Toxic Effects of Copper Fungicides on the Development and Behavior of Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Characterization of PEG@Cu NCs and Kocide® 3000
2.3. Maintenance of Zebrafish and Embryo Collection
2.4. Acute Toxicity Test of Copper Fungicides on Embryos
2.5. Developmental Toxicity Test of Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages
2.6. Locomotor Behavior of Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of PEG@Cu NCs and Kocide® 3000
3.2. Acute Toxicity Test of Copper Fungicides on Embryos
3.3. Developmental Toxicity of Copper Fungicides in Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages
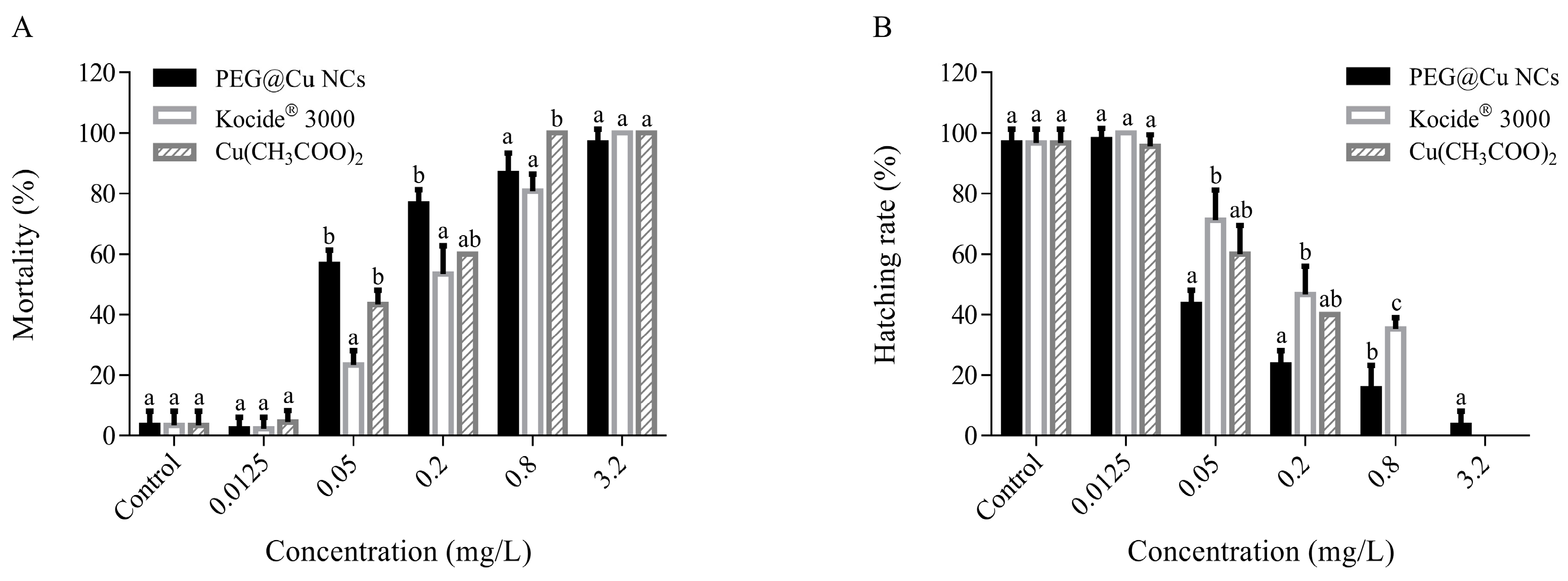
3.3.1. Mortality of Embryo
3.3.2. Hatching Rate of Embryos
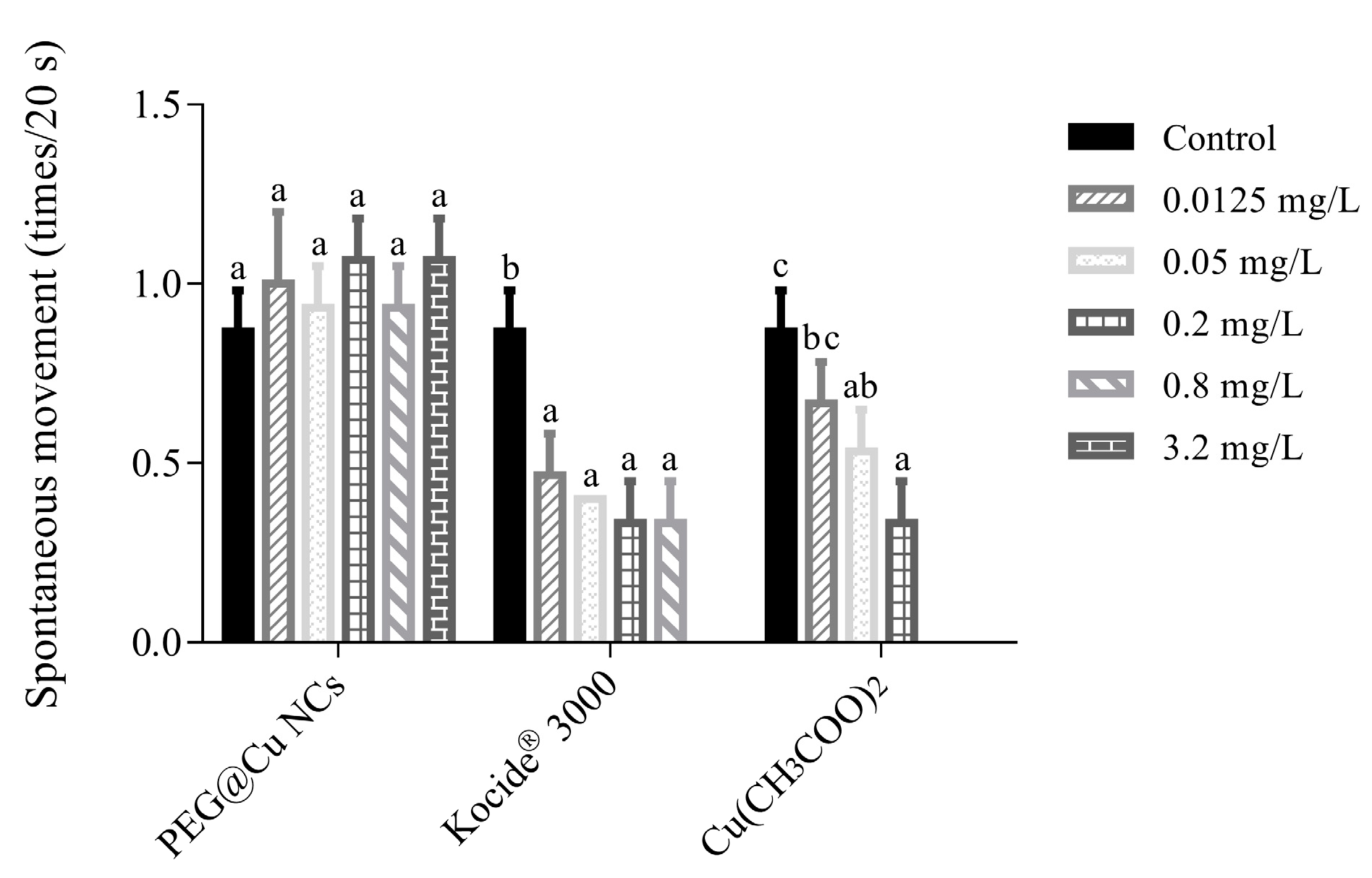
3.3.3. Autonomous Movement of Embryos
3.3.4. Heartbeat of Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages
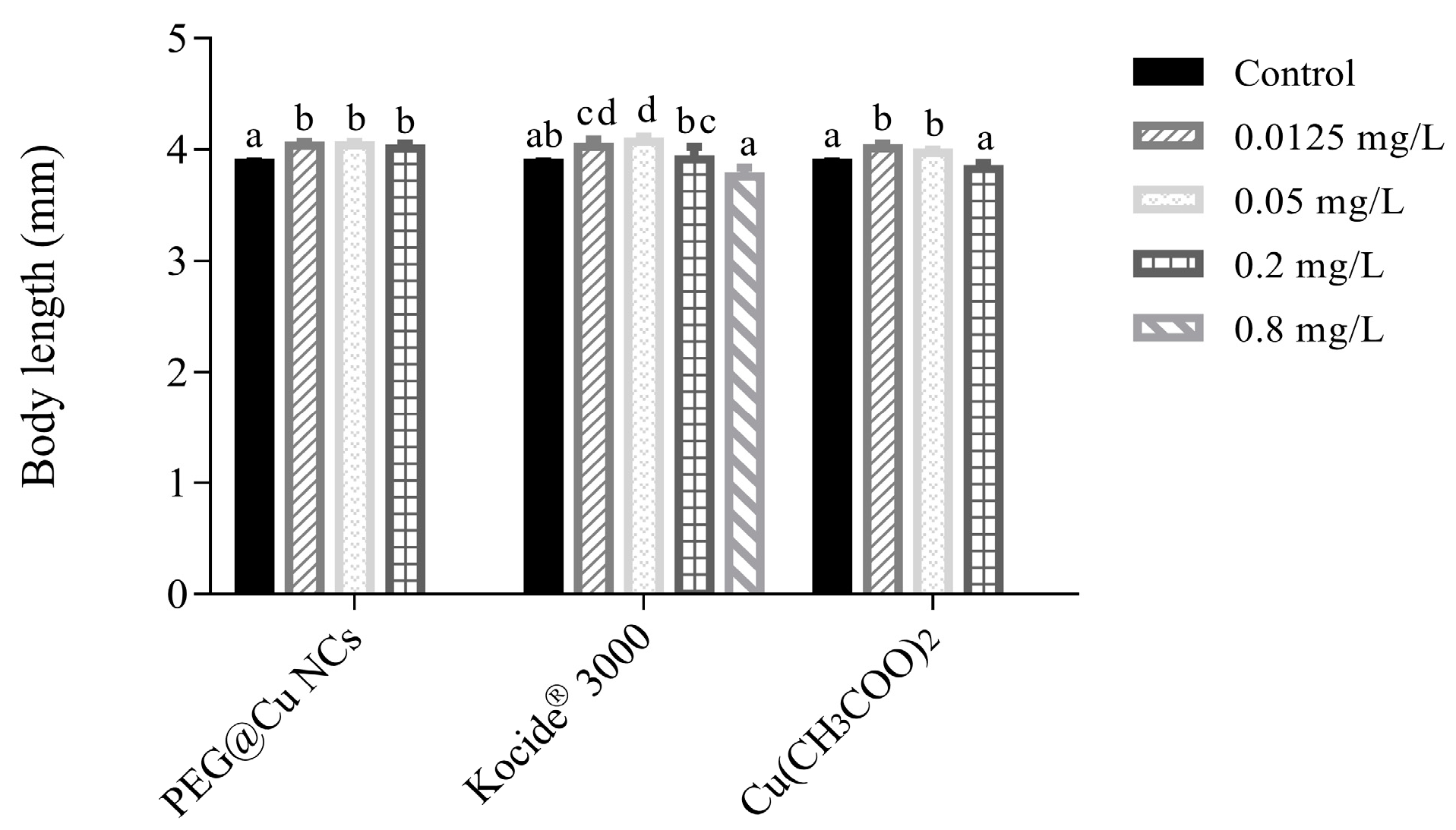
3.3.5. Body Length of Zebrafish Larvae
3.4. Behavioral Responses of Zebrafish Larvae
3.4.1. Total Movement Distance and Average Velocity
3.4.2. Absolute Turn Angle
3.4.3. Absolute Sinuosity and Absolute Angular Velocity
4. Discussion
4.1. Developmental Toxicity of Copper Fungicides to Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages
4.2. Behavioral Toxicity of Copper Fungicides to Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Comber, S.; Deviller, G.; Wilson, I.; Peters, A.; Merrington, G.; Borrelli, P.; Baken, S. Sources of Copper into the European Aquatic Environment. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2023, 19, 1031–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakubo, T.; Kumano, T.; Ohta, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kobayashi, M. Copper Amine Oxidases Catalyze the Oxidative Deamination and Hydrolysis of Cyclic Imines. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, B.R.; Solioz, M.; Krewski, D.; Aggett, P.; Aw, T.-C.; Baker, S.; Crump, K.; Dourson, M.; Haber, L.; Hertzberg, R.; et al. Copper and Human Health: Biochemistry, Genetics, and Strategies for Modeling Dose-Response Relationships. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2007, 10, 157–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachim, S.; Roussel, H.; Bonzom, J.-M.; Thybaud, E.; Mebane, C.A.; Van Den Brink, P.; Gauthier, L. A Long-Term Copper Exposure in a Freshwater Ecosystem Using Lotic Mesocosms: Invertebrate Community Responses: Effects of Copper on Aquatic Invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2698–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampietro, R.; Spinelli, F.; Contino, M.; Colabufo, N.A. The Pivotal Role of Copper in Neurodegeneration: A New Strategy for the Therapy of Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Song, C.; Shi, Y. Pharmacological Inhibition of ALCAT1 Mitigates Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis by Attenuating SOD1 Protein Aggregation. Mol. Metab. 2022, 63, 101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, N.; Ger, T.-R.; Uapipatanakul, B.; Huang, J.-C.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. Review of Copper and Copper Nanoparticle Toxicity in Fish. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilehvar, A.; Town, R.M.; Blust, R. The Effect of Copper on Behaviour, Memory, and Associative Learning Ability of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksakal, F.I.; Arslan, H. Detoxification and Reproductive System-Related Gene Expression Following Exposure to Cu(OH)2 Nanopesticide in Water Flea (Daphnia magna Straus 1820). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 6103–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.; Beckerman, A.P. Copper Mediates Life History Responses of Daphnia Pulex to Predation Threat. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 983923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.-K.; Chu, W.-L.; Kok, Y.-Y.; Cheong, K.-W. Assessing the Toxicity of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles and Copper Sulfate in a Tropical Chlorella. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 3153–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Tan, L.; Wang, J. Combined Toxicities of Copper Nanoparticles with Carbon Nanotubes on Marine Microalgae Skeletonema costatum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 13127–13133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, J.R.; Osdaghi, E.; Behlau, F.; Köhl, J.; Jones, J.B.; Aubertot, J.-N. Thirteen Decades of Antimicrobial Copper Compounds Applied in Agriculture. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Final Renewal Report for the Active Substances Copper Compounds Finalised in the Standing Committee on Plants, Animals, Food and Feed at Its Meeting on 27 November 2018 in View of the Renewal of the Approval of the Active Substances Copper Compounds, as Candidate for Substitution, in Accordance with Regulation (EC) No 1107/20091; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; pp. 13–15.
- ICAMA. Available online: http://www.chinapesticide.org.cn/zgnyxxw/zwb/dataCenter?hash=reg-info (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Vignardi, C.P.; Muller, E.B.; Tran, K.; Couture, J.L.; Means, J.C.; Murray, J.L.S.; Ortiz, C.; Keller, A.A.; Smith Sanchez, N.; Lenihan, H.S. Conventional and Nano-Copper Pesticides Are Equally Toxic to the Estuarine Amphipod Leptocheirus plumulosus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 224, 105481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, M.; Beulke, S.; Tiede, K.; Hofmann, T. Nanopesticides: State of Knowledge, Environmental Fate, and Exposure Modeling. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 1823–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaverde, J.J.; Sevilla-Morán, B.; López-Goti, C.; Alonso-Prados, J.L.; Sandín-España, P. Considerations of Nano-QSAR/QSPR Models for Nanopesticide Risk Assessment within the European Legislative Framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, A.F.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. The Lethal and Sub-Lethal Effects of Fluorinated and Copper-Based Pesticides—A Review. IJERPH 2023, 20, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 7346-2:1996; Water Quality—Determination of the Acute Lethal Toxicity of Substances to a Freshwater Fish [Brachydanio rerio Hamiltone-Buchanan (Teleostei, Cyprinidae)]—Part 2: Semi-Static Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- Yuan, Z.; Ma, C.; Jia, M.; Qian, K. An Eco-Friendly Synthetic Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Copper Nanoclusters for Efficiently Suppress Alternaria alternata in Tobacco and Safety Evaluation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 201, 116955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 212: Fish, Short-Term Toxicity Test on Embryo and Sac-Fry Stages; OECD: Paris, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- De La Paz, J.; Beiza, N.; Paredes-Zúñiga, S.; Hoare, M.; Allende, M. Triazole Fungicides Inhibit Zebrafish Hatching by Blocking the Secretory Function of Hatching Gland Cells. IJMS 2017, 18, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Carew, E.; Sloman, K. The Effects of Copper on the Morphological and Functional Development of Zebrafish Embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 84, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksakal, F.I.; Sisman, T. Developmental Toxicity Induced by Cu(OH)2 Nanopesticide in Zebrafish Embryos. Environ. Toxicol. 2020, 35, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, E.B.; Lin, S.; Nisbet, R.M. Quantitative Adverse Outcome Pathway Analysis of Hatching in Zebrafish with CuO Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11817–11824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Sun, H.; Chen, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, T.; Yi, M.; Liu, J.-X. Copper Inhibits Hatching of Fish Embryos via Inducing Reactive Oxygen Species and Down-Regulating Wnt Signaling. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 205, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Nallathamby, P.D.; Browning, L.M.; Osgood, C.J.; Xu, X.-H.N. In Vivo Imaging of Transport and Biocompatibility of Single Silver Nanoparticles in Early Development of Zebrafish Embryos. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.P.; Flahaut, E.; Cheng, S.H. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes on Developing Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadian, M.; Nabiuni, M.; Parivar, K.; Fathi, M.; Pazooki, J. Toxic Effects of Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles on Early Developmental and Larval Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Félix, L.; Luzio, A.; Parra, S.; Cabecinha, E.; Bellas, J.; Monteiro, S.M. Toxicological Effects Induced on Early Life Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) after an Acute Exposure to Microplastics Alone or Co-Exposed with Copper. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klüver, N.; König, M.; Ortmann, J.; Massei, R.; Paschke, A.; Kühne, R.; Scholz, S. Fish Embryo Toxicity Test: Identification of Compounds with Weak Toxicity and Analysis of Behavioral Effects To Improve Prediction of Acute Toxicity for Neurotoxic Compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7002–7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Liao, X.; Meng, Z.; Xiao, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Z.; Lu, H. Toxic Effects of Oxine-Copper on Development and Behavior in the Embryo-Larval Stages of Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 210, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustein, E.; Saint-Amant, L.; Buss, R.R.; Chong, M.; McDearmid, J.R.; Drapeau, P. Steps during the Development of the Zebrafish Locomotor Network. J. Physiol. 2003, 97, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fraga, J.; Dipp-Alvarez, V.; Bardullas, U. Quantification of Spontaneous Tail Movement in Zebrafish Embryos Using a Novel Open-Source MATLAB Application. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksakal, F.I.; Ciltas, A. Impact of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles (CuO NPs) Exposure on Embryo Development and Expression of Genes Related to the Innate Immune System of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 223, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Liu, K. Developmental Toxicity and Cardiac Effects of Butyl Benzyl Phthalate in Zebrafish Embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 192, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, D.; Luzio, A.; Matos, C.; Bellas, J.; Monteiro, S.M.; Félix, L. Microplastics Alone or Co-Exposed with Copper Induce Neurotoxicity and Behavioral Alterations on Zebrafish Larvae after a Subchronic Exposure. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 235, 105814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, A.S.; Salierno, J.D.; Brewer, S.K. Fish Models in Behavioral Toxicology: Automated Techniques, Updates and Perspectives. In Methods in Aquatic Toxicology; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; Volume 2, pp. 559–590. [Google Scholar]
- Tierney, K.B. Behavioural Assessments of Neurotoxic Effects and Neurodegeneration in Zebrafish. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, G.; He, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cui, J. Effects of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles on Developing Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae. IJN 2016, 11, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, L.; Wu, J.-J.; Wang, W.-M.; Mei, J.; Ma, X.-F.; Liu, J.-X. Transcriptional Responses and Mechanisms of Copper-Induced Dysfunctional Locomotor Behavior in Zebrafish Embryos. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 148, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fungicides | 96 hpf—LC50 (mg/L) | 95% Confidence Limit (mg/L) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEG@Cu NCs | 0.166 | 0.086–0.312 | 0.96 |
| Kocide® 3000 | >2.0 | - | - |
| Cu(CH3COO)2 | 0.276 | 0.256–0.296 | 0.96 |
| Fungicides | Mortality | Hatching Rate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 dpf—LC50 (mg/L) | 95% CL (mg/L) | R2 | 9 dpf—EC50 (mg/L) | 95% CL (mg/L) | R2 | |
| PEG@Cu NCs | 0.077 | 0.005–0.343 | 0.87 | 0.079 | 0.003–0.396 | 0.87 |
| Kocide® 3000 | 0.174 | 0.107–0.280 | 0.98 | 0.210 | 0.039–1.160 | 0.96 |
| Cu(CH3COO)2 | 0.088 | 0.028–0.252 | 0.90 | 0.092 | 0.035–0.231 | 0.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, F.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Qian, K.; Zheng, M. Toxic Effects of Copper Fungicides on the Development and Behavior of Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192629
Gao F, Yuan Z, Zhang L, Peng Y, Qian K, Zheng M. Toxic Effects of Copper Fungicides on the Development and Behavior of Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(19):2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192629
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Fei, Zitong Yuan, Lingling Zhang, Yiyuan Peng, Kun Qian, and Mingqi Zheng. 2023. "Toxic Effects of Copper Fungicides on the Development and Behavior of Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages" Nanomaterials 13, no. 19: 2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192629
APA StyleGao, F., Yuan, Z., Zhang, L., Peng, Y., Qian, K., & Zheng, M. (2023). Toxic Effects of Copper Fungicides on the Development and Behavior of Zebrafish in Early-Life Stages. Nanomaterials, 13(19), 2629. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13192629





