Effect of Nano-Zinc Oxide, Rice Straw Compost, and Gypsum on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Yield and Soil Quality in Saline–Sodic Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
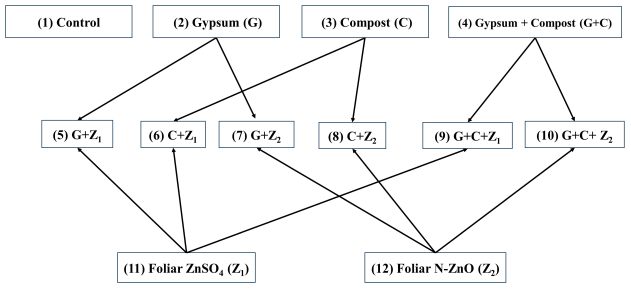
2.1. Experimental Location and Design
2.2. N-ZnO Preparation and Characterization
2.3. Soil Analysis
2.4. Plant Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
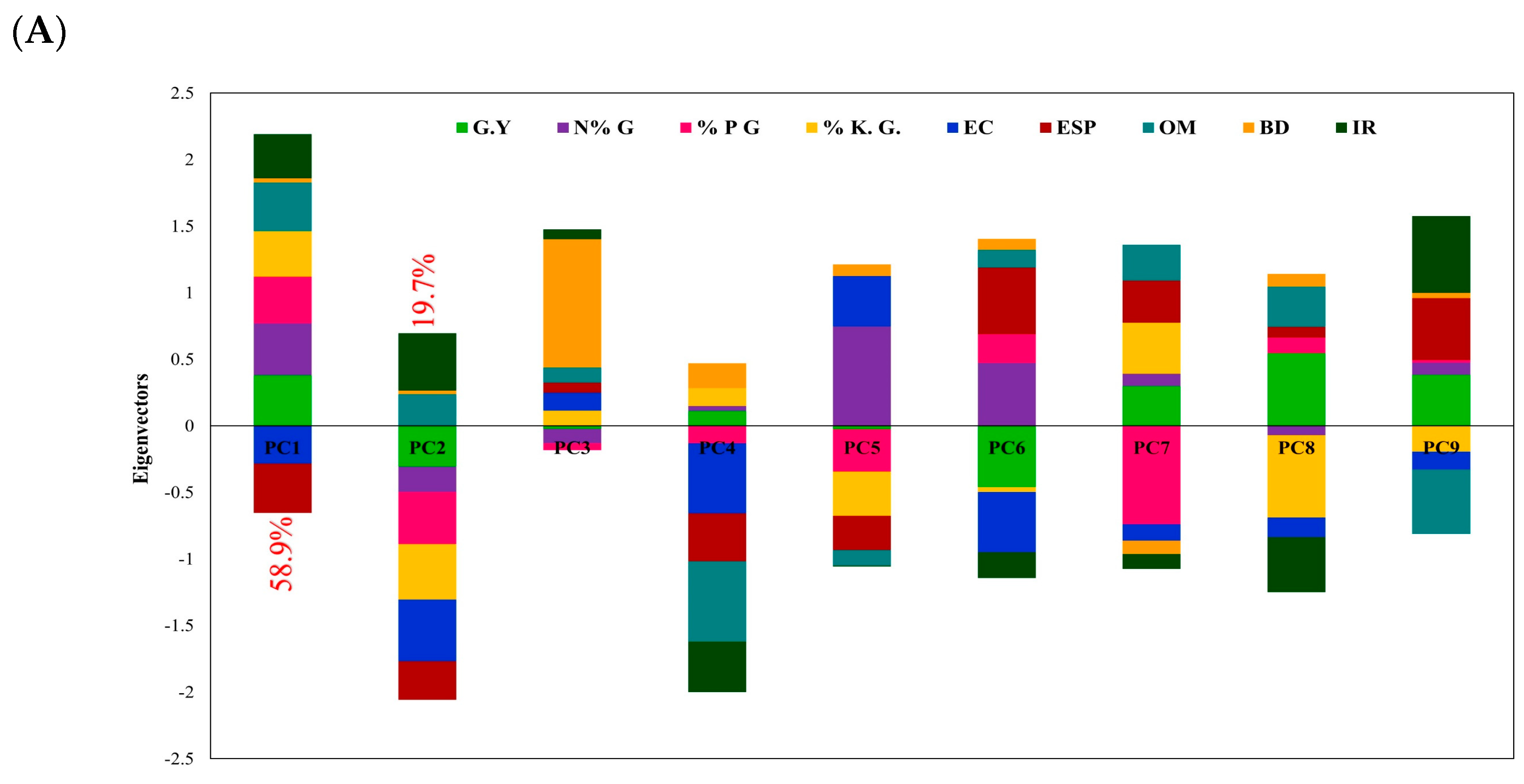
3. Results
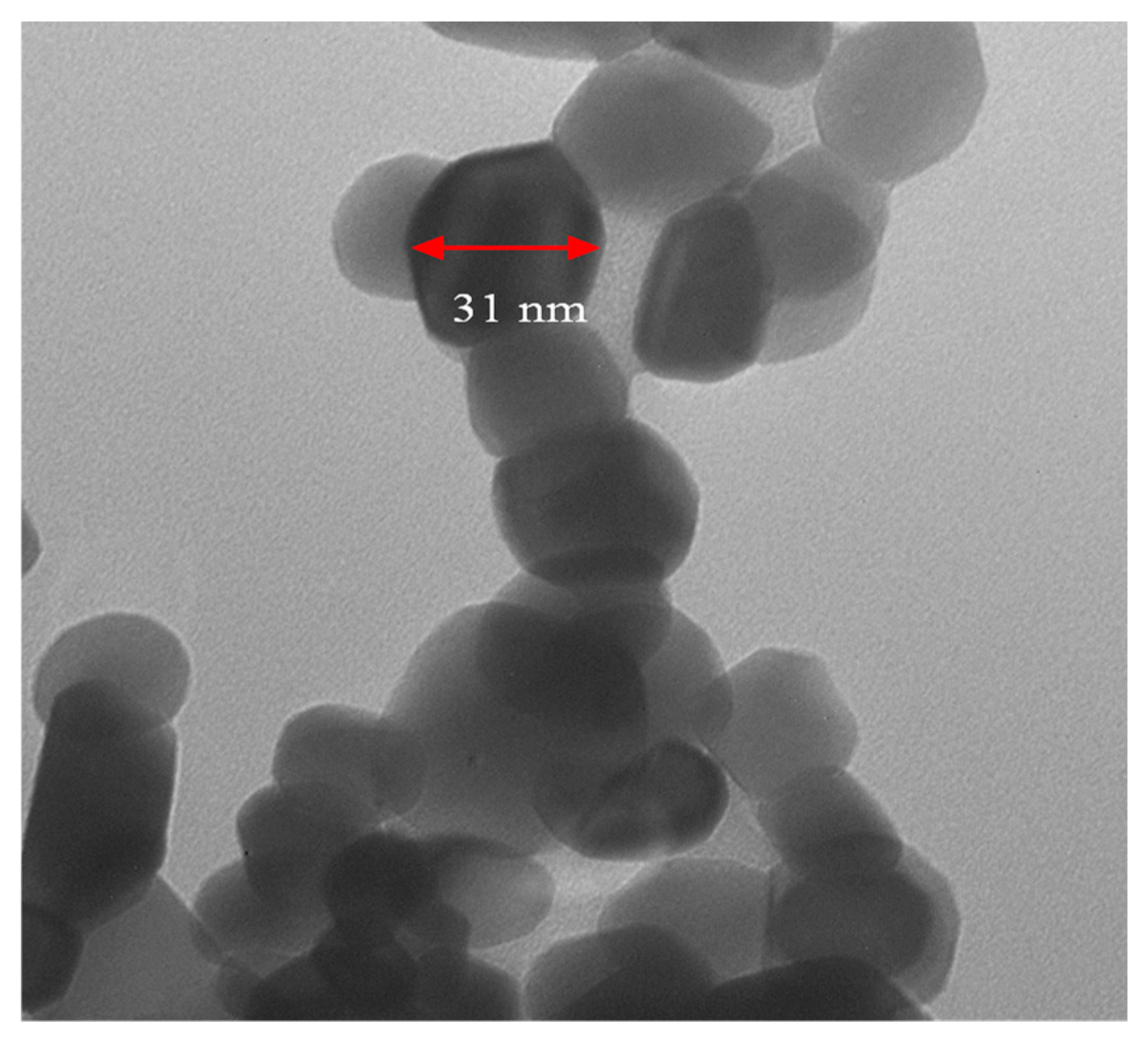
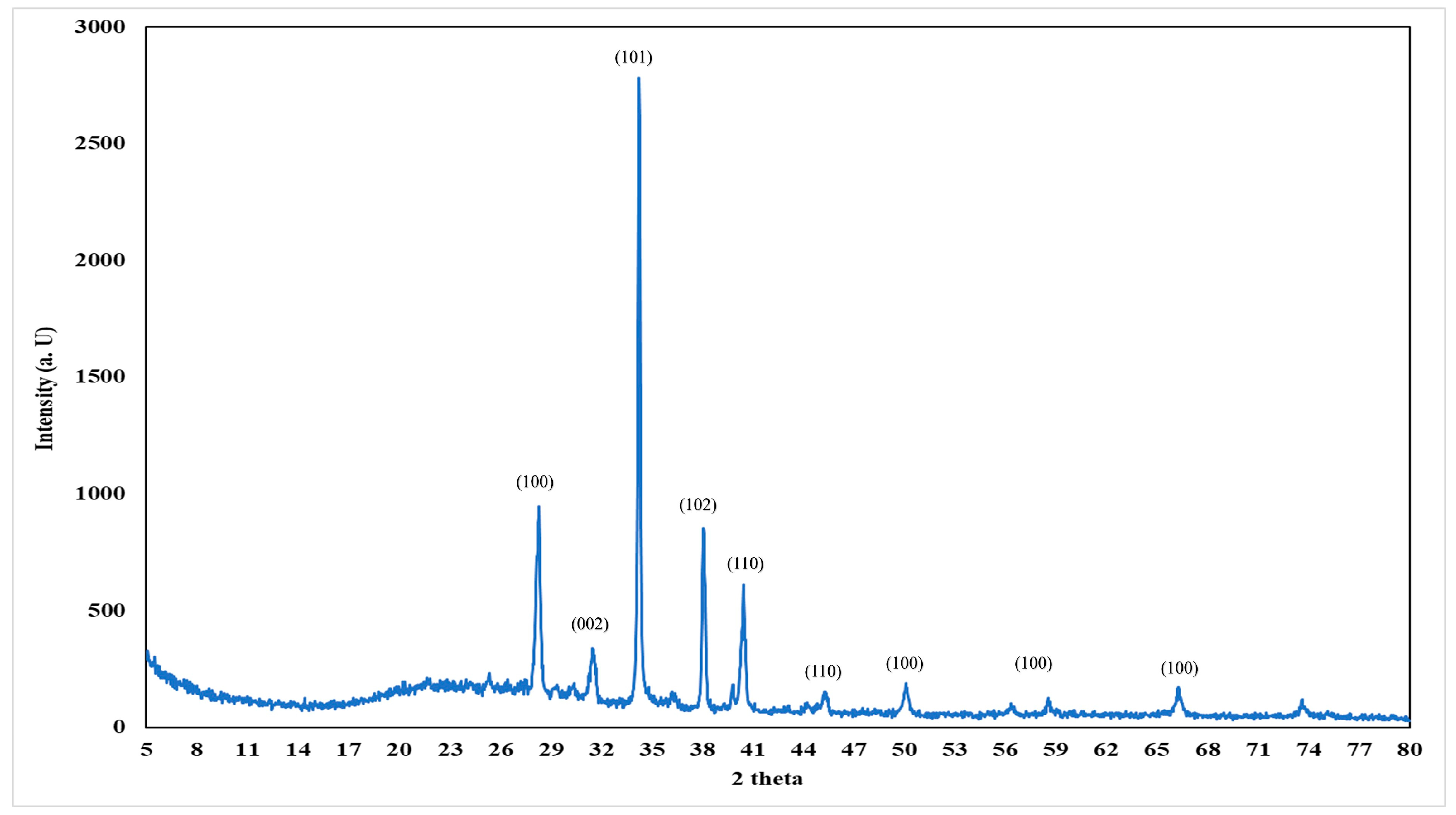
3.1. TEM Image and XRD of Prepared N-ZnO
3.2. Effect of Studied Soil Amendments on Some Soil Characteristics
3.3. Effect of Studied Soil Amendments on Yield and Biomass of Wheat Plants
3.4. Effect of Studied Soil Amendments on Nutrient Content of Wheat Plants
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Characteristics
4.2. Wheat Plant Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdalla, A.; Stellmacher, T.; Becker, M. Trends and Prospects of Change in Wheat Self-Sufficiency in Egypt. Agriculture 2023, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeltová, Z.; Hálová, P.; Malec, K.; Bartoňová, K.; Blažek, V.; Maitah, M.; Koželský, R.; Phiri, J.; Appiah-Kubi, S.N.K.; Tomšík, K.; et al. Geopolitical risks for Egypt wheat supply and trade. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1137526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmageed, K.; Chang, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Tao, Z. Evolution of varieties and development of production technology in Egypt wheat: A review. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, F.; Olivos-Hernández, K.; Stange, C.; Handford, M. Abiotic stress in crop species: Improving tolerance by applying plant metabolites. Plants 2021, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, A.; Skalicky, M.; Brestic, M.; Maitra, S.; Ashraful Alam, M.; Syed, M.A.; Hossain, J.; Sarkar, S.; Saha, S.; Bhadra, P. Consequences and mitigation strategies of abiotic stresses in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under the changing climate. Agronomy 2021, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S. Present scenario of global salt affected soils, its management and importance of salinity research. Int. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, K.T. Management of Soil Problems, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Duke, N.C. Halophytes–A resource for the future. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 9, 455–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Khan, M.Y.; Carvalhais, L.C.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Yan, L.; Crawford, M.; Dennis, P.G.; Singh, B.; Schenk, P.M. Soil amendments with ethylene precursor alleviate negative impacts of salinity on soil microbial properties and productivity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, M.S.; El-Beshsbeshy, T.R.; Mahmoud, E.K.; Abdelkader, N.I.; Al-Shal, R.M.; Missaoui, A.M. Response of Alfalfa under Salt Stress to the Application of Potassium Sulfate Nanoparticles. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Crohn, D.M. Evaluating the relative contribution of physiochemical and biological factors in ameliorating a saline–sodic soil amended with composts and biochar and leached with reclaimed water. Geoderma 2015, 259, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellouzi, H.; Hamed, K.B.; Cela, J.; Müller, M.; Abdelly, C.; Munné-Bosch, S. Increased sensitivity to salt stress in tocopherol-deficient Arabidopsis mutants growing in a hydroponic system. Plant Signal Behav. 2013, 8, e23136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, P.; Singh, R.; Trivedi, M.; Tiwari, R.K. Sodic soil: Management and reclamation strategies. In Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Development: Volume 2: Biodiversity, Soil and Waste Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhinandan, K.; Skori, L.; Stanic, M.; Hickerson, N.M.N.; Jamshed, M.; Samuel, M.A. Abiotic stress signaling in wheat–an inclusive overview of hormonal interactions during abiotic stress responses in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Ma, H.; Sedano, F.; Lewis, P.; Liang, S.; Wu, Q.; Su, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, D. Evaluation of Regional Estimates of Winter Wheat Yield by Assimilating Three Remotely Sensed Reflectance Datasets into the Coupled WOFOST–PROSAIL Model. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 102, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezapour, S.; Asadzadeh, F.; Barin, M.; Nouri, A. Organic amendments improved the chemical–nutritional quality of saline-sodic soils. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 19, 4659–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y. The effects of biochar addition on soil physicochemical properties: A review. Catena 2021, 202, 105284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, S.; Yao, B.; Peng, Y.; Gao, C.; Qin, T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C.; Quan, W. Effects of straw return and straw biochar on soil properties and crop growth: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 986763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.K.; Alayafi, A.H.; AL-Solaimani, S.G.; Abo-Elyousr, K.A.M. Mitigating Soil Salinity Stress with Gypsum and Bio-Organic Amendments: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.P.; Arora, S.; Mishra, V.K.; Singh, A.K. Synergizing Microbial Enriched Municipal Solid Waste Compost and Mineral Gypsum for Optimizing Rice-Wheat Productivity in Sodic Soils. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashmi, I.; Meena, B.P.; Rajendiran, S.; Jayaraman, S.; Joshy, C.G.; Ali, S.; Mina, B.L.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, A.; Kumawat, A.; et al. Can gypsum and organic amendments achieve sustainability, productivity and maintain soil health under soybean-mustard cropping in sodic soils of western India. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 240, 106075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leogrande, R.; Vitti, C. Use of organic amendments to reclaim saline and sodic soils: A review. Arid. Land Res. Manag. 2019, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, S.; An, F.; Zhang, L.; Tóth, T.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z. Effects of Different Organic Amendments on Soil Improvement, Bacterial Composition, and Functional Diversity in Saline–Sodic Soil. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, P.K.; Mondal, S. Agri-nanotechniques for Plant Availability of Nutrients BT—Plant Nanotechnology: Principles and Practices; Kole, C., Kumar, D.S., Khodakovskaya, M.V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 263–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; White, J.C.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Nano-enabled fertilizers to control the release and use efficiency of nutrients. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 6, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemike, E.E.; Uzoh, I.M.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Babalola, O.O. The Role of Nanotechnology in the Fortification of Plant Nutrients and Improvement of Crop Production. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lal, R. Potentials of engineered nanoparticles as fertilizers for increasing agronomic productions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, E.E.; Elbakry, H.F.H.; Ibrahim, K.S.; El Sayed, E.M.; Salama, D.M.; Farrag, A.R.H. The effect of white kidney bean fertilized with nano-zinc on nutritional and biochemical aspects in rats. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 23, e00357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair Hassan, M.; Aamer, M.; Umer Chattha, M.; Haiying, T.; Shahzad, B.; Barbanti, L.; Nawaz, M.; Rasheed, A.; Afzal, A.; Liu, Y.; et al. The Critical Role of Zinc in Plants Facing the Drought Stress. Agriculture 2020, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, A.; Ghazanfar, M.; Khan, J.S.; Pervaiz, S.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Alamri, S. Zinc Absorption through Leaves and Subsequent Translocation to the Grains of Bread Wheat after Foliar Spray. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanha, G.S.; Rodrigues, E.S.; Romeu, S.L.Z.; de Almeida, E.; Reis, A.R.; Lavres, J.; Pereira de Carvalho, H.W. Zinc uptake from ZnSO4 (aq) and Zn-EDTA (aq) and its root-to-shoot transport in soybean plants (Glycine max) probed by time-resolved in vivo X-ray spectroscopy. Plant Sci. 2020, 292, 110370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-López, J.I.; Niño-Medina, G.; Olivares-Sáenz, E.; Lira-Saldivar, R.H.; Barriga-Castro, E.D.; Vázquez-Alvarado, R.; Rodríguez-Salinas, P.A.; Zavala-García, F. Foliar Application of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Zinc Sulfate Boosts the Content of Bioactive Compounds in Habanero Peppers. Plants 2019, 8, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raliya, R.; Saharan, V.; Dimkpa, C.; Biswas, P. Nanofertilizer for Precision and Sustainable Agriculture: Current State and Future Perspectives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6487–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.K.S.H.; Qayyum, M.F.; Abdel-Hadi, A.M.; Rehman, R.A.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M. Interactive effect of salinity and silver nanoparticles on photosynthetic and biochemical parameters of wheat. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 63, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, F.; Hashim, A.; Anees, S. Efficacy of nanoparticles as nanofertilizer production: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; Singh, U.; Bindraban, P.S.; Elmer, W.H.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; White, J.C. Zinc oxide nanoparticles alleviate drought-induced alterations in sorghum performance, nutrient acquisition, and grain fortification. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, F.; Shoaib, S.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Datta, R. Green synthesis of zinc nanoparticles and their effects on growth and yield of Pisum sativum. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydar, M.S.; Ghosh, D.; Roy, S. Slow and controlled release nanofertilizers as an efficient tool for sustainable agriculture: Recent understanding and concerns. Plant Nano Biol. 2024, 7, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, G.; Ibrahim, M.; Tahir, M.A.; Iftikhar, Y.; Haider, M.S.; Han, K.H.; Ha, S.K.; Zhang, Y.S. Effect of compost and gypsum application on the chemical properties and fertility status of saline-sodic soil. Korean J. Soil. Sci. Fert. 2011, 44, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellavalle, N.B.; Walworth, J. Determining the Gypsum Requirement for Reclamation of Sodic and Sodium-Impacted Soils. Crops Soils 2020, 53, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, G.; Datta, S.P.; Singh, R.D.; Datta, S.C.; Vakada, M. Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles–comparison of acetate (precursor) based methods. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2022, 52, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinila, V.S.; Isac, J. Synthesis and structural studies of superconducting perovskite GdBa2Ca3Cu4O10.5+δ nanosystems. In Design, Fabrication, and Characterization of Multifunctional Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheldrick, B.H. Particle size distribution. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; Lewis Publishers: Stockport, UK, 1993; pp. 499–512. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, D.J. Soils: Sources and Methods in Geography; Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd.: London, UK, 1977; Volume 192. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S. Physical Properties of Soils BT—Current Topics in Soil Science: An Environmental Approach; Mukherjee, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 53–65. ISBN 978-3-030-92669-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.L.; Miller, R.H.; Keeney, D.R. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Agronomy Monographs; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods, 5.3; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 961–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil, S.S. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.; Natural Resources Conservation Service and Agriculture Department: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; USDA Circular No. 939; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, C.M.; Zhao, C.W.; Sun, X.J.; Wang, Z.C. Estimating Exchangeable Sodium Percentage from Sodium Adsorption Ratio of Salt-Affected Soil in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.R.; Lee, S.H.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; Kim, W.I.; Kim, K.H. Effect of gypsum on exchangeable sodium percentage and electrical conductivity in the Daeho reclaimed tidal land soil in Korea—A field scale study. J. Soil Sediment. 2018, 18, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, A. Role of soil amendments, plant growth regulators and amino acids in improvement salt affected soils properties and wheat productivity. J. Agric. Eng. 2017, 8, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metho, L.A.; Hammes, P.S. The harvest index of individual ears of four South African wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2000, 17, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.D.; Pratt, P.F. Method of Analysis for Soils, Plants and Waters; University of California (Riverside), Division of Agriculture Sciences: Riverside, CA, USA; Agricultural Publishing Office, University Hall University California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1961; pp. 1–309. [Google Scholar]
- Cottenie, A.; Verloo, M.; Kiekens, L. Chemical Analysis of Plants and Soils; Laboratory of Analytical and Agrochemistry: Gent, Belgium, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Y.; Zhang, W.; Pang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.Z.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S.; Zou, C.Q. Effects of zinc application rate and zinc distribution relative to root distribution on grain yield and grain Zn concentration in wheat. Plant Soil. 2017, 411, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xin, H.L.; Hovden, R.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Muller, D.A.; DiSalvo, F.J.; Abruña, H.D. Structurally ordered intermetallic platinum–cobalt core–shell nanoparticles with enhanced activity and stability as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moezzi, A.; McDonagh, A.M.; Cortie, M.B. Zinc oxide particles: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 185, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, J.I.; Louër, D.; Scardi, P. Effect of a crystallite size distribution on X-ray diffraction line profiles and whole-powder-pattern fitting. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2000, 33, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowri Babu, K.; Ramachandra Reddy, A.; Sujatha, C.; Venugopal Reddy, K.; Mallika, A.N. Synthesis and optical characterization of porous ZnO. J. Adv. Ceram. 2013, 2, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumy, M.A.; Khalifa, T.H.H.; Aboelsoud, H.M. Impact of some organic and inorganic amendments on some soil properties and wheat production under saline-sodic soil. J. Agric. Eng. 2019, 10, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Azom, M.G.; Sultan, M.T.; Mandal, S.; Islam, M.A.; Khatun, R.; Billah, S.M.; Ali, A.H.M.Z. Amelioration of saline soil by the application of gypsum, calcium chloride, rice husk and cow dung. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2019, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Choo, B.K.; Cho, J.Y. Effect of gypsum and rice straw compost application on improvements of soil quality during desalination of reclaimed coastal tideland soils: Ten years of long-term experiments. Catena 2017, 156, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.; El-shahawy, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Abd El-Halim, A.E.-H.A.; Abo-Ogiala, A.; Shokr, M.S.; Mohamed, E.S.; Rebouh, N.Y.; Ismail, S.M. Enhancing Maize Yield and Soil Health through the Residual Impact of Nanomaterials in Contaminated Soils to Sustain Food. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundhari, T.; Thilagavathi, T.; Baskar, M.; Thuvasan, T.; Eazhilkrishna, N. Effect of gypsum incubated organics used as an amendment for sodic soil in green gram. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2018, 6, 304–308. [Google Scholar]
- Elsawy, H.; El-shahawy, A.; Ibrahim, M.; El-Halim, A.E.-H.A.; Talha, N.; Sedky, A.; Alfwuaires, M.; Alabbad, H.; Almeri, N.; Mahmoud, E. Properties of Recycled Nanomaterial sand Their Effect on Biological Activity and Yield of Canola in Degraded Soils. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Abid, M.; Abou-Shanab, R.A.I. Amelioration of salt affected soils in rice paddy system by application of organic and inorganic amendments. Plant Soil Environ. 2013, 59, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cui, J.; Tian, X.; Zhao, A.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Jia, Z.; Liu, K. Effect of straw amendment on soil Zn availability and ageing of exogenous water-soluble Zn applied to calcareous soil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M.; Garcia, C.; Gonzalez, J.L.; Hernandez, M.T. Use of organic amendment as a strategy for saline soil remediation: Influence on the physical, chemical and biological properties of soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Umar, S.; Mahmooduzzafar, F. Nano-fertilization to enhance nutrient use efficiency and productivity of crop plants. In Nanomaterials and Plant Potential; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 473–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Das, R.; George Kerry, R.; Biswal, B.; Sinha, T.; Sharma, S.; Arora, P.; Kumar, M. Promising management strategies to improve crop sustainability and to amend soil salinity. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10, 962581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, S.; Zhao, S.; Xu, X.; He, P.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, N.; et al. Carbon Storage in an Arable Soil Combining Field Measurements, Aggregate Turnover Modeling and Climate Scenarios. Catena 2023, 220, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, S.; Oliva, G.; Vigliotta, G.; Novello, G.; Gamalero, E.; Lingua, G.; Cicatelli, A.; Guarino, F. Effects of compost amendment on glycophyte and halophyte crops grown on saline soils: Isolation and characterization of rhizobacteria with plant growth promoting features and high salt resistance. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H.; Larsen, P.; Koci, J.; Edwards, W.; Nelson, P.N. Long-term effects of gypsum on the chemistry of sodic soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 233, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Xie, W. Coupled effects of saline solutions and temperature on the swelling deformation property of GMZ bentonite-sand mixtures. Soils Found. 2019, 59, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade Foronda, D.; Colinet, G. Combined Application of Organic Amendments and Gypsum to Reclaim Saline–Alkali Soil. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadak, M.S.; Bakry, B.A. Zinc-oxide and nano ZnO oxide effects on growth, some biochemical aspects, yield quantity, and quality of flax (Linum uitatissimum L.) in absence and presence of compost under sandy soil. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2020, 44, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, G.; Mentler, A.; Keiblinger, K. Plant roots for sustainable soil structure management in cropping systems. In The Root Systems in Sustainable Agricultural Intensification; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 45–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Li, X. An Innovative Approach to Alleviate Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Stress on Wheat through Nanobubble Irrigation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar Zaka, M.; Ahmed, K.; Rafa, H.; Sarfraz, M.; Schmeisk, H. Effectiveness of compost and gypsum for amelioration of saline sodic soil in rice wheat cropping system. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2018, 6, 514–523. [Google Scholar]
- Day, S.J.; Norton, J.B.; Strom, C.F.; Kelleners, T.J.; Aboukila, E.F. Gypsum, langbeinite, sulfur, and compost for reclamation of drastically disturbed calcareous saline–sodic soils. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Murtaza, B.; Usman, H.M.; Ghafoor, A. Amelioration of Saline-sodic Soil using Gypsum and Low Quality Water in Following Sorghum-berseem Crop Rotation. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2013, 15, 640–648. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, J.L.; Fang, T.; Dimkpa, C.O.; Britt, D.W.; McLean, J.E.; Jacobson, A.; Anderson, A.J. The phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles on wheat varies with soil properties. BioMetals 2015, 28, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, M.M.; Abou-Baker, N.H. The contribution of nano-zinc to alleviate salinity stress on cotton plants. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.; EL-Aziz, M.A.; Khalifa, T. Effect of nano-zinc application combined with sulfur and compost on saline-sodic soil characteristics and faba bean productivity. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ramady, H.; Abdalla, N.; Sári, D.; Ferroudj, A.; Muthu, A.; Prokisch, J.; Fawzy, Z.F.; Brevik, E.C.; Solberg, S. Nanofarming: Promising solutions for the future of the global agricultural industry. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellan, A.; Yun, J.; Morais, B.P.; Clement, E.T.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Lowry, G.V. Critical review: Role of inorganic nanoparticle properties on their foliar uptake and in planta translocation. Environ. Sci. Tech. 2021, 55, 13417–13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayub, M.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Umar, W.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Waris, A.A.; Fatima, H.; Nadeem, M.; Iftikhar, I. Accumulation, partitioning, and bioavailability of micronutrients in plants and their crosstalk with phytohormones. In Plant Growth Regulators: Signalling under Stress Conditions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 39–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semida, W.M.; Abdelkhalik, A.; Mohamed, G.F.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Abd El-Mageed, S.A.; Rady, M.M.; Ali, E.F. Foliar application of zinc oxide nanoparticles promotes drought stress tolerance in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Plants 2021, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, Y.; González-Moscoso, M.; Hernández-Hernández, H.; Méndez-López, A.; Juárez-Maldonado, A. Induction of Stress Tolerance in Crops by Applying Nanomaterials. In Nanotechnology in Plant Growth Promotion and Protection; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 129–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkar, S.; Sharma, L.; Singh, R.K.; Pandey, B.; Rathore, S.S.; Singh, A.K.; Porwal, P.; Singh, S.P. Plant Stress Hormones Nanobiotechnology BT—Nanobiotechnology: Mitigation of Abiotic Stress in Plants; Al-Khayri, J.M., Ansari, M.I., Singh, A.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 349–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardi, A.; Mohajjel Shoja, H.; Mohajel Kazemi, E. Comparative study of growth responses, photosynthetic pigment content, and gene expression pattern in tobacco plants treated with ZnO nano and ZnO bulk particles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2022, 24, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Ali, A.; Xu, Y.L.; Jiang, L.M.; Lv, G.H. Soil moisture and salinity as main drivers of soil respiration across natural xeromorphic vegetation and agricultural lands in an arid desert region. Catena 2019, 177, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.K.; Song, X.P.; Joshi, A.; Tian, D.D.; Rajput, V.D.; Singh, M.; Arora, J.; Minkina, T.; Li, Y.R. Recent Trends in Nano-Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture under Climate Change for Global Food Security. Nanomater 2022, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, U.; Saini, M.; Kumar, P. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth and antioxidant system of chickpea seedlings. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2013, 95, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eynard, A.; Lal, R.; Wiebe, K. Crop Response in Salt-Affected Soils. J. Sustain. Agric. 2005, 27, 5–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffland, E.; Kuyper, T.W.; Comans, R.N.J.; Creamer, R.E. Eco-functionality of organic matter in soils. Plant Soil 2020, 455, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudina, A.V.; Klyueva, V.V.; Romanenko, K.A.; Fomin, D.S. Micro- within macro: How micro-aggregation shapes the soil pore space and water-stability. Geoderma 2022, 415, 115771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renwick, L.L.R.; Deen, W.; Silva, L.; Gilbert, M.E.; Maxwell, T.; Bowles, T.M.; Gaudin, A.C.M. Long-term crop rotation diversification enhances maize drought resistance through soil organic matter. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 84067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, N. Role of Plant Nutrients in Plant Growth and Physiology BT—Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Hasanuzzaman, M., Fujita, M., Oku, H., Nahar, K., Hawrylak-Nowak, B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 51–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitienei, M.; Otieno, A.; Anapapa, A. An Application of K-Nearest-Neighbor Regression in Maize Yield Prediction. Asian J. Probab. Stat. 2023, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Feng, Q.; Yin, D. Winter Wheat Yield Prediction at County Level and Uncertainty Analysis in Main Wheat-Producing Regions of China with Deep Learning Approaches. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chemical Characteristics | Value | Physical Characteristics | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soluble Ions, EC and pH | Particle Size Distribution (%) | ||||
| ECe (dS m−1) | 6.48 | Clay | 49.68 | ||
| pH (soil suspension 1:2.5) | 8.37 | Silt | 29.71 | ||
| Soluble ions (mmol·L−1) | Sand | 20.61 | |||
| Na+ | 42.7 | Texture class | Clayey | ||
| K+ | 2.6 | Soil type | Saline–Sodic | ||
| Ca++ | 13.8 | OM % | 1.18 | ||
| Mg++ | 5.7 | Total CaCO3 (%) | 2.28 | ||
| Cl− | 36.7 | CEC (cmolc kg−1) | 38.20 | ||
| HCO3− | 22.9 | Bulk density (g cm−3) | 1.43 | ||
| SO4= | 5.2 | Total porosity (%) | 46.04 | ||
| SAR (%) | 13.69 | Field capacity (%) | 38.96 | ||
| ESP % | 16.05 | Wilting point (%) | 21.17 | ||
| Available macronutrients (mg kg−1) | |||||
| N | 31.76 | P | 8.16 | K | 305.7 |
| Traits | Units | Values |
|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 7.62 |
| EC | dS m−1 | 4.12 |
| N | % | 2.53 |
| P | % | 1.23 |
| K | % | 1.41 |
| Moisture ratio | - | 17.80 |
| B.D | g cm−3 | 0.57 |
| O.M | % | 55.78 |
| Total-C | % | 26.89 |
| C/N Ratio | - | 11.20 |
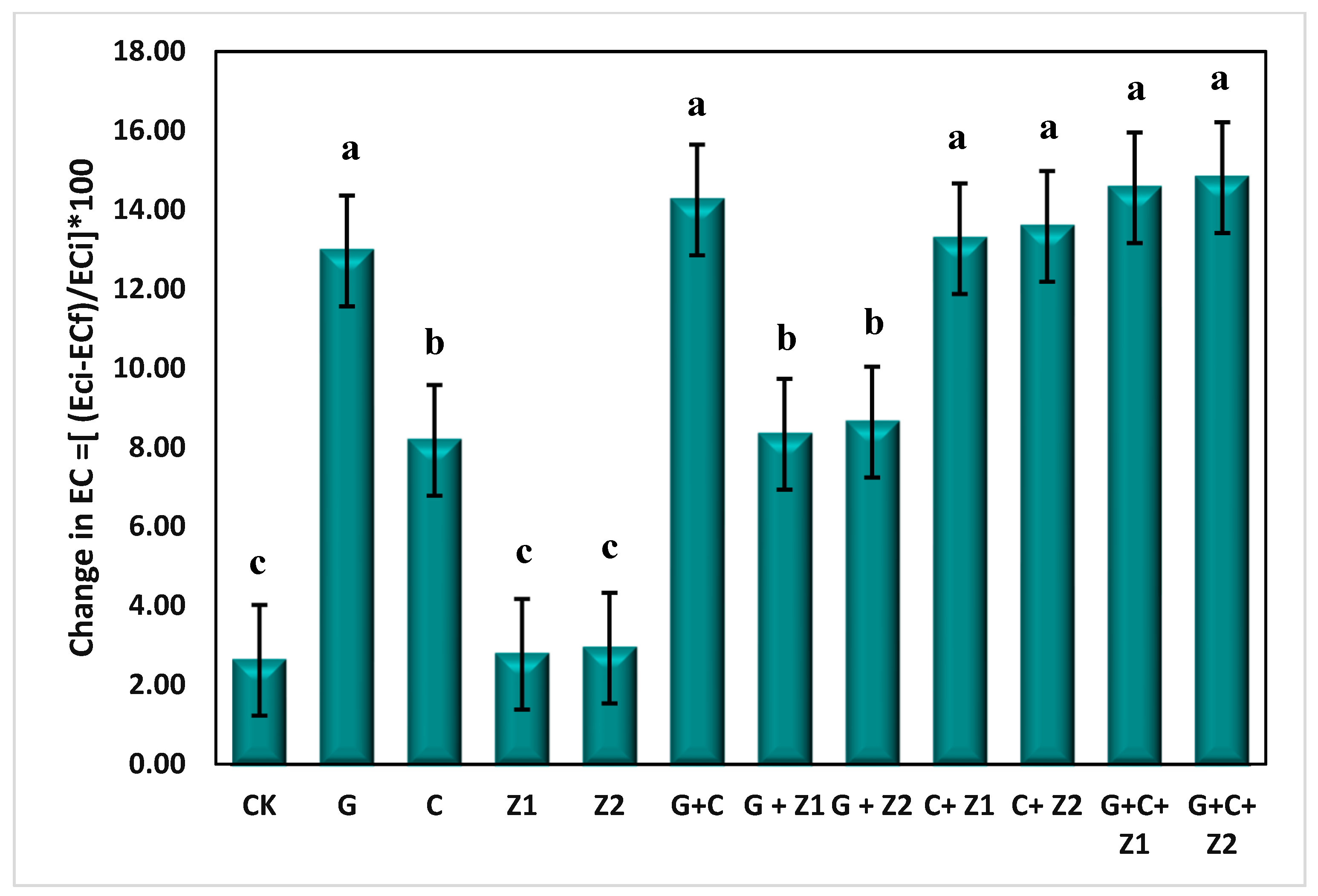
| Treatments | ECe (dS m−1) | SAR (%) | ESP (%) | RSE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.31 ± 0.01 a | 13.19 ± 0.01 a | 15.54 ± 0.05 a | 3.20 ± 0.01 i |
| G | 5.64 ± 0.04 c | 8.97 ± 0.02 d | 11.19 ± 0.01 d | 30.29 ± 0.01 e |
| C | 5.95 ± 0.02 b | 9.32 ± 0.02 c | 11.55 ± 0.01 c | 28.04 ± 0.01 g |
| Z1 | 6.30 ± 0.30 a | 10.71 ± 0.01 b | 12.98 ± 0.01 b | 19.12 ± 0.01 h |
| Z2 | 6.29 ± 0.01 a | 10.70 ± 0.01 b | 12.97 ± 0.01 b | 19.18 ± 0.01 h |
| G + C | 5.56 ± 0.06 c | 8.88 ± 0.01 f | 11.10 ± 0.10 d | 30.86 ± 0.01 b |
| G + Z1 | 5.62 ± 0.02 c | 8.95 ± 0.04 de | 11.17 ± 0.01 d | 30.41 ± 0.01 d |
| G + Z2 | 5.60 ± 0.10 c | 8.93 ± 0.03 e | 11.15 ± 0.03 d | 30.54 ± 0.05 c |
| C + Z1 | 5.94 ± 0.04 b | 9.31 ± 0.01 c | 11.52 ± 0.02 c | 28.10 ± 0.10 g |
| C + Z2 | 5.92 ± 0.02 b | 9.29 ± 0.01 c | 11.52 ± 0.02 c | 28.23 ± 0.03 f |
| G + C + Z1 | 5.54 ± 0.04 c | 7.84 ± 0.04 g | 10.15 ± 0.22 e | 37.54 ± 0.05 a |
| G + C + Z2 | 5.52 ± 0.02 c | 7.83 ± 0.03 g | 10.01 ± 0.01 e | 37.60 ± 0.010 a |
| LSD (0.05) | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.08 |
| Treatments | O.M (%) | B.D (g cm−3) | Total Porosity (%) | Infiltration Rate (cm h−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.17 ± 0.01 d | 1.42 ± 0.01 a | 46.42 ± 0.02 ef | 0.5 ± 0.1 c |
| G | 1.26± 0.01 c | 1.40 ± 0.10 abc | 47.17 ± 0.02 cde | 0.91 ± 0.01 b |
| C | 1.37 ± 0.02 b | 1.37 ± 0.01 abcd | 48.30 ± 0.20 abcd | 1.1 ± 0.1 a |
| Z1 | 1.17 ± 0.01 d | 1.42 ± 0.02 a | 46.42 ± 0.02 ef | 0.5 ± 0.01 c |
| Z2 | 1.18 ± 0.01 d | 1.41 ± 0.01 ab | 46.79 ± 0.01 def | 0.51 ± 0.01 c |
| G+C | 1.42 ± 0.01 a | 1.36 ± 0.02 abcd | 49.43 ± 0.03 a | 1.12 ± 0.02 a |
| G + Z1 | 1.24 ± 0.01 c | 1.40 ± 0.02 abc | 45.17 ± 3.48 f | 0.91 ± 0.01 b |
| G + Z2 | 1.25 ± 0.02 c | 1.39 ± 0.01 abcd | 47.68 ± 0.28 cde | 0.91 ± 0.01 b |
| C+ Z1 | 1.39 ± 0.02 b | 1.36 ± 0.01 abcd | 48.68 ± 0.28 abc | 1.09 ± 0.01 a |
| C+ Z2 | 1.39 ± 0.01 b | 1.35 ± 0.05 bcd | 49.06 ± 0.01 ab | 1.08 ± 0.02 a |
| G + C+ Z1 | 1.42 ± 0.02 a | 1.34 ± 0.04 cd | 49.43 ± 0.04 a | 1.11 ± 0.03 a |
| G + C+ Z2 | 1.43 ± 0.02 a | 1.33 ± 0.03 d | 49.81 ± 0.01 a | 1.12 ± 0.03 a |
| LSD (0.05) | 0.02 | 0.07 | 1.72 | 0.07 |
| Treatments | Grain Yield (Mg ha−1) | Straw Yield (Mg ha−1) | 1000 Grain Weight (Mg ha−1) | Harvest Index (%) | Plant Height (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.85 ± 0.03 h | 7.77 ± 0.28 f | 32.34 ± 0.21 h | 33.12 ± 0.25 d | 63.33 ± 1.15 h |
| G | 5.25 ± 0.13 fg | 8.00 ± 0.25 def | 40.09 ± 0.95 fg | 39.64 ± 0.13 bc | 71.33 ± 2.52 g |
| C | 5.59 ± 0.03 ef | 8.33 ± 0.30 def | 42.67 ± 0.19 ef | 40.16 ± 0.29 bc | 77.33 ± 2.08 ef |
| Z1 | 6.13 ± 0.25 cd | 8.38 ± 0.22 cde | 46.77 ± 1.91 cd | 42.24 ± 0.13 ab | 78.33 ± 2.31 ef |
| Z2 | 6.67 ± 0.31 b | 8.62 ± 0.22 c | 50.91 ± 2.4 b | 43.61 ± 0.18 a | 80.33 ± 3.31 de |
| G + C | 6.92 ± 0.19 ab | 9.40 ± 0.02 ab | 52.82 ± 1.45 b | 42.40 ± 0.20 ab | 88.00 ± 0.00 bc |
| G + Z1 | 4.96 ± 0.19 g | 7.91 ± 0.39 ef | 37.86 ± 1.46 g | 38.54 ± 0.24 c | 70.67 ± 1.15 g |
| G + Z2 | 5.83 ± 0.31 de | 8.00 ± 0.29 def | 44.55 ± 2.40 de | 42.19 ± 0.03 ab | 74.33 ± 2.52 fg |
| C + Z1 | 6.13 ± 0.25 cd | 8.56 ± 0.26 sd | 46.77 ± 1.91 cd | 41.70 ± 0.03 ab | 79.67 ± 2.52 de |
| C + Z2 | 6.29 ± 0.31 c | 8.89 ± 0.64 bc | 48.05 ± 2.40 c | 41.48 ± 0.40 abc | 83.33 ± 5.86 cd |
| G + C + Z1 | 6.83 ± 0.07 ab | 9.54 ± 0.31 a | 52.18 ± 0.55 b | 41.74 ± 0.25 ab | 89.00 ± 3.00 b |
| G + C + Z2 | 7.07 ± 0.16 a | 9.93 ± 0.40 a | 57.03 ± 1.21 a | 41.58 ± 0.25 abc | 98.00 ± 3.00 a |
| LSD | 0.37 | 0.57 | 2.79 | 0.37 | 4.81 |
| Treatments | Grains | Straw | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | P (%) | K (%) | Zn (mg kg−1) | N (%) | P (%) | K (%) | Zn (mg kg−1) | |
| CK | 0.98 ± 0.04 h | 0.07 ± 0.01 h | 0.30 ± 0.01 f | 9.57 ± 0.00 i | 0.51 ± 0.03 g | 0.02 ± 0.00 h | 0.89 ± 0.07 d | 3.14 ± 0.00 h |
| G | 1.16 ± 0.10 g | 0.10 ± 0.02 gh | 0.32 ± 0.03 e | 10.68 ± 0.10 h | 0.61 ± 0.03 efg | 0.04 ± 0.01 gh | 0.96 ± 0.07 d | 3.46 ± 0.00 gh |
| C | 1.24 ± 0.04 fg | 0.13 ± 0.05 fg | 0.34 ± 0.01 e | 11.90 ± 0.01 f | 0.55 ± 0.06 fg | 0.07 ± 0.01 f | 0.97 ± 0.05 d | 3.62 ± 0.01 fg |
| Z1 | 1.37 ± 0.01 de | 0.19 ± 0.01 cd | 0.40 ± 0.01 cd | 11.22 ± 0.00 g | 0.69 ± 0.06 cde | 0.11 ± 0.01 e | 1.18 ± 0.03 bc | 3.90 ± 0.10 def |
| Z2 | 1.49 ± 0.00 c | 0.22 ± 0.01 bc | 0.41 ± 0.01 abc | 12.64 ± 0.10 de | 0.66 ± 0.02 def | 0.17 ± 0.02 c | 1.28 ± 0.04 a | 4.21 ± 0.00 bcd |
| G + C | 1.54 ± 0.05 c | 0.24 ± 0.01 ab | 0.43 ± 0.01 ab | 13.03 ± 0.67 c | 0.76 ± 0.03 abcd | 0.21 ± 0.03 ab | 1.24 ± 0.09 ab | 4.49 ± 0.37 ab |
| G + Z1 | 1.31 ± 0.01 ef | 0.09 ± 0.01 h | 0.32 ± 0.02 e | 10.76 ± 0.01 h | 0.71 ± 0.06 bcde | 0.06 ± 0.01 fg | 0.93 ± 0.02 d | 3.78 ± 0.00 efg |
| G + Z2 | 1.45 ± 0.01 cd | 0.15 ± 0.01 ef | 0.38 ± 0.02 d | 12.43 ± 0.01 e | 0.80 ± 0.02 abc | 0.14 ± 0.02 d | 1.15 ± 0.05 c | 4.04 ± 0.00 cde |
| C + Z1 | 1.47 ± 0.08 cd | 0.17 ± 0.01 de | 0.41 ± 0.01 bc | 13.10 ± 0.10 c | 0.83 ± 0.07 ab | 0.19 ± 0.01 bc | 1.23 ± 0.02 abc | 4.26 ± 0.03 bc |
| C + Z2 | 1.66 ± 0.06 b | 0.21 ± 0.04 bc | 0.39 ± 0.02 cd | 12.87 ± 0.01 cd | 0.85 ± 0.11 a | 0.16 ± 0.00 cd | 1.15 ± 0.04 c | 4.38 ± 0.54 bc |
| G + C+ Z1 | 1.78 ± 0.15 a | 0.24 ± 0.02 ab | 0.41 ± 0.01 bc | 14.18 ± 0.01 b | 0.84 ± 0.17 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 ab | 1.23 ± 0.05 abc | 4.42 ± 0.00 b |
| G + C+ Z2 | 1.81 ± 0.00 a | 0.25 ± 0.02 a | 0.43 ± 0.01 a | 15.55 ± 0.01 a | 0.82 ± 0.07 ab | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 1.29 ± 0.06 a | 4.81 ± 0.01 a |
| LSD (0.05) | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Sharkawy, M.; Alotaibi, M.O.; Li, J.; Mahmoud, E.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Ramadan, M.S.; Shabana, M. Effect of Nano-Zinc Oxide, Rice Straw Compost, and Gypsum on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Yield and Soil Quality in Saline–Sodic Soil. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171450
El-Sharkawy M, Alotaibi MO, Li J, Mahmoud E, Ghoneim AM, Ramadan MS, Shabana M. Effect of Nano-Zinc Oxide, Rice Straw Compost, and Gypsum on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Yield and Soil Quality in Saline–Sodic Soil. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(17):1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171450
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Sharkawy, Mahmoud, Modhi O. Alotaibi, Jian Li, Esawy Mahmoud, Adel M. Ghoneim, Mohamed S. Ramadan, and Mahmoud Shabana. 2024. "Effect of Nano-Zinc Oxide, Rice Straw Compost, and Gypsum on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Yield and Soil Quality in Saline–Sodic Soil" Nanomaterials 14, no. 17: 1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171450
APA StyleEl-Sharkawy, M., Alotaibi, M. O., Li, J., Mahmoud, E., Ghoneim, A. M., Ramadan, M. S., & Shabana, M. (2024). Effect of Nano-Zinc Oxide, Rice Straw Compost, and Gypsum on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Yield and Soil Quality in Saline–Sodic Soil. Nanomaterials, 14(17), 1450. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14171450








