Interfacial Properties of Anisotropic Monolayer SiAs Transistors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
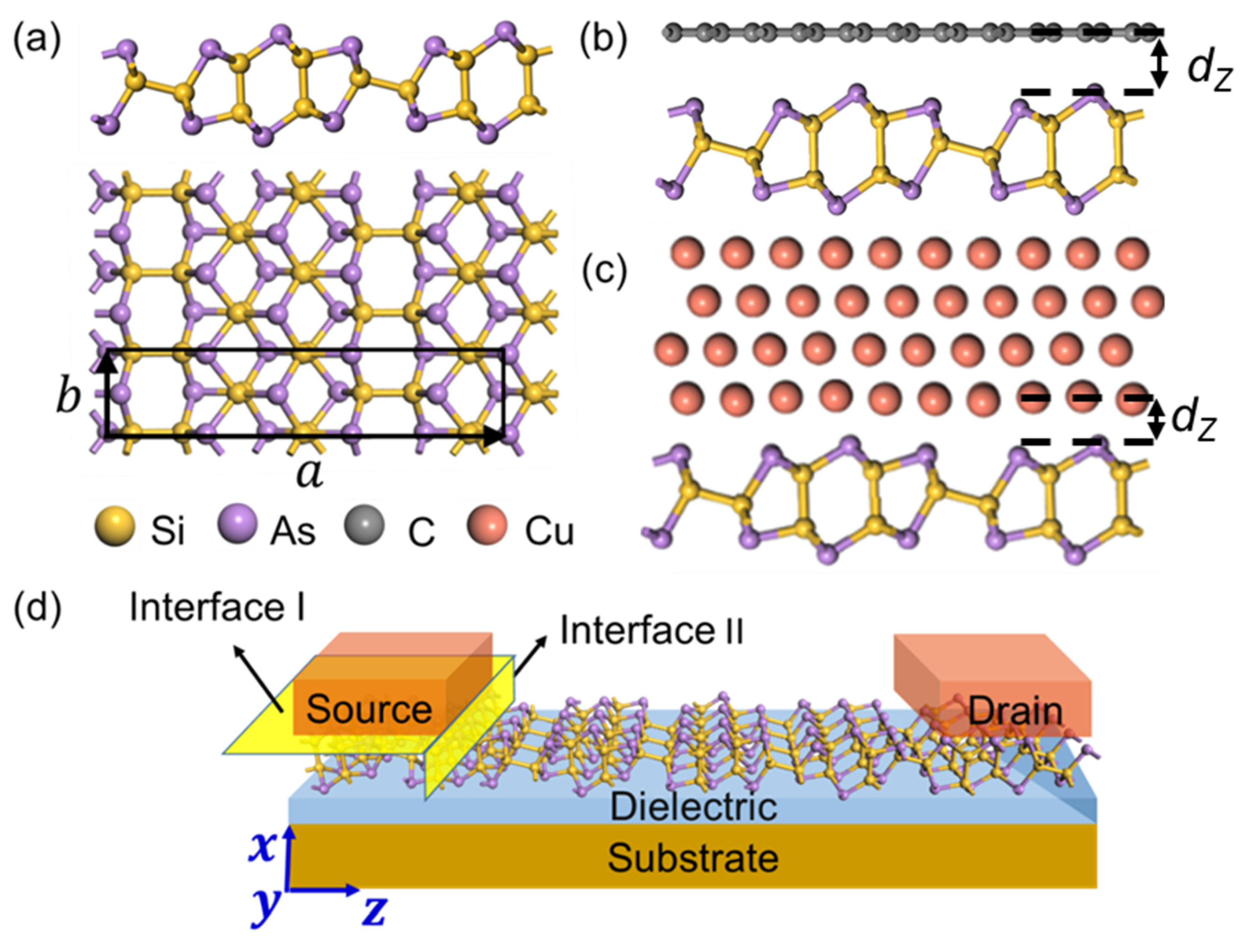
2.1. Interface and Device Models
2.2. Computational Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Binding Degree and Electronic Structure of the ML SiAs/Electrode Interfaces
3.2. Schottky and Tunneling Barrier in ML SiAs Transistors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shalf, J. The future of computing beyond Moore’s Law. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Duan, X.D.; Shin, H.J.; Park, S.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X. Promises and prospects of two-dimensional transistors. Nature 2021, 591, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Duan, X.D.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X. Two-dimensional transistors beyond graphene and TMDCs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6388–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Sebastian, A.; Pop, E.; McClellan, C.J.; Franklin, A.D.; Grasser, T.; Knobloch, T.; Illarionov, Y.; Penumatcha, A.V.; Appenzeller, J.; et al. Transistors based on two-dimensional materials for future integrated circuits. Nat. Electron. 2021, 4, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, T.X.; Boyle, A.; Bahreman, A.; Bao, L.; Jing, Q.; Xue, H.; Kieltyka, R.; Kros, A.; Schneider, G.F.; et al. Dielectric-modulated biosensing with ultrahigh-frequency-operated graphene field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2106666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quhe, R.G.; Liu, J.C.; Wu, J.X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, T.; Guo, Y.; Yang, J.; Peng, H.; et al. High-performance sub-10 nm monolayer Bi2O2Se transistors. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.M.; Ying, J.S.; Yan, M.Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Li, S.S.; Chen, T.W.; Gao, G.Y.; Liao, F.; Luo, H.S.; Zhang, T.; et al. Optoelectronic coincidence detection with two-dimensional Bi2O2Se ferroelectric field-effect transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.B.; Madhvapathy, S.R.; Sachid, A.B.; Llinas, J.P.; Wang, Q.; Ahn, G.H.; Pitner, G.; Kim, M.J.; Bokor, J.; Hu, C.; et al. MoS2 transistors with 1-nanometer gate lengths. Science 2016, 354, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Tian, H.; Shen, Y.; Hou, Z.; Ren, J.; Gou, G.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.-L. Vertical MoS2 transistors with sub-1-nm gate lengths. Nature 2022, 603, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, B.; Xu, L.; Yan, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, J. Sub-5 nm monolayer MoS2 transistors toward low-power devices. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.W.; Dong, B.J.; Wang, H.D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Z.V.; Zhang, H. In-plane anisotropic electronics based on low-symmetry 2D materials: Progress and prospects. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Guo, Q.S.; Xie, Y.J.; Zhao, H.; Li, C.; Cha, J.J.; Xia, F.; Wang, H. Anisotropic black phosphorus synaptic device for neuromorphic applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4991–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.F.; Wu, J.B.; Zhou, L.; Qiao, J.; Shi, W.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ji, W.; Tan, P.H. Polytypism and unexpected strong interlayer coupling in two-dimensional layered ReS2. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 8324–8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.J.; Cheng, K.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Chand, P.K.; Paul Inbaraj, C.R.; Peng, Y.-L.; Yang, J.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-T. Near-infrared electroluminescent light-emitting transistors based on CVD-synthesized ambipolar ReSe2 nanosheets. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2102580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quhe, R.G.; Chen, J.X.; Lu, J. A sub-10 nm monolayer ReS2 transistor for low-power applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Yin, K.; Yang, Z.J.; Huang, H.; Li, X.; Shu, Z.; Duan, H.; He, J.; Jiang, J. Polarization-perceptual anisotropic two-dimensional ReS2 neuro-transistor with reconfigurable neuromorphic vision. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.Y.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhu, C.; Shen, W.; Hu, C.; Fu, W.; Yan, L.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, L.; Lei, H.; et al. Penta-PdPSe: A new 2D pentagonal material with highly in-plane optical, electronic, and optoelectronic anisotropy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dushaq, G.; Rasras, M. Planar Multilayered 2D GeAs Schottky Photodiode for High-Performance Visible-Near-Infrared Photodetection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21499–21506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cui, X.; Huang, Q.; Zeng, H. Adsorption behavior of small molecule on monolayered SiAs and sensing application for NO2 toxic gas. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 613, 156010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreteau, C.; Michon, B.; Besnard, C.; Giannini, E. High-pressure melt growth and transport properties of SiP, SiAs, GeP, and GeAs 2D layered semiconductors. J. Cryst. Growth 2016, 443, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Park, K.; Lee, J.H.; Kwon, I.S.; Kwak, I.H.; Park, J. Anisotropic 2D SiAs for high-performance UV-visible photodetectors. Small 2021, 17, 2006310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagami, S.; Urakami, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Hashimoto, Y. Solid-source vapor growth and optoelectronic properties of arsenic-based layered group-IV monopnictides. CrystEngComm 2022, 24, 4085–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xie, L.; Ma, Z.; Qian, Z.; Liao, J.; Hussain, S.; Liu, H.; Qiu, H.; Wu, J.; Hu, Z. High-Performance Photodetectors Based on the 2D SiAs/SnS2 Heterojunction. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.F.; Wu, W.J.; Xu, Y.H.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Ye, Y.; Liang, C.; Zeng, X.C. Two-dimensional IV-V monolayers with highly anisotropic carrier mobility and electric transport properties. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, B.; Rabczuk, T. Anisotropic mechanical properties and strain tuneable band-gap in single-layer SiP, SiAs, GeP and GeAs. Phys. E Low. Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2018, 103, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.Q.; He, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, H.; Chen, R.S. Monolayered silicon and germanium monopnictide semiconductors: Excellent stability, high absorbance, and strain engineering of electronic properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5133–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.F.; Fu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Wan, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, B.; Shao, L.; Ho, C.H.; et al. Integrated digital inverters based on two-dimensional anisotropic ReS2 field-effect transistors. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.N.; Wang, H.; Jia, Y.C. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Zhou, S.; Liu, N.S.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, J. Selecting electrode materials for monolayer ReS2 with an Ohmic contact. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 6764–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.y.; Ma, D.; Wang, B. Design of MXene contacts for high-performance WS2 transistors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 527, 146701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Colombo, L.; Wallace, R.M.; Cho, K. The unusual mechanism of partial fermi level pinning at metal—MoS2 interfaces. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1714–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Moon, I.; Lee, D.; Choi, M.S.; Ahmed, F.; Nam, S.; Cho, Y.; Shin, H.-J.; Park, S.; Yoo, W.J. Fermi level pinning at electrical metal contacts of monolayer molybdenum dichalcogenides. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1588–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, K.; Dandu, M.; Watanabe, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Majumdar, K. Accurate extraction of schottky barrier height and universality of fermi level de-pinning of van der Waals contacts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2010513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Guo, Y.Z.; Robertson, J. Reduced fermi level pinning at physisorptive sites of moire-MoS2/metal Schottky barriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 11903–11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.L.; Luo, P.; Han, W.; Yang, S.; Zhou, S.; Li, H.; Zhai, T. Approaching ohmic contact to two-dimensional semiconductors. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Ren, J.C.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, S.; Liu, W. van der Waals stacking induced transition from Schottky to Ohmic contacts: 2D metals on multilayer InSe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3110–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Li, Q.H.; Quhe, R.; Yang, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Schottky barrier heights in two-dimensional field-effect transistors: From theory to experiment. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2021, 84, 056501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 59, 1758–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jií, K.; Bowler, D.R.; Michaelides, A. Chemical accuracy for the van der Waals density functional. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 022201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidstrup, S.; Markussen, T.; Vancraeyveld, P.; Wellendorff, J.; Schneider, J.; Gunst, T.; Verstichel, B.; Stradi, D.; Khomyakov, P.A.; Vej-Hansen, U.G.; et al. QuantumATK: An integrated platform of electronic and atomic-scale modelling tools. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2020, 32, 015901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Ye, M.; Quhe, R.; Zhong, H.; Song, Z.; Peng, X.; Yu, D.; Yang, J.; Shi, J.; et al. Monolayer phosphorene–metal contacts. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Dan, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Ye, M.; Zhang, H.; Quhe, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Guo, W.; Yang, L.; et al. Schottky barriers in bilayer phosphorene transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12694–12705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Pan, Y.Y.; Ye, M.; Quhe, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dan, Y.; Song, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Three-layer phosphorene-metal interfaces. Nano Res. 2017, 11, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Kim, K.S. Carbon nanotube, graphene, nanowire, and molecule-based electron and spin transport phenomena using the nonequilibrium Green’s function method at the level of first principles theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.J. GeAs and SiAs monolayers: Novel 2D semiconductors with suitable band structures. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2018, 95, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; et al. n-Type Ohmic contact and p-type Schottky contact of monolayer InSe transistors. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 24641–24651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quhe, R.G.; Wang, Y.Y.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Lu, P.; Lei, M.; Lu, J. Black phosphorus transistors with van der Waals-type electrical contacts. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14047–14057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.; Nazir, M.A.; Shen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Kang, W.; Wang, Q. First-principles study of the structural, electronic, and enhanced optical properties of SnS/TaS2 heterojunction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Shen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhou, Z. Graphene/g-GeC bilayer heterostructure: Modulated electronic properties and interface contact via external vertical strains and electric fileds. Carbon 2019, 146, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Quhe, R.G.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, L.; Pan, Y.; Lei, M.; Lu, J. Ohmic contacts between monolayer WSe2 and two-dimensional titanium carbides. Carbon 2018, 135, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Dai, J.R.; Liu, Z.H.; Wu, M.; Hu, H.; Lu, J. Ohmic contacts of monolayer Tl2O field-effect transistors. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 11439–11450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhu, E.; Liao, L.; Lee, S.J.; Ding, M.; Shakir, I.; Gambin, V.; Huang, Y.; Duan, X. Approaching the Schottky-Mott limit in van der Waals metal-semiconductor junctions. Nature 2018, 557, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Cho, Y.; Byun, K.E.; Shin, K.W.; Nam, S.G.; Kim, C.; Kim, H.; Han, S.A.; Kim, S.W.; Shin, H.J.; et al. Two-Dimensional Materials Inserted at the Metal/Semiconductor Interface: Attractive Candidates for Semiconductor Device Contacts. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4878–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-S.; Ding, G.; Zhou, Y.; Han, S.-T. Fermi-level depinning of 2D transition metal dichalcogenide transistors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 11407–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gong, X.; Yu, Z.; Ma, L.; Sun, W.; Gao, S.; Köroğlu, Ç.; Wang, W.; Liu, L.; Li, T.; et al. Approaching the quantum limit in two-dimensional semiconductor contacts. Nature 2023, 613, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.S.; Ding, G.L.; Feng, Z.H.; Zhang, S.R.; Mo, W.A.; Han, S.T.; Zhou, Y. MoS2 transistor with weak fermi level pinning via MXene contacts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczęśniak, D.; Hoehn, R.D.; Kais, S. Canonical Schottky barrier heights of transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers in contact with a metal. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 195315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, D.; Robertson, J. 3D Behavior of Schottky Barriers of 2D Transition-Metal Dichalcogenides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25709–25715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Graphene | V2CO2 | Au | Ag | Cu | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.15 | 2.81 | 2.84 | 2.84 | 2.39 | |
| 3.29 | 2.55 | 2.31 | 2.30 | 2.07 | |
| 0.32 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.74 | |
| 4.24 | 6.60 | 5.13 | 4.43 | 4.78 | |
| 1.51 | 1.67 | 0.40 | 0.28 | 0.45 | |
| 0.34 | 0 | 1.28 | 1.42 | 1.35 | |
| 1.56 | 1.67 | 0.47 | 0.27 | 0.33 | |
| 0.28 | 0 | 1.36 | 1.55 | 1.49 | |
| 1.85 | 1.67 | 1.68 | 1.70 | 1.80 | |
| 1.84 | 1.67 | 1.83 | 1.82 | 1.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, F.; Cong, Y.; Song, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, Q. Interfacial Properties of Anisotropic Monolayer SiAs Transistors. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030238
Zou F, Cong Y, Song W, Liu H, Li Y, Zhu Y, Zhao Y, Pan Y, Li Q. Interfacial Properties of Anisotropic Monolayer SiAs Transistors. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(3):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030238
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Feihu, Yao Cong, Weiqi Song, Haosong Liu, Yanan Li, Yifan Zhu, Yue Zhao, Yuanyuan Pan, and Qiang Li. 2024. "Interfacial Properties of Anisotropic Monolayer SiAs Transistors" Nanomaterials 14, no. 3: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030238
APA StyleZou, F., Cong, Y., Song, W., Liu, H., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhao, Y., Pan, Y., & Li, Q. (2024). Interfacial Properties of Anisotropic Monolayer SiAs Transistors. Nanomaterials, 14(3), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030238








