Enhanced Ionic Polymer–Metal Composites with Nanocomposite Electrodes for Restoring Eyelid Movement of Patients with Ptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Design of Models A and B
2.3. Simulation Methodology
2.3.1. Percolation Theory
2.3.2. Calculation of the Electrical Conductivity and Permittivity
2.3.3. Calculation of the Electrical Conductivity Using Bruggeman’s Symmetric Equation
2.3.4. Calculation of the Permittivity Using the Maxwell–Garnett Model
2.3.5. Grid Independence Study
3. Results
3.1. Data Validation
3.2. Optimal Electrical Conductivity
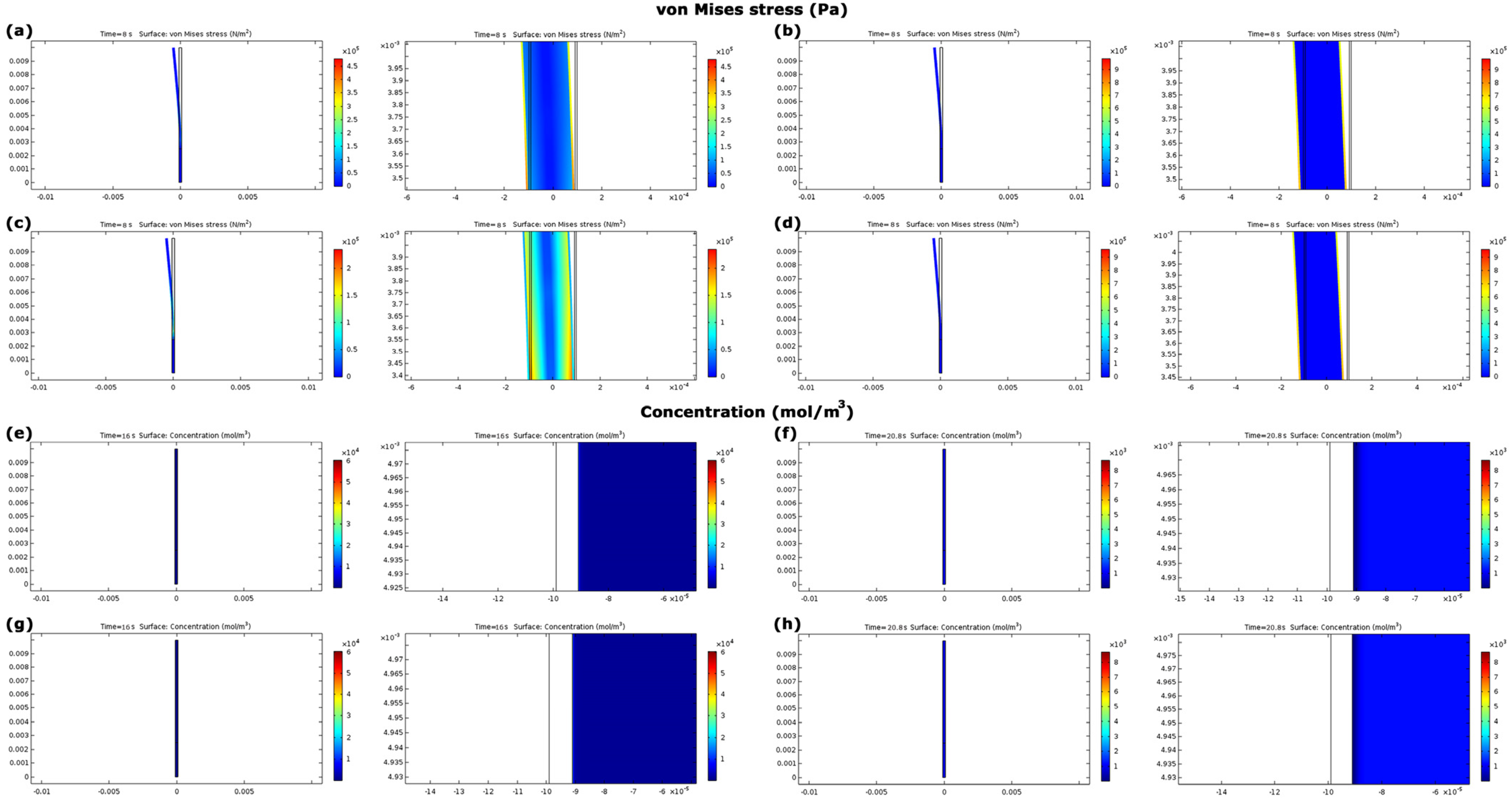
3.3. Evaluation of Model A
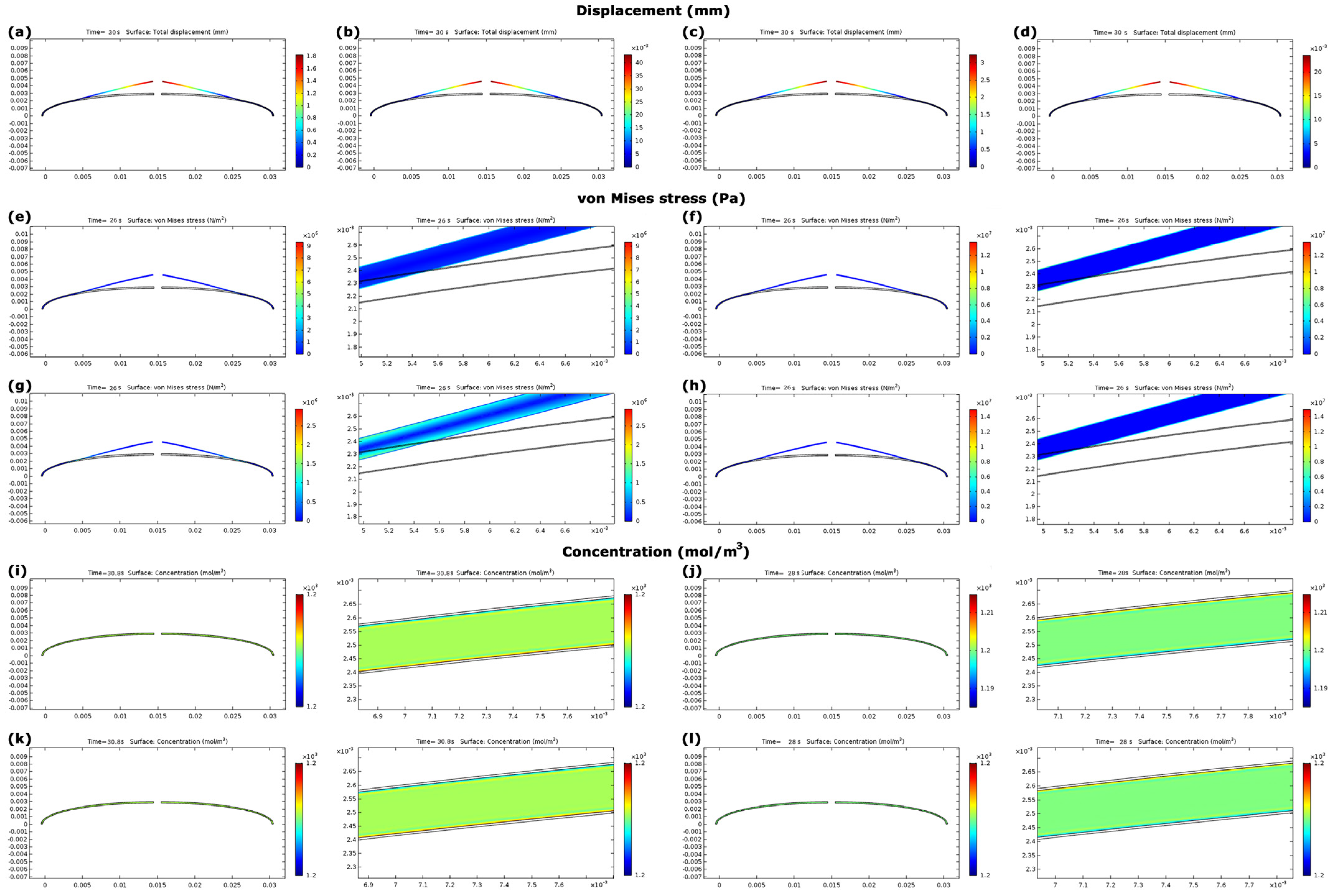
3.4. Evaluation of Model B
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schrom, T.; Bast, F. Chirurgische Korrektur des paralytischen Lagophthalmus. HNO 2010, 58, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcelli, E.; Cavallari, P.; Frigerio, A.; Colletti, G.; Biglioli, F.; Fanti, R.; Plicchi, G.; Cercenelli, L. A new gyro-based method for quantifying eyelid motion. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2013, 36, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ge, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, M.; Wu, D.; Peng, X.; Zhang, B. Hydrocephalus due to aqueductal stenosis presenting with acute bilateral ptosis: Case report. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 34, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Matsubara, T.; Kanamaru, K.; Kojima, T. Chronic hydrocephalus presenting with bilateral ptosis after minor head injury: Case report. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadlani, R.; Dadlani, R.; Ghosal, N.; Hegde, A. Occam’s razor in the management of ventriculoperitoneal shunt dysfunction: Diagnosis and management of an unusual pediatric case. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2015, 10, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamate, M.; Kurbet, S. Bilateral ptosis: A rare presentation of hydrocephalus. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Luciano, M.G.; Benzel, E.C. Acute respiratory arrest following partial suboccipital cranioplasty for cerebellar ptosis from Chiari malformation decompression: Report of 2 cases. Neurosurg. Focus. 2008, 25, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muthusamy, P.; Matte, G.; Kosmorsky, G.; Chémali, K.R. Chiari type I malformation: A mimicker of myasthenia gravis. Neurol. 2011, 17, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledgerwood, L.G.; Tinling, S.; Senders, C.; Wong-Foy, A.; Prahlad, H.; Tollefson, T.T. Artificial muscle for reanimation of the paralyzed face: Durability and biocompatibility in a gerbil model. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2012, 14, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Manera, J.; Luna, S.; Roig, C. Ocular ptosis: Differential diagnosis and treatment. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozaki, Y.; Matsushiro, N.; Suzuki, K. A wearable soft robot for movement assistance on eyelid closure. ROBOMECH J. 2018, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iida, F.; Laschi, C. Soft robotics: Challenges and perspectives. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 7, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasmat, S.; McPherson, S.; Suaning, G.J.; Lovell, N.H.; Low, T.H.; Clark, J.R. Recreation of eyelid mechanics using the sling concept. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2020, 73, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, P.; Shin, M.; Santamaria, A. Shape Memory Alloy As Artificial Muscles for Facial Prosthesis. In ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: Tampa, FL, USA, 2017; Volume 58363, p. V003T04A077. [Google Scholar]
- Senders, C.W.; Tollefson, T.T.; Curtiss, S.; Wong-Foy, A.; Prahlad, H. Force requirements for artificial muscle to create an eyelid blink with eyelid sling. Arch. Facial Plast. Surg. 2010, 12, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Shahinpoor, M. Ionic polymer–metal composites: II. Manufacturing techniques. Smart Mater. Struct. 2003, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramzadeh, Y.; Shahinpoor, M. A review of ionic polymeric soft actuators and sensors. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinpoor, M. Ionic polymer–conductor composites as biomimetic sensors, robotic actuators and artificial muscles—A review. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, Z.J.; Kim, K.J.; Oh, I.K. Developing next generation ionic polymer–metal composite materials: Perspectives for enabling robotics and biomimetics. Polym. Int. 2021, 70, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, Z.J.; Kim, K.J. A reduced dimensional mapping approach for modeling IPMCs with computational efficiency and rapid design development applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 125012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Cohen, Y.; Bao, X.; Sherrit, S.; Lih, S.S. Characterization of the electromechanical properties of ionomeric polymer-metal composite (IPMC). In Smart Structures and Materials 2002: Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD); SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 4695, pp. 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.L.; Kim, W.Y.; Cheng, T.H.; Oh, I.K. A helical ionic polymer–metal composite actuator for radius control of biomedical active stents. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S.; Frim, D.; Yamini, B. Long-term recovery behavior of brain tissue in hydrocephalus patients after shunting. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S. FSI simulation of CSF hydrodynamic changes in a large population of non-communicating hydrocephalus patients during treatment process with regard to their clinical symptoms. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gholampour, S.; Fatouraee, N.; Seddighi, A.S.; Seddighi, A. Numerical simulation of cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics in the healing process of hydrocephalus patients. J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 2017, 58, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimenko, A.Y.; Ichkitidze, L.P.; Podgaetsky, V.M.; Selishchev, S.V. Biomedical applications of promising nanomaterials with carbon nanotubes. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 48, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichkitidze, L.P.; Podgaetsky, V.M.; Prihodko, A.S.; Putra, B.M.; Blagov, E.V.; Pavlov, A.A.; Galperin, V.A.; Kitsyuk, E.P.; Shaman, Y.P. A conductive composite nanomaterial with biocompatible matrix and multilayer carbon nanotubes. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 47, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichkitidze, L.P.; Selishchev, S.V.; Gerasimenko, A.Y.; Podgaetsky, V.M. Mechanical properties of bulk nanocomposite biomaterial. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 49, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichkitidze, L.P.; Selishchev, S.V.; Pavlov, A.A.; Gavryushina, M.L.; Shaman, Y.P. Biocompatible conductive nanomaterials and prospects for their use in medical practice. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus), Moscow, Russia, 1 February 2017; pp. 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ichkitidze, L.P.; Gerasimenko, A.Y.; Podgaetsky, V.M.; Selishchev, S.V.; Dudin, A.A.; Pavlov, A.A. Electrical conductivity of the nanocomposite layers for use in biomedical systems. Mater. Phys. Mech. 2018, 37, 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhurbina, N.N.; Kurilova, U.E.; Ichkitidze, L.P.; Podgaetsky, V.M.; Selishchev, S.V.; Suetina, I.A.; Mezentseva, M.V.; Eganova, E.M.; Pavlov, A.A.; Gerasimenko, A.Y. Investigation of cell proliferative activity on the surface of the nanocomposite material produced by laser radiation. In Proceedings of the SPIE 9917, Saratov Fall Meeting 2015: Third International Symposium on Optics and Biophotonics and Seventh Finnish-Russian Photonics and Laser Symposium (PALS), Bellingham, WA, USA, 21 April 2016; p. 991718. [Google Scholar]
- Gerasimenko, A.Y.; Ichkitidze, L.P.; Piyankov, E.S.; Pyanov, I.V.; Rimshan, I.B.; Ryabkin, D.I.; Savelyev, M.S.; Podgaetskii, V.M. Use of Indocyanine Green in Nanocomposite Solders to Increase Strength and Homogeneity in Laser Welding of Tendons. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 50, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, S.; Maroufkhani, M.; Mohammadzadeh-Komuleh, S.; Khoubi-Arani, Z. Polymer nanocomposites for biomedical applications. In Fundamentals of Bionanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 175–215. [Google Scholar]
- Aghaei, A.; Sheikhzadeh, G.A.; Goodarzi, M.; Hasani, H.; Damirchi, H.; Afrand, M. Effect of horizontal and vertical elliptic baffles inside an enclosure on the mixed convection of a MWCNTs-water nanofluid and its entropy generation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2018, 133, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Hassani, M.; Goodarzi, M.; Afrand, M.; Manafi, S. Appraising influence of COOH-MWCNTs on thermal conductivity of antifreeze using curve fitting and neural network. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 514, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamalizadeh, E.; Pahlevanzadeh, F.; Ghani, K.; Karimipour, A.; Nguyen, T.K.; Safaei, M.R. Simulation of water/FMWCNT nanofluid forced convection in a microchannel filled with porous material under slip velocity and temperature jump boundary conditions. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 30, 2329–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.; Amiri, A.; Goodarzi, M.S.; Safaei, M.R.; Karimipour, A.; Languri, E.M.; Dahari, M. Investigation of heat transfer and pressure drop of a counter flow corrugated plate heat exchanger using MWCNT based nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 66, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimipour, A.; Bagherzadeh, S.A.; Taghipour, A.; Abdollahi, A.; Safaei, M.R. A novel nonlinear regression model of SVR as a substitute for ANN to predict conductivity of MWCNT-CuO/water hybrid nanofluid based on empirical data. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 521, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, M.R.; Togun, H.; Vafai, K.; Kazi, S.N.; Badarudin, A. Investigation of heat transfer enhancement in a forward-facing contracting channel using FMWCNT nanofluids. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2014, 66, 1321–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugal, D.; Stalbaum, T.; Palmre, V.; Kim, K.J. Modeling ionic polymer metal composites with COMSOL: Step-by-step guide. In Ionic Polymer Metal Composites (IPMCs): Smart Multi-Functional Materials and Artificial Muscles; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 185–214. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, R.J.; Rowe, R.C. The compaction of pharmaceutical and other model materials—A pragmatic approach. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1987, 42, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J.; Rowe, R.C.; York, P. The Poisson’s ratio of microcrystalline cellulose. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 105, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.J.; Rowe, R.C. The Young’s modulus of pharmaceutical materials. Int. J. Pharm. 1987, 37, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
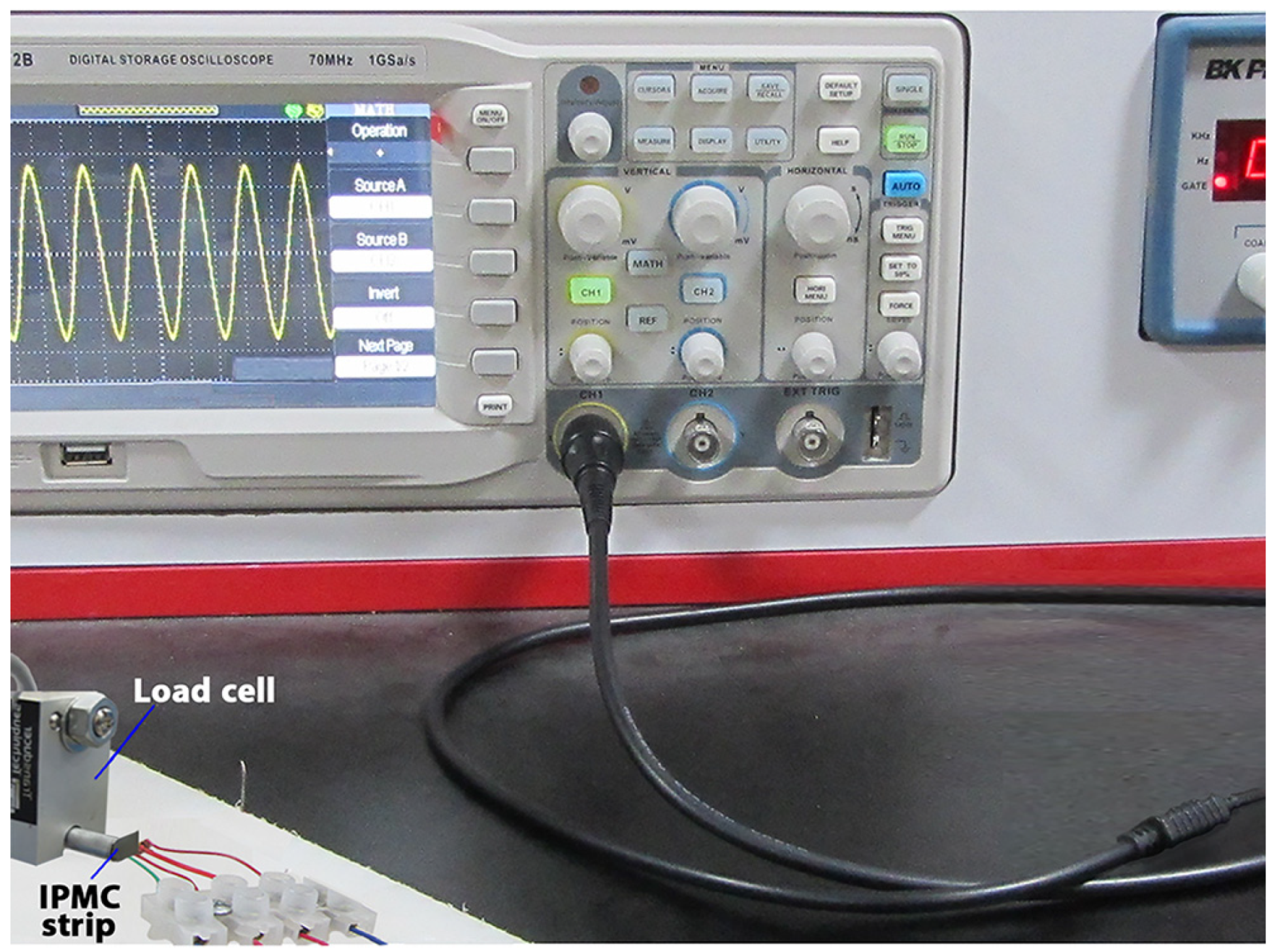
- Ofir, S.; Belkin, A.; Nemet, A.Y. A novel technique for measuring eyelid force. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 34, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaie, F.; Malekie, S.; Larijani, M.M. Simulation of a Novel Dosimeter Based on Electrical Characteristics of Polymethyl Methacrylate-Carbon Nanotube Composite. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Malekie, S.; Ziaie, F. Aspect ratio effects of single-walled carbon nanotubes on electrical conductivity of high density polyethylene/carbon nanotube nano-composites. In Proceedings of the 5th International Congress on Nanoscience & Nanotechnology (ICNN2014), Tehran, Iran, 22–24 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Malekie, S.; Ziaie, F. Study on a novel dosimeter based on polyethylene–carbon nanotube composite. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2015, 791, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekie, S.; Ziaie, F. A two-dimensional simulation to predict the electrical behavior of carbon nanotube/polymer composites. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 37, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; McLachlan, D.S. Percolation exponents and threshold in two nearly ideal anisotropic continuum systems. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 1997, 241, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebbor, N.; Bri, S. Effective permittivity of periodic composite materials: Numerical modeling by the finite element method. J. Electrost. 2012, 70, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, R.C.; Bernardini, F.P.; Khouri, L.; Moin, M.; Roumeliotis, A.A.; Kulwin, D.R. Unilateral frontalis sling for the surgical correction of unilateral poor-function ptosis. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 21, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hontanilla, B.; Marre, D. Eyelid reanimation with gold weight implant and tendon sling suspension: Evaluation of excursion and velocity using the FACIAL CLIMA system. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2013, 66, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.L.; Kubacki, G.W. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and the corrosion of metallic biomaterials: Corrosion causes biology and biology causes corrosion. In Oxidative Stress and Biomaterials; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 59–88. [Google Scholar]
- Palmre, V.; Pugal, D.; Leang, K.K.; Kim, K. The effects of electrode surface morphology on the actuation performance of IPMC. In Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD); SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 8687, pp. 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, B.; Du, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, P. Research on the Synthesis and Properties of PPY Modified Electrode IPMC. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Wuhan, China, 2019; Volume 493, p. 012048. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, L.; Li, Y.; Lian, H.; Hu, Y.; Chang, W.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Ao, X.; Li, Q.; Cui, X. The Enhancement Effect of Mesoporous Graphene on Actuation of Nafion-Based IPMC. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2016, 301, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, T.; Kawashima, N.; Tsunekuni, T.; Imagawa, K.; Miyasaka, M. A blinking periorbital prosthesis using surface electromyographic signals of the orbicularis oculi muscle. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2015, 38, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.H.; Ham, D.S.; Lee, J.H.; Huh, K.M.; Cho, S.K. Fabrication of Poly (methyl methacrylate) Beads Monolayer Using Rod-coater and Effects of Solvents, Surfactants and Plasma Treatment on Monolayer Structure. J. Adhes. Interface 2019, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Moorthy, V.M.; Sugantharathnam, M.; Rathnasami, J.D.; Pattan, S. Design and characterisation of graphene-based nano-photodiode array device for photo-stimulation of subretinal implant. Micro Nano Lett. 2019, 14, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalva, N.; Uthaman, S.; Jang, E.H.; Augustine, R.; Jeon, S.H.; Huh, K.M.; Park, I.K.; Kim, I. Aggregation-induced emission-active hyperbranched polymer-based nanoparticles and their biological imaging applications. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 186, 108975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, A.A.; Aubakirov, R.R.; Mindubaev, A.E.; Gurov, K.O.; Telyshev, D.V.; Selishchev, S.V. An Algorithm for the Computer Aided Design of Coil Couple for a Misalignment Tolerant Biomedical Inductive Powering Unit. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 70755–70769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, A.; Cavallari, P. A closed-loop stimulation system supplemented with motoneurone dynamic sensitivity replicates natural eye blinks. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cultrera, F.; D′Andrea, M.; Battaglia, R.; Chieregato, A. Unilateral oculomotor nerve palsy: Unusual sign of hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2009, 53, 67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ding, B. Superstable and Intrinsically Self-Healing Fibrous Membrane with Bionic Confined Protective Structure for Breathable Electronic Skin. Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202200226. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; He, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, K.; Jiang, S.; Duan, G.; Zhang, K. Nanocellulose and Its Derived Composite Electrodes toward Supercapacitors: Fabrication, Properties, and Challenges. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
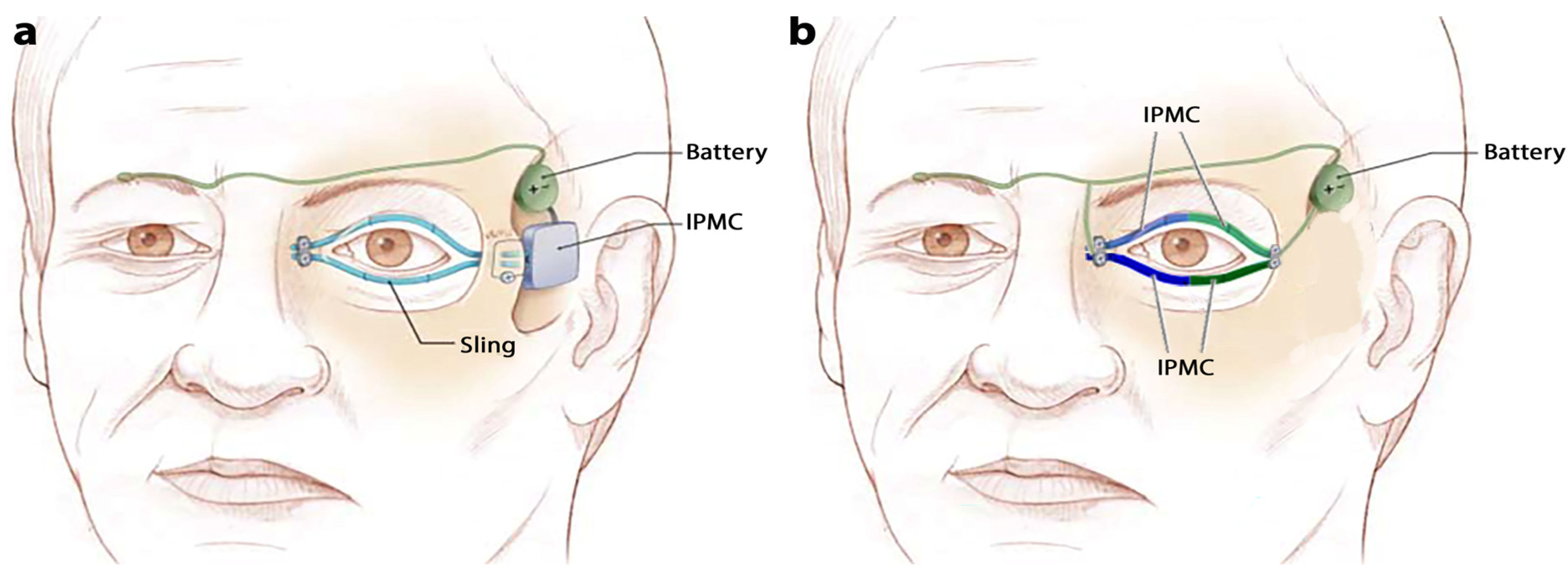

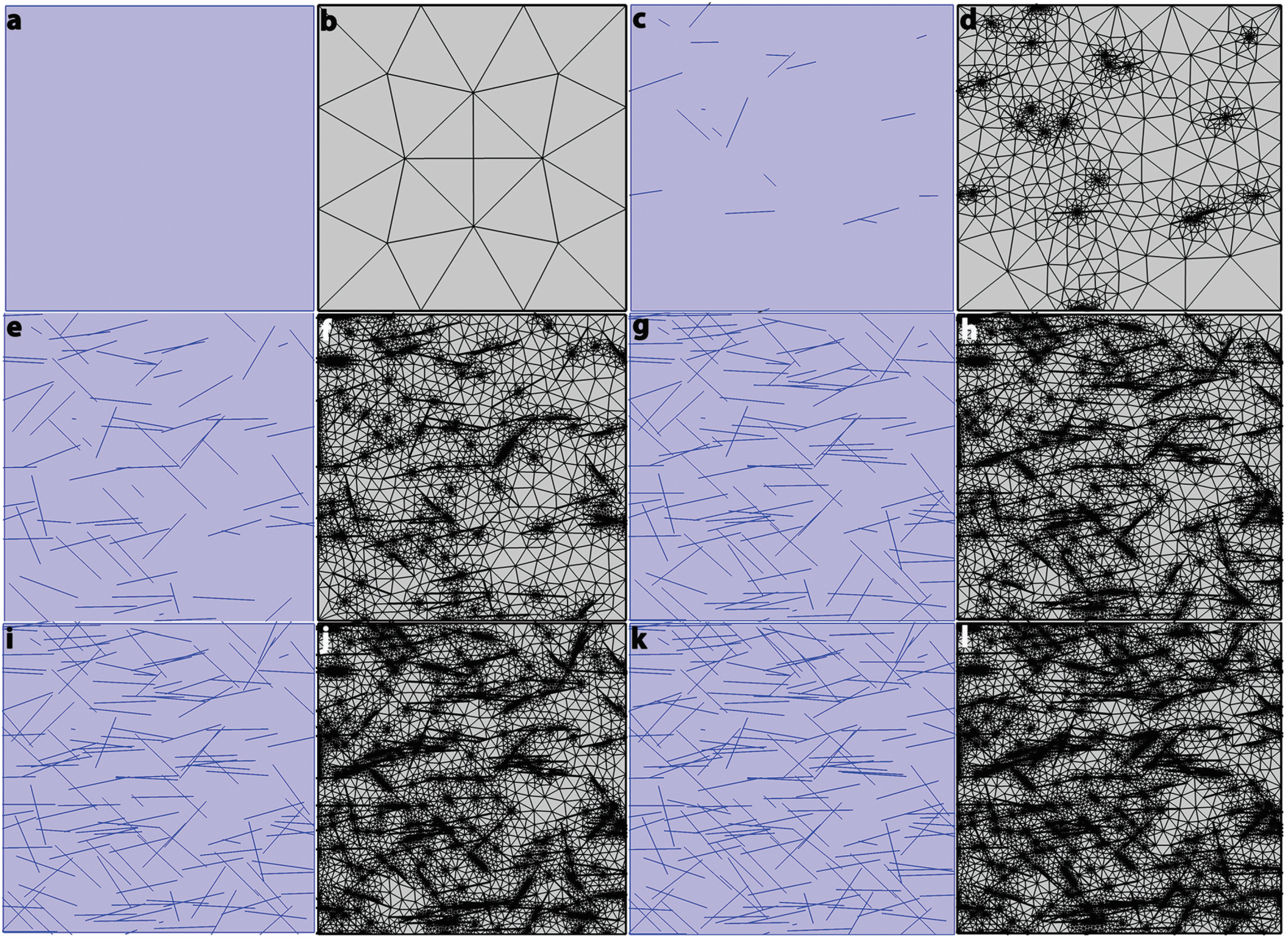
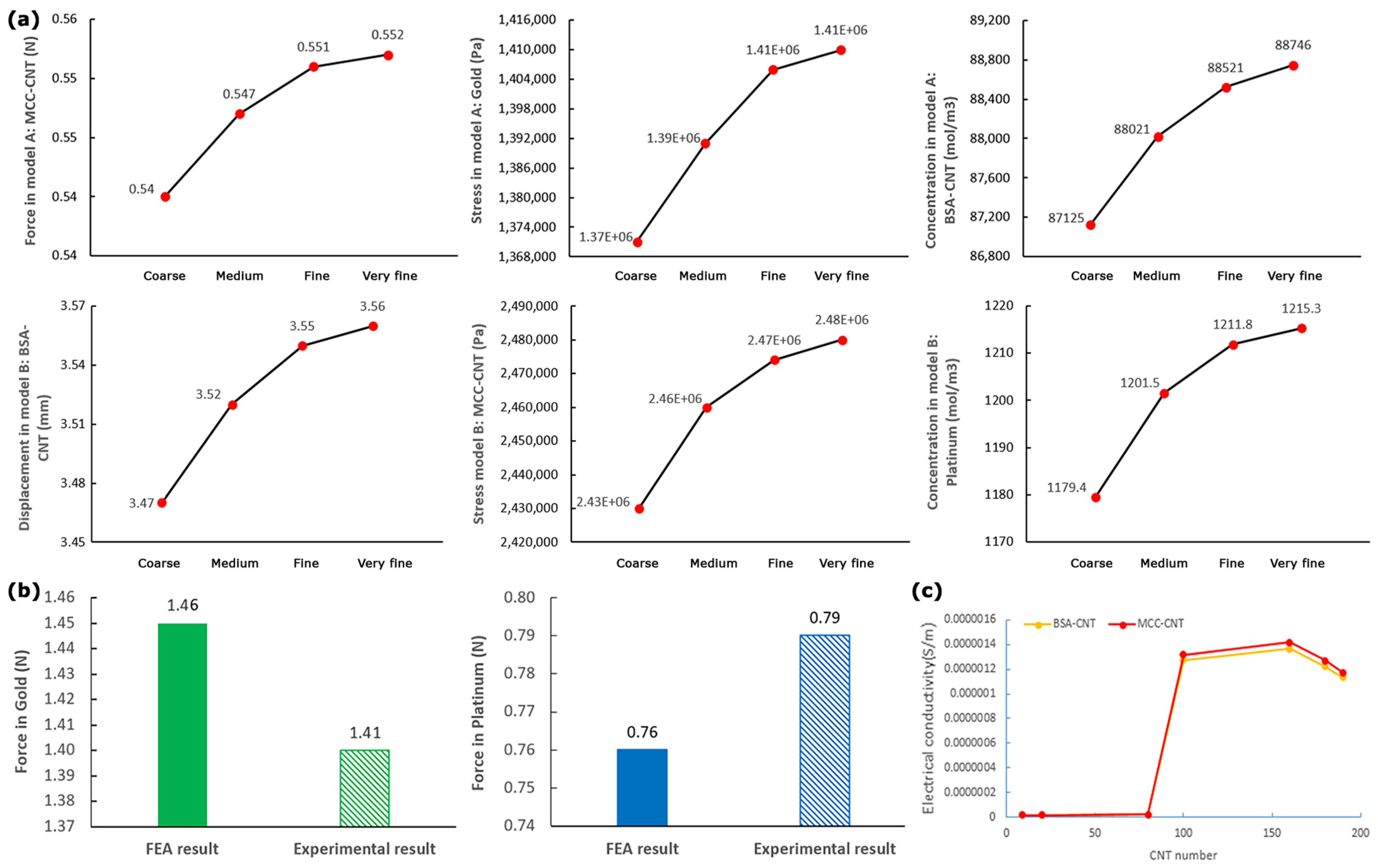

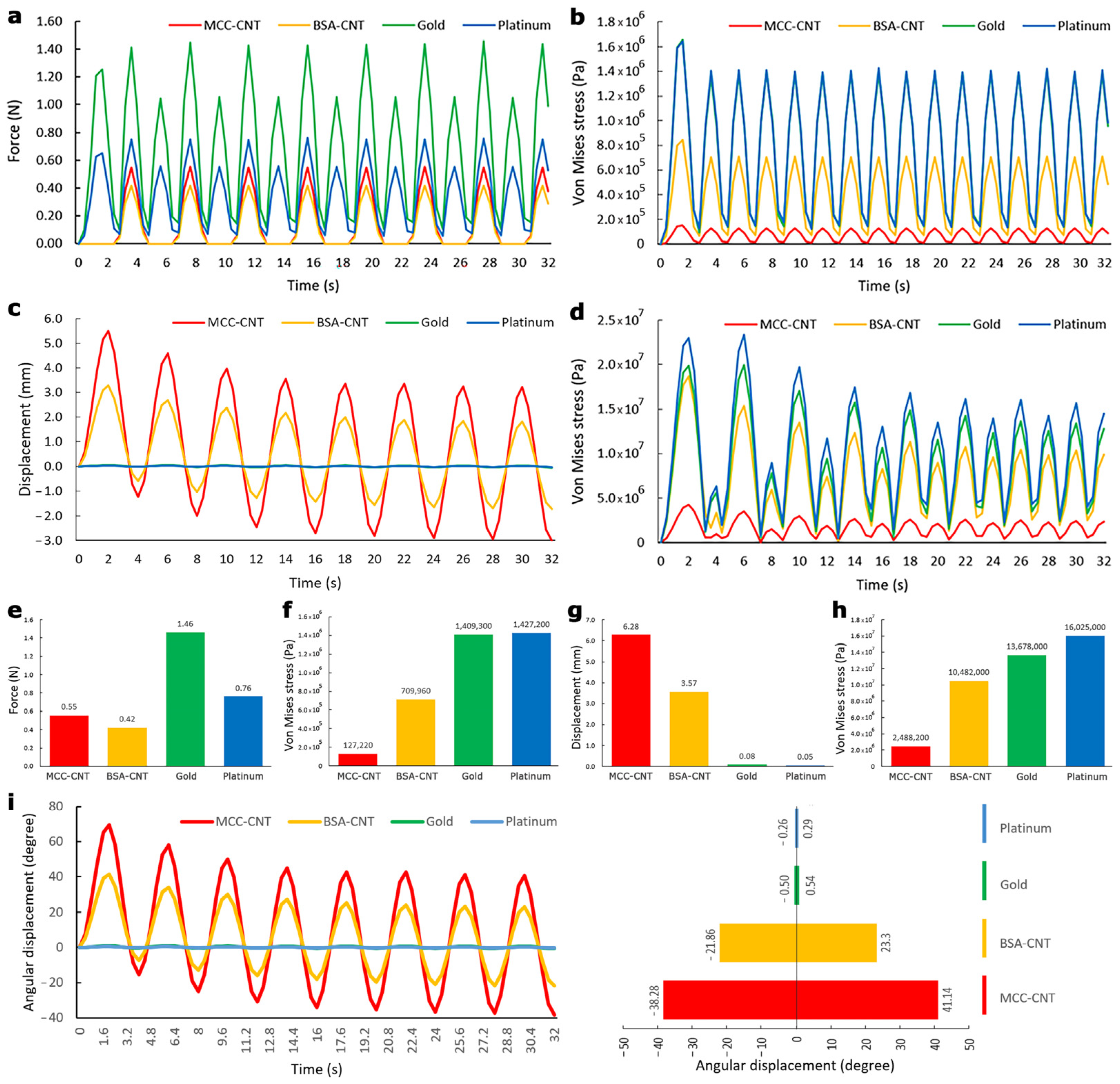

| Material Properties | Membrane (Nafion) | Platinum | Gold | BSA-CNT | MCC-CNT | CNT | BSA | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Young modulus (Pa) | 0.249 109 | 1.58 1011 | 1010 | 109 | 108 | 1012 | 109 | 108 |
| Poisson ratio | 0.48 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.23 | 0.30 | 0.3 | 0.23 | 0.3 |
| Density (gr/cm3) | 1.97 | 2.13 | 1.92 | 1.25 | 1.75 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 1.5 |
| Electrical conductivity (S/m) | - | 8.74 × 107 | 4.44 × 107 | 1.27 × 10−6 * | 1.31 × 10−6 * | 107 | 10−14 | 10−10 |
| Permittivity | - | 0.14 | 1.62 | 10 | 2 | 1200 | 10 | 1.85 |
| MCC–MWCNT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNT wt% | CNT Number | Electric Field Norm (V/m) | Current Density Norm (A/m2) | Electrical Conductivity (S/m) |
| 0.0099471 | 9 | 14,128 | 2.74E-02 | 1.94E-08 |
| 0.022104 | 20 | 14,425 | 2.74E-02 | 1.90E-08 |
| 0.088399 | 80 | 14,815 | 3.52E-02 | 2.37E-08 |
| 0.11049 | 100 | 28,414 | 9.30E+00 | 1.31E-06 |
| 0.17676 | 160 | 30,535 | 4.3184 | 1.41E-06 |
| 0.19884 | 180 | 30,027 | 3.8108 | 1.27E-06 |
| 0.20988 | 190 | 29,287 | 3.4376 | 1.17E-06 |
| MCC–SWCNT | ||||
| 0.0014211 | 9 | 14,128 | 2.74E-02 | 1.94E-08 |
| 0.0031579 | 20 | 14,425 | 2.74E-02 | 1.90E-08 |
| 0.012632 | 80 | 14815 | 3.52E-02 | 2.37E-08 |
| 0.01579 | 100 | 28,414 | 9.30E+00 | 1.31E-06 |
| 0.025263 | 160 | 30,535 | 4.3184 | 1.41E-06 |
| 0.028421 | 180 | 30,027 | 3.8108 | 1.27E-06 |
| 0.03 | 190 | 29,287 | 3.4376 | 1.17E-06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hosseini, S.S.; Yamini, B.; Ichkitidze, L.; Asadi, M.; Fernandez, J.; Gholampour, S. Enhanced Ionic Polymer–Metal Composites with Nanocomposite Electrodes for Restoring Eyelid Movement of Patients with Ptosis. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030473
Hosseini SS, Yamini B, Ichkitidze L, Asadi M, Fernandez J, Gholampour S. Enhanced Ionic Polymer–Metal Composites with Nanocomposite Electrodes for Restoring Eyelid Movement of Patients with Ptosis. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(3):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030473
Chicago/Turabian StyleHosseini, Sara Sadat, Bakhtiar Yamini, Levan Ichkitidze, Majid Asadi, Julie Fernandez, and Seifollah Gholampour. 2023. "Enhanced Ionic Polymer–Metal Composites with Nanocomposite Electrodes for Restoring Eyelid Movement of Patients with Ptosis" Nanomaterials 13, no. 3: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030473
APA StyleHosseini, S. S., Yamini, B., Ichkitidze, L., Asadi, M., Fernandez, J., & Gholampour, S. (2023). Enhanced Ionic Polymer–Metal Composites with Nanocomposite Electrodes for Restoring Eyelid Movement of Patients with Ptosis. Nanomaterials, 13(3), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13030473







