A Self-Powered Flexible Displacement Sensor Based on Triboelectric Effect for Linear Feed System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design and Fabrication
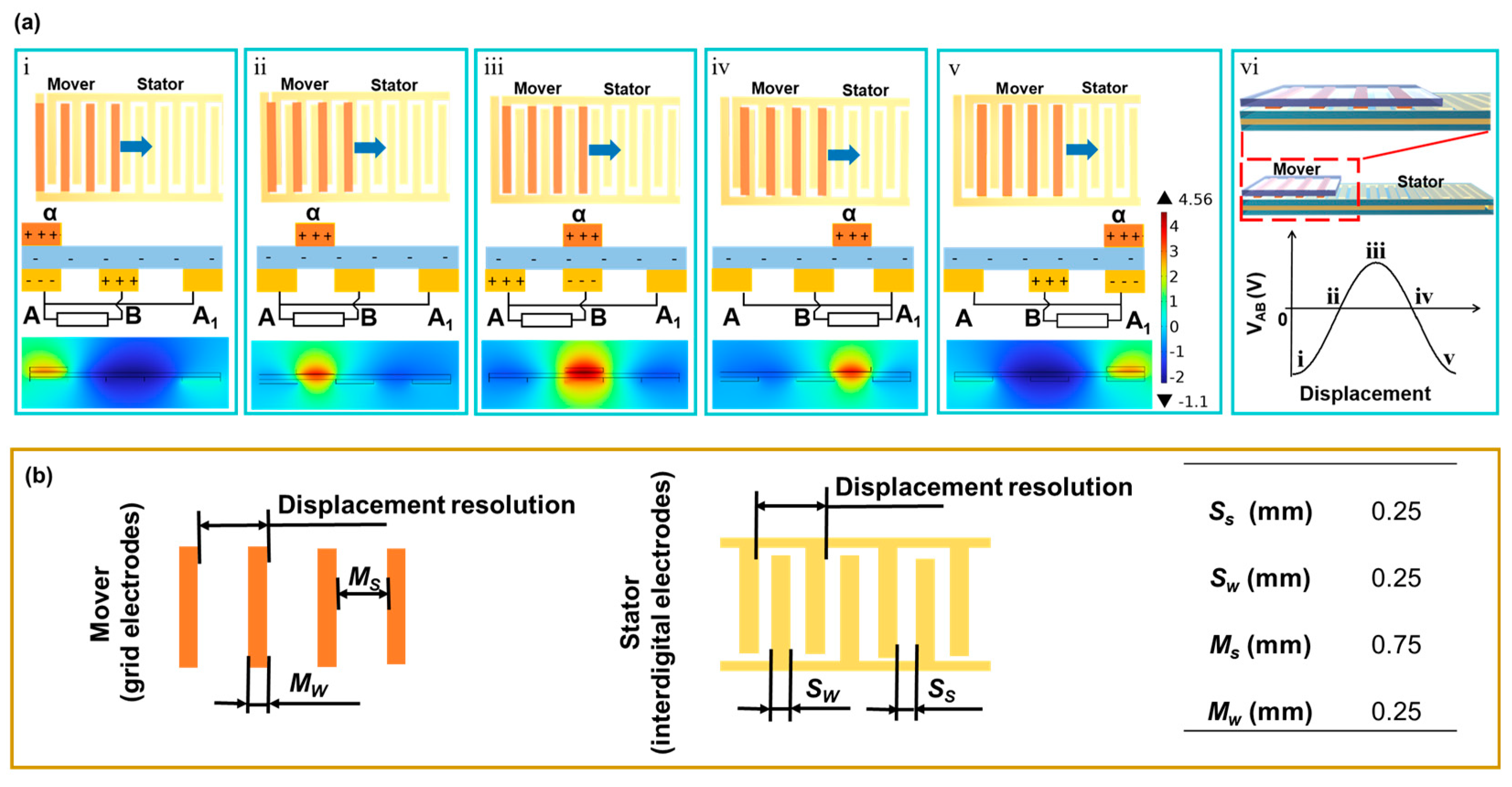
2.1. Working Principle of the Displacement Sensor
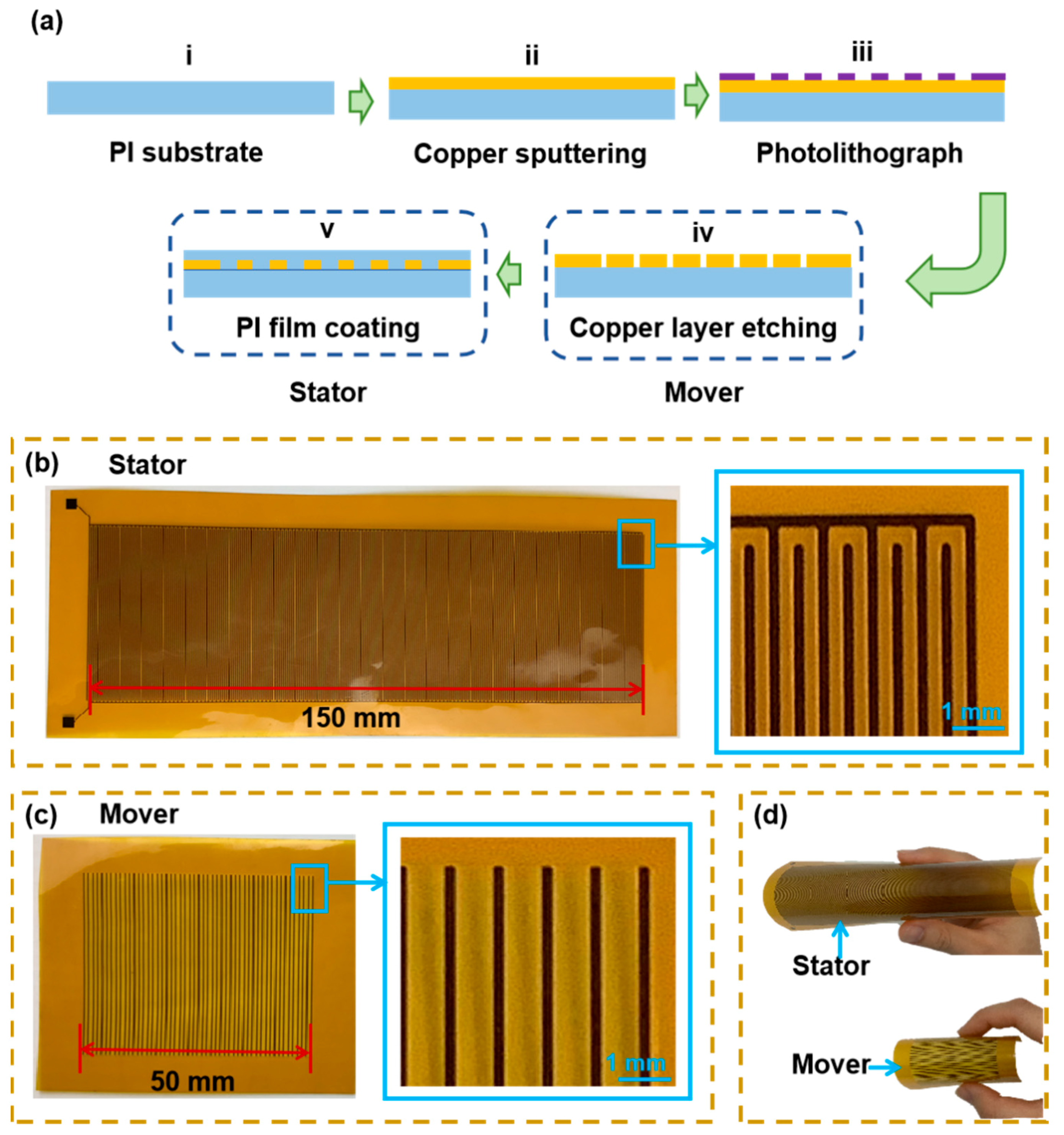
2.2. Fabrication Process of the Displacement Sensor
2.3. Experimental Setup
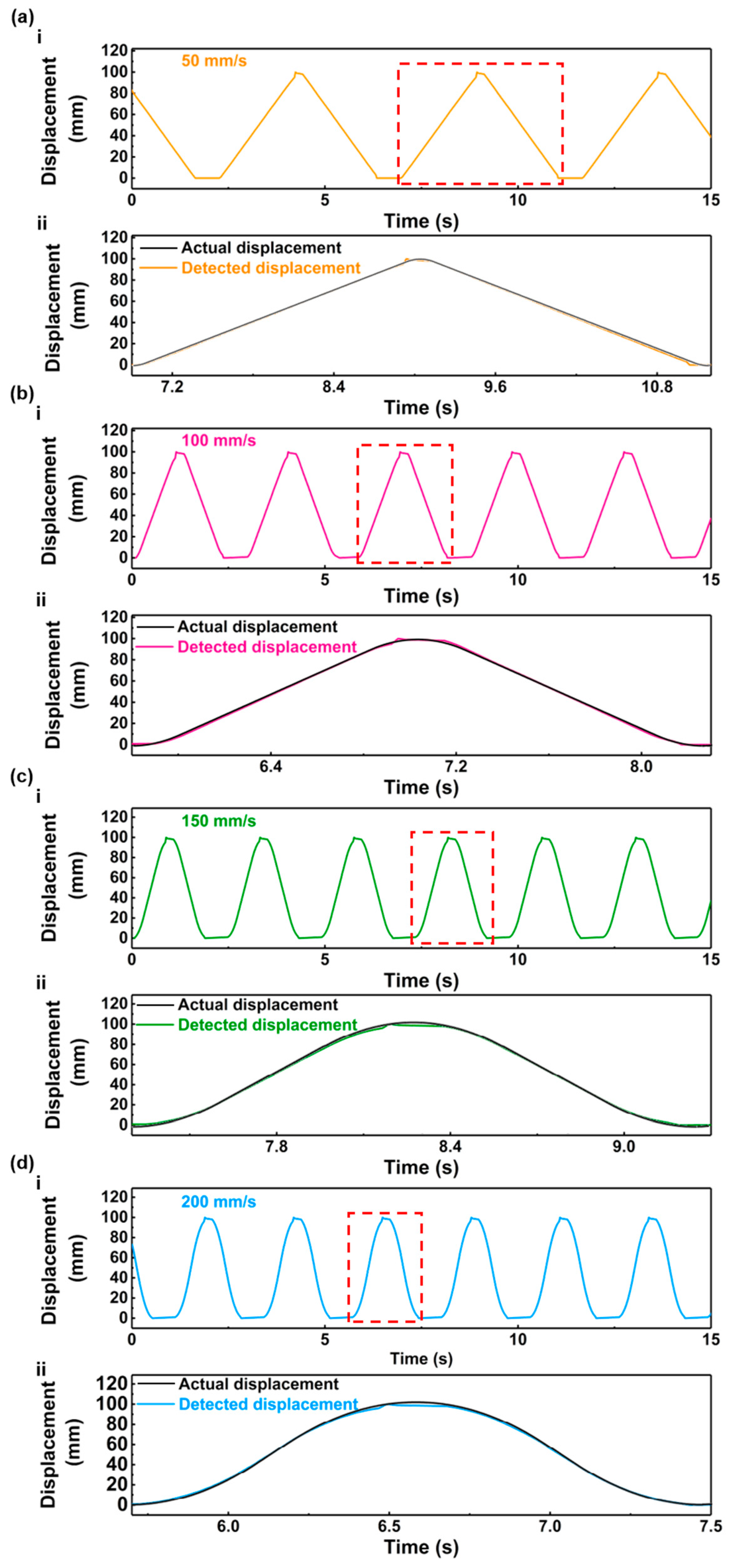
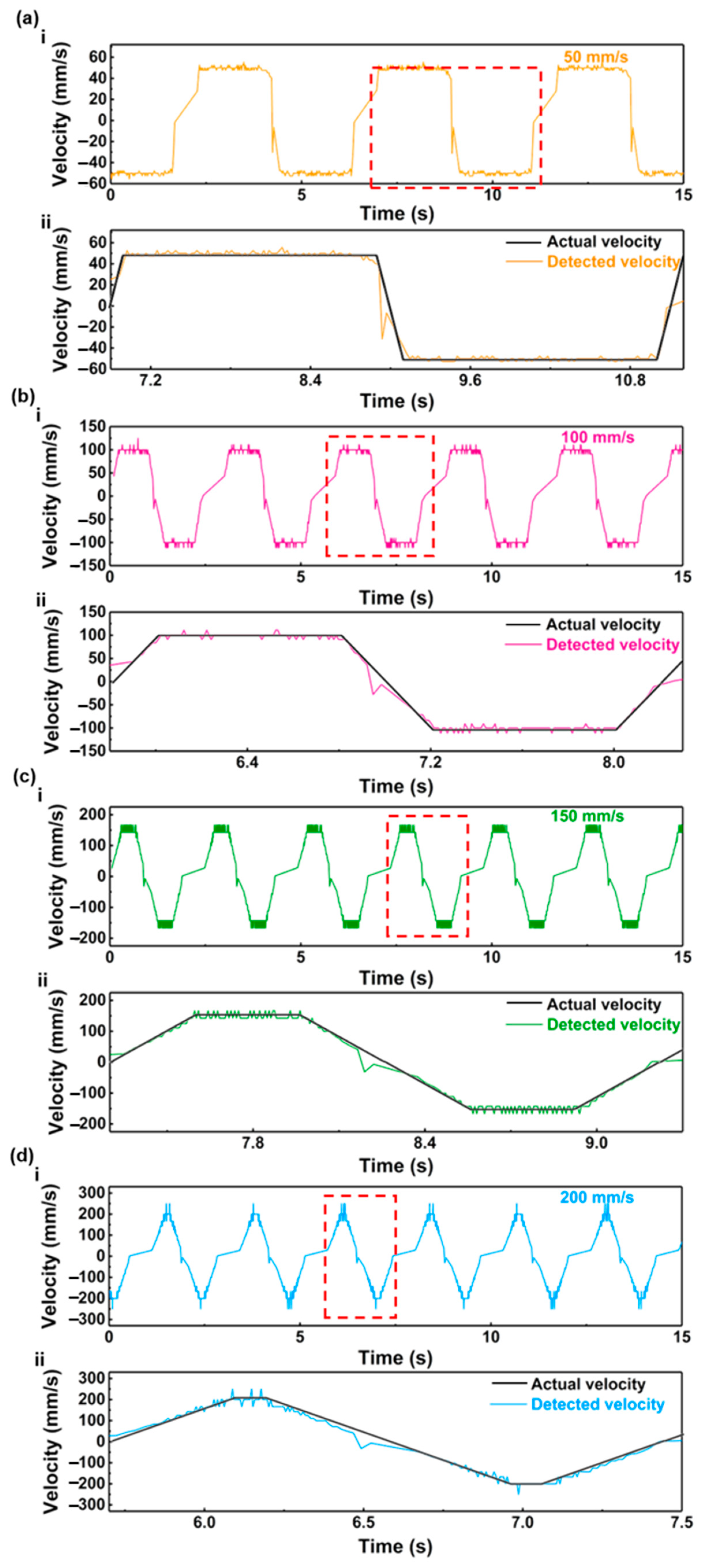
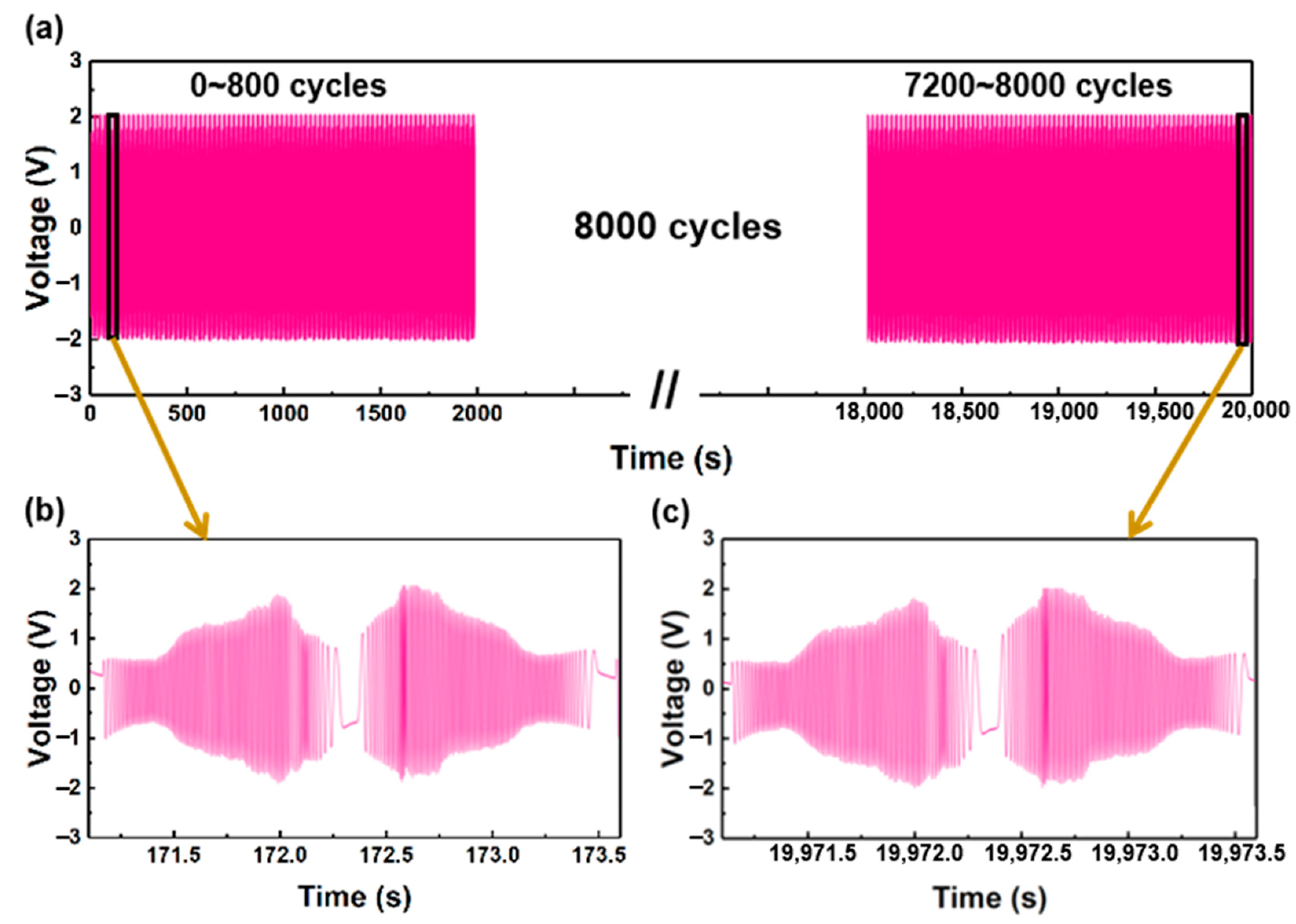
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Z.Q.; Cui, W.; Zhang, W.B.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, B.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Hu, N.; Bi, X.Y.; Hu, W. A New Performance Optimization Method for Linear Motor Feeding System. Actuators 2023, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wen, B.C. Dynamics analysis on the MDOF model of ball screw feed system considering the assembly error of guide rails. Mech. Syst. Signal Pract. 2022, 178, 109290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, D.S.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.; Mei, X.S.; Gong, G.F. Experiment-based thermal error modeling method for dual ball screw feed system of precision machine tool. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 82, 1693–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Y.; Verl, A.; Brecher, C.; Uriarte, L.; Pritschow, G. Machine tool feed drives. Cirp. Annals 2011, 60, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Huang, Y.K.; Cheng, C.C. Mechanical model and contouring analysis of high-speed ball-screw drive systems with compliance effect. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2004, 24, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.L.; Zhang, F. Rational design of self-powered sensors with polymer nanocomposites for human–machine interaction. Chinese J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Nisitani, H.; Kubo, A.; Yue, Y. Autonomous form measurement on machining centers for free-form surfaces. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manu. 2004, 44, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, D.X.; Zhou, C.X.; Zhao, W.H. Experiment-based thermal behavior research about the feed drive system with linear scale. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, Z.G.; Yu, C.; Feng, X.Y.; Li, P.G. Identification and compensation of friction for a novel two-axis differential micro-feed system. Mech. Syst. Signal Pract. 2018, 106, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkorkmaz, K.; Wong, W. Rapid identification technique for virtual CNC drives. Int. J. Mach. Tool. Manu. 2007, 47, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, N.; Abolmasoumi, A.H.; Soleymani, M. Sliding mode trajectory tracking control of a ball-screw-driven shake table based on online state estimations using EKF/UKF. Struct. Control Health 2018, 25, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milić, P.; Marinković, D.; Klinge, S.; Ćojbašić, Ž. Reissner-Mindlin Based Isogeometric Finite Element Formulation for Piezoelectric Active Laminated Shells. Teh. Vjesn. 2023, 30, 416–425. [Google Scholar]
- Milić, P.; Marinković, D.; Klinge, S.; Ćojbašić, Ž. Geometrically Nonlinear Analysis of Piezoelectric Active Laminated Shells by Means of Isogeometric FE Formulation. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Cao, B.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. A Moving Magnetic Grid-Type Long-Range Linear Absolute Displacement Sensor. Sensors 2023, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatini, R.; Richardson, M.A.; Gardi, A.; Ramasamy, S. Airborne laser sensors and integrated systems. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2015, 79, 15–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, J.; Shao, L.-Y.; Caucheteur, C. Tilted fiber Bragg grating sensors. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, T.Q.; Lee, N.E. Flexible and Stretchable Physical Sensor Integrated Platforms for Wearable Human-Activity Monitoring and Personal Healthcare. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4338–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; He, L.; Liu, R. Recent Developments for Flexible Pressure Sensors: A Review. Micromachines 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Kosel, J. Wearable Flexible Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3949–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.P.; Zhang, F.J.; Di, C.A.; Zhu, D.B. Advances of flexible pressure sensors toward artificial intelligence and health care applications. Mater. Horiz. 2015, 2, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.; Qaiser, N.; Yun, T.; Cheong, J.; Lim, S.; Hwang, B. Sensing Mechanism and Application of Mechanical Strain Sensor: A Mini-Review. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2023, 20, 2–2276723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Sun, Z.; Chen, T.; Lee, C. Low cost exoskeleton manipulator using bidirectional triboelectric sensors enhanced multiple degree of freedom sensory system. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.S.; Zhu, G.; Niu, S.; Liu, Y.; Bai, P.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Nanometer resolution self-powered static and dynamic motion sensor based on micro-grated triboelectrification. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Shu, S.; Tang, W. A Self-Powered Vector Angle/Displacement Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Micromachines 2021, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.Q.; Wu, Y.; Yao, B.C.; Gong, Y.A. Optimization study on graphene-coated microfiber Bragg grating structures for ammonia gas sensing. Photonic Sens. 2014, 5, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Jing, Q.; Yang, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Grating-structured freestanding triboelectric-layer nanogenerator for harvesting mechanical energy at 85% total conversion efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6599–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Liu, G.X.; Jiang, D.D.; Wang, C.; Li, W.; Guo, T.; Zhao, J.Q.; Xi, F.B.; Liu, W.B.; Zhang, C. Interdigitated Electrode-Based Triboelectric Sliding Sensor for Security Monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.J.; Jing, Q.S.; Wang, Z.L. Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, T.; Li, D.; Cui, P.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Meng, X.; Hou, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H. A Self-Powered Flexible Displacement Sensor Based on Triboelectric Effect for Linear Feed System. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243100
Zhao T, Li D, Cui P, Zhang Z, Sun Y, Meng X, Hou Z, Zheng Z, Huang Y, Liu H. A Self-Powered Flexible Displacement Sensor Based on Triboelectric Effect for Linear Feed System. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(24):3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243100
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Tingting, Dongsheng Li, Peijuan Cui, Zhongbin Zhang, Yuyang Sun, Xingyou Meng, Zhanlin Hou, Zaiping Zheng, Yuping Huang, and Huicong Liu. 2023. "A Self-Powered Flexible Displacement Sensor Based on Triboelectric Effect for Linear Feed System" Nanomaterials 13, no. 24: 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243100
APA StyleZhao, T., Li, D., Cui, P., Zhang, Z., Sun, Y., Meng, X., Hou, Z., Zheng, Z., Huang, Y., & Liu, H. (2023). A Self-Powered Flexible Displacement Sensor Based on Triboelectric Effect for Linear Feed System. Nanomaterials, 13(24), 3100. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13243100







