A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Synthesis
2.2. Cell Fabrication
2.3. Characterisation Techniques
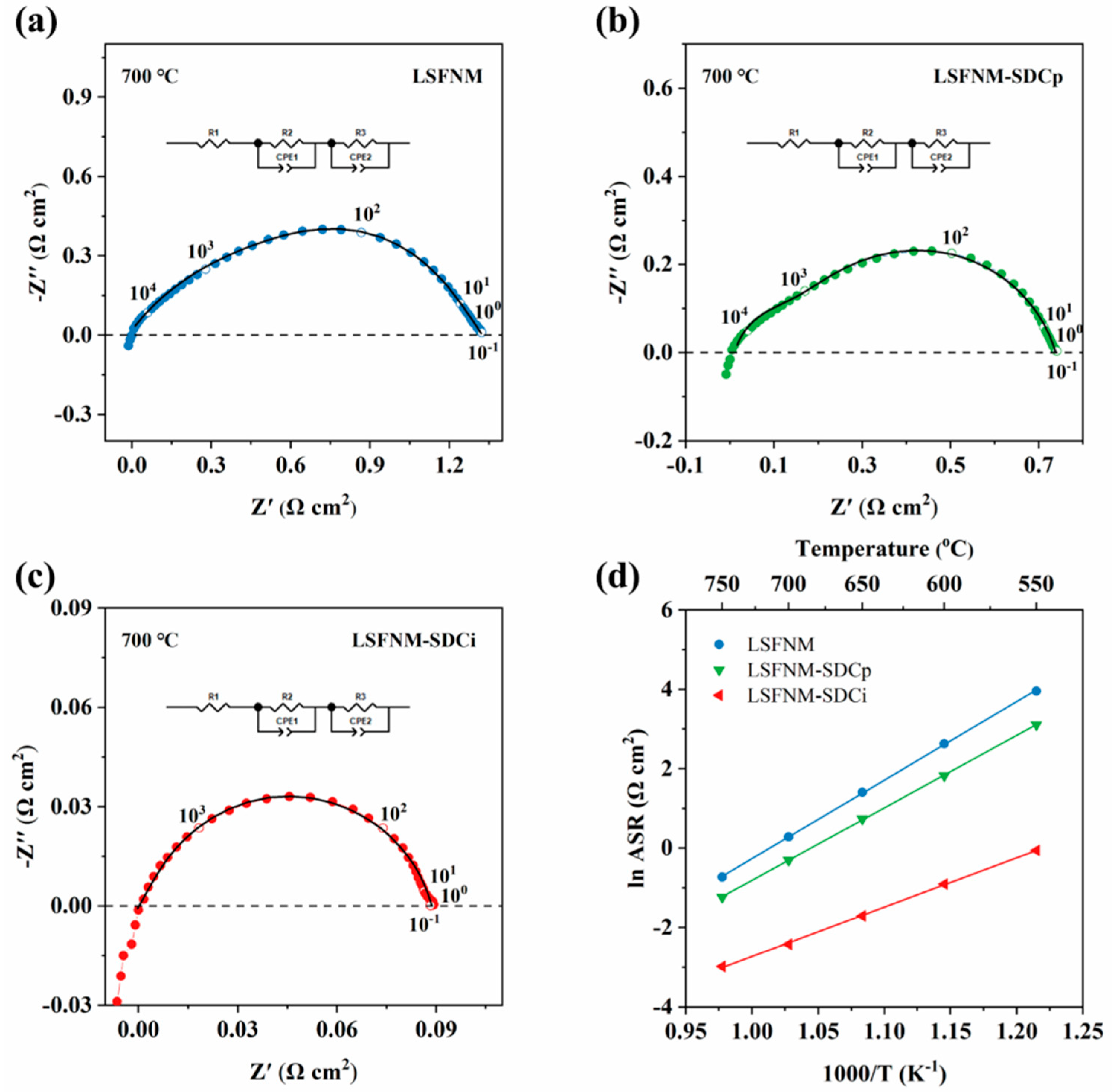
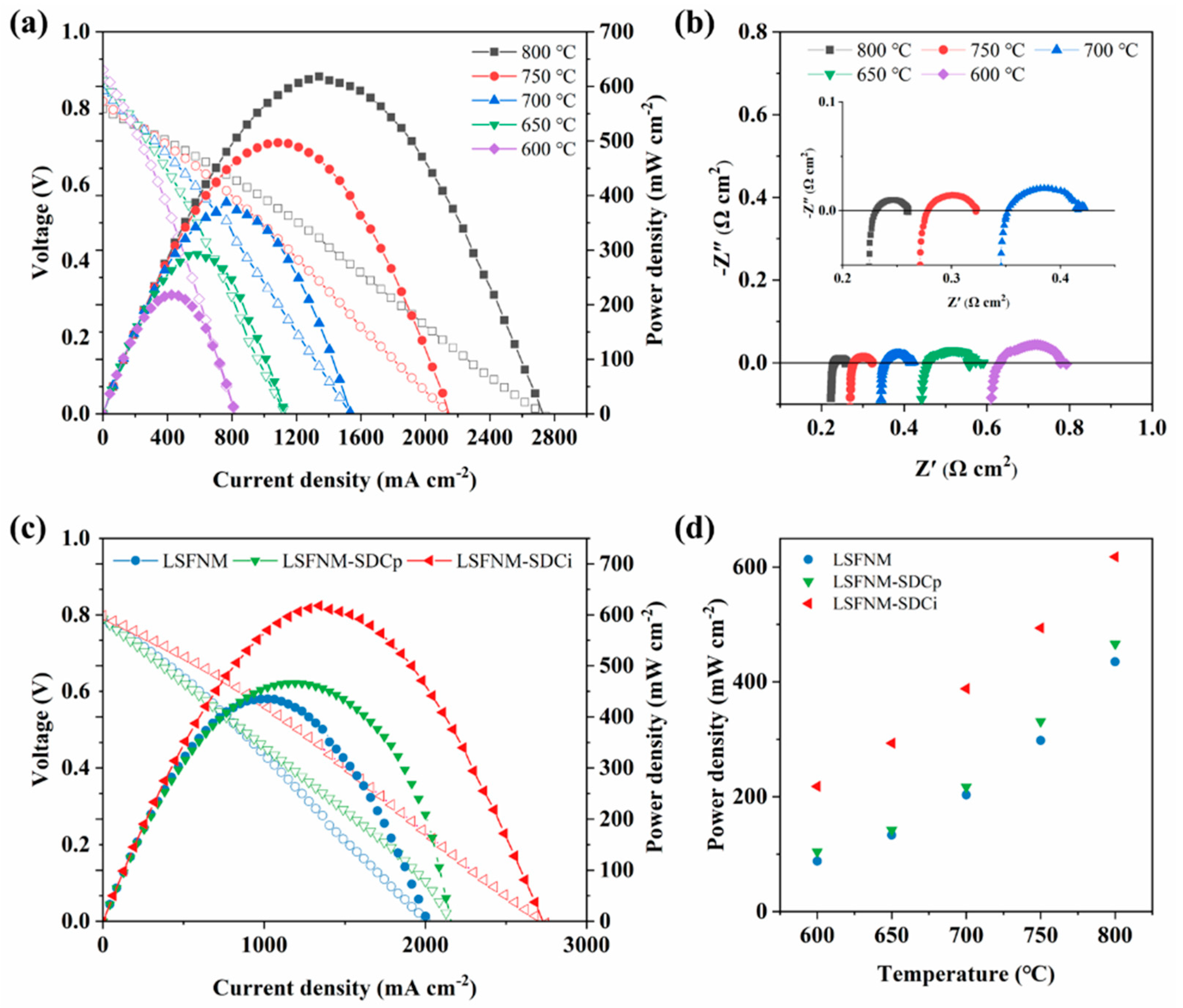
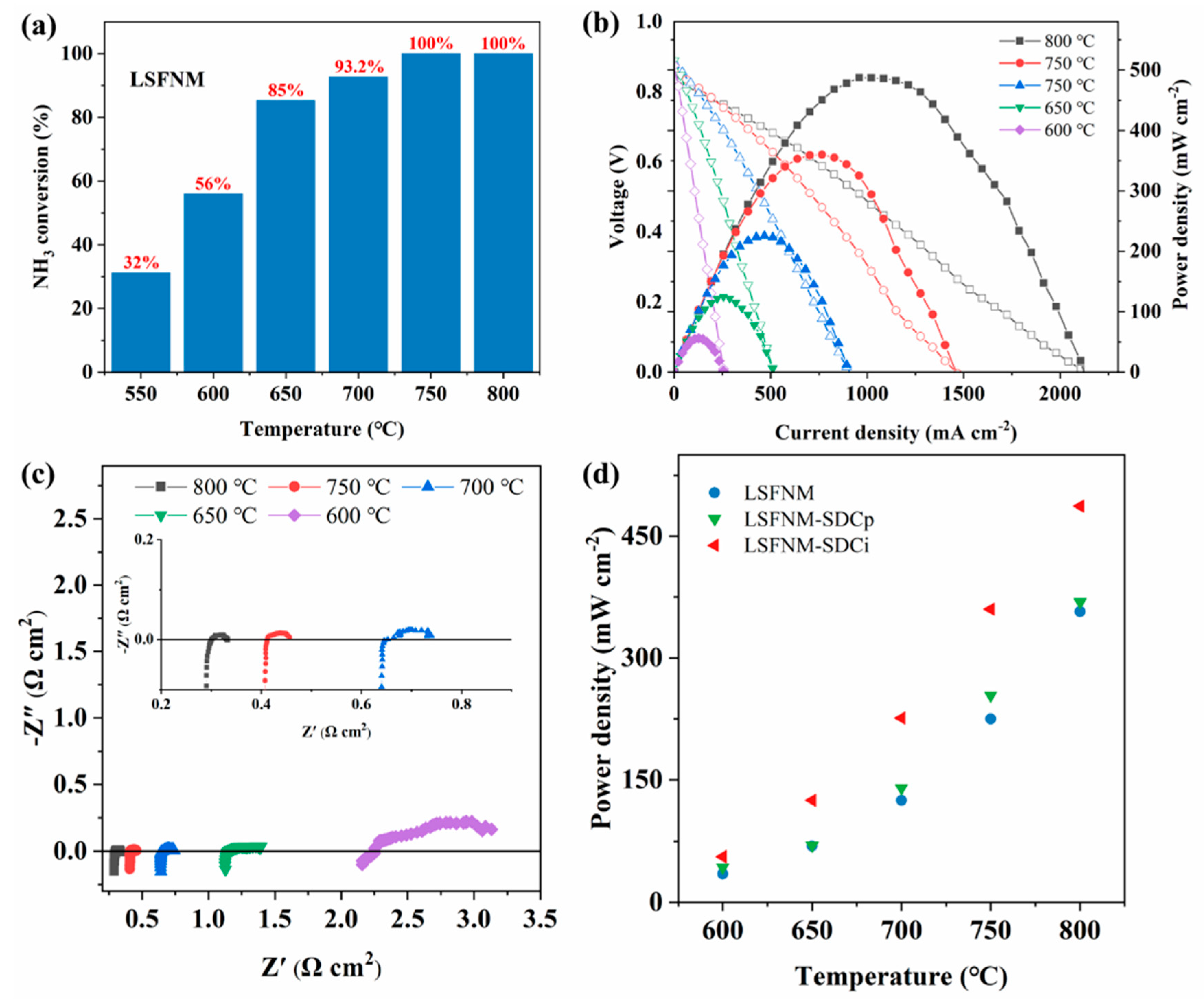
3. Results and Discussion
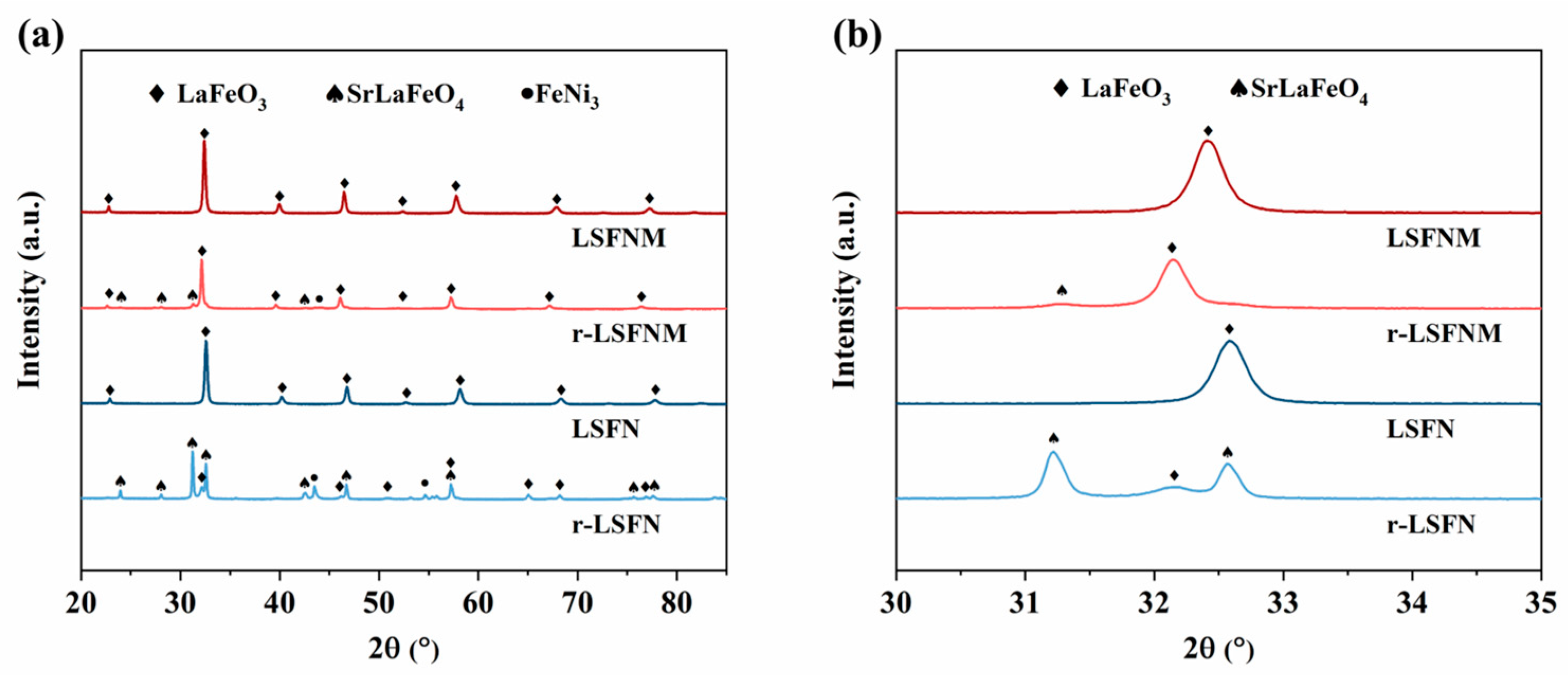
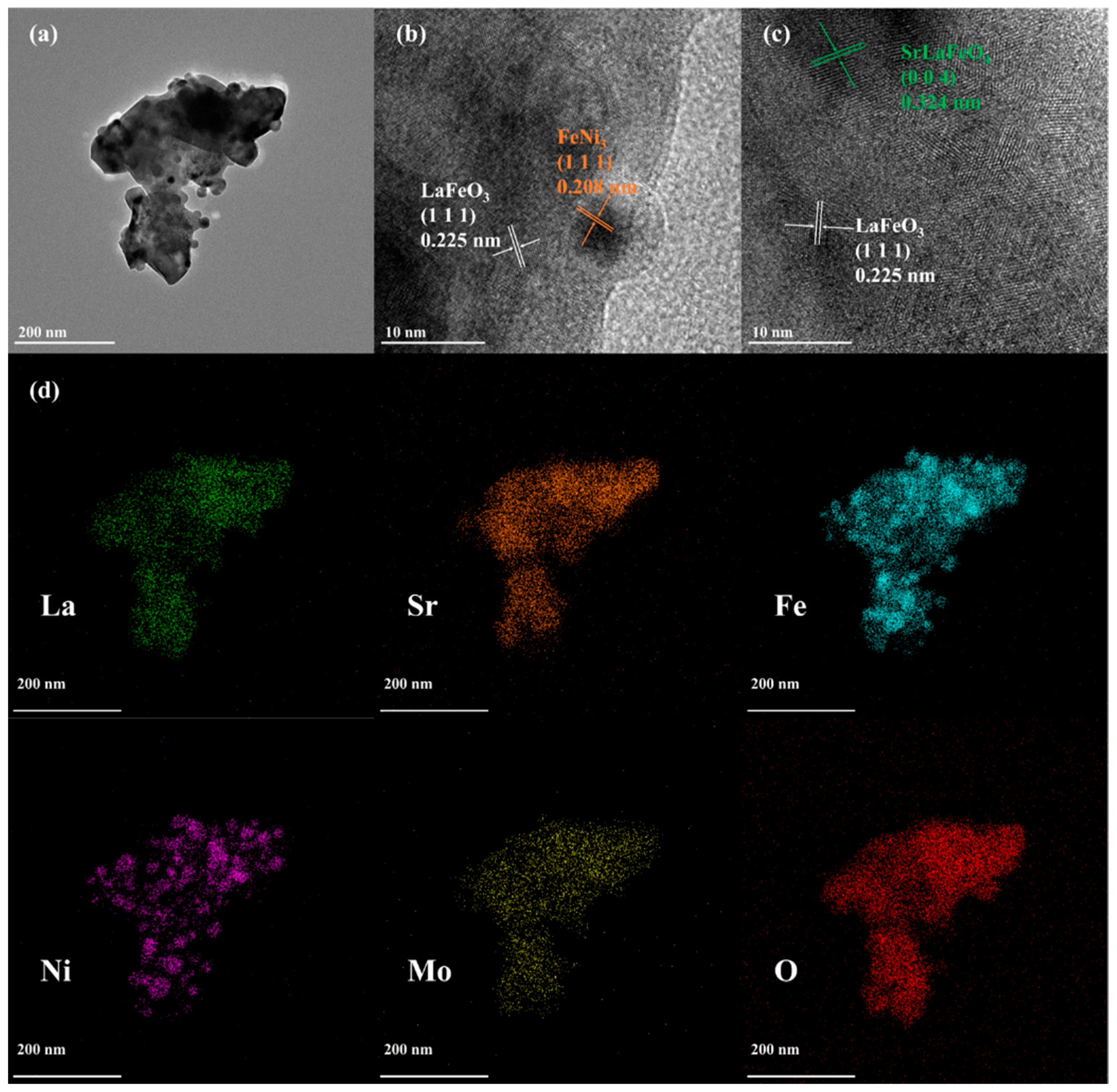
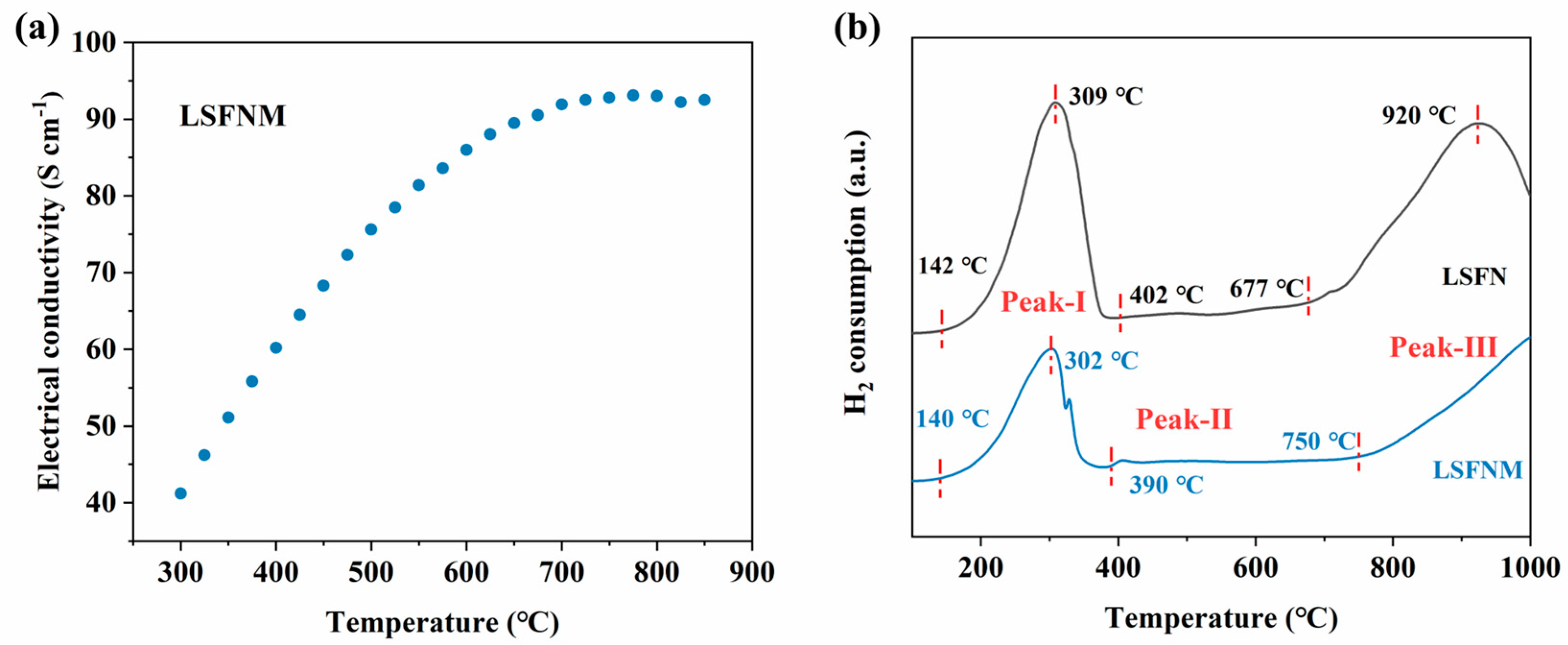
3.1. Basic Characterisation of LSFNM
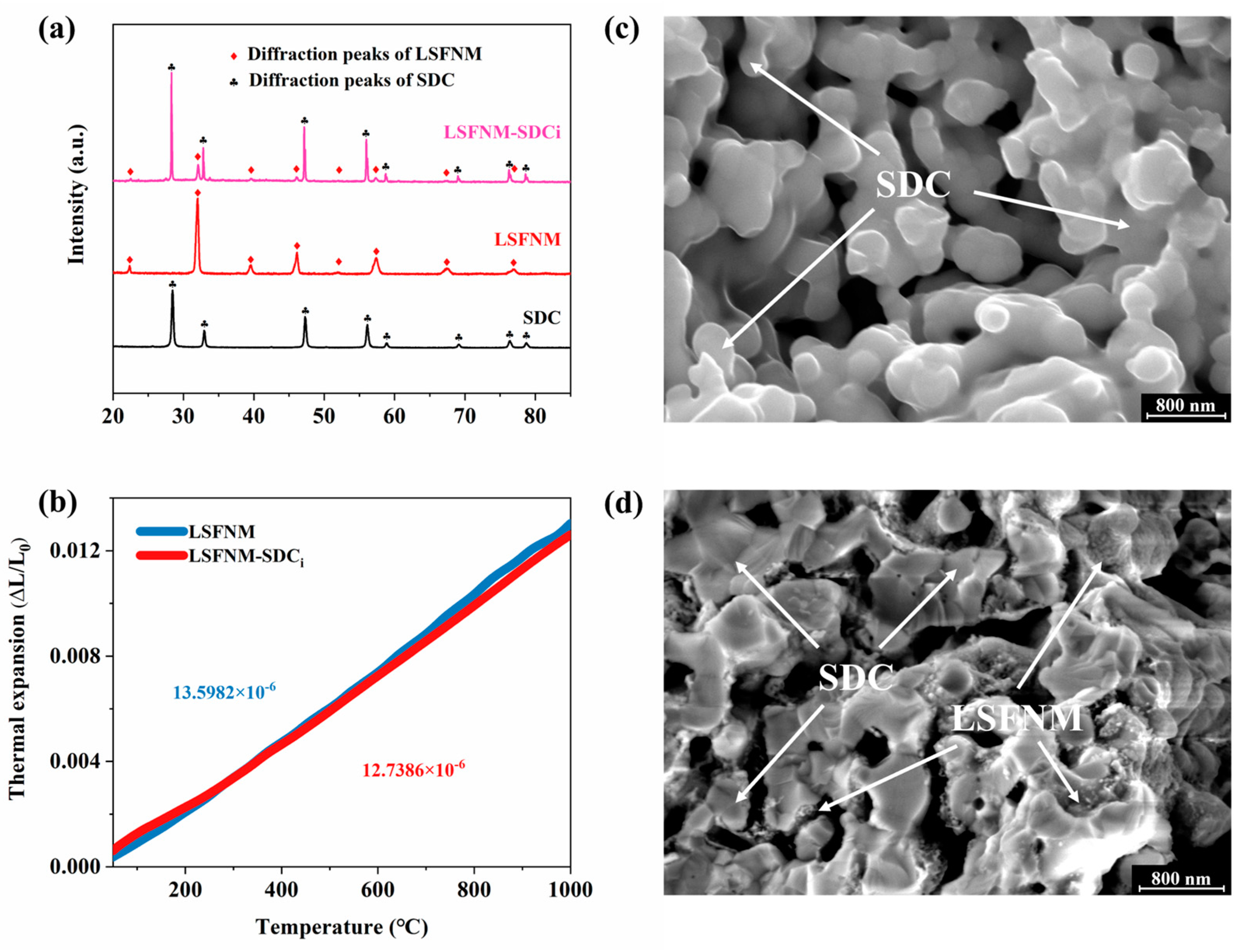
3.2. Basic Characterisation of LSFNM-Infiltrated SDC
3.3. Electrocatalytic Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Ru, X.; Yang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, S.; Hong, C.; Peng, F.; Qu, M.; Xue, C.; Lu, J.; et al. Flexible silicon solar cells with high power-to-weight ratios. Nature 2024, 626, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Wang, W.; Shao, Z. Cation-deficient perovskites for clean energy conversion. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Pang, Y.P.; Su, C.; Jiang, S.S.; Ge, L. Toward High Performance Mixed Ionic and Electronic Conducting Perovskite-Based Oxygen Permeable Membranes: An Overview of Strategies and Rationales. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 7042–7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Su, C.; Zhu, Z.H.; Wang, H.; Ge, L. Composite cathodes for protonic ceramic fuel cells: Rationales and materials. Compos. B. Eng. 2022, 238, 109881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qiu, H.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, D.; Su, C. Enhanced ORR activity of A-site-deficient SrCo0.8Nb0.1Ti0.1O3−δ as a bifunctional air electrode for low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 6740–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, T.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, T.; Dong, D.; Wang, Z. Direct ethanol solid oxide fuel cells integrated with internal reforming for renewable power generation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.T.; Wu, Y.X.; Li, L.; Xie, Z.H.; Xie, Y.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Meng, X.X.; Yu, F.Y.; Yang, N.T. A high-performance direct carbon solid oxide fuel cell powered by barium-based catalyst-loaded biochar derived from sunflower seed shell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 38747–38756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawale, D.S.; Biswas, S.; Kaur, G.; Giddey, S. Challenges and advancement in direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cells: A review. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 6176–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Sun, W.; Luo, H.; Li, C.M. Recent progress in electrochemical synthesis of carbon-free hydrogen carrier ammonia and ammonia fuel cells: A review. Mater. Rep. Energy 2022, 2, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhongde, V.; Singh, A.; Kala, J.; Anjum, U.; Haider, M.A.; Basu, S. Radio-frequency magnetron sputtered thin-film La0.5Sr0.5Co0.95Nb0.05O3−δ perovskite electrodes for intermediate temperature symmetric solid oxide fuel cell (IT-SSOFC). Mater. Rep. Energy 2022, 2, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, T.; Gong, F.; Othman, M.H.D.; Xiao, R. Ammonia as a green energy carrier: Electrochemical synthesis and direct ammonia fuel cell—A comprehensive review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 235, 107380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, S.S.; Biswas, S.; Fini, D.; Kulkarni, A.P.; Giddey, S. Direct ammonia solid-oxide fuel cells: A review of progress and prospects. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 35365–35384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, S.; Gotsch, T.; Klotzer, B. Increasing complexity approach to the fundamental surface and interface chemistry on SOFC anode materials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Molouk, A.F.S.; Okanishi, T.; Muroyama, H.; Matsui, T.; Eguchi, K. A stability study of Ni/Yttria-stabilized zirconia anode for direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28701–28707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yu, J.; Huang, X.; Zou, D.; Song, Y.; Xu, M.; Ran, R.; Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z. Slightly ruthenium doping enables better alloy nanoparticle exsolution of perovskite anode for high-performance direct-ammonia solid oxide fuel cells. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 125, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazzani, J.; Squizzato, E.; Brusamarello, E.; Glisenti, A. Exsolution in Ni-doped lanthanum strontium titanate: A perovskite-based material for anode application in ammonia-fed solid oxide fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 13921–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, M.; Yang, G.; Shao, Z. Infiltrated NiCo alloy nanoparticle decorated perovskite oxide: A highly active, stable, and antisintering anode for direct-ammonia solid oxide fuel cells. Small 2020, 16, 2001859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istomin, S.Y.; Lyskov, N.V.; Mazo, G.N.; Antipov, E.V. Electrode materials based on complex d-metal oxides for symmetrical solid oxide fuel cells. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2021, 90, 644–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuterbekov, K.A.; Nikonov, A.; Bekmyrza, K.Z.; Pavzderin, N.B.; Kabyshev, A.M.; Kubenova, M.M.; Kabdrakhimova, G.D.; Aidarbekov, N. Classification of solid oxide fuel cells. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Sun, C.; Ma, C.; Wu, H.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, L. Ni doped La0.6Sr0.4FeO3-δ symmetrical electrode for solid oxide fuel cells. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zuo, Y.; Zsurzsan, G.; Zhang, Z. La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ perovskite with in-situ exsolved Ni-Fe nanoparticles as high activity catalyst for symmetric solid oxide electrolysis cells. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 156, 111984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jia, L.; Yang, J.; Chi, B.; Pu, J.; Li, J. Cobalt-free perovskite oxide La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ as active and robust oxygen electrode for reversible solid oxide cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xi, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Medvedev, D.; Luo, J.; Fu, X. In-situ exsolved FeNi nanoparticles on perovskite matrix anode for co-production of ethylene and power from ethane in proton conducting fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 393, 139096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.M.; Su, C.; Shi, H.G.; Zhu, Y.L.; Song, Y.F.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z.P. Toward reducing the operation temperature of solid oxide fuel cells: Our past 15 years of efforts in cathode development. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 15169–15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Bian, L.; Chen, N.; Chou, K. High performance of Mo-doped La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.9Ni0.1O3−δ perovskites as anode for solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 292, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xuan, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, S.; Xia, C. Hollow La0.6Sr0.4Ni0.2Fe0.75Mo0.05O3−δ electrodes with exsolved FeNi3 in quasi-symmetrical solid oxide electrolysis cells for direct CO2 electrolysis. Electrochem. Commun. 2022, 134, 107188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, Q.; Tian, D.; Yu, W.; Lin, B. Mo-doped Pr0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ as potential electrodes for intermediate-temperature symmetrical solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 227, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Komvokis, V.G.; Amiridis, M.D.; Heyden, A.; Ma, S.; Chen, F. Synthesis and characterization of Mo-doped SrFeO3−δ as cathode materials for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2012, 202, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tian, Y.; Pu, J.; Chi, B. Anion fluorine-doped La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ perovskite cathodes with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for solid oxide electrolysis cell direct CO2 electrolysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xi, X.; Medvedev, D.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Luo, J.-L.; Fu, X.-Z. Emerging anode materials architectured with NiCoFe ternary alloy nanoparticles for ethane-fueled protonic ceramic fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 515, 230634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B.; Huang, Y.-H. Alternative anode materials for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 173, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S. Solid oxide fuel cell: Materials for anode, cathode and electrolyte. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 23988–24013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, M.; Song, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Cai, H.; Su, X.; Han, X.; Wang, S.; et al. In situ growth of LaSr(Fe,Mo)O4 ceramic anodes with exsolved Fe-Ni nanoparticles for SOFCs: Electrochemical performance and stability in H2, CO, and syngas. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 4537–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Rath, M.K.; Kwak, H.H.; Kim, H.J.; Han, J.W.; Hong, S.-T.; Lee, K.T. A highly active and redox-stable SrGdNi0.2Mn0.8O4±δ anode with in situ exsolution of nanocatalysts. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y. Molybdenum modified CeAlOx catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 386, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deganello, F.; Liotta, L.F.; Marcì, G.; Fabbri, E.; Traversa, E. Strontium and iron-doped barium cobaltite prepared by solution combustion synthesis: Exploring a mixed-fuel approach for tailored intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cell cathode materials. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2013, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Su, C.; Chen, Y.; Tadé, M.O.; Shao, Z. Nano La0.6Ca0.4Fe0.8Ni0.2O3−δ decorated porous doped ceria as a novel cobalt-free electrode for “symmetrical” solid oxide fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 19526–19535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Qiu, H.; Wang, W.; Miller, E.; Su, C. Fluorine anion-doped Ba0.6Sr0.4Co0.7Fe0.2Nb0.1O3−δ as a promising cathode for protonic ceramic fuel cells. Catalysts 2023, 13, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, W.; Qu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhou, W.; Shao, Z. Rational design of perovskite-vased anode with decent activity for hydrogen electro-oxidation and beneficial effect of sulfur for promoting power generation in solid oxide fuel cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 41257–41267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Li, P.; Zhu, Q.; Kumar, A.; Sun, K.; Tian, S.; Sun, X. Atomically precise electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem 2023, 9, 280–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, A.E.; Erdosy, D.P.; Costentin, C.; Mason, J.A.; Nocera, D.G. Enhanced activity for the oxygen reduction reaction in microporous water. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.C.; Pei, K.; Pan, Y.X.; Xu, K.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, B.T.; Sasaki, K.; Choi, Y.M.; Chen, Y.; et al. An efficient and durable anode for ammonia protonic ceramic fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yuan, W.; Sasaki, K.; Choi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, M. A high-performance and durable direct NH3 tubular protonic ceramic fuel cell integrated with an internal catalyst layer. Appl. Catal. B 2022, 306, 121071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Oh, M.J.; Hong, J.; Yoon, K.J.; Ji, H.I.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, H.; Son, J.W.; Yang, S. A comprehensive investigation of direct ammonia-fueled thin-film solid-oxide fuel cells: Performance, limitation, and prospects. iScience 2022, 25, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.Y.; Kwon, O.; Gorte, R.J.; Vohs, J.M. Metal exsolution to enhance the catalytic activity of electrodes in solid oxide fuel cells. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, W.; Fujimoto, T.; Saito, M.; Inaba, M.; Yoshida, H.; Inagaki, T. Ni-Fe/Sm-doped CeO2 anode for ammonia-fueled solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2014, 256, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, G.G.M.; Cumming, I.W.; Hellgardt, K. High performance direct ammonia solid oxide fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yin, Y.-M.; Zhou, N.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z.-F. Sulfur tolerant redox stable layered perovskite SrLaFeO4−δ as anode for solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 76, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, T. Improved thermal expansion and electrochemical performance of La1−δSrδFe0.7Ni0.3O3−δ cathodes for intermediate-temperature SOFCs. Solid State Sci. 2020, 108, 106356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Electrolyte | Anode | Cathode | Electrolyte Thickness (µm) | PPD at 800 °C (mW cm−2) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDC | LSFNM-SDCi | LSFNM-SDCi | 300 | 487 | This work |
| SDC | Pr0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.78O3−δ | BaCo0.4Fe0.4Zr0.1Y0.1O3−δ | 400 | 288 | [15] |
| SDC | Pr0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.75Ru0.05O3−δ | BaCo0.4Fe0.4Zr0.1Y0.1O3−δ | 400 | 374 | [15] |
| SDC | La0.52Sr0.28Ti0.94Ni0.06O3−δ-SDC | Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ | 350 | 161 | [17] |
| SDC | La0.52Sr0.28Ti0.94Co0.06O3−δ-SDC | Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ | 350 | 98 | [17] |
| SDC | La0.52Sr0.28Ti0.94Ni0.03Co0.03O3−δ-SDC | Ba0.5Sr0.5Co0.8Fe0.2O3−δ | 350 | 361 | [17] |
| La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.85 | Ni-SDC | Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3−δ | 500 | 118 | [46] |
| La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.85 | Ni(40)Fe(60)-SDC | Sm0.5Sr0.5CoO3−δ | 500 | 250 | [46] |
| 6mol% YSZ | Ni-YSZ | Ag | 400 | 75 | [47] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Liang, Z.; Qiu, H.; Yi, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Su, C.; Yang, T. A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080673
Jiang H, Liang Z, Qiu H, Yi Y, Jiang S, Xu J, Wang W, Su C, Yang T. A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode. Nanomaterials. 2024; 14(8):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080673
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Hao, Zhixian Liang, Hao Qiu, Yongning Yi, Shanshan Jiang, Jiahuan Xu, Wei Wang, Chao Su, and Tao Yang. 2024. "A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode" Nanomaterials 14, no. 8: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080673
APA StyleJiang, H., Liang, Z., Qiu, H., Yi, Y., Jiang, S., Xu, J., Wang, W., Su, C., & Yang, T. (2024). A High-Performance and Durable Direct-Ammonia Symmetrical Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Nano La0.6Sr0.4Fe0.7Ni0.2Mo0.1O3−δ-Decorated Doped Ceria Electrode. Nanomaterials, 14(8), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14080673








