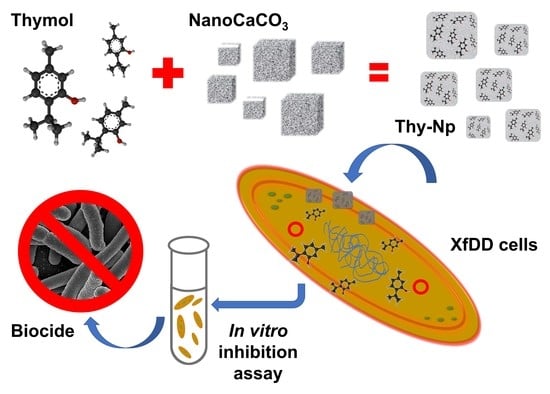
Thymol-Nanoparticles as Effective Biocides against the Quarantine Pathogen Xylella fastidiosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
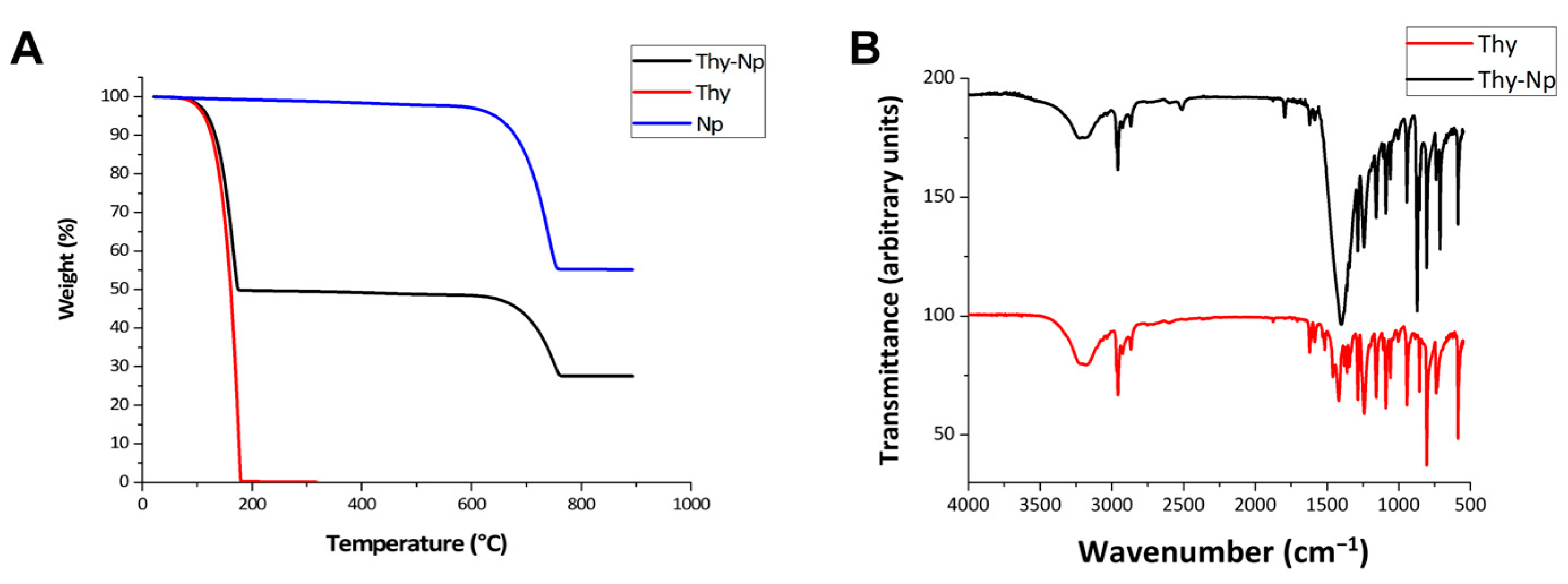
2.2. Thymol-Nanoparticles Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Xylella Fastidiosa Strain
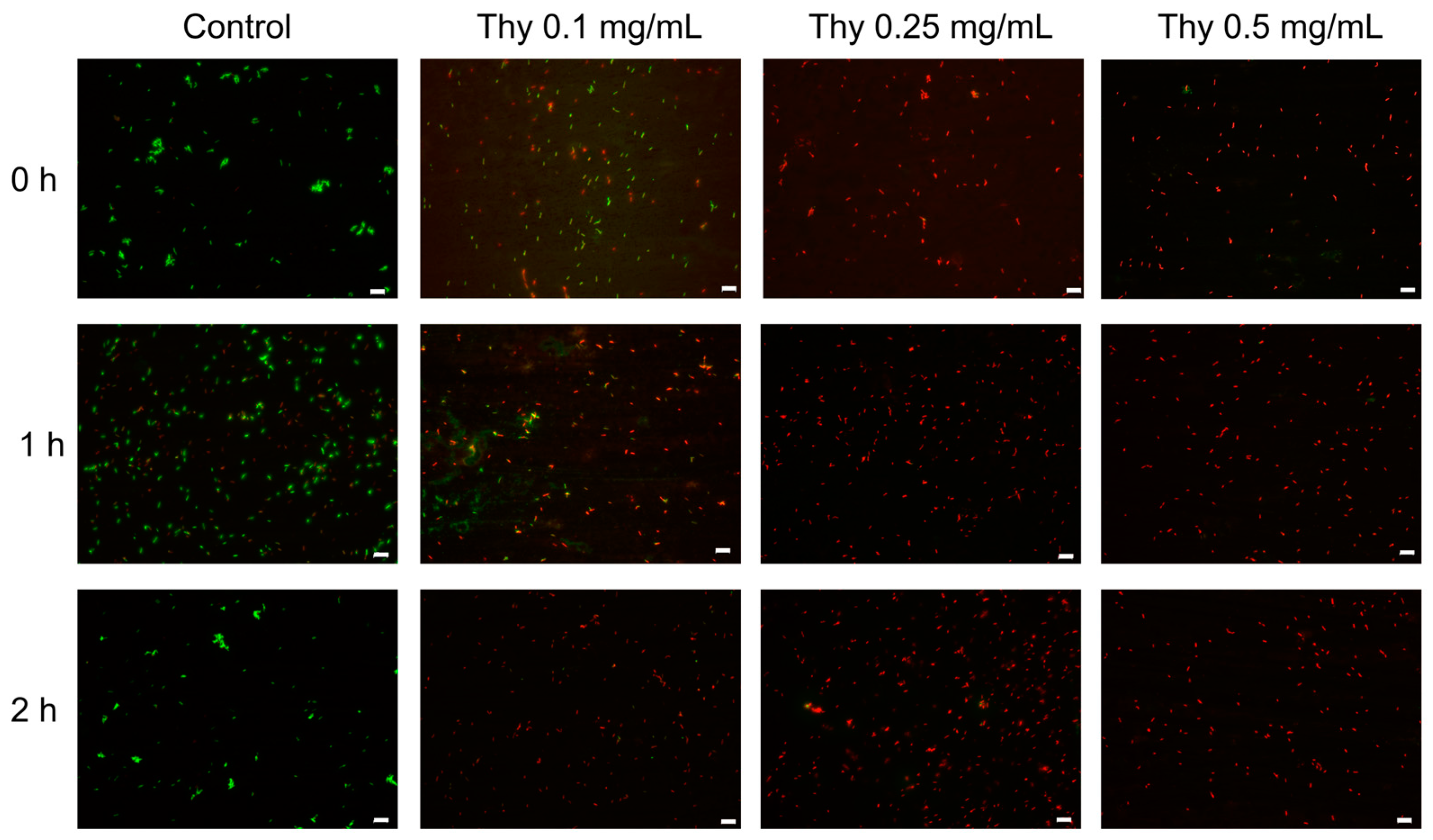
2.4. Fluorescent Assay (Live/Dead Cell Viability Assay)
2.5. In Vitro Inhibition Assay
Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thymol Nanoparticles
3.2. Antibacterial Activity of Thy and Thy-Np on X. fastidiosa
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martyniuk, C.J.; Mehinto, A.C.; Denslow, N.D. Organochlorine pesticides: Agrochemicals with potent endocrine-disrupting properties in fish. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 507, 110764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, R.S.; Kumar, S.; Datta, R.; Lal, R.; Vijayakumar, V.; Brtnicky, M.; Sharma, M.; Yadav, G.; Jhariya, M.; Jangir, C.; et al. Impact of Agrochemicals on Soil Microbiota and Management: A Review. Land 2020, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.M.; Kuo, Y.; Blumberg, B. Agrochemicals and obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 515, 110926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, L.; Gomez, A.L.; Altamirano, G.A. Relationship between agrochemical compounds and mammary gland development and breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 508, 110789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, T.; Gopal, G.; Kundu, R.; Mukherjee, A. Nanocomposites for Delivering Agrochemicals: A Comprehensive Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 3691–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.; Sun, C.; Li, N.; Huang, B.; Jiang, J.; Shen, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Zhan, S.; Gao, F.; et al. Nanomaterials and nanotechnology for the delivery of agrochemicals: Strategies towards sustainable agriculture. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y. Application of food-grade natural antimicrobials for the control of crop disease caused by phytopathogens. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, D.; Francesconi, S.; Bischetti, G.; Giovanale, G.; Fortunati, E.; Balestra, G.M. Antibacterial activity of coumarin as an innovative organic control strategy for Xanthomonas euvesicatoria pv. euvesicatoria. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2022, 129, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, A.; Mazzaglia, A.; Muganu, M.; Paolocci, M.; Sguizzato, M.; Esposito, E.; Cortesi, R.; Balestra, G.M. Microparticles containing gallic and ellagic acids for the biological control of bacterial diseases of kiwifruit plants. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2017, 124, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, F.; Vergaro, V.; De Castro, F.; Biondo, F.; Suranna, G.P.; Papadia, P.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Rongai, D.; Ciccarella, G. Enhanced Bioactivity of Pomegranate Peel Extract following Controlled Release from CaCO3 Nanocrystals. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 2022, 6341298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, P.S.; Tupe, S. Antifungal activity and mechanism of action of carvacrol and thymol against vineyard and wine spoilage yeasts. Food Control 2014, 46, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, A.; Erdogan Orhan, I.; Daglia, M.; Barbieri, R.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Nabavi, S.F.; Gortzi, O.; Izadi, M. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of thymol: A brief review of the literature. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombetta, D.; Castelli, F.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Venuti, V.; Cristani, M.; Daniele, C.; Saija, A.; Mazzanti, G.; Bisignano, G. Mechanisms of antibacterial action of three monoterpenes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2474–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbaszadeh, S.; Sharifzadeh, A.; Shokri, H.; Khosravi, A.R.; Abbaszadeh, A. Antifungal efficacy of thymol, carvacrol, eugenol and menthol as alternative agents to control the growth of food-relevant fungi. J. Mycol. Med. 2014, 24, e51–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.; Momol, M.T.; Olson, S.M.; Pradhanang, P.M.; Jones, J.B. Evaluation of Thymol as Biofumigant for Control of Bacterial Wilt of Tomato under Field Conditions. Plant Dis. 2005, 89, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hossain, M.I.; Rahaman Mizan, M.F.; Toushik, S.H.; Roy, P.K.; Jahid, I.K.; Park, S.H.; Ha, S.-D. Antibiofilm effect of nisin alone and combined with food-grade oil components (thymol and eugenol) against Listeria monocytogenes cocktail culture on food and food-contact surfaces. Food Control 2022, 135, 108796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikeli, F.; Vinciguerra, V.; Sennato, S.; Scarascia Mugnozza, G.; Romagnoli, M. Preparation of Lignin Nanoparticles with Entrapped Essential Oil as a Bio-Based Biocide Delivery System. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattos, B.D.; Tardy, B.L.; Pezhman, M.; Kämäräinen, T.; Linder, M.; Schreiner, W.H.; Magalhães, W.L.E.; Rojas, O.J. Controlled biocide release from hierarchically-structured biogenic silica: Surface chemistry to tune release rate and responsiveness. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Pan, X.; Gao, T.; He, T.; Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Fu, X.; Huang, Q. Controlled Release of Thymol by Cyclodextrin Metal-Organic Frameworks for Preservation of Cherry Tomatoes. Foods 2022, 11, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, E.; Caro, N.; Abugoch, L.; Gamboa, A.; Díaz-Dosque, M.; Tapia, C. Chitosan thymol nanoparticles improve the antimicrobial effect and the water vapour barrier of chitosan-quinoa protein films. J. Food Eng. 2019, 240, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Choudhary, R.C.; Kumaraswamy, R.V.; Bhagat, D.; Pal, A.; Raliya, R.; Biswas, P.; Saharan͙, V. Zinc-functionalized thymol nanoemulsion for promoting soybean yield. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 145, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckler, C.; Marques Maders Silva, C.; Ayres Cacciatore, F.; Daroit, D.J.; da Silva Malheiros, P. Thymol and carvacrol in nanoliposomes: Characterization and a comparison with free counterparts against planktonic and glass-adhered Salmonella. LWT 2020, 127, 109382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Sheng, J.; Lu, Y.; Sun, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y. Preparation and Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity of Thymol Immobilized on Different Silica Nanoparticles with Application in Apple Juice. Coatings 2022, 12, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddox, C.E.; Laur, L.M.; Tian, L. Antibacterial Activity of Phenolic Compounds Against the Phytopathogen Xylella fastidiosa. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 60, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cariddi, C.; Saponari, M.; Boscia, D.; De Stradis, A.; Loconsole, G.; Nigro, F.; Porcelli, F.; Potere, O.; Martelli, G.P. Isolation of a Xylella fastidiosa strain infecting olive and oleander in Apulia, Italy. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 96, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scortichini, M.; Loreti, S.; Pucci, N.; Scala, V.; Tatulli, G.; Verweire, D.; Oehl, M.; Widmer, U.; Codina, J.; Hertl, P.; et al. Progress towards Sustainable Control of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca in Olive Groves of Salento (Apulia, Italy). Pathogens 2021, 10, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassarre, F.; Tatulli, G.; Vergaro, V.; Mariano, S.; Scala, V.; Nobile, C.; Pucci, N.; Dini, L.; Loreti, S.; Ciccarella, G. Sonication-assisted production of Fosetyl-Al nanocrystals: Investigation of human toxicity and in vitro antibacterial efficacy against Xylella Fastidiosa. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, F.; De Stradis, A.; Altamura, G.; Vergaro, V.; Citti, C.; Cannazza, G.; Capodilupo, A.L.; Dini, L.; Ciccarella, G. Application of calcium carbonate nanocarriers for controlled release of phytodrugs against Xylella fastidiosa pathogen. Pure Appl. Chem. 2020, 92, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldassarre, F.; Allegretti, C.; Tessaro, D.; Carata, E.; Citti, C.; Vergaro, V.; Nobile, C.; Cannazza, G.; D’Arrigo, P.; Mele, A.; et al. Biocatalytic Synthesis of Phospholipids and Their Application as Coating Agents for CaCO3 Nano–crystals: Characterization and Intracellular Localization Analysis. Chemistryselect 2016, 1, 6507–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jiao, X.; Shang, Y.; Wen, Y. Encapsulation of Thymol in Biodegradable Nanofiber via Coaxial Eletrospinning and Applications in Fruit Preservation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Min, T.; Zhang, X.; Wen, Y. Microencapsulation of Thymol in Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA): Physical and Antibacterial Properties. Materials 2019, 12, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto-Schalch, N.O.; Pinho, S.G.B.; de Barros-Alexandrino, T.T.; Dacanal, G.C.; Assis, O.B.G.; Martelli-Tosi, M. Production and characterization of chitosan-TPP/cellulose nanocrystal system for encapsulation: A case study using folic acid as active compound. Cellulose 2020, 27, 5855–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, M.; Beltran, O.; Encinas-Basurto, D.A.; Ballesteros-Monrreal, M.G.; Topete, A.; Hassan, N.; López-Mata, M.A.; Reyes-Márquez, V.; Valdez, M.A.; Juarez, J. High antibacterial performance of hydrophobic chitosan-based nanoparticles loaded with Carvacrol. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 209, 112191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisorio, R.; Piliego, C.; Striccoli, M.; Cosma, P.; Fini, P.; Gigli, G.; Mastrorilli, P.; Suranna, G.P.; Nobile, C.F. Influence of Keto Groups on the Optical, Electronic, and Electroluminescent Properties of Random Fluorenone-Containing Poly(fluorenylene-vinylene)s. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 20076–20087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.M.; Raju, B.C.; Nyland, G.; Lowe, S.K. Medium for Isolation and Growth of Bacteria Associated with Plum Leaf Scald and Phony Peach Diseases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1981, 42, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harper, S.J.; Ward, L.I.; Clover, G.R.G. Development of LAMP and Real-Time PCR Methods for the Rapid Detection of Xylella fastidiosa for Quarantine and Field Applications. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadia, P.; Tyagi, S.; Bhagat, S.; Nair, A.; Panchal, P.; Dave, H.; Dang, S.; Singh, S. Calcium carbonate nano- and microparticles: Synthesis methods and biological applications. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, V.; Pisano, I.; Grisorio, R.; Baldassarre, F.; Mallamaci, R.; Santoro, A.; Suranna, G.P.; Papadia, P.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Ciccarella, G. CaCO3 as an environmentally friendly renewable material for drug delivery systems: Uptake of HSA-CaCO3 nanocrystals conjugates in cancer cell lines. Materials 2019, 12, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.H.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, X.A.; Gong, D.M.; Wang, M.S. Combination of microbiological, spectroscopic and molecular docking techniques to study the antibacterial mechanism of thymol against Staphylococcus aureus: Membrane damage and genomic DNA binding. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 409, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| [Loading Solution] | AE | AC |
|---|---|---|
| 2 mg/mL | - | - |
| 5 mg/mL | 20 ± 1.6% | - |
| 25 mg/mL | 90.7 ± 0.95% | 95.4 ± 5.5% |
| SEM Measurement (nm) | DLS Measurement (nm) | PdI |
|---|---|---|
| 82 ± 22 | 800 ± 0.1 | 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldassarre, F.; Schiavi, D.; Ciarroni, S.; Tagliavento, V.; De Stradis, A.; Vergaro, V.; Suranna, G.P.; Balestra, G.M.; Ciccarella, G. Thymol-Nanoparticles as Effective Biocides against the Quarantine Pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071285
Baldassarre F, Schiavi D, Ciarroni S, Tagliavento V, De Stradis A, Vergaro V, Suranna GP, Balestra GM, Ciccarella G. Thymol-Nanoparticles as Effective Biocides against the Quarantine Pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(7):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071285
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldassarre, Francesca, Daniele Schiavi, Serena Ciarroni, Vincenzo Tagliavento, Angelo De Stradis, Viviana Vergaro, Gian Paolo Suranna, Giorgio Mariano Balestra, and Giuseppe Ciccarella. 2023. "Thymol-Nanoparticles as Effective Biocides against the Quarantine Pathogen Xylella fastidiosa" Nanomaterials 13, no. 7: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071285
APA StyleBaldassarre, F., Schiavi, D., Ciarroni, S., Tagliavento, V., De Stradis, A., Vergaro, V., Suranna, G. P., Balestra, G. M., & Ciccarella, G. (2023). Thymol-Nanoparticles as Effective Biocides against the Quarantine Pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. Nanomaterials, 13(7), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13071285