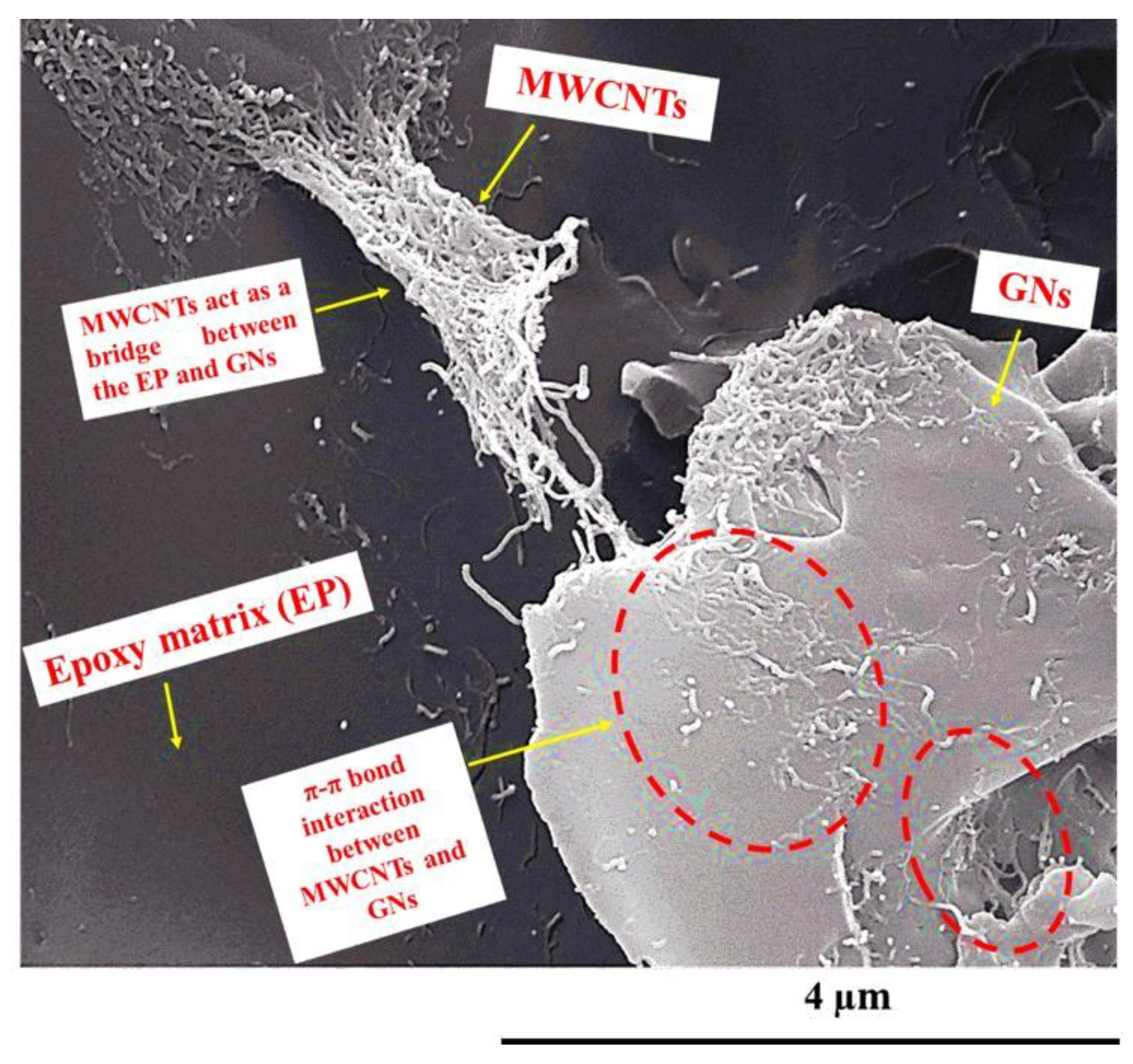
- Formation of a three-dimensional hybrid structure between CNTs and GNs, which hinders face-to-face aggregation of GNs and increases the contact surface area with the matrix.
- CNTs acting as bridges between adjacent GNs, enhancing load transfer and electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Dispersion of CNTs between GNs, creating a conductive network perpendicular to the plane of GNs, improving heat dissipation and electromagnetic shielding.
- Cross-plane thermal conductivity of reduced graphene oxide/CNT hybrid papers increased with increasing CNT loading, reaching a maximum value of 0.1199 W m−1 K−1 for a 20 wt% paper. CNTs acted as scaffolds, restraining graphene sheets from corrugating and providing more phonon transmission channels [29].
- Epoxy composites reinforced with both graphene nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes exhibited a higher tensile strength and modulus compared to those reinforced with either graphene or carbon nanotubes alone. The synergistic effect resulted from the improved dispersion and interfacial bonding of carbon nanomaterials within the epoxy matrix [25].
- Incorporating multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) significantly improved the fatigue life and crack growth resistance of epoxy composites, surpassing the performance of pure epoxy or composites reinforced with only MWCNTs or GNPs. The synergistic effect was attributed to the formation of a three-dimensional network structure that increased the fracture toughness and crack bridging ability [22].
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
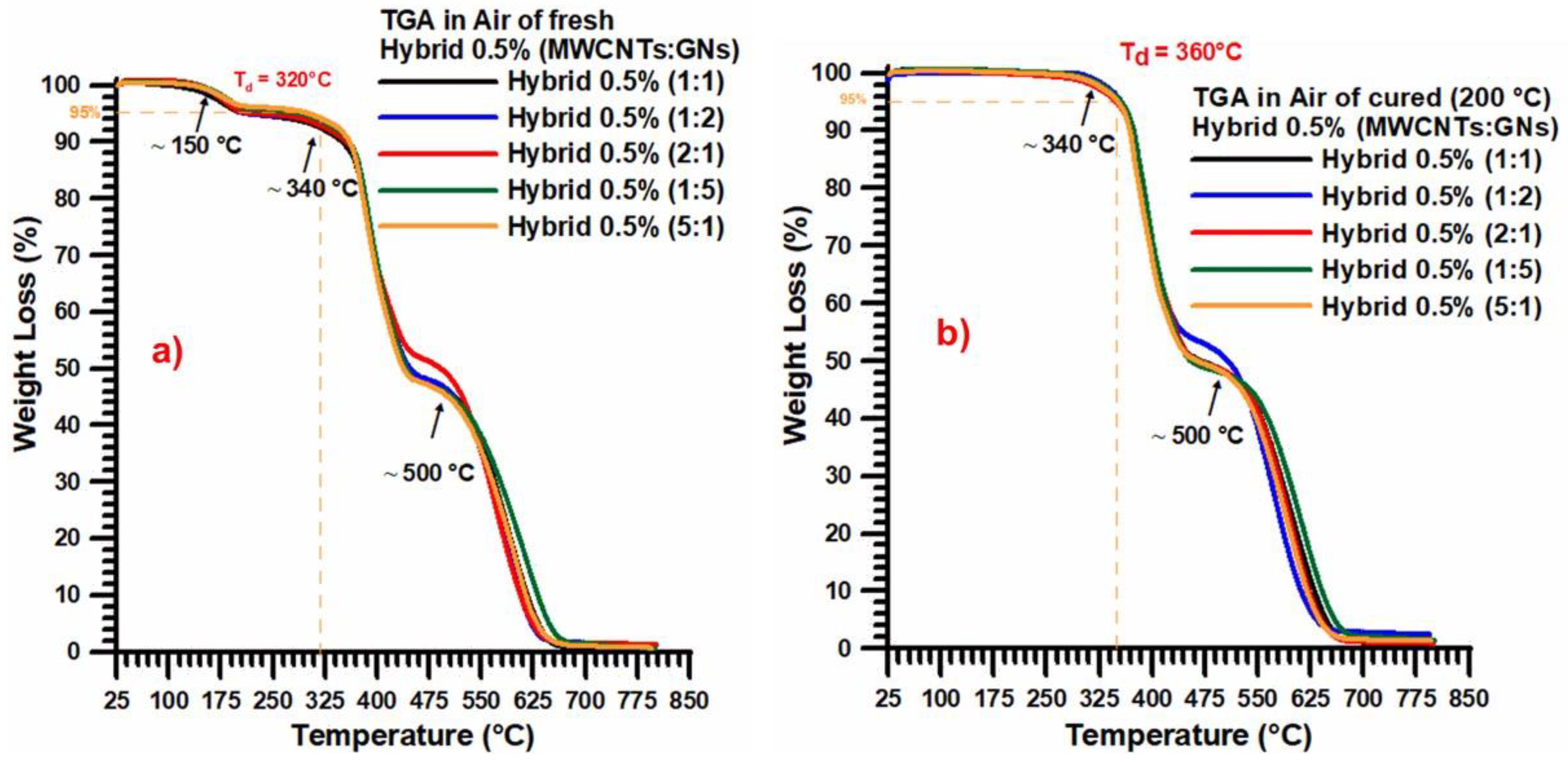
3.1. Thermal Analysis
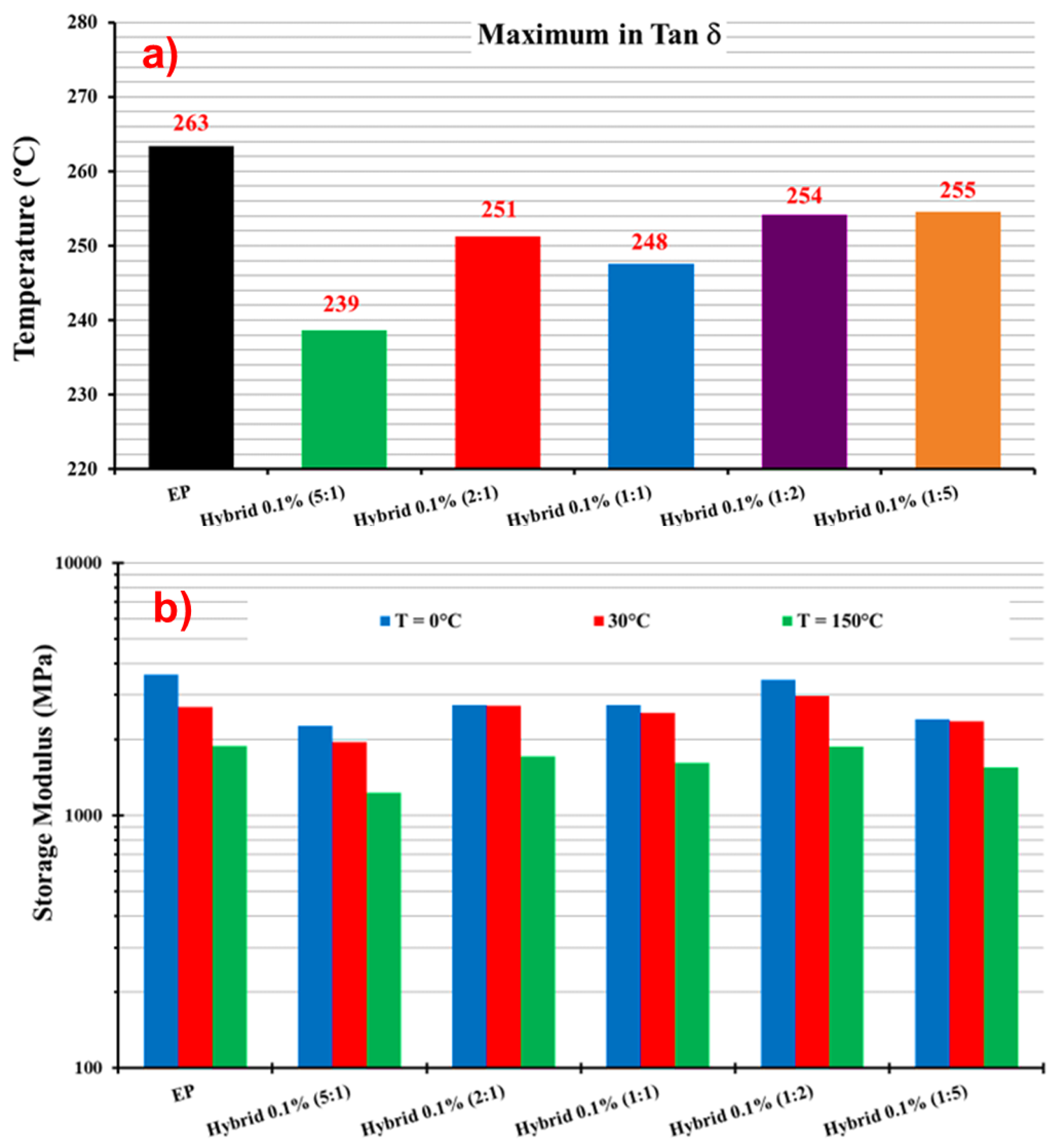
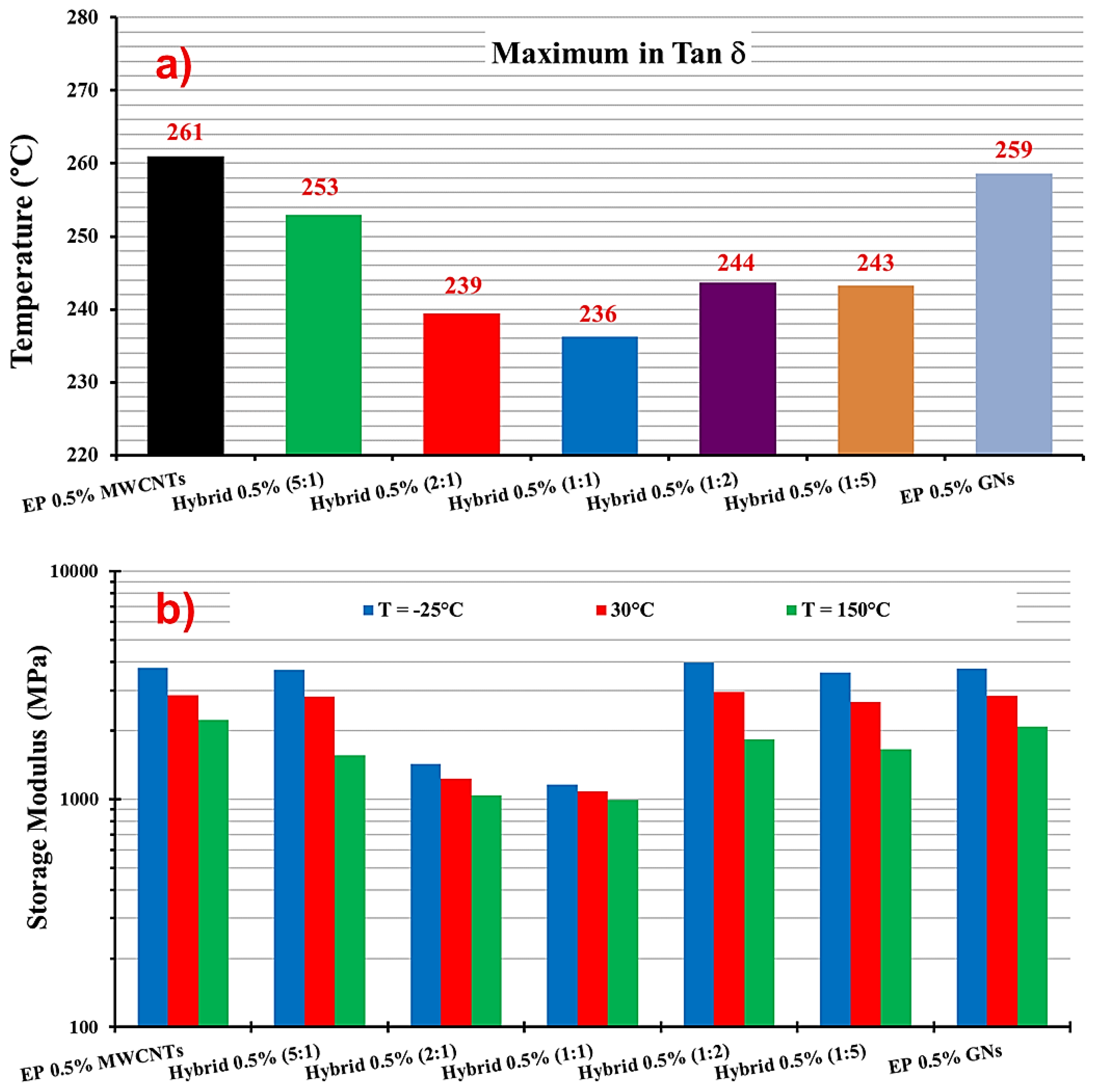
3.2. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis
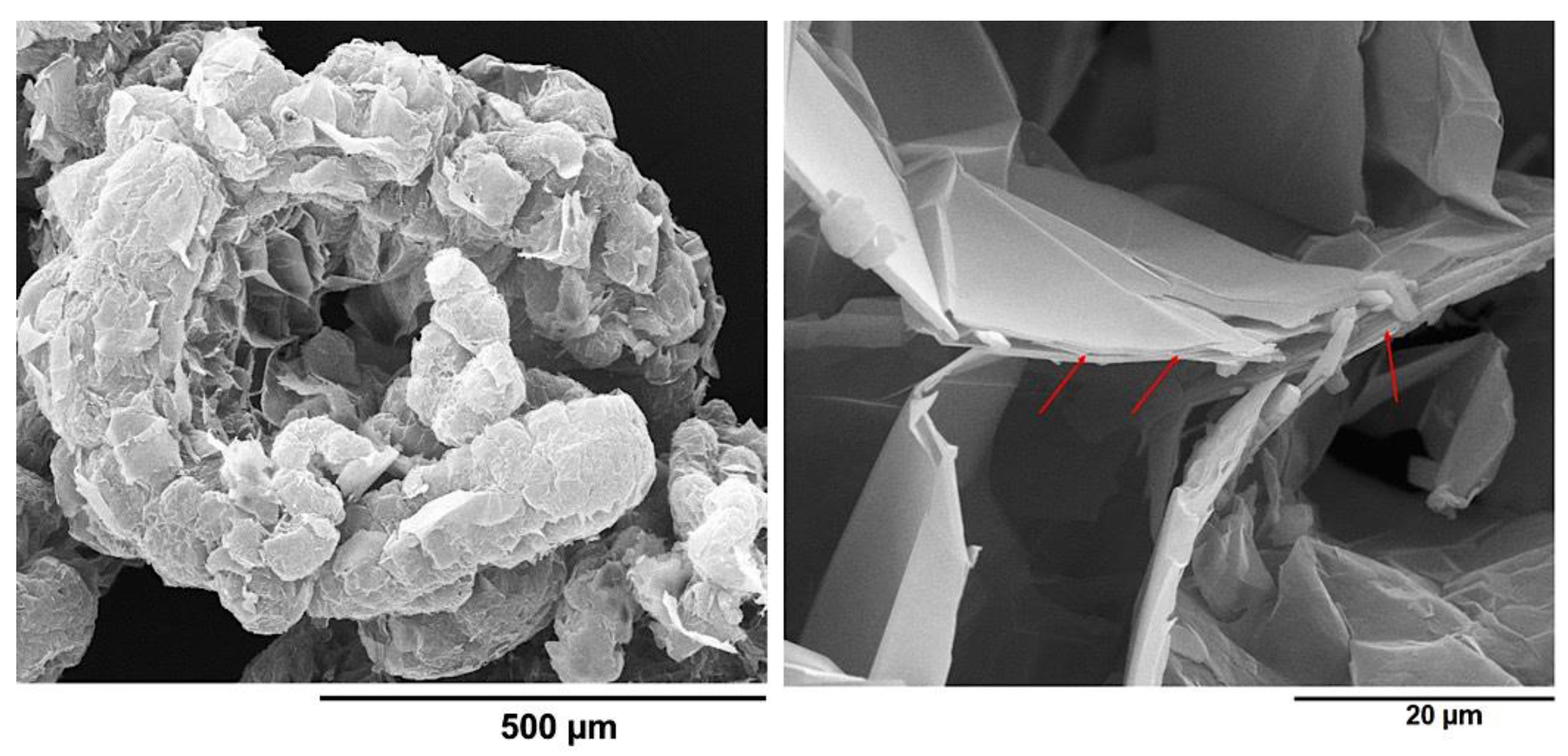
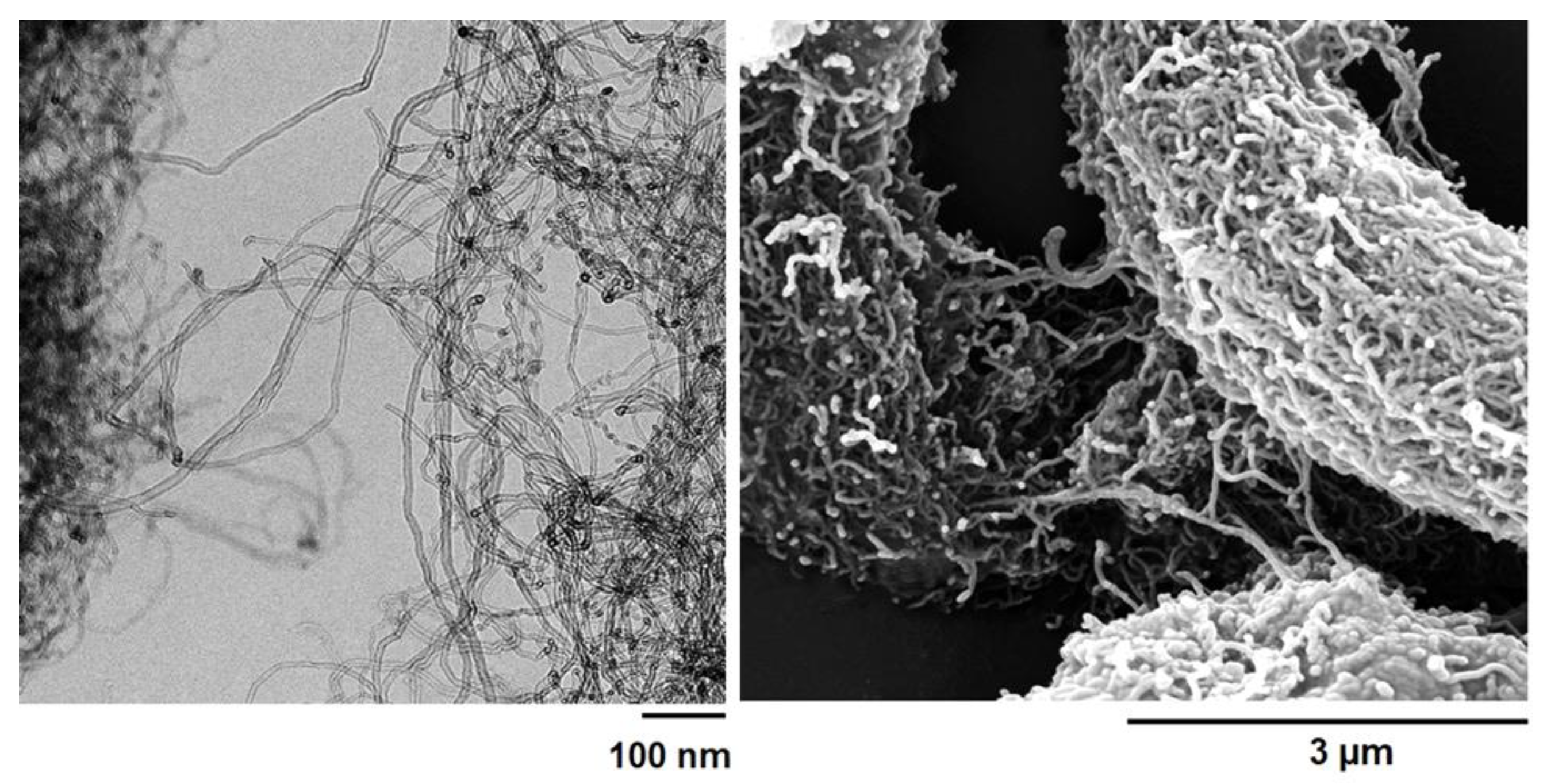
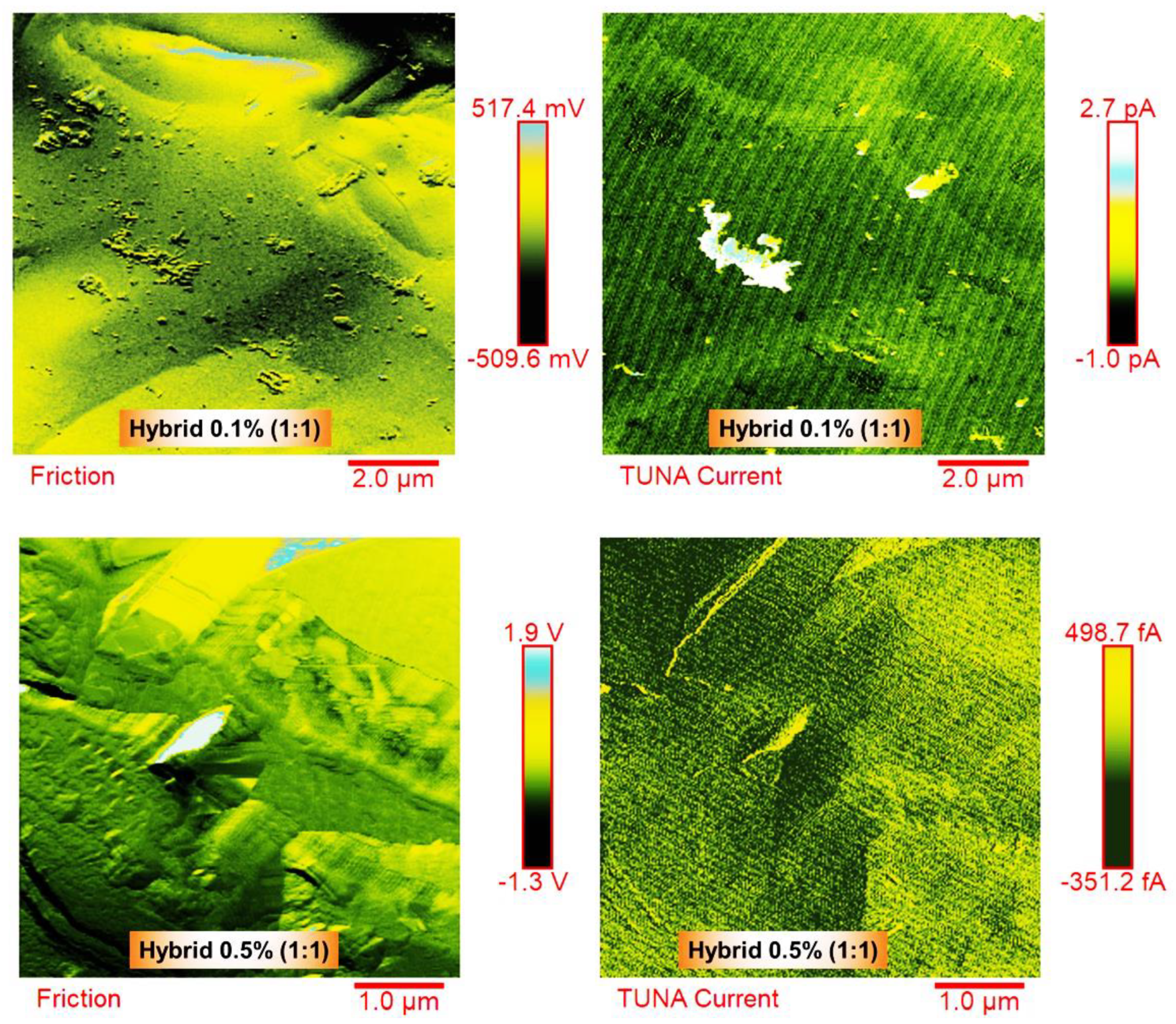
3.3. Morphological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinloch, I.A.; Suhr, J.; Lou, J.; Young, R.J.; Pulickel, M.A. Composites with carbon nanotubes and graphene: An outlook. Science 2018, 362, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchegolkov, A.V.; Shchegolkov, A.V. Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes Using Microwave Radiation: Technology, Properties, and Structure. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2022, 92, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchegolkov, A.V.; Jang, S.-H.; Shchegolkov, A.V.; Rodionov, Y.V.; Glivenkova, O.A. Multistage Mechanical Activation of Multilayer Carbon Nanotubes in Creation of Electric Heaters with Self-Regulating Temperature. Materials 2021, 14, 4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midriver, G.; Jin, W. Carbon nanomaterials: Synthesis, properties and applications in electrochemical sensors and energy conversion systems. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 272, 115341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Dutta, D.; Sarkara, A.; Chattopadhyay, P. Functionalized carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, properties and applications in water purification, drug delivery, and material and biomedical sciences. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 5722–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, M.; Donati, G.; Milano, G.; Guadagno, L. Hybrid composites based on carbon nanotubes and graphene nanosheets outperforming their single-nanofiller counterparts. FlatChem 2022, 36, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, M.; Naddeo, C.; Vertuccio, L.; Bonnaud, L.; Dubois, P.; Binder, W.H.; Sorrentino, A.; Guadagno, L. Multifunctionality of structural nanohybrids: The crucial role of carbon nanotube covalent and non-covalent functionalization in enabling high thermal, mechanical and self-healing performance. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 225708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Vertuccio, L.; Naddeo, C.; Raimondo, M.; Barra, G.; De Nicola, F.; Volponi, R.; Lamberti, P.; Spinelli, G.; Tucci, V. Electrical Current Map and Bulk Conductivity of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Nanocomposites. Polymers 2019, 11, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, M.; Naddeo, C.; Vertuccio, L.; Lafdi, K.; Sorrentino, A.; Guadagno, L. Carbon-Based Aeronautical Epoxy Nanocomposites: Effectiveness of Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) in Investigating the Dispersion of Different Carbonaceous Nanoparticles. Polymers 2019, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Pantelakis, S.; Strohmayer, A.; Raimondo, M. High-Performance Properties of an Aerospace Epoxy Resin Loaded with Carbon Nanofibers and Glycidyl Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane. Aerospace 2022, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, M.R.; Raimondo, M.; Naddeo, C.; Guadagno, L. Rheological and Morphological Properties of Non-Covalently Functionalized Graphene-Based Structural Epoxy Resins with Intrinsic Electrical Conductivity and Thermal Stability. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Vertuccio, L.; Barra, G.; Arena, M.; Viscardi, M. Vibro-acoustic characteristics of multifunctional carbon fiber reinforced panel. Def. Technol. 2023, 24, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.R.; Estaji, S.; Kiaei, H.; Mansourian-Tabaei, M.; Nouranian, S.; Jafari, S.H.; Ruckdäschel, H.; Arjmand, M.; Khonakdar, H.A. A review of electrical and thermal conductivities of epoxy resin systems reinforced with carbon nanotubes and graphene-based nanoparticles. Polym. Test. 2022, 112, 107645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benra, J.; Forero, S. Epoxy resins reinforced with carbon nanotubes. Lightweight Des. Worldw. 2018, 11, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, M.; Guadagno, L.; Speranza, V.; Bonnaud, L.; Dubois, P.; Lafdi, K. Multifunctional graphene/POSS epoxy resin tailored for aircraft lightning strike protection. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 140, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Aliberti, F.; Longo, R.; Raimondo, M.; Pantani, R.; Sorrentino, A.; Catauro, M.; Vertuccio, L. Electrical anisotropy controlled heating of acrylonitrile butadiene styrene 3D printed parts. Mater. Des. 2023, 225, 111507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigione, M.; Lettieri, M. Recent Advances and Trends of Nanofilled/Nanostructured Epoxies. Materials 2020, 13, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badjian, H.; Setoodeh, A.R.; Bavi, O.; Rabczuk, T. Enhanced mechanical properties of epoxy-based nanocomposites reinforced with functionalized carbon nanobuds. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmand, M.; Jahanpeyma, F.; Gholaminejad, A.; Azimzadehet, M.; Malaei, F.; Shoaie, N. Carbon nanostructures: A comprehensive review of potential applications and toxic effects. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, A.; Abadchi, M.R.; Mirzaee, M.; Tabar, F.A.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Recent advances and future perspectives for carbon nanostructures reinforced organic coating for anti-corrosion application. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 23, 100994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoum, A.; Shalan, A.E.; El-Hout, S.I.; Ali, G.A.; Abdelbasir, S.M.; Abu Serea, E.S.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Pal, K.; Shalan, A.E.; El-Hout, S.I. A Broad Family of Carbon Nanomaterials: Classification, Properties, Synthesis, and Emerging Applications. In Handbook of Nanofibers; Barhoum, A., Bechelany, M., Makhlouf, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, Y.-M.; Huang, J.-C.; Zheng, K.-Y. Synergistic Effect of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Nanoplatelets on the Monotonic and Fatigue Properties of Uncracked and Cracked Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2020, 12, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wu, R.; Zhang, J.; Hou, L.; Zhang, M. Synergistic effect of carbon nanotube and graphene nanoplatelet addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 prepared using hot-pressing sintering. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 4261–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Tang, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Shi, X.; Qin, J. Synergistic effect of carbon nanotube and graphene nanoplates on the mechanical, electrical and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of polymer composites and polymer composite foams. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 353, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Cheng, Q. Synergistic reinforcing effect from graphene and carbon nanotubes. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Soutis, C.; Gresil, M. Fracture Toughness of Hybrid Carbon Fibre/Epoxy Enhanced by Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2021, 28, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.C.; Lubna, M.M.; Mohammed, Z.; Ul Iqbal, M.H.; Hoque, M.E. Graphene and Carbon Nanotube-Based Hybrid Nanocomposites: Preparation to Applications. In Graphene and Nanoparticles Hybrid Nanocomposites; Qaiss, A.e.K., Bouhfid, R., Jawaid, M., Eds.; Composites Science and Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.K.; Sharma, K. Improvement in mechanical and thermal properties of epoxy hybrid composites by functionalized graphene and carbon-nanotubes. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 125323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, K.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L. Synergistic effect of reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanotube hybrid papers on cross-plane thermal and mechanical properties. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 19144–19153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, N.; Safwan, A.; Sanyang, M.L.; Mohammad, F.; Pervaiz, M.; Jawaid, M.; Alothman, O.Y.; Sain, M. Thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of cellulose nanofibers reinforced epoxy composites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenes Benega, M.A.; Silva, W.M.; Schnitzler, M.C.; Espanhol Andrade, R.J.; Ribeiro, H. Improvements in thermal and mechanical properties of composites based on epoxy-carbon nanomaterials—A brief landscape. Polym. Test. 2021, 98, 107180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Qiu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Chen, S.; Shi, M.; Huang, Z. Enhanced thermal and mechanical properties of carbon fiber/epoxy composites interleaved with graphene/SiCnw nanostructured films. Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 162, 107129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandin, A. Thermal properties of graphene and nanostructured carbon materials. Nat. Mater 2011, 10, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlier, J.C.; Eklund, P.C.; Zhu, J.; Ferrari, A.C. Electron and Phonon Properties of Graphene: Their Relationship with Carbon Nanotubes. In Carbon Nanotubes. Topics in Applied Physics; Jorio, A., Dresselhaus, G., Dresselhaus, M.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liang, Y. Molecular dynamics investigation of the thermal properties in single-walled boron nitride nanotube. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 025025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, L.; Broido, D.A. Optimized Tersoff and Brenner empirical potential parameters for lattice dynamics and phonon thermal transport in carbon nanotubes and graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 205441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Vertuccio, L.; Mauro, M.; Guerra, G.; Lafdi, K.; De Vivo, B.; Lamberti, P.; Spinelli, G.; Tucci, V. Optimization of graphene-based materials outperforming host epoxy matrices. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 36969–36978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertuccio, L.; De Santis, F.; Pantani, R.; Lafdi, K.; Guadagno, L. Effective de-icing skin using graphene-based flexible heater. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 162, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Naddeo, C.; Raimondo, M.; Barra, G.; Vertuccio, L.; Russo, S.; Lafdi, K.; Tucci, V.; Spinelli, G.; Lamberti, P. Influence of carbon nanoparticles/epoxy matrix interaction on mechanical, electrical and transport properties of structural advanced materials. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 094001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Vertuccio, L.; Naddeo, C.; Barra, G.; Longo, P.; Lamberti, P.; Spinelli, G.; Nobile, M. Morphological, rheological and electrical properties of composites filled with carbon nanotubes functionalized with 1-pyrenebutyric acid. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 147, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, L.; Sorrentino, A.; Longo, R.; Raimondo, M. Multifunctional Properties of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes (POSS)-Based Epoxy Nanocomposites. Polymers 2023, 15, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, B.K.; Horrocks, A.R.; Myler, P.; Blair, D. Thermal characterisation of thermoset matrix resins. In Fire and Polymers; ACS Symposium Series, Nelson, G.L., Wilkie, C.A., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 344–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, M.; Russo, S.; Guadagno, L.; Longo, P.; Chirico, S.; Mariconda, A.; Bonnaud, L.; Murariu, O.; Dubois, P. Effect of incorporation of POSS compounds and phosphorous hardeners on thermal and fire resistance of nanofilled aeronautic resins. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10974–10986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.K.; Goyat, M.S.; Kumar, A. A review on the effect of oxide nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, and their hybrid structure on the toughening of epoxy nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 13202–13232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irzhak, V. Epoxy Nanocomposites with Carbon Fillers. Rev. Adv. Chem. 2022, 12, 22–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.-J.; Li, G.; Yao, Y.-M.; Zeng, X.-L.; Zhu, P.-L.; Sun, R. Recent advances in polymer-based electronic packaging materials. Compos. Commun. 2020, 19, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertzen, W.K.; Kessler, M.R. Dynamic mechanical analysis of carbon/epoxy composites for structural pipeline repair. Compos. Part B Eng. 2007, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Shu, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Shen, W.; et al. Graphene sheets from worm-like exfoliated graphite. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3367–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
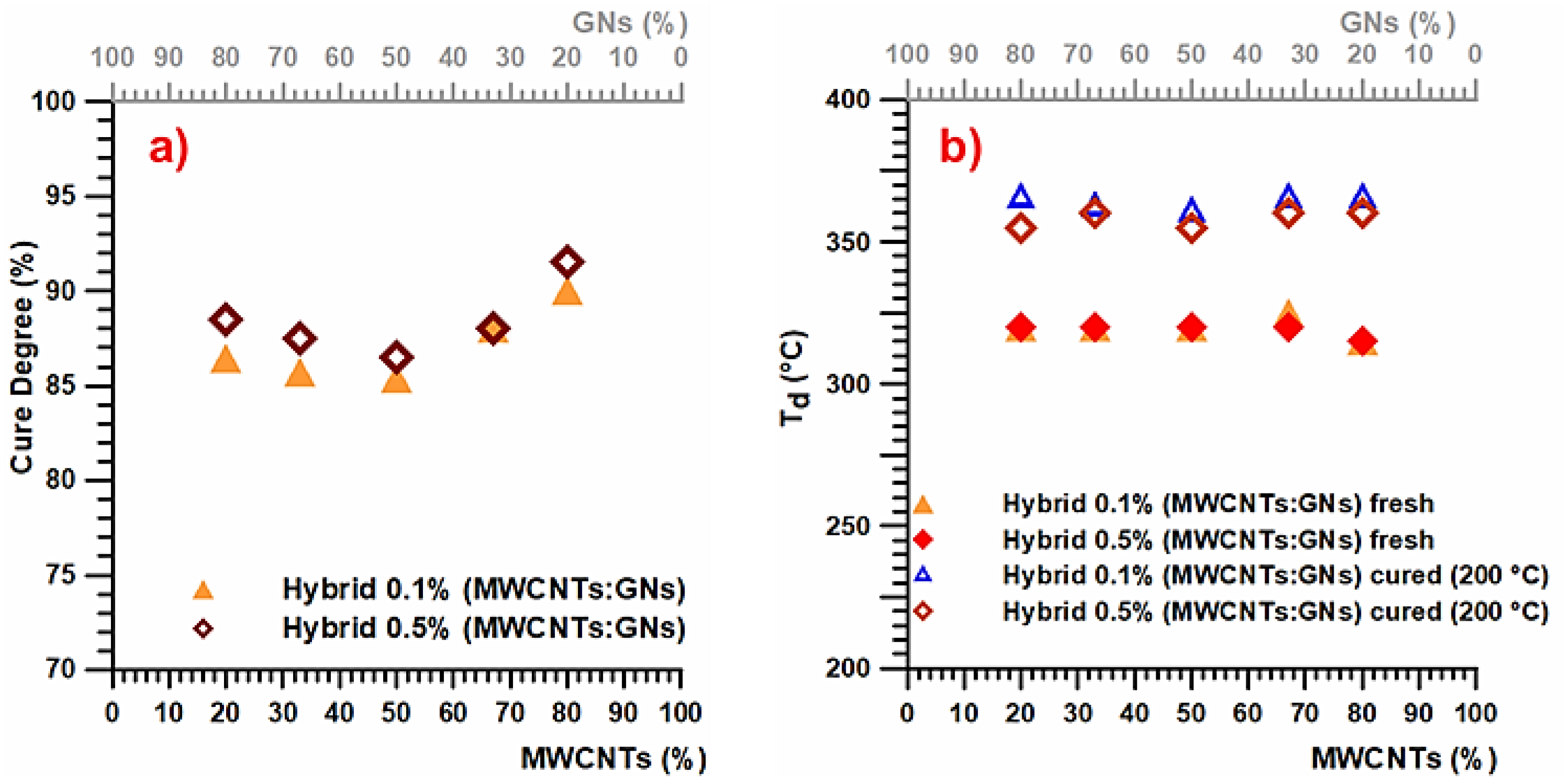
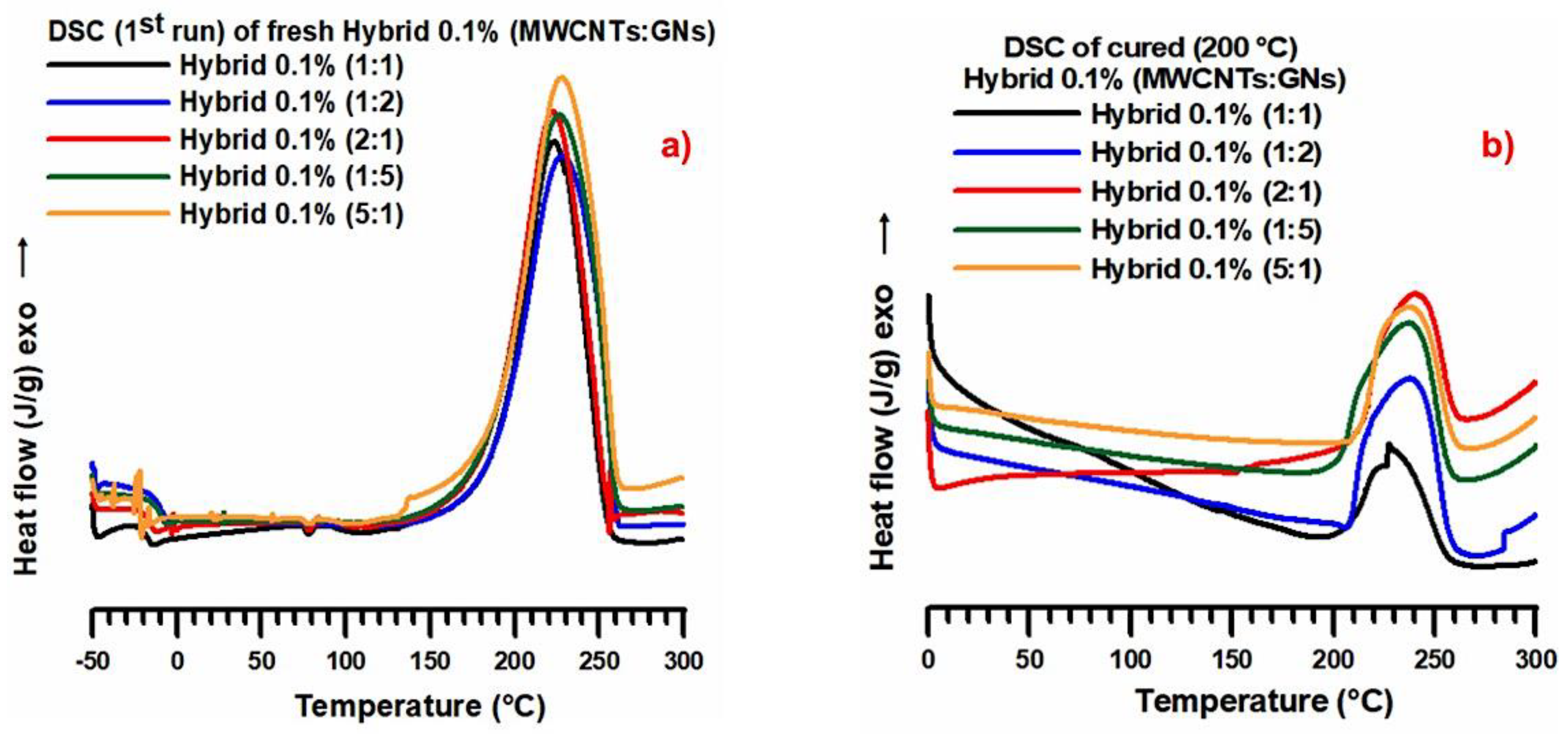

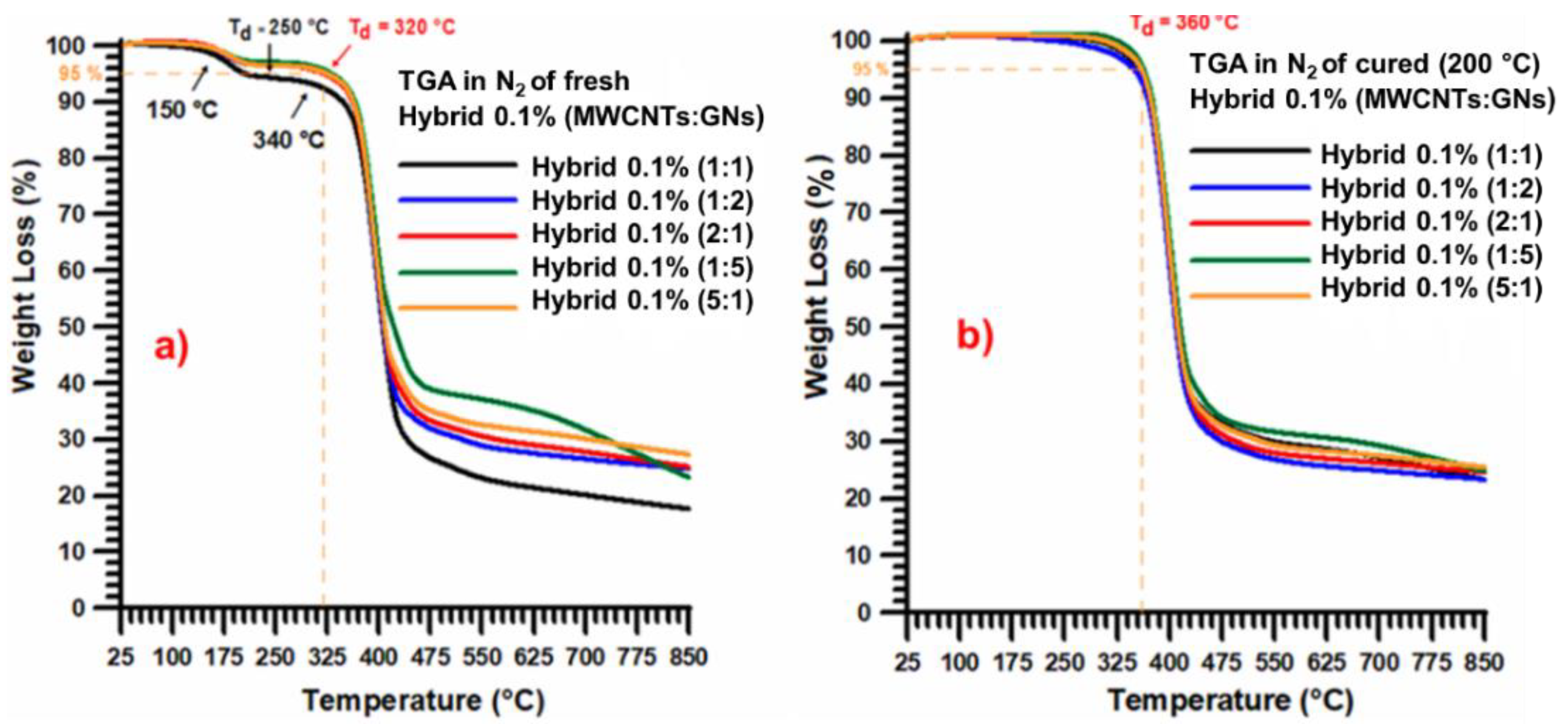
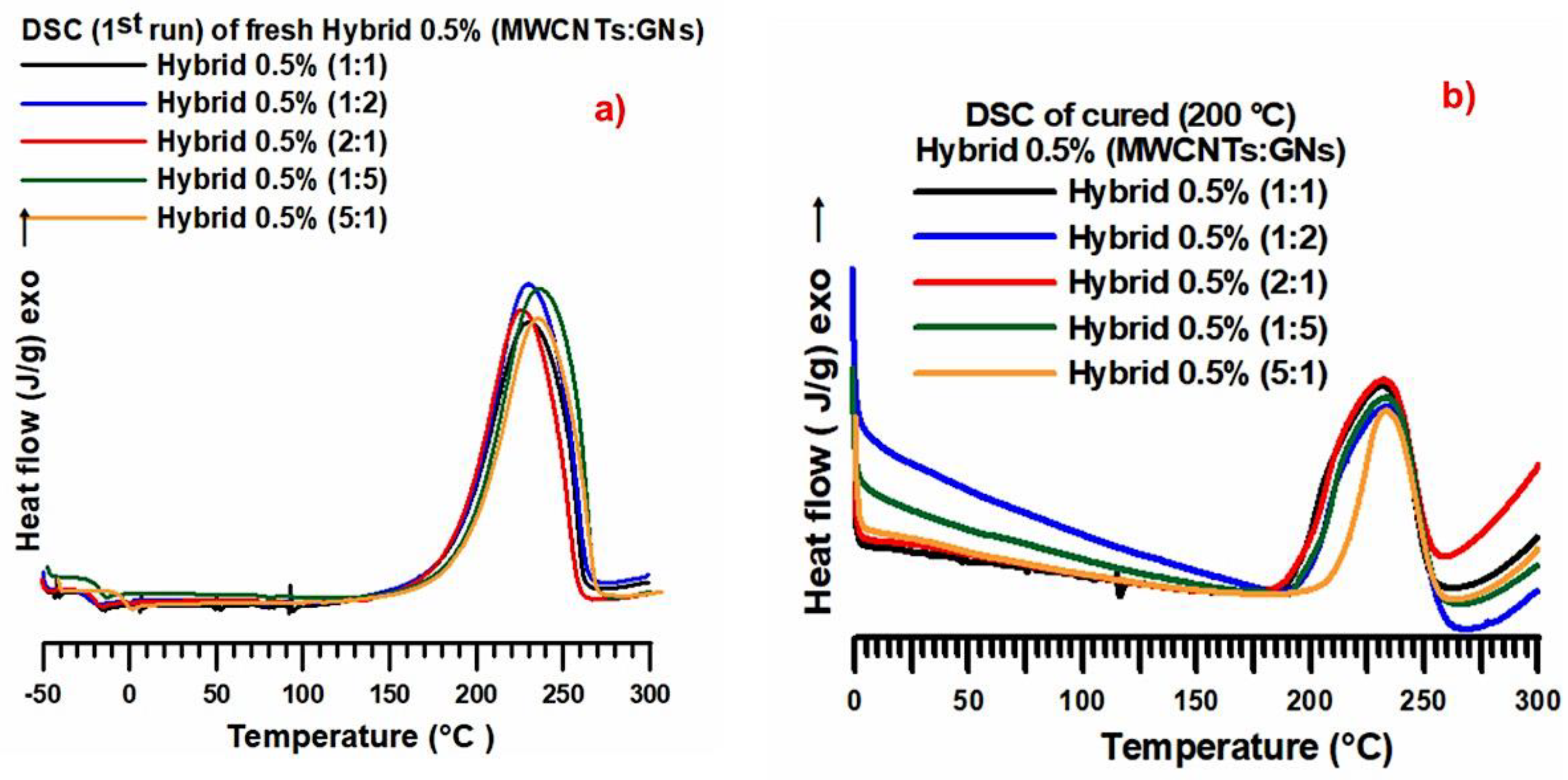



| Mix Ratios MWCNT:GN | wt% MWCNT | wt% GN |
|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 50 | 50 |
| 1:2 | 33 | 67 |
| 1:5 | 20 | 80 |
| 2:1 | 67 | 33 |
| 5:1 | 80 | 20 |
| Nanocomposite | Degradation Temperature (Td) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Epoxy resin filled with 0.5 wt% multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and 0.5 wt% graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) | 374 °C | [22] |
| Epoxy resin filled with 0.5 wt% silica nanoparticles (SiO2) and 0.5 wt% MWCNTs | 390 °C | [44] |
| Epoxy resin filled with 0.5 wt% MWCNTs | 380 °C | [45] |
| Epoxy resin filled with 0.5 wt% graphene oxide (GO) | 385 °C | [45] |
| Epoxy resin filled with 0.5 wt% reduced graphene oxide (rGO) | 390 °C | [45] |
| Epoxy resin filled with 0.5 wt% hybrid nanofiller composed of a mix of multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and graphene nanosheets (GNs) | 360 °C | [This paper] |
| Epoxy resin filled with 0.1 wt% hybrid nanofiller composed of a mix of multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and graphene nanosheets (GNs) | 360 °C | [This paper] |
| Sample | Tg | SM (T = 0 °C) | SM (T = 30 °C) | SM (T = 150 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP | 263 | 3603 | 2690 | 1883 |
| Hybrid 0.1% (5:1) | 239 | 2259 | 1950 | 1231 |
| Hybrid 0.1% (2:1) | 251 | 2732 | 2724 | 1717 |
| Hybrid 0.1% (1:1) | 248 | 2737 | 2541 | 1617 |
| Hybrid 0.1% (1:2) | 254 | 3438 | 2977 | 1874 |
| Hybrid 0.1% (1:5) | 255 | 2400 | 2357 | 1551 |
| Sample | Tg | SM (T = −25 °C) | SM (T = 30 °C) | SM (T = 150 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP 0.5% MWCNTs | 261 | 3759 | 2850 | 2221 |
| Hybrid 0.5% (5:1) | 253 | 3688 | 2827 | 1562 |
| Hybrid 0.5% (2:1) | 239 | 1428 | 1232 | 1043 |
| Hybrid 0.5% (1:1) | 236 | 1158 | 1086 | 994 |
| Hybrid 0.5% (1:2) | 244 | 3975 | 2956 | 1834 |
| Hybrid 0.5% (1:5) | 243 | 3604 | 2676 | 1657 |
| EP 0.5% GNs | 259 | 3729 | 2831 | 2084 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guadagno, L.; Naddeo, C.; Sorrentino, A.; Raimondo, M. Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Epoxy Hybrid System Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172427
Guadagno L, Naddeo C, Sorrentino A, Raimondo M. Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Epoxy Hybrid System Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(17):2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172427
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuadagno, Liberata, Carlo Naddeo, Andrea Sorrentino, and Marialuigia Raimondo. 2023. "Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Epoxy Hybrid System Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 13, no. 17: 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172427
APA StyleGuadagno, L., Naddeo, C., Sorrentino, A., & Raimondo, M. (2023). Thermo-Mechanical Performance of Epoxy Hybrid System Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 13(17), 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13172427









