The Impact of ZIF-8 Particle Size Control on Low-Humidity Sensor Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of ZIF-8
2.2. Fabrication of Copper Electrode
2.3. Fabrication Method of Humidity Sensor
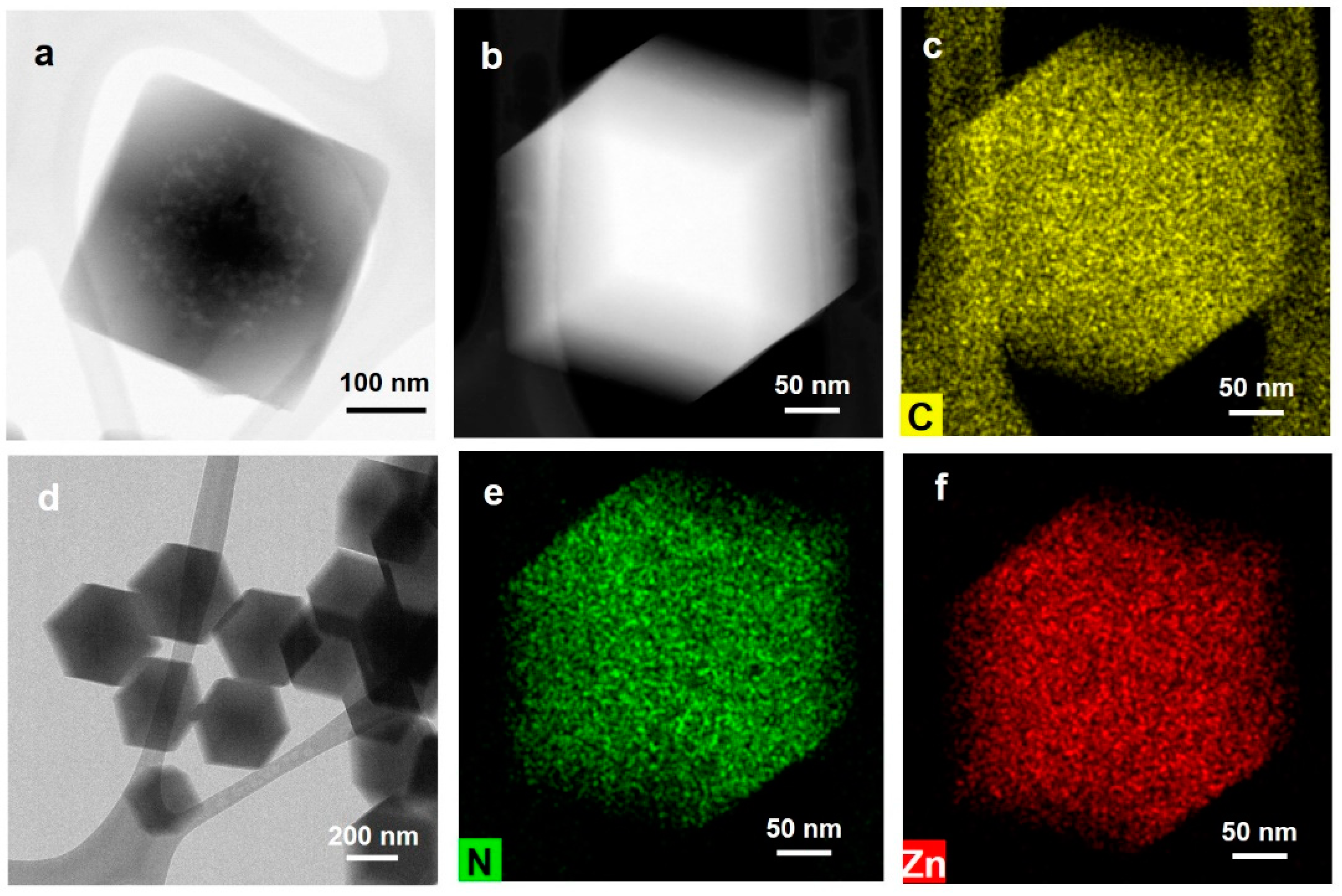
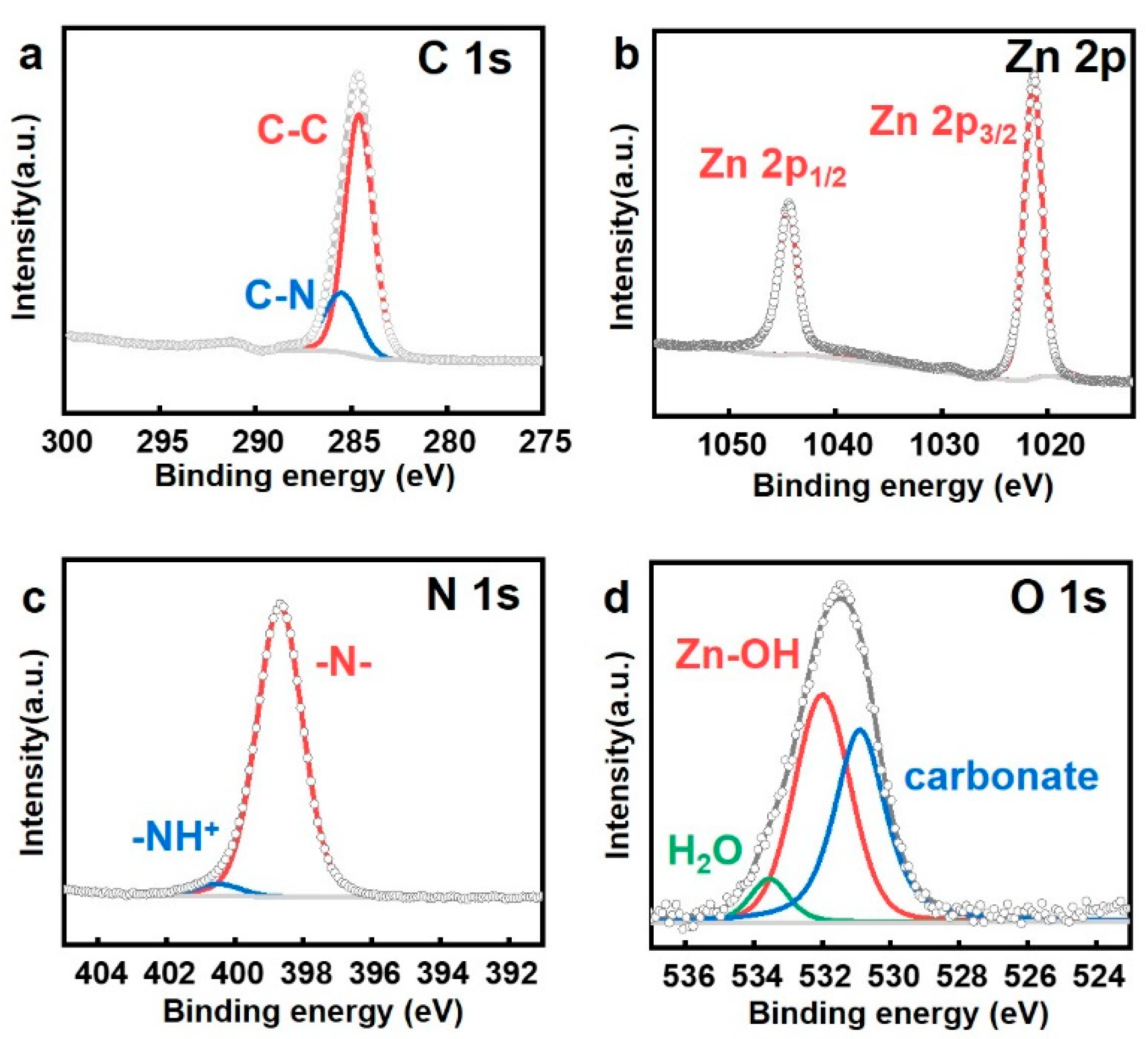
2.4. Structural Analysis of ZIF-8
2.5. Humidity Measurement Method
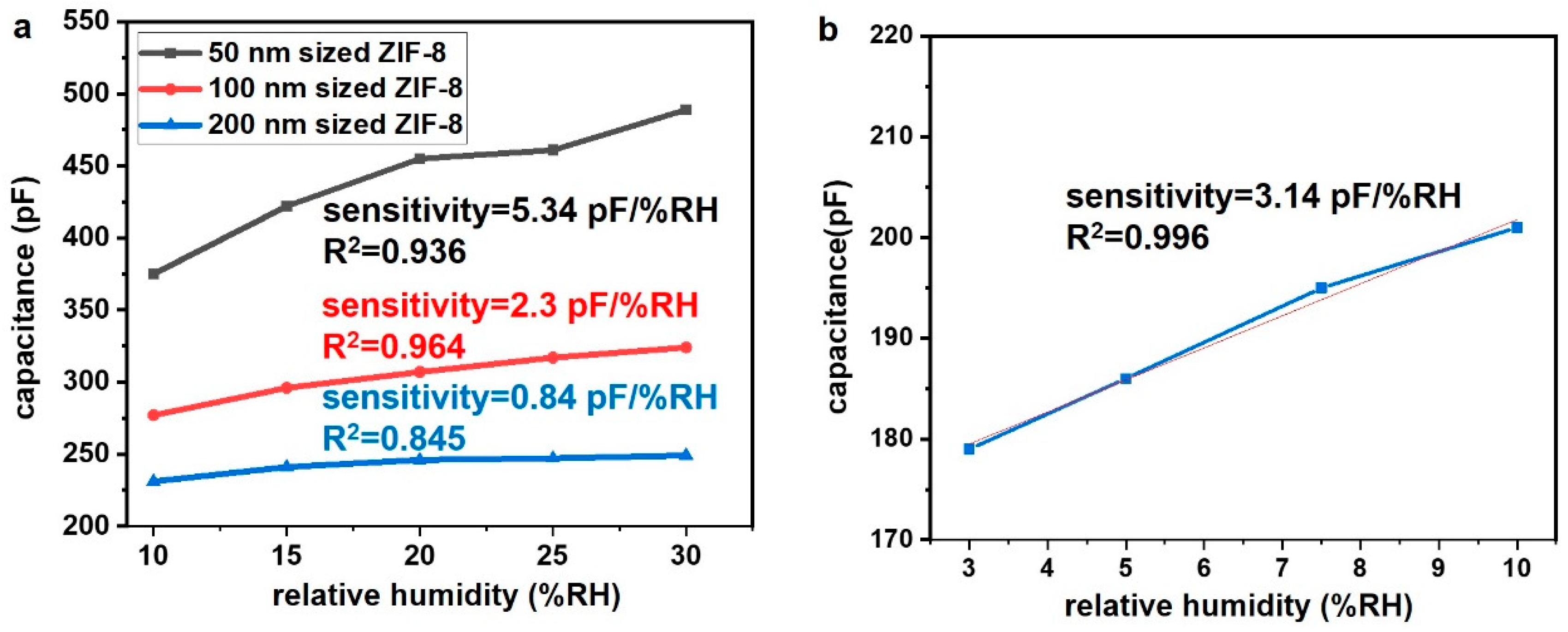
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuzubasoglu, B.A. Recent Studies on the Humidity Sensor: A Mini Review. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 4797–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, T.A.; Eksperiandova, L.P.; Belikov, K.N. Recent trends of ceramic humidity sensors development: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 416–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliszczynska-Swiglo, A.; Chmielewski, J. Electronic Nose as a Tool for Monitoring the Authenticity of Food. A Review. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1800–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkoff, P. Indoor air humidity, air quality, and health—An overview. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2018, 221, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xia, S.S.; Cao, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.G. Effect of Humidity on Properties of Lithium-ion Batteries. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 210554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Li, S.; Liang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Tai, H. High performance humidity sensor based on 3D mesoporous Co3O4 hollow polyhedron for multifunctional applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 585, 152698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, Y.A.; Evitts, R.W.; Cree, D.E.; Wilson, L.D. Polyaniline/biopolymer composite systems for humidity sensor applications: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, W.; Anwer, S.; Khan, M.U.; Sajjad, M.; Alazzam, A. 2D Ti3C2Tx-MXene nanosheets and graphene oxide based highly sensitive humidity sensor for wearable and flexible electronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 480, 147981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhen, Y.; Tai, H. Daily writing carbon ink: Novel application on humidity sensor with wide detection range, low detection limit and high detection resolution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 339, 129884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tai, H. Amorphous carbon material of daily carbon ink: Emerging applications in pressure, strain, and humidity sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 5585–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rani, R.; Zoolfakar, A.S.; Mohamad Ryeeshyam, M.F.; Ismail, A.S.; Mamat, M.H.; Alrokayan, S.; Khan, H.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Mahmood, M.R. High Surface Area to Volume Ratio 3D Nanoporous Nb2O5 for Enhanced Humidity Sensing. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 3805–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, J.; Gong, T.; Jiao, L.; Jiang, H.-L. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) beyond crystallinity: Amorphous MOFs, MOF liquids and MOF glasses. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 10562–10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Jo, S.G.; Park, G.R.; Lee, E.B.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.W. Recent Research Trend of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-67 for Bifunctional Catalyst. Korean J. Mater. Res. 2022, 32, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.M.; Jo, S.G.; Lee, E.B.; Lee, S.-K.; Lee, J.W. Recent research trend of supercapacitor and chemical sensor using composite of ZIF-8 and carbon-based material. J. Korean Inst. Surf. Eng. 2022, 55, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, T.; Gu, Y.; Li, F. Progress and potential of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for gas storage and separation: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Banga, I.K.; Muthukumar, S.; Prasad, S. Engineering the ZIF-8 pore for electrochemical sensor applications—A mini review. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 26993–27003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Khan, U.A.; Iqbal, N.; Noor, T. Zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF)-derived porous carbon materials for supercapacitors: An overview. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 43733–43750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, Y.; Song, W.J. Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for use in electrochemical and optical chemical sensing and biosensing: A review. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.G.; Joshi, B.N.; Samuel, E.; An, S.; Swihart, M.T.; Lee, J.S.; Hwang, Y.K.; Chang, J.S.; Yoon, S.S. Supersonically sprayed gas- and water-sensing MIL-100(Fe) films. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 722, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, H.Y.; Liang, B.K.; Mahmood, J.; Noh, H.J.; Hambsch, M.; Wang, M.C.; Wang, M.; Ly, K.H.; et al. In-Plane Oriented Two-Dimensional Conjugated Metal-Organic Framework Films for High-Performance Humidity Sensing. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.S.; Zeinali, S. Capacitive humidity sensing using a metal-organic framework nanoporous thin film fabricated through electrochemical in situ growth. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 3701–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, M.A.; Vijjapu, M.T.; Surya, S.G.; Shekhah, O.; Salama, K.N.; Serre, C.; Eddaoudi, M.; Roubeau, O.; Gascón, I. Methanol and Humidity Capacitive Sensors Based on Thin Films of MOF Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 4155–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Yu, Y.L.; Hou, Z.N.; Guan, X.; Zhao, H.R.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. A humidity sensor based on ionic liquid modified metal organic frameworks for low humidity detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 355, 131136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schejn, A.; Balan, L.; Falk, V.; Aranda, L.; Medjahdi, G.; Schneider, R. Controlling ZIF-8 nano- and microcrystal formation and reactivity through zinc salt variations. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 4493–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torad, N.L.; Hu, M.; Kamachi, Y.; Takai, K.; Imura, M.; Naito, M.; Yamauchi, Y. Facile synthesis of nanoporous carbons with controlled particle sizes by direct carbonization of monodispersed ZIF-8 crystals. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2521–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, M.C.; Mori, K.; Futamura, Y.; Kuwahara, Y.; Navlani-García, M.; An, T.C.; Yamashita, H. PdAg Nanoparticles within Core-Shell Structured Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework as a Dual Catalyst for Formic Acid-based Hydrogen Storage/Production. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.L.; Shen, Y.J.; Ding, J.T.; Zhou, H.B.; Zhang, Y.H.; Feng, Q.K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, K.; Xu, P.X.; Zhang, P.Y. A Combined Experimental and Computational Study on the Adsorption Sites of Zinc-Based MOFs for Efficient Ammonia Capture. Molecules 2022, 27, 5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Vyas, G.; Paul, P.; Srivastava, D.N. Gold-Nanoparticle-Encapsulated ZIF-8 for a Mediator-Free Enzymatic Glucose Sensor by Amperometry. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 3600–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luanwuthi, S.; Krittayavathananon, A.; Srimuk, P.; Sawangphruk, M. Synthesis of permselective zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/graphene oxide composites: Rotating disk electrode and Langmuir adsorption isotherm. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46617–46623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; An, X.H.; Qian, X.R. Methyl Orange-Doped Polypyrrole Promoting Growth of ZIF-8 on Cellulose Fiber with Tunable Tribopolarity for Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Polymers 2022, 14, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, J.; Wang, L.Y.; Li, R.; Chen, P.; Rao, X.; Deng, L.H.; Rong, L.; Lei, J.D. NiO-PTA supported on ZIF-8 as a highly effective catalyst for hydrocracking of Jatropha oil. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-J.; Xue, Q.-Z.; Ma, M.; Zhou, X.-Y. Capacitive humidity sensor based on amorphous carbon film/n-Si heterojunctions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Li, S.H.; Shen, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.Y. The sized controlled synthesis of MIL-101(Cr) with enhanced CO2 adsorption property. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2018, 96, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.; Bae, J.-S.; Lee, J.W. The Impact of ZIF-8 Particle Size Control on Low-Humidity Sensor Performance. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030284
Kim SJ, Lee J, Bae J-S, Lee JW. The Impact of ZIF-8 Particle Size Control on Low-Humidity Sensor Performance. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(3):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030284
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sang Jun, Jaemin Lee, Jong-Seong Bae, and Jung Woo Lee. 2024. "The Impact of ZIF-8 Particle Size Control on Low-Humidity Sensor Performance" Nanomaterials 14, no. 3: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030284
APA StyleKim, S. J., Lee, J., Bae, J.-S., & Lee, J. W. (2024). The Impact of ZIF-8 Particle Size Control on Low-Humidity Sensor Performance. Nanomaterials, 14(3), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14030284








