Hardware-Intrinsic Physical Unclonable Functions by Harnessing Nonlinear Conductance Variation in Oxide Semiconductor-Based Diode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
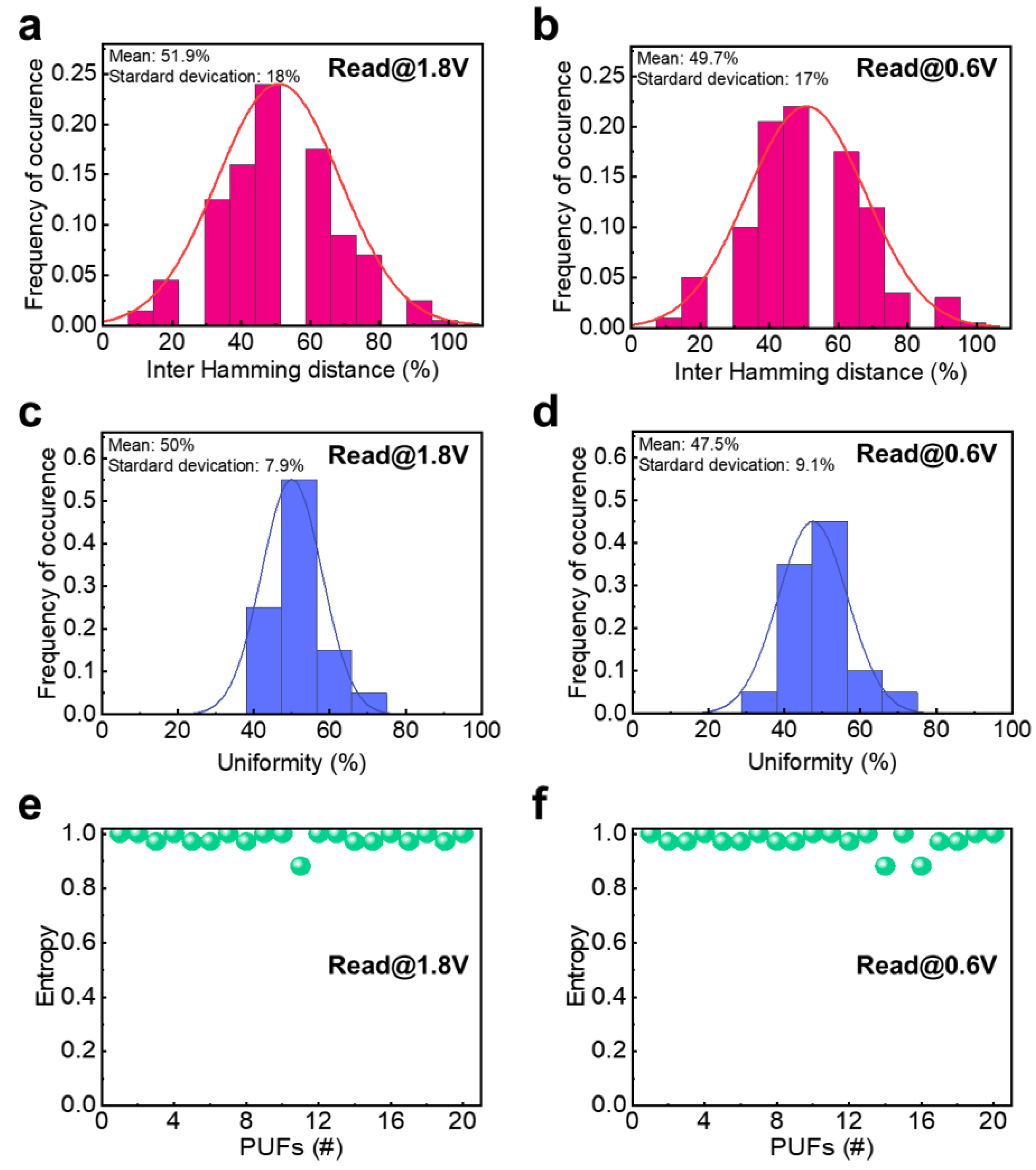
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, Z.H.; Ali, H.A.; Badawy, M.M. Internet of Things (IoT): Definitions, challenges and recent research directions. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2015, 128, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Dave, B.; Kubler, S.; Främling, K.; Koskela, L. Opportunities for enhanced lean construction management using Internet of Things standards. Autom. Constr. 2016, 61, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, X.; Fan, Y. The internet of things in healthcare: An overview. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2016, 1, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Elmi, Z.; Krishna Meriga, V.; Pasha, J.; Dulebenets, M.A. Internet of Things for sustainable railway transportation: Past, present, and future. Clean. Logist. Supply Chain 2022, 4, 100065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Elmi, Z.; Lau, Y.-Y.; Borowska-Stefańska, M.; Wiśniewski, S.; Dulebenets, M.A. Blockchain and AI technology convergence: Applications in transportation systems. Veh. Commun. 2022, 38, 100521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.A.; Shah, N.; Vishwanath, S.K.; Ng, S.E.; Febriansyah, B.; Jagadeeswararao, M.; Chang, C.H.; Basu, A.; Mathews, N. Halide perovskite memristors as flexible and reconfigurable physical unclonable functions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.R.; Naccache, D. Towards Hardware-Intrinsic Security: Foundations and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kömmerling, O.; Kuhn, M.G. Design Principles for Tamper-Resistant Smartcard Processors. Smartcard 1999, 99, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Al-Sarawi, S.F.; Abbott, D. Physical unclonable functions. Nat. Electron. 2020, 3, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodda, A.; Subbulakshmi Radhakrishnan, S.; Schranghamer, T.F.; Buzzell, D.; Sengupta, P.; Das, S. Graphene-based physically unclonable functions that are reconfigurable and resilient to machine learning attacks. Nat. Electron. 2021, 4, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graybeal, S.N.; McFate, P.B. Getting out of the STARTing block. Sci. Am. 1989, 261, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuet, L.; Ngo, X.T.; Cherif, Z.; Fischer, V. A PUF Based on a Transient Effect Ring Oscillator and Insensitive to Locking Phenomenon. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2014, 2, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baturone, I.; Roman, R.; Corbacho, A. A Unified Multibit PUF and TRNG based on Ring Oscillators for Secure IoT Devices. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfikar, Z.; Soin, N.; Wan Muhamad Hatta, S.F.; Abu Talip, M.S.; Jaafar, A. Routing Density Analysis of Area-Efficient Ring Oscillator Physically Unclonable Functions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, D.P.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Chakraborty, R.S.; Nguyen, P.H. A Multiplexer-Based Arbiter PUF Composition with Enhanced Reliability and Security. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2018, 67, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeger, T.; Cheng, W.; Danger, J.-L.; Guilley, S.; Karimi, N. Cross-PUF Attacks: Targeting FPGA Implementation of Arbiter-PUFs. J. Electron. Test. 2022, 38, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfy, A.; Kaveh, M.; Martin, D.; Mosavi, M.R. An Efficient Design of Anderson PUF by Utilization of the Xilinx Primitives in the SLICEM. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 23025–23034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guajardo, J.; Kumar, S.S.; Schrijen, G.-J.; Tuyls, P. FPGA intrinsic PUFs and their use for IP protection. In Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems—CHES 2007; Paillier, P., Verbauwhede, I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4727, pp. 63–80. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, J.-W.; Ahn, J.-H.; Hong, J.-P. Compact SRAM-Based PUF Chip Employing Body Voltage Control Technique. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 22311–22319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Kim, T.T.-H. A High Reliable SRAM-Based PUF With Enhanced Challenge-Response Space. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinodoushan, M.; Cambou, B.; Afghah, F.; Philabaum, C.R.; Burke, I. Reliable, Secure, and Efficient Hardware Implementation of Password Manager System Using SRAM PUF. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 155711–155725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rührmair, U.; Sehnke, F.; Sölter, J.; Dror, G.; Devadas, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Modeling attacks on physical unclonable functions. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Chicago, IL, USA, 4–8 October 2010; pp. 237–249. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.-D.; Devadas, S. Secure and robust error correction for physical unclonable functions. IEEE Des. Test. Comput. 2010, 27, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nili, H.; Adam, G.C.; Hoskins, B.; Prezioso, M.; Kim, J.; Mahmoodi, M.R.; Bayat, F.M.; Kavehei, O.; Strukov, D.B. Hardware-intrinsic security primitives enabled by analogue state and nonlinear conductance variations in integrated memristors. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kim, S.; Choi, J.; Cha, J.-H.; Im, S.G.; Jang, B.C.; Choi, S.-Y. Memristor-Based Security Primitives Robust to Malicious Attacks for Highly Secure Neuromorphic Systems. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2200177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Comeras, J.; Park, H.; Tang, J.; Afzali, A.; Tulevski, G.S.; Hannon, J.B.; Liehr, M.; Han, S.J. Physically unclonable cryptographic primitives using self-assembled carbon nanotubes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.S.; Lee, G.S.; Park, T.E.; Lee, K.Y.; Ju, H. Bio-inspired electronic fingerprint PUF device with single-walled carbon nanotube network surface mediated by M13 bacteriophage template. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Security keys from paired up nanotube devices. Nat. Electron. 2022, 5, 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Kim, H.; Kim, I.-D. Overview of electroceramic materials for oxide semiconductor thin film transistors. J. Electroceram. 2013, 32, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migani, A.; Sousa, C.; Illas, F. Chemisorption of atomic chlorine on metal surfaces and the interpretation of the induced work function changes. Surf. Sci. 2005, 574, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.C.; Nam, Y.; Koo, B.J.; Choi, J.; Im, S.G.; Park, S.-H.K.; Choi, S.-Y. Memristive Logic-in-Memory Integrated Circuits for Energy-Efficient Flexible Electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, K.; Kamiya, T.; Ikenaga, E.; Yanagi, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Hosono, H. Depth analysis of subgap electronic states in amorphous oxide semiconductor, a-In-Ga-Zn-O, studied by hard x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 073726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A. Surface oxygen vacancy origin of electron accumulation in indium oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 261910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierwagen, O.; Speck, J.S.; Nagata, T.; Chikyow, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Kobayashi, K. Depletion of the In2O3 (001) and (111) surface electron accumulation by an oxygen plasma surface treatment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 172101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Wenckstern, H.; Splith, D.; Schmidt, F.; Grundmann, M.; Bierwagen, O.; Speck, J.S. Schottky contacts to In2O3. APL Mater. 2014, 2, 046104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, R.; Monakhov, E.V.; Grossner, U.; Svensson, B.G. Electrical characteristics of palladium Schottky contacts to hydrogen peroxide treated hydrothermally grown ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 193507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schifano, R.; Monakhov, E.V.; Svensson, B.G.; Diplas, S. Surface passivation and interface reactions induced by hydrogen peroxide treatment of n-type ZnO (0001). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 132101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosbacker, H.L.; Strzhemechny, Y.M.; White, B.D.; Smith, P.E.; Look, D.C.; Reynolds, D.C.; Litton, C.W.; Brillson, L.J. Role of near-surface states in ohmic-Schottky conversion of Au contacts to ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 012102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, T.; Bierwagen, O.; White, M.E.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Speck, J.S. Study of the Au Schottky contact formation on oxygen plasma treated n-type SnO2 (101) thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 033707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, M.; Tsukazaki, A.; Gunji, R.Y.; Ueno, K.; Ohtomo, A.; Fukumura, T.; Kawasaki, M. Schottky contact on a ZnO (0001) single crystal with conducting polymer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 142113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, R.W.; Winograd, N. Oxidation of polycrystalline indium studied by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and static secondary ion mass spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 1980, 51, 2620–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remashan, K.; Hwang, D.K.; Park, S.D.; Bae, J.W.; Yeom, G.Y.; Park, S.J.; Jang, J.H. Effect of N2O Plasma Treatment on the Performance of ZnO TFTs. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2008, 11, H55–H59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-P.; Hussain, A.M.; Hwang, D.-K.; Woo, S.-H.; Lyu, H.-K.; Baek, S.-H.; Jang, Y.; Kim, J.-H. Work Function Modification of Indium–Tin Oxide by Surface Plasma Treatments Using Different Gases. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 021601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, K.-B.; Tak, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-L. Mechanism for the increase of indium-tin-oxide work function by O2 inductively coupled plasma treatment. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Kubendran, R.; Gao, B.; Joshi, S.; Raina, P.; Wu, H.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Wong, H.-S.P. A Voltage-Mode Sensing Scheme with Differential-Row Weight Mapping For Energy-Efficient RRAM-Based In-Memory Computing. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, Honolulu, HI, USA, 16–19 June 2020; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Crippa, L.; Micheloni, R.; Motta, I.; Sangalli, M. Nonvolatile Memories: NOR vs. NAND Architectures. In Memories in Wireless Systems; Micheloni, R., Campardo, G., Olivo, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 29–53. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Wu, H.; Pang, Y.; Qian, H.; Yu, S. Experimental Characterization of Physical Unclonable Function Based on 1 kb Resistive Random Access Memory Arrays. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 36, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.; Plusquellic, J.; Bhunia, S. A Non-Volatile Memory Based Physically Unclonable Function without Helper Data. In Proceedings of the the 2014 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Jose, CA, USA, 3–6 November 2014; pp. 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.M.; Yun, G.J.; Kim, M.S.; Han, J.K.; Kim, D.J.; Choi, Y.K. A Poly-Crystalline Silicon Nanowire Transistor with Independently Controlled Double-Gate for Physically Unclonable Function by Multi-States and Self-Destruction. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 2000989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.M.; Park, J.Y.; Bae, H.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, C.K.; Seo, M.; Im, H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, G.B.; et al. Nano-electromechanical Switch Based on a Physical Unclonable Function for Highly Robust and Stable Performance in Harsh Environments. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 12547–12552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, N.; Jeon, S.-B.; Jang, B.C. Hardware-Intrinsic Physical Unclonable Functions by Harnessing Nonlinear Conductance Variation in Oxide Semiconductor-Based Diode. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040675
Kim N, Jeon S-B, Jang BC. Hardware-Intrinsic Physical Unclonable Functions by Harnessing Nonlinear Conductance Variation in Oxide Semiconductor-Based Diode. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(4):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040675
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Namju, Seung-Bae Jeon, and Byung Chul Jang. 2023. "Hardware-Intrinsic Physical Unclonable Functions by Harnessing Nonlinear Conductance Variation in Oxide Semiconductor-Based Diode" Nanomaterials 13, no. 4: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040675
APA StyleKim, N., Jeon, S.-B., & Jang, B. C. (2023). Hardware-Intrinsic Physical Unclonable Functions by Harnessing Nonlinear Conductance Variation in Oxide Semiconductor-Based Diode. Nanomaterials, 13(4), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13040675




