Ultrasonic Spray Coating to Optimize Performance of Bio-Electrochemical Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
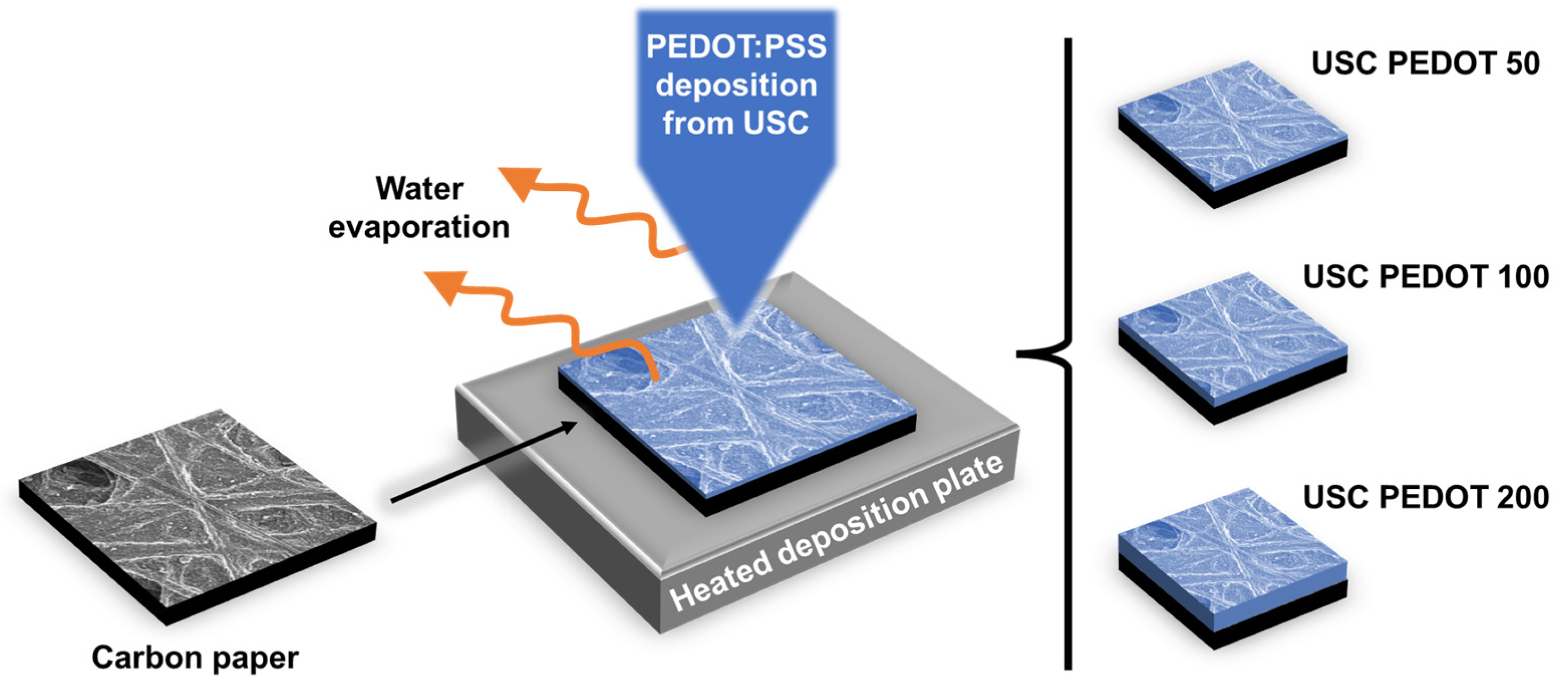
2.1. Anode Fabrication via Ultrasonic Spray Coating (USC)
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.2.1. Morphological and Physical–Chemical Characterizations of Electrodes
2.2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry Characterizations of Electrodes
2.2.3. SCMFCs Fabrication and Electrical and Electrochemical Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological and Physical–Chemical Characterizations
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization on Electrodes
3.3. Electrodes Operation in MFCs
3.3.1. MFC Output Potential Monitoring
3.3.2. Electrochemical Characterizations on MFCs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santoro, C.; Arbizzani, C.; Erable, B.; Ieropoulos, I. Microbial Fuel Cells: From Fundamentals to Applications. A Review. J. Power Sources 2017, 356, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slate, A.J.; Whitehead, K.A.; Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. Microbial Fuel Cells: An Overview of Current Technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 101, 60–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E. Microbial Fuel Cells; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Ma, H.; Han, P.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Qing, R.; et al. Investigating the Effect of Anode Materials on the Performance and Microbial Community in an Integrated Chamber-Free Microbial Fuel Cell. Fuel 2024, 357, 129648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, I.; Kerzenmacher, S.; Santiago, Ó. Stainless Steel Wool as Novel Bioanode for Microbial Electrolysis Cells: A Systematic Study of Materials. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1119090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul, Z.; Sánchez-Peña, P.; Baeza, M.; Sulonen, M.; Gabriel, D.; Baeza, J.A.; Guisasola, A. Systematic Screening of Carbon-based Anode Materials for Bioelectrochemical Systems. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2023, 98, 1402–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Zhao, J.; Li, F.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z. Advances in Anode Materials for Microbial Fuel Cells. Energy Technol. 2022, 10, 2200824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, I.; Bampos, G.; Soto Beobide, A.; Dailianis, S.; Voyiatzis, G.; Bebelis, S.; Lyberatos, G.; Antonopoulou, G. The Effect of Anode Material on the Performance of a Hydrogen Producing Microbial Electrolysis Cell, Operating with Synthetic and Real Wastewaters. Energies 2021, 14, 8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.-L.; Pinto, D.; Laberty-Robert, C. Electrospun Carbon Fibers for Microbial Fuel Cells: A Novel Bioanode Design Applied to Wastewater Treatment. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 373, 137864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Meng, L.; Chen, G.; Xi, Y.; Jiang, N.; Song, J.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhen, G.; Huang, M. Application of Advanced Anodes in Microbial Fuel Cells for Power Generation: A Review. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 125985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salar-García, M.J.; Ieropoulos, I. Optimisation of the Internal Structure of Ceramic Membranes for Electricity Production in Urine-Fed Microbial Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2020, 451, 227741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Yu, E.H.; Daud, W.R.W.; Kim, B.H.; Scott, K. Bioanode as a Limiting Factor to Biocathode Performance in Microbial Electrolysis Cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, W.; Gu, Z. Poly (3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Promotes Direct Electron Transfer at the Interface between Shewanella loihica and the Anode in a Microbial Fuel Cell. J. Power Sources 2015, 277, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-G.; Rhee, C.; Jadhav, D.A.; Eisa, T.; Al-Mayyahi, R.B.; Shin, S.G.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Chae, K.-J. Tailoring a Highly Conductive and Super-Hydrophilic Electrode for Biocatalytic Performance of Microbial Electrolysis Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaglia, G.; Frascella, F.; Chiadò, A.; Sacco, A.; Marasso, S.L.; Cocuzza, M.; Pirri, C.F.; Quaglio, M. Electrospun Nanofibers: From Food to Energy by Engineered Electrodes in Microbial Fuel Cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaglia, G.; Margaria, V.; Fiorentin, M.R.; Pasha, K.; Sacco, A.; Castellino, M.; Chiodoni, A.; Bianco, S.; Pirri, F.C.; Quaglio, M. Nonwoven Mats of N-Doped Carbon Nanofibers as High-Performing Anodes in Microbial Fuel Cells. Mater. Today Energy 2020, 16, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.L.; Pichiah, S.; Ibrahim, S. Facile Reconstruction of Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) Anode with Enhanced Exoelectrogens Selection for Intensified Electricity Generation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, J.J.L.; Pehlivaner Kara, M.O.; Frey, M.W.; Angenent, L.T. Performance of Electro-Spun Carbon Nanofiber Electrodes with Conductive Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Coatings in Bioelectrochemical Systems. J. Power Sources 2017, 356, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.L.; Ibrahim, S.; Pichiah, S. Synergetic Effect of Conductive Polymer Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) with Different Structural Configuration of Anode for Microbial Fuel Cell Application. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, D.; Isikgor, F.H.; Ouyang, J. Review on Application of PEDOTs and PEDOT:PSS in Energy Conversion and Storage Devices. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 4438–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimzadeh, Z.; Naghib, S.M.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. An Overview on the Synthesis and Recent Applications of Conducting Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) in Industry and Biomedicine. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 7575–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Yu, J.; Tian, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, S.; Zang, L. Application of PEDOT:PSS and Its Composites in Electrochemical and Electronic Chemosensors. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A.; Rather, R.A.; Shalla, A.H. PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS Conducting Polymeric Hydrogels: A Report on Their Emerging Applications. Synth. Met. 2021, 273, 116709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Pu, K.-B.; Cai, W.-F.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Li, F.-J. Characteristics of Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Modified Stainless Steel as Anode in Air-Cathode Microbial Fuel Cells. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 6633–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Malla, M.A.; Gupta, S.K.; Mishra, P.; Malla, M.A.; Gupta, S.K. Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-Modified Graphite Felt and Carbon Cloth Anodes for Use in Microbial Fuel Cells. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, R. Maximizing the Use of Platinum Catalyst by Ultrasonic Spray Application. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 014501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, F.; Matsumoto, A.; Zoetebier, B.; Peressinotto, V.S.; Hirata, M.K.; de Sousa, D.A.; Maciel, R. Handheld and Automated Ultrasonic Spray Deposition of Conductive PEDOT:PSS Films and Their Application in AC EL Devices. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, M.; Rohde, S.; Liu, D.J.; Gollas, B.; Hacker, V. Recent Advancements in High Performance Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Electrode Fabrication–Novel Materials and Manufacturing Processes. J. Power Sources 2023, 562, 232734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtayeva, Z.; Xu, F.; Dillet, J.; Mozet, K.; Peignier, R.; Celzard, A.; Maranzana, G. Manufacturing Catalyst-Coated Membranes by Ultrasonic Spray Deposition for PEMFC: Identification of Key Parameters and Their Impact on PEMFC Performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 16165–16178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, S.; Eroglu, I. Ultrasonic Spray Coating Technique for High-Performance PEM Fuel Cell Electrode Manufacturing. In Progress in Clean Energy, Volume 2; Dincer, I., Colpan, C.O., Kizilkan, O., Ezan, M.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 481–492. ISBN 978-3-319-17030-5. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, J.; Ryan, A.J.; Lidzey, D.G. Solution Modification of PEDOT:PSS Inks for Ultrasonic Spray Coating. Org. Electron. 2017, 41, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonakar, G.S.; Mahajan, M.S.; Ghosh, S.S.; Sali, J.V. Modeling Thin Film Formation by Ultrasonic Spray Method: A Case of PEDOT:PSS Thin Films. Org. Electron. 2012, 13, 2575–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spisni, G.; Massaglia, G.; Pirri, C.F.; Bianco, S.; Quaglio, M. Nanostructured Layer Based on Intrinsically Conductive Polymers for Optimising Carbon Electrodes’ Surface: Electrospray and Ultrasonic Spray Coating. Mater. Proc. 2023, 14, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Quaglio, M.; Massaglia, G.; Vasile, N.; Margaria, V.; Chiodoni, A.; Salvador, G.P.; Marasso, S.L.; Cocuzza, M.; Saracco, G.; Pirri, F.C. A Fluid Dynamics Perspective on Material Selection in Microbial Fuel Cell-Based Biosensors. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 4533–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Logan, B.E. Power Densities Using Different Cathode Catalysts (Pt and CoTMPP) and Polymer Binders (Nafion and PTFE) in Single Chamber Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, H.; Heidrich, E.S.; Leicester, D.D.; Theodosiou, P. Pilot-Scale Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs): A Meta-Analysis Study to Inform Full-Scale Design Principles for Optimum Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 131227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Garriga, M.; Reparaz, J.S.; Alonso, M.I. Advanced Optical Characterization of PEDOT:PSS by Combining Spectroscopic Ellipsometry and Raman Scattering. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 39429–39436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, S.; Feng, Y.; Merrill, M.D.; Saito, T.; Logan, B.E. Use of Carbon Mesh Anodes and the Effect of Different Pretreatment Methods on Power Production in Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6870–6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Long, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Meng, H.; Jiang, C.; Dong, W.; Lu, N. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Applied to Microbial Fuel Cells: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 973501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostino, V.; Ahmed, D.; Sacco, A.; Margaria, V.; Armato, C.; Quaglio, M. Electrochemical Analysis of Microbial Fuel Cells Based on Enriched Biofilm Communities from Freshwater Sediment. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 237, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Benetton, X.; Sevda, S.; Vanbroekhoven, K.; Pant, D. The Accurate Use of Impedance Analysis for the Study of Microbial Electrochemical Systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaglia, G.; Sacco, A.; Chiodoni, A.; Pirri, C.F.; Quaglio, M. Living Bacteria Directly Embedded into Electrospun Nanofibers: Design of New Anode for Bio-Electrochemical Systems. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Fu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Liao, Q. Response of Anodic Biofilm and the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cells to Different Discharging Current Densities. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 233, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Chang, I.S.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. Accurate Measurement of Internal Resistance in Microbial Fuel Cells by Improved Scanning Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 366, 137388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Electrode | EASA (cm2) | α (a.u.) |
|---|---|---|
| Control (carbon paper) | 6.6 ± 0.3 | 1 |
| USC PEDOT 50 | 15.9 ± 0.3 | 2.40 ± 0.04 |
| USC PEDOT 100 | 17 ± 2 | 2.6 ± 0.2 |
| USC PEDOT 200 | 15 ± 2 | 2.3 ± 0.3 |
| MFC Device | Erec (J·m−3) | Rct Anode (Ω) |
|---|---|---|
| Control (carbon paper) | 4.3 ± 0.5 | 11 ± 2 |
| USC PEDOT 50 | 6.2 ± 0.6 | 10 ± 3 |
| USC PEDOT 100 | 11.7 ± 0.9 | 11 ± 2 |
| USC PEDOT 200 | 13 ± 2 | 19 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spisni, G.; Massaglia, G.; Pirri, F.C.; Bianco, S.; Quaglio, M. Ultrasonic Spray Coating to Optimize Performance of Bio-Electrochemical Systems. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13222926
Spisni G, Massaglia G, Pirri FC, Bianco S, Quaglio M. Ultrasonic Spray Coating to Optimize Performance of Bio-Electrochemical Systems. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(22):2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13222926
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpisni, Giacomo, Giulia Massaglia, Fabrizio C. Pirri, Stefano Bianco, and Marzia Quaglio. 2023. "Ultrasonic Spray Coating to Optimize Performance of Bio-Electrochemical Systems" Nanomaterials 13, no. 22: 2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13222926
APA StyleSpisni, G., Massaglia, G., Pirri, F. C., Bianco, S., & Quaglio, M. (2023). Ultrasonic Spray Coating to Optimize Performance of Bio-Electrochemical Systems. Nanomaterials, 13(22), 2926. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13222926







