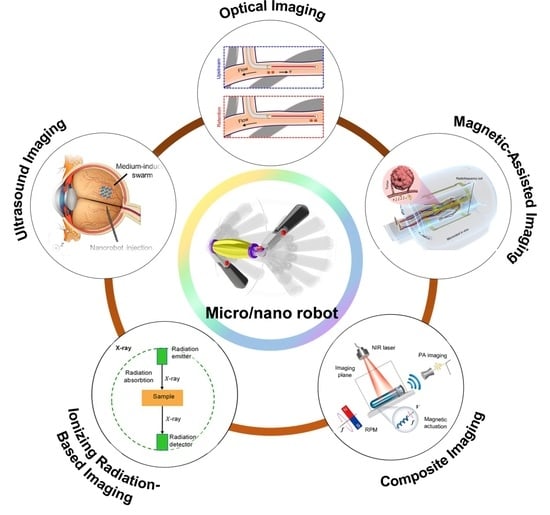
Medical Imaging Technology for Micro/Nanorobots
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Micro/Nanorobot Imaging Techniques and Applications
2.1. Optical Imaging Technology
2.1.1. Fluorescence Imaging Technology
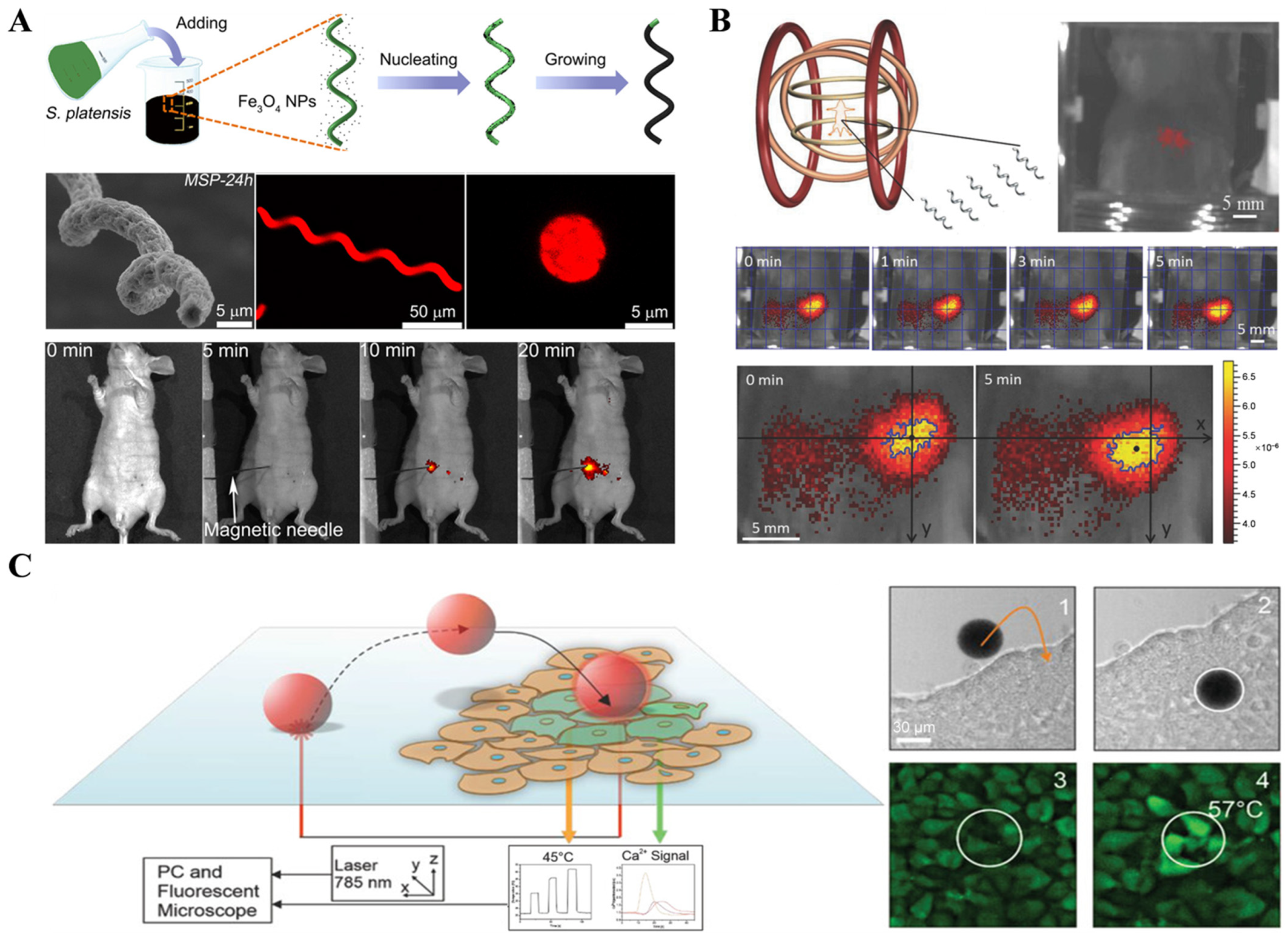
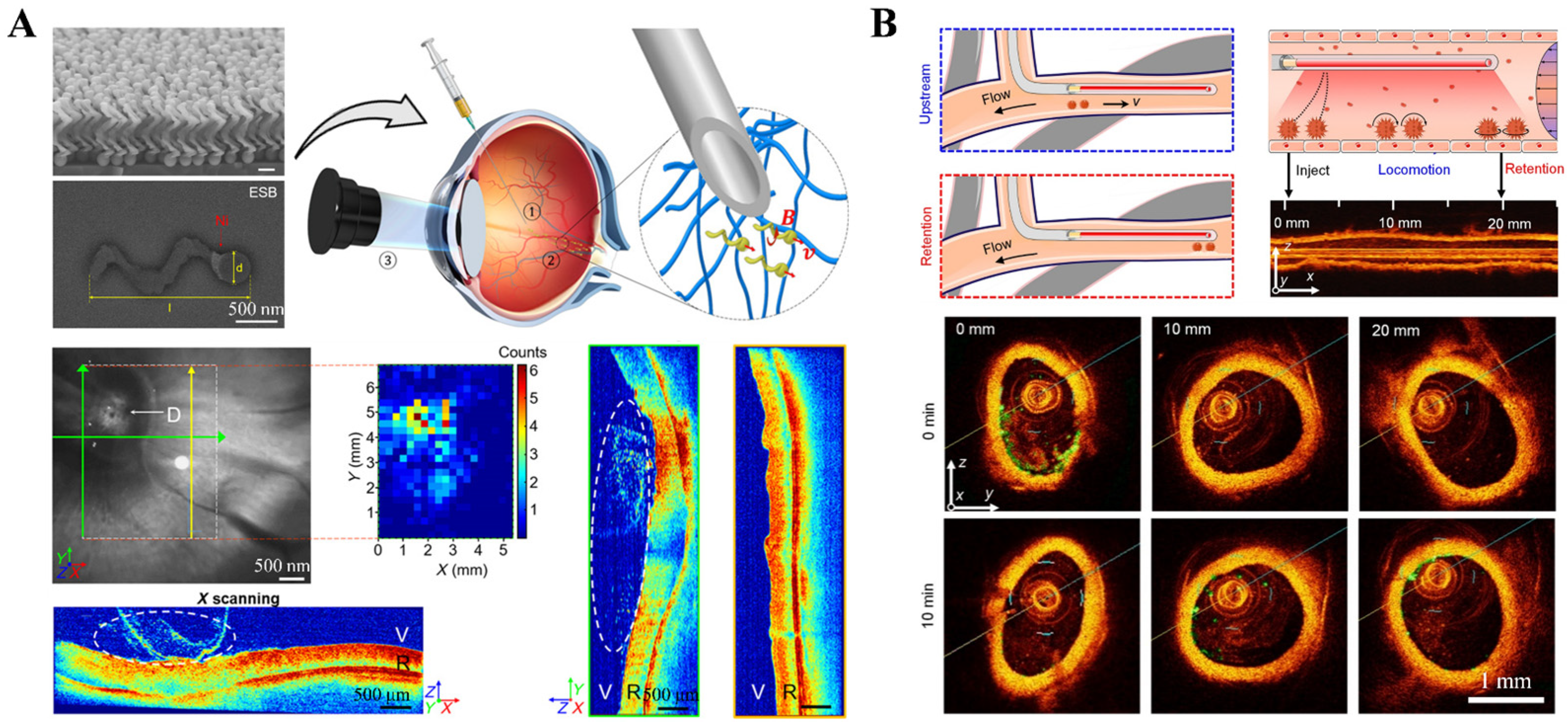
2.1.2. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Imaging Technology
2.2. Magnetic Field-Assisted Imaging Techniques
2.2.1. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
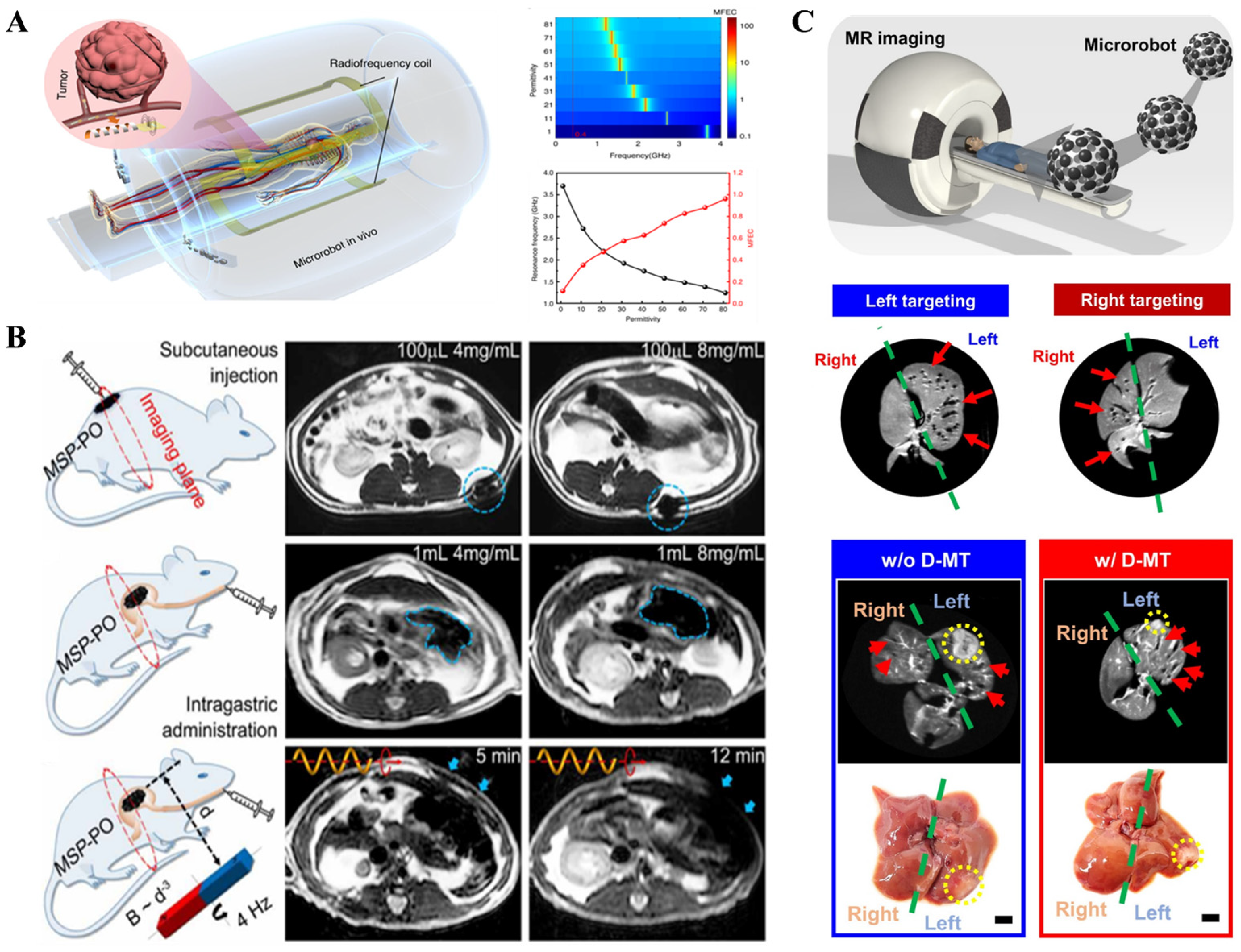
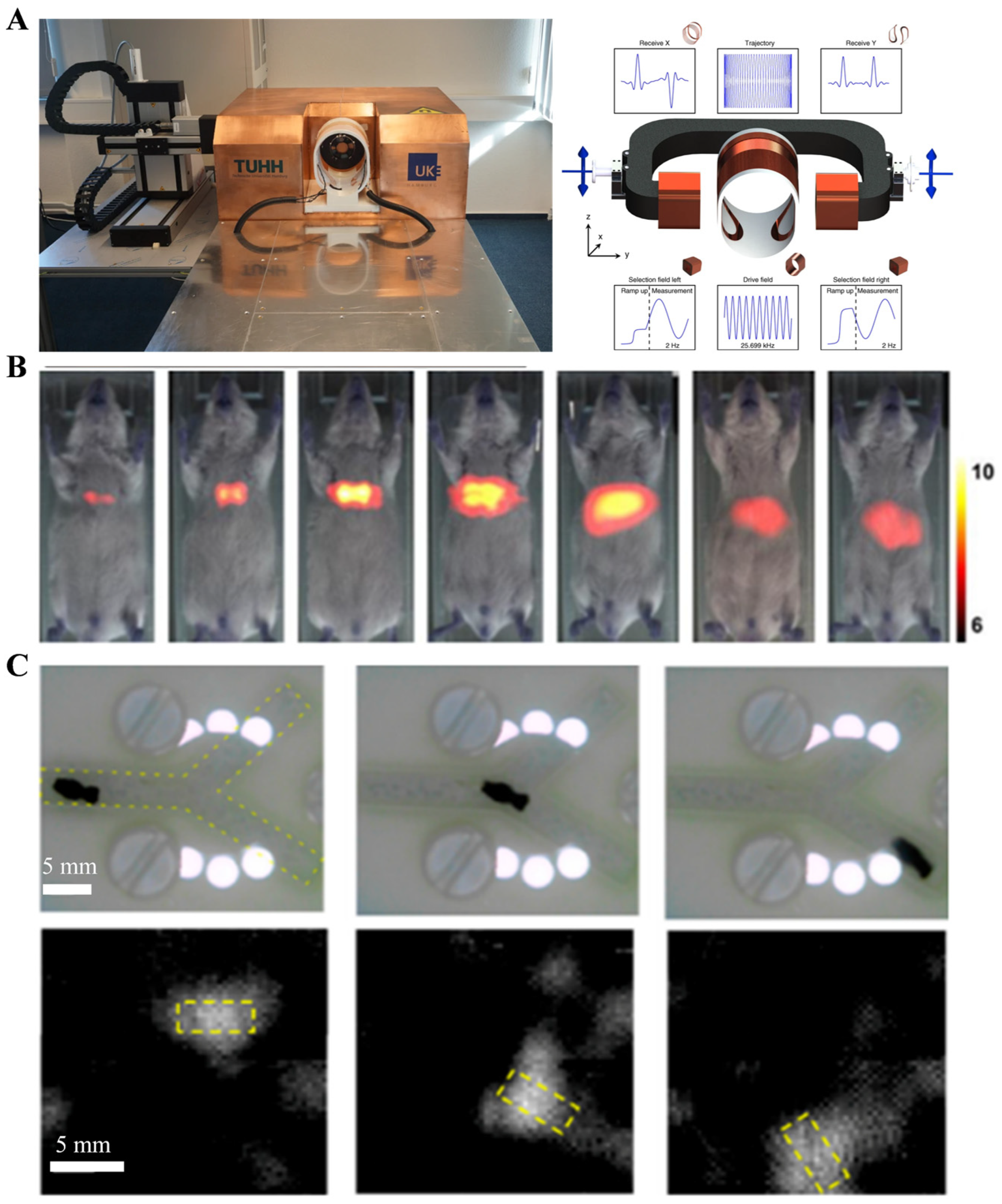
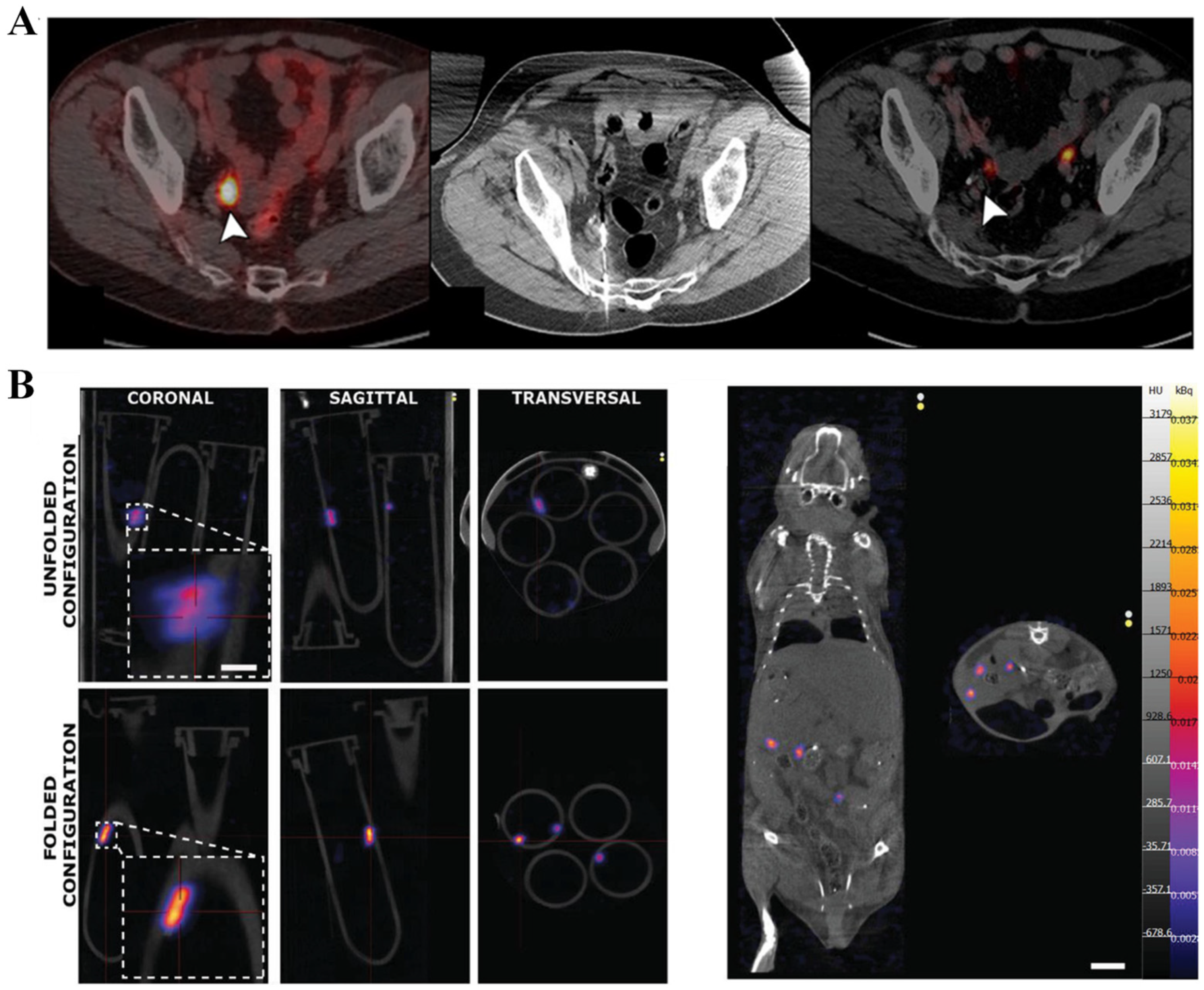
2.2.2. Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI)
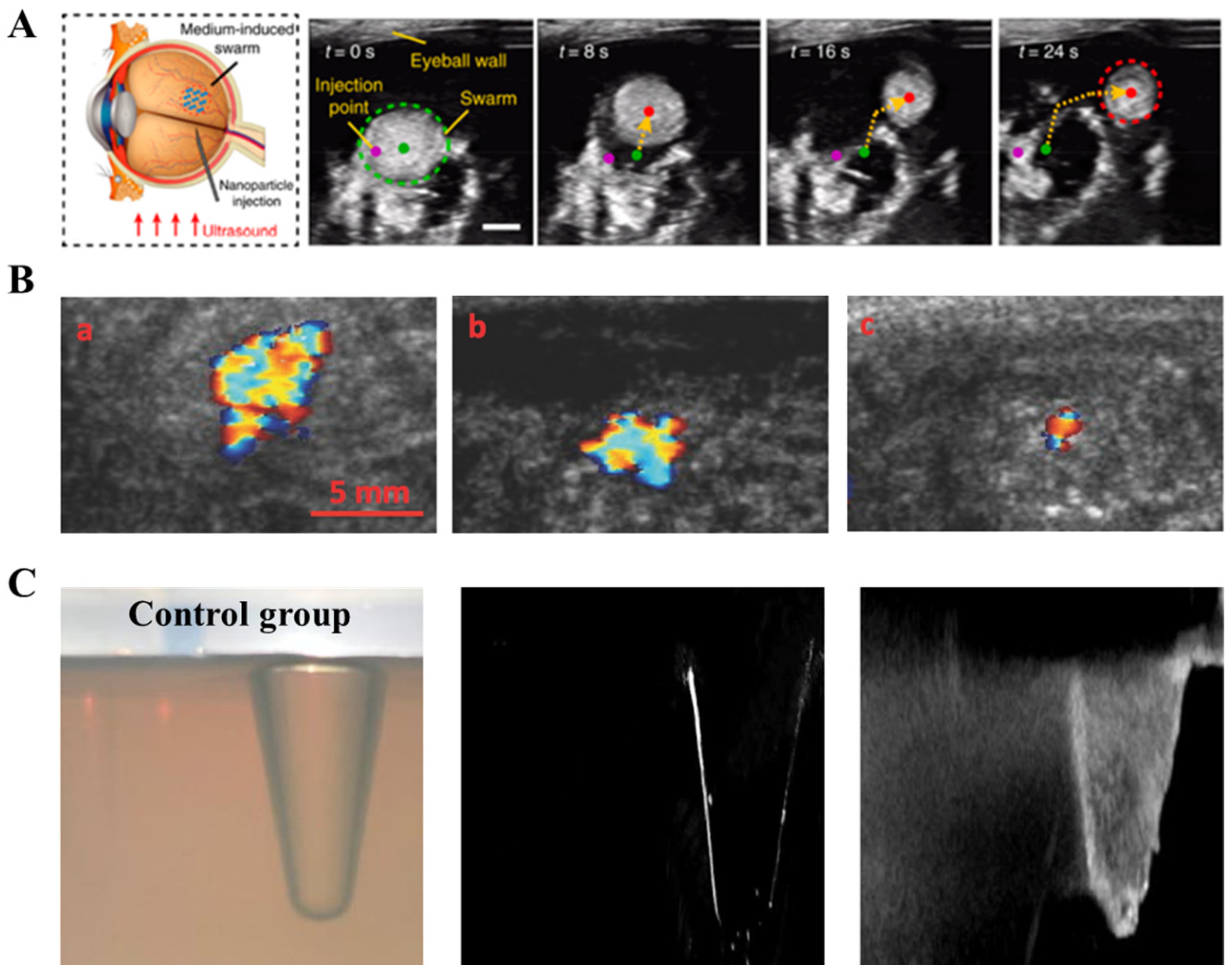
2.3. Ultrasound Imaging (Ultrasound)
2.4. Ionizing Radiation-Based Techniques
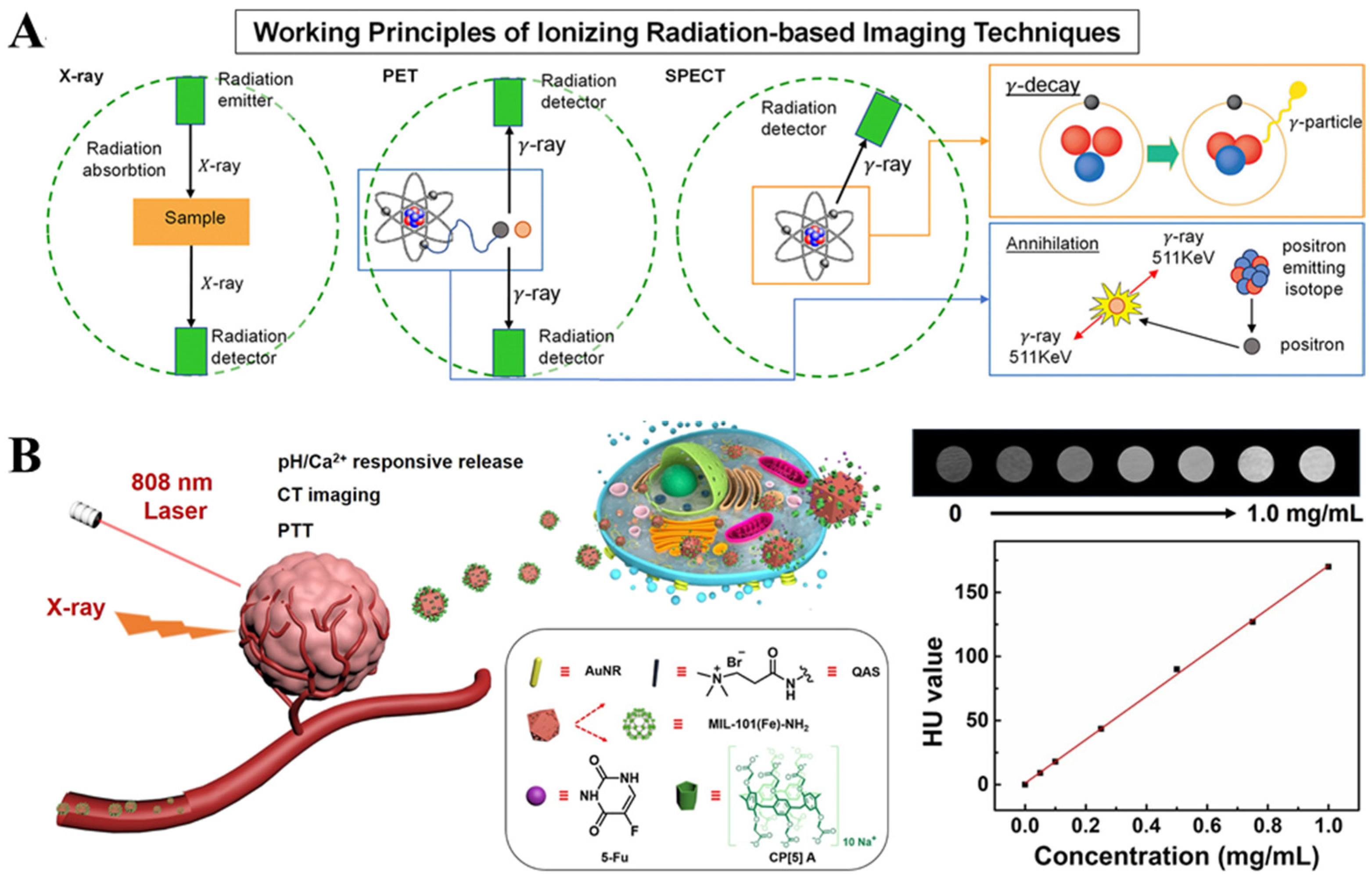
2.5. Composite Imaging Techniques
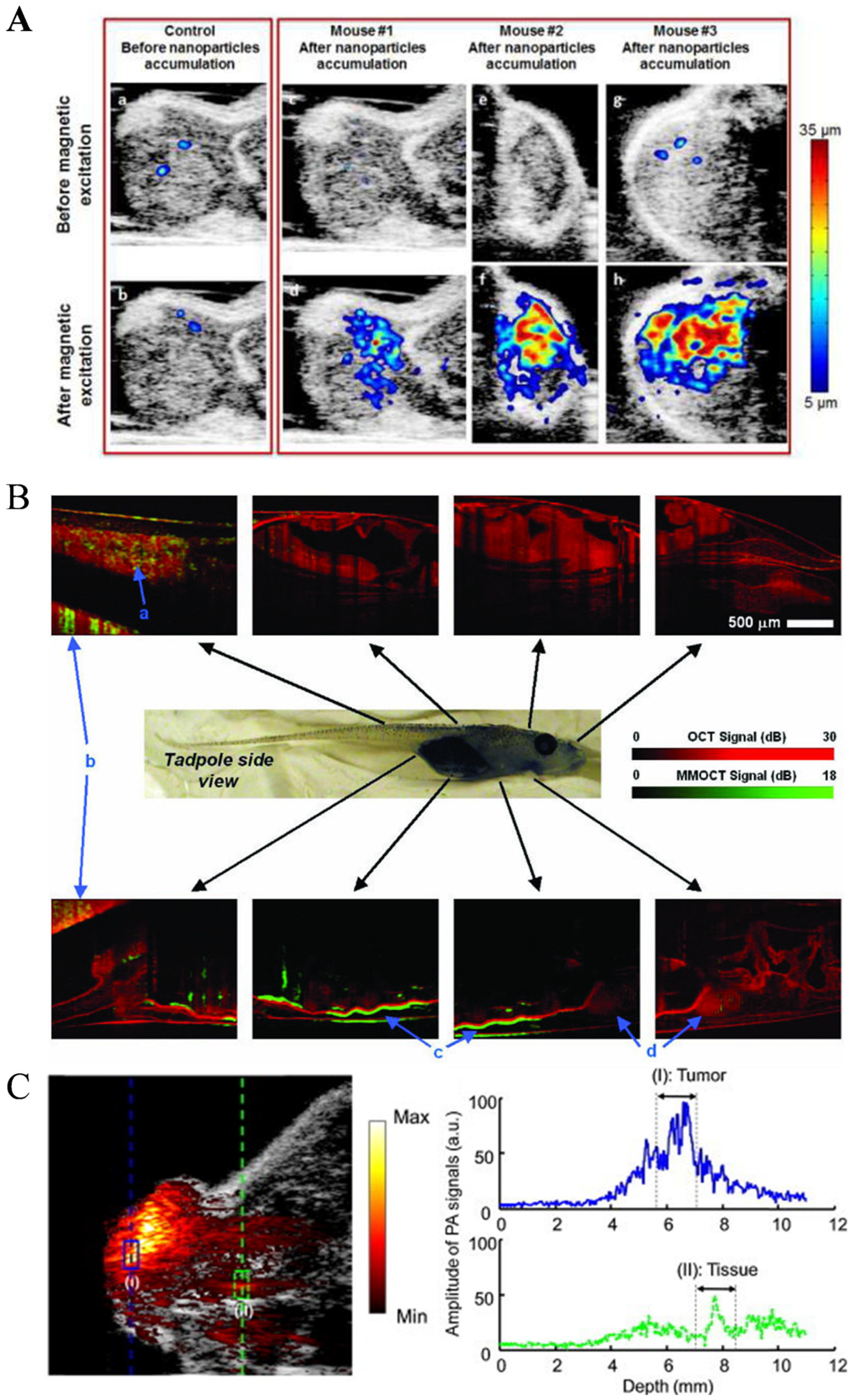
2.5.1. Photoacoustic Imaging (PAI)
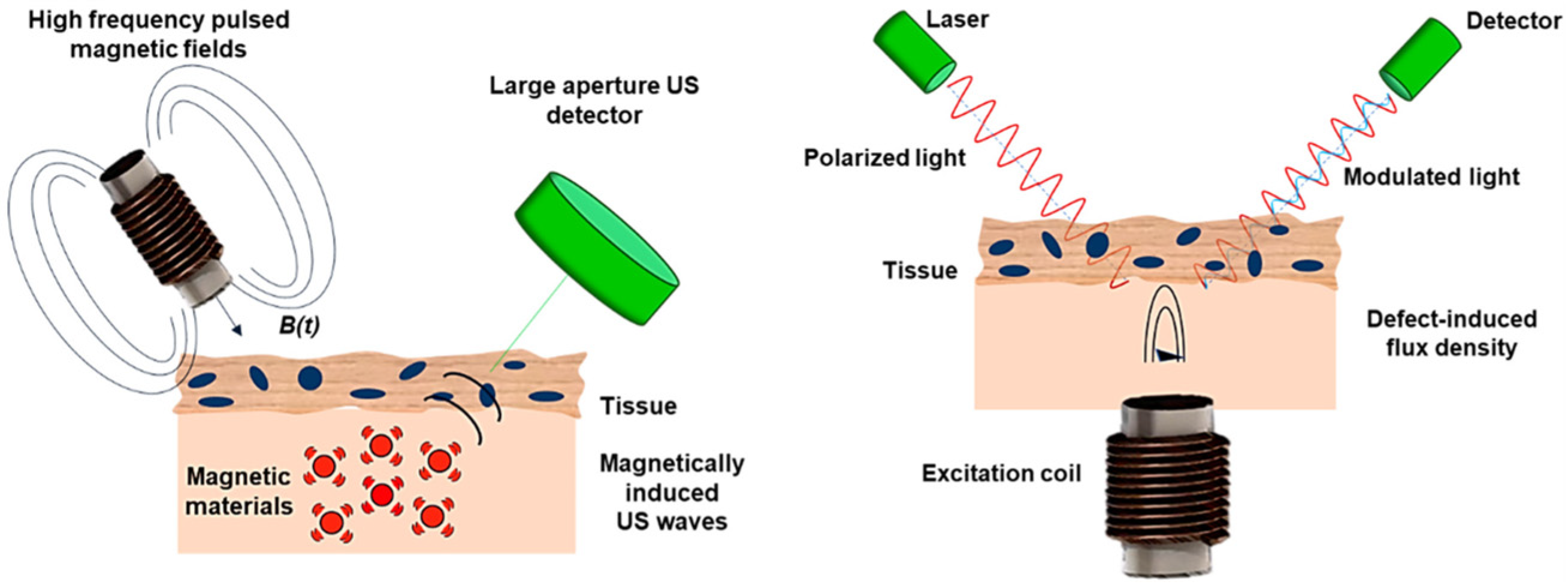
2.5.2. Magnetomotive Assisted Imaging
3. Summary and Future Outlook of Imaging Techniques
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joudeh, N.; Linke, D. Nanoparticle classification, physicochemical properties, characterization, and applications: A comprehensive review for biologists. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Medina-Sanchez, M.; Koch, B.; Schmidt, O.G. Medibots: Dual-action biogenic microdaggers for single-cell surgery and drug release. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.X.; de Avila, B.E.F.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.F.; Wang, J. Micro/nanorobots for biomedicine: Delivery, surgery, sensing, and detoxification. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaam6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallouk, T.E.; Sen, A. Powering nanorobots. Sci. Am. 2009, 300, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Dong, R.F.; Wu, H.Y.; Cai, Y.P.; Ren, B.Y. A review on artificial micro/nanomotors for cancer-targeted delivery, diagnosis, and therapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.Z.; Huang, T.Y.; Luo, Z.C.; Testa, P.; Gu, H.R.; Chen, X.Z.; Nelson, B.J.; Heyderman, L.J. Nanomagnetic encoding of shape-morphing micromachines. Nature 2019, 575, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Lum, G.Z.; Mastrangeli, M.; Sitti, M. Small-scale soft-bodied robot with multimodal locomotion. Nature 2018, 554, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Pané, S.; Nelson, B.J. Soft micro- and nanorobotics. Annu. Rev. Control. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2018, 1, 53–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Sanchez, M.; Xu, H.; Schmidt, O.G. Micro-and nano-motors: The new generation of drug carriers. Ther. Deliv. 2018, 9, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ho, C.; Tsatskis, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Dai, C.; Wang, F.; Tan, M.; Hopyan, S.; McNeill, H.; et al. Intracellular manipulation and measurement with multi-pole magnetic tweezers. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaav6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Will future microrobots be task-specific customized machines or multi-purpose “all in one” vehicles. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. External power-driven microrobotic swarm: From fundamental understanding to imaging-guided delivery. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 149–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.; Pane, S.; Iacovacci, V.; Koukourakis, N.; Czarske, J.; Menciassi, A.; Medina-Sanchez, M.; Schmidt, O.G. Medical imaging of microrobots: Toward in vivo applications. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10865–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.K.; Medina-Sánchez, M.; Edmondson, R.J.; Schmidt, O.G. Engineering microrobots for targeted cancer therapies from a medical perspective. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeles, C.; Kratochvil, B.E.; Nelson, B.J. Visually servoing magnetic intraocular microdevices. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.X.; Zhang, G.Q.; Ding, D. Design of superior phototheranostic agents guided by Jablonski diagrams. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8179–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steager, E.B.; Sakar, M.S.; Magee, C.; Kennedy, M.; Cowley, A.; Kumar, V. Automated biomanipulation of single cells using magnetic microrobots. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2013, 32, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, S.; Ramesh, B.; Seifalian, A.M. Fluorescence nanoparticles “quantum dots” as drug delivery system and their toxicity: A review. J. Drug Target. 2011, 19, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhou, Q.; Vincent, M.; Deng, Y.; Yu, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, T.; Tang, T.; Bian, L.; Wang, Y.-X.J.; et al. Multifunctional biohybrid magnetite microrobots for imaging-guided therapy. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaaq1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnermann, M. Organic dyes for deep bioimaging. Nature 2017, 551, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servant, A.; Qiu, F.; Mazza, M.; Kostarelos, K.; Nelson, B.J. Controlled in vivo swimming of a swarm of bacteria-like microrobotic flagella. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felfoul, O.; Mohammadi, M.; Taherkhani, S.; De Lanauze, D.; Xu, Y.Z.; Loghin, D.; Essa, S.; Jancik, S.; Houle, D.; Lafleur, M.; et al. Magneto-aerotactic bacteria deliver drug-containing nanoliposomes to tumour hypoxic regions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, P.; Iyisan, N.; Wang, C.; Kohler, F.; Neb, I.; Lahm, H.; Dressen, M.; Krane, M.; Dietz, H.; Oezkale, B. A Laser Driven Microrobot for Thermal Stimulation of Single Cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2300904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ourak, M.; De Simone, A.; Tamadazte, B.; Laurent, G.J.; Menciassi, A.; Andreff, N. Automated in-plane OCT-probe positioning towards repetitive optical biopsies. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 4186–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psomadakis, C.E.; Marghoob, N.; Bleicher, B.; Markowitz, O. Optical coherence tomography. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 39, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Troll, J.; Jeong, H.-H.; Wei, Q.; Stang, M.; Ziemssen, F.; Wang, Z.; Dong, M.; Schnichels, S.; Qiu, T.; et al. A swarm of slippery micropropellers penetrates the vitreous body of the eye. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yu, S.; Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Song, C.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Grattan, K.T.V.; et al. Bioinspired claw-engaged and biolubricated swimming microrobots creating active retention in blood vessels. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Dong, D.; Lam, W.; Xing, L.; Wei, T.; Sun, D. Automated in vivo navigation of magnetic-driven microrobots using OCT imaging feedback. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 67, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tous, C.; Li, N.; Dimov, I.P.; Kadoury, S.; Tang, A.; Häfeli, U.O.; Nosrati, Z.; Saatchi, K.; Moran, G.; Couch, M.J.; et al. Navigation of microrobots by mri: Impact of gravitational, friction and thrust forces on steering success. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 49, 3724–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryaki, M.E.; Demir, S.O.; Sitti, M. Deep learning-based 3D magnetic microrobot tracking using 2D MR images. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 6982–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Wang, K.; Hou, C.J.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, F.Q.; Ren, W.; Dong, L.X.; Zhao, J. Self-sensing intelligent microrobots for noninvasive and wireless monitoring systems. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, E.M.; Skrtic, S.; Sharer, K.; Hill, J.M.; Dunbar, C.E.; Koretsky, A.P. MRI detection of single particles for cellular imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10901–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, G.; Yoo, A.; Nguyen, K.T.; Nan, M.; Darmawan, B.A.; Zheng, S.; Kang, B.; Kim, C.S.; Bang, D.; Lee, S.; et al. Multifunctional microrobot with real-time visualization and magnetic resonance imaging for chemoembolization therapy of liver cancer. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabq8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouponneau, P.; Leroux, J.-C.; Soulez, G.; Gaboury, L.; Martel, S. Co-encapsulation of magnetic nanoparticles and doxorubicin into biodegradable microcarriers for deep tissue targeting by vascular MRI navigation. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3481–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, S. Magnetic navigation control of microagents in the vascular network: Challenges and strategies for endovascular magnetic navigation control of microscale drug delivery carriers. IEEE Control. Syst. Mag. 2013, 33, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgert, J.; Schmidt, J.D.; Schmale, I.; Rahmer, J.; Bontus, C.; Gleich, B.; David, B.; Eckart, R.; Woywode, O.; Weizenecker, J.; et al. Fundamentals and applications of magnetic particle imaging. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2012, 6, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothnagel, N.; Rahmer, J.; Gleich, B.; Halkola, A.; Buzug, T.M.; Borgert, J. Steering of magnetic devices with a magnetic particle imaging system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleich, B.; Weizenecker, J. Tomographic imaging using the nonlinear response of magnetic particles. Nature 2005, 435, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeser, M.; Thieben, F.; Szwargulski, P.; Werner, F.; Gdaniec, N.; Boberg, M.; Griese, F.; Möddel, M.; Ludewig, P.; van de Ven, D.; et al. Human-sized magnetic particle imaging for brain applications. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Song, Z.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Tang, X.; Jiang, Z. The applications of magnetic particle imaging: From cell to body. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakenecker, A.C.; von Gladiss, A.; Friedrich, T.; Heinen, U.; Lehr, H.; Ludtke-Buzug, K.; Buzug, T.M. Actuation and visualization of a magnetically coated swimmer with magnetic particle imaging. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 473, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.J.; Patrick, P.S.; Yu, Y.; Lythgoe, M.F.; Kalber, T.L.; Ma, F.; Ja, B.; Wa, L.; Tr, H.; Aw, N.; et al. Advanced cell therapies: Targeting, tracking and actuation of cells with magnetic particles. Regen. Med. 2015, 10, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, C.M.; Thomson, A.J.W. Preclinical ultrasound imaging-a review of techniques and imaging applications. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Zhang, L. Ultrasound imaging and tracking of micro/nanorobots: From individual to collectives. IEEE Open J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 1, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebgott, H.; Rodriguez-Molares, A.; Cervenansky, F.; Jensen, J.A.; Bernard, O. Plane-wave imaging challenge in medical ultrasound. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Tours, France, 18–21 September 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, K.; Alkhatib, M.; Folio, D.; Ferreira, A. USMicroMagSet: Using deep learning analysis to benchmark the performance of microrobots in ultrasound images. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 3254–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrage, M.; Medany, M.; Ahmed, D. Ultrasound microrobots with reinforcement learning. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheggi, S.; Yoon, C.K.; Ghosh, A.; Gracias, D.H.; Misra, S. A GPU-accelerated model-based tracker for untethered submillimeter grippers. Robot. Auto. Syst. 2018, 103, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Jin, D.; Chan, K.F.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, L. Active generation and magnetic actuation of microrobotic swarms in bio-fluids. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongaro, F.; Niehoff, D.; Mohanty, S.; Misra, S. A contactless and biocompatible approach for 3D active microrobotic targeted drug delivery. Micromachines 2019, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, L. Characterizing nanoparticle swarms with tuneable concentrations for enhanced imaging contrast. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2942–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.V.; Ansari, M.H.D.; Dayan, C.B.; Giltinan, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Kishore, V.; Laux, P.; Luch, A.; Sitti, M. Multifunctional magnetic hairbot for untethered osteogenesis, ultrasound contrast imaging and drug delivery. Biomaterials 2019, 219, 119394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lavery, L.; Kim, K. Super-resolution ultrasound imaging method for microvasculature in vivo with a high temporal accuracy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberman, A.; Wang, J.; Lu, N.; Viveros, R.D.; Allen, C.A.; Mattrey, R.F.; Blair, S.L.; Trogler, W.C.; Kim, M.J.; Kummel, A.C. Mechanically tunable hollow silica ultrathin nanoshells for ultrasound contrast agents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4049–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.W.; Chang, X.C.; Liu, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, T.L.; Li, L.Q. Multi-response biocompatible Janus micromotor for ultrasonic imaging contrast enhancement. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 23, 101026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.R.; Desjardins, A.E.; Ourselin, S.; Vercauteren, T.; Xia, W.F. Minimally invasive photoacoustic imaging: Current status and future perspectives. Photoacoustics 2019, 16, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, A.; Magdanz, V.; Schmidt, O.G.; Misra, S. Magnetic control of self-propelled microjets under ultrasound image guidance. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 12–15 August 2014; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, K.; Flohr, T.; Knez, A.; Rist, C.; Wintersperger, B.; Johnson, T.; Reiser, M.F.; Becker, C.R. Advances in cardiac CT imaging: 64-Slice Scanner. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2004, 20, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishkov, O.; Chen, C.; Madonna, C.A.; Jayaram, K.; Peleg, O. Strength-mass scaling law governs mass distribution inside honey bee swarms. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.B.; Kang, B.; Bappy, D.M.; Choi, E.; Park, S.; Ko, S.Y.; Park, J.-O.; Kim, C.-S. Real-time microrobot posture recognition via biplane X-ray imaging system for external electromagnetic actuation. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2018, 13, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, M.; Lee, H.; Feng, S.-P.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.T. X-ray powered micromotors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 15727–15732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Choi, H.; Go, G.; Lee, C.; Lim, K.S.; Sim, D.S.; Jeong, M.H.; Ko, S.Y.; Park, J.-O.; Park, S. Penetration of an artificial arterial thromboembolism in a live animal using an intravascular therapeutic microrobot system. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedantham, S.; Karellas, A.; Suryanarayanan, S. Solid-state fluoroscopic imager for high-resolution angiography: Parallel cascaded linear systems analysis. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Yu, H.M.; Wu, M.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Sun, M.; Qin, J.C.; Ma, L.; Yang, Y.W. AuNRs@MIL-101-based stimuli-responsive nanoplatform with supramolecular gates for image-guided chemo-photothermal therapy. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 23, 100716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Nauber, R.; Iglesias, A.S.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Schmidt, O.G.; Medina-Sánchez, M. Imaging and control of nanomaterial-decorated micromotors. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Manipulation, Automation and Robotics at Small Scales, Toronto, ON, Canada, 25–29 July 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wang, L.; Yin, C.; Zhong, T.; Lu, Z.; Yao, L. The voyage of micro/nanorobots inside the human body. ChemNanoMat 2022, 8, e202100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.B.; Cornelis, F. Interventional molecular imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wen, Q.; Lin, S.; Wen, Q.; Lu, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, J.; Xiao, S.; et al. Bacteria-driven tumor microenvironment-sensitive nanoparticles targeting hypoxic regions enhances the chemotherapy outcome of lung cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovacci, V.; Blanc, A.; Huang, H.; Ricotti, L.; Schibli, R.; Menciassi, A.; Behe, M.; Pane, S.; Nelson, B.J. High-resolution SPECT imaging of stimuli-responsive soft microrobots. Small 2019, 15, 1900709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, D.; Cossio, U.; Parmar, J.; Martinez-Villacorta, A.M.; Gomez-Vallejo, V.; Llop, J.; Sanchez, S. Medical imaging for the tracking of micromotors. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1220–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taruttis, A.; Ntziachristos, V. Advances in real-time multispectral optoacoustic imaging and its applications. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.; Aguirre, J.; Ntziachristos, V. Optoacoustic mesoscopy for biomedicine. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 354–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jing, W.; Mehrmohammadi, M. Photoacoustic imaging to track magnetic-manipulated micro-robots in deep tissue. Sensors 2020, 20, 2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Song, W.; Dai, L.; Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Li, T. Magnetic microswarm for MRI contrast enhancer. Chem.–Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, L. Review of photoacoustic imaging for microrobots tracking in vivo. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2021, 19, 111701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Mehrmohammadi, M.; Jing, W. Non-invasive photoacoustic imaging of magnetic microrobot through deep non-transparent tissue. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Manipulation, Automation and Robotics at Small Scales, IEEE, Toronto, ON, Canada, 13–17 July 2020; pp. 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.; Hester, S.; Basij, M.; Paul, A.; Xavierselvan, M.; Mehrmohammadi, M.; Mallidi, S. Niche preclinical and clinical applications of photoacoustic imaging with endogenous contrast. Photoacoustics 2023, 32, 100533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.V.; Hu, S. Photoacoustic tomography: In vivo imaging from organelles to organs. Science 2012, 335, 1458–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Baik, J.W.; Kim, C. Review on practical photoacoustic microscopy. Photoacoustics 2019, 15, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Pang, X.; Yan, X.; Dai, Q.; Lin, H.; Ye, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Photoacoustic imaging-trackable magnetic microswimmers for pathogenic bacterial infection treatment. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2880–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.; Nauber, R.; Iglesias, A.S.; Tang, M.; Ma, L.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Schmidt, O.G.; Medina-Sánchez, M. Nanomaterial-decorated micromotors for enhanced photoacoustic imaging. J. Micro-Bio Robot. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.G.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.R.; Hu, P.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.Y.O.; Wang, L.V.; Gao, W. A microrobotic system guided by photoacoustic computed tomography for targeted navigation in intestines in vivo. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaax0613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrede, P.; Degtyaruk, O.; Kalva, S.K.; Deán-Ben, X.L.; Bozuyuk, U.; Aghakhani, A.; Akolpoglu, B.; Sitti, M.; Razansky, D. Real-time 3D optoacoustic tracking of cell-sized magnetic microrobots circulating in the mouse brain vasculature. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm9132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrmohammadi, M.; Oh, J.; Ma, L. Imaging of iron oxide nanoparticles using magneto-motive ultrasound. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium Proceedings, New York, NY, USA, 28–31 October 2007; pp. 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evertsson, M.; Ramalli, A.; Pavan, T.Z. Towards real-time magnetomotive ultrasound imaging. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evertsson, M.; Cinthio, M.; Fredriksson, S.; Olsson, F.; Persson, H.; Jansson, T. Frequency-and phase-sensitive magnetomotive ultrasound imaging of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2013, 60, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evertsson, M.; Cinthio, M.; Kjellman, P. In vivo magnetomotive ultrasound imaging of rat lymph nodes—A pilot study. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Taipei, Taiwan, China, 21–24 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Feldman, M.D.; Kim, J.; Condit, C.; Emelianov, S.; Milner, T.E. Detection of magnetic nanoparticles in tissue using magneto-motive ultrasound. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4183–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrmohammadi, M.; Shin, T.-H.; Qu, M.; Kruizinga, P.; Truby, R.L.; Lee, J.-H.; Cheon, J.; Emelianov, S.Y. In vivo pulsed magneto-motive ultrasound imaging using high-performance magnetoactive contrast nanoagents. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11179–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldenburg, A.L.; Crecea, V.; Rinne, S.A.; Rezaeipoor, R.; Chaney, E.J.; Boppart, S.A. Spectral-domain magnetomotive OCT imaging of magnetic nanoparticle biodistribution. In Proceedings of the Coherence Domain Optical Methods and Optical Coherence Tomography in Biomedicine XII, San Jose, CA, USA, 19–24 January 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crecea, V.; Oldenburg, A.L.; Ralston, T.S.; Boppart, S.A. Phase-resolved spectral-domain magnetomotive optical coherence tomography. In Proceedings of the Coherence Domain Optical Methods and Optical Coherence Tomography in Biomedicine XI, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–25 January 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, A.L.; Toublan, F.-J.; Suslick, K.S.; Wei, A.; Boppart, S.A. Magnetomotive contrast for in vivo optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 6597–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, R.; Rezaeipoor, R.; Adie, S.G.; Chaney, E.J.; Oldenburg, A.L.; Marjanovic, M.; Haldar, J.P.; Sutton, B.P.; Boppart, S.A. In vivo magnetomotive optical molecular imaging using targeted magnetic nanoprobes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8085–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesinghe, R.E.; Park, K.; Kim, D.-H.; Jeon, M.; Kim, J. In vivo imaging of melanoma-implanted magnetic nanoparticles using contrast-enhanced magneto-motive optical Doppler tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oldenburg, A.L.; Gallippi, C.M.; Tsui, F.; Nichols, T.C.; Beicker, K.N.; Chhetri, R.K.; Spivak, D.; Richardson, A.; Fischer, T.H. Magnetic and contrast properties of labeled platelets for magnetomotive optical coherence tomography. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, A.L.; Wu, G.; Spivak, D.; Tsui, F.; Wolberg, A.S.; Fischer, T.H. Imaging and elastometry of blood clots using magnetomotive optical coherence tomography and labeled platelets. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2012, 18, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimalla, P.; Werner, T.; Winkler, K.; Mueller, C.; Wicht, S.; Gaertner, M.; Mehner, M.; Walther, J.; Rellinghaus, B.; Wittig, D.; et al. Imaging of nanoparticle-labeled stem cells using magnetomotive optical coherence tomography, laser speckle reflectometry, and light microscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 036018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.W.; Xia, J.J.; Pelivanov, I.; Jia, C.X.; Huang, S.W.; Hu, X.G.; Gao, X.H.; O’Donnell, M. Magnetomotive photoacoustic imaging: In vitro studies of magnetic trapping with simultaneous photoacoustic detection of rare circulating tumor cells. J. Biophotonics 2013, 6, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Xia, J.; Pelivanov, I.; Hu, X.; Gao, X.; O’Donnell, M. Trapping and dynamic manipulation with magnetomotive photoacoustic imaging of targeted microspheres mimicking metastatic cancer cells trafficking in the vasculature. In Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing 2012; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8223, pp. 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, M.; Mehrmohammadi, M.; Emelianov, S. Detection of nanoparticle endocytosis using magneto-photoacoustic imaging. Small 2011, 7, 2858–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Mallidi, S.; Mehrmohammadi, M.; Truby, R.; Homan, K.; Joshi, P.; Chen, Y.S.; Sokolov, K.; Emelianov, S. Magneto-photo-acoustic imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Mehrmohammadi, M.; Truby, R.; Graf, I.; Homan, K.; Emelianov, S. Contrast-enhanced magneto-photo-acoustic imaging in vivo using dual-contrast nanoparticles. Photoacoustics 2014, 2, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariappan, L.; Shao, Q.; Jiang, C.; Yu, K.; Ashkenazi, S.; Bischof, J.C.; He, B. Magneto acoustic tomography with short pulsed magnetic field for in vivo imaging of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Imaging Modalities | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Penetration Depth Indicators | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic particle imaging (MPI) | 1~10 mm | Millisecond level | Hundreds of millimeters |
|
|
| Optical coherence tomography (OCT) | 5~20 µm | Millisecond level | Hundreds of millimeters |
|
|
| Fluorescence imaging (F) | 100~1000 µm | >1 min | A few millimeters |
|
|
| Ultrasound imaging (US) | 100~1000 µm | Millisecond level | Hundreds of millimeters to centimeters |
|
|
| Nuclear medicine imaging (PET/SPECT) | 1~5 mm | >10 s | In the millimeter to centimeter scale |
|
|
| X-ray imaging (X-ray) | 10~500 µm | >1 min | >1 cm |
|
|
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | 10~200 µm | >1 min | >10 cm |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Jing, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Zhu, Y.; Dai, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, S. Medical Imaging Technology for Micro/Nanorobots. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13212872
Liu X, Jing Y, Xu C, Wang X, Xie X, Zhu Y, Dai L, Wang H, Wang L, Yu S. Medical Imaging Technology for Micro/Nanorobots. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(21):2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13212872
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuejia, Yizhan Jing, Chengxin Xu, Xiaoxiao Wang, Xiaopeng Xie, Yanhe Zhu, Lizhou Dai, Haocheng Wang, Lin Wang, and Shimin Yu. 2023. "Medical Imaging Technology for Micro/Nanorobots" Nanomaterials 13, no. 21: 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13212872
APA StyleLiu, X., Jing, Y., Xu, C., Wang, X., Xie, X., Zhu, Y., Dai, L., Wang, H., Wang, L., & Yu, S. (2023). Medical Imaging Technology for Micro/Nanorobots. Nanomaterials, 13(21), 2872. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13212872