Effect of Graphene-Graphene Oxide Modified Anode on the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Electrode Fabrication
2.3. MFC Construction and Operation
2.4. Measurement and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
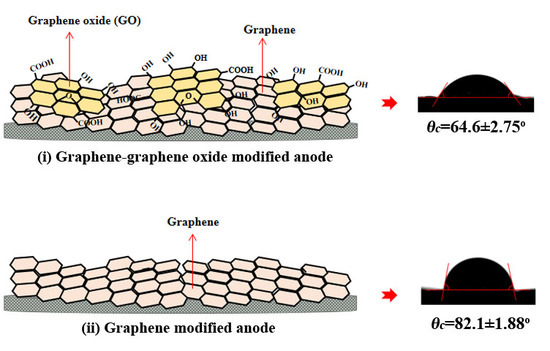
3.1. Hydrophilicity of G-GO Anodes
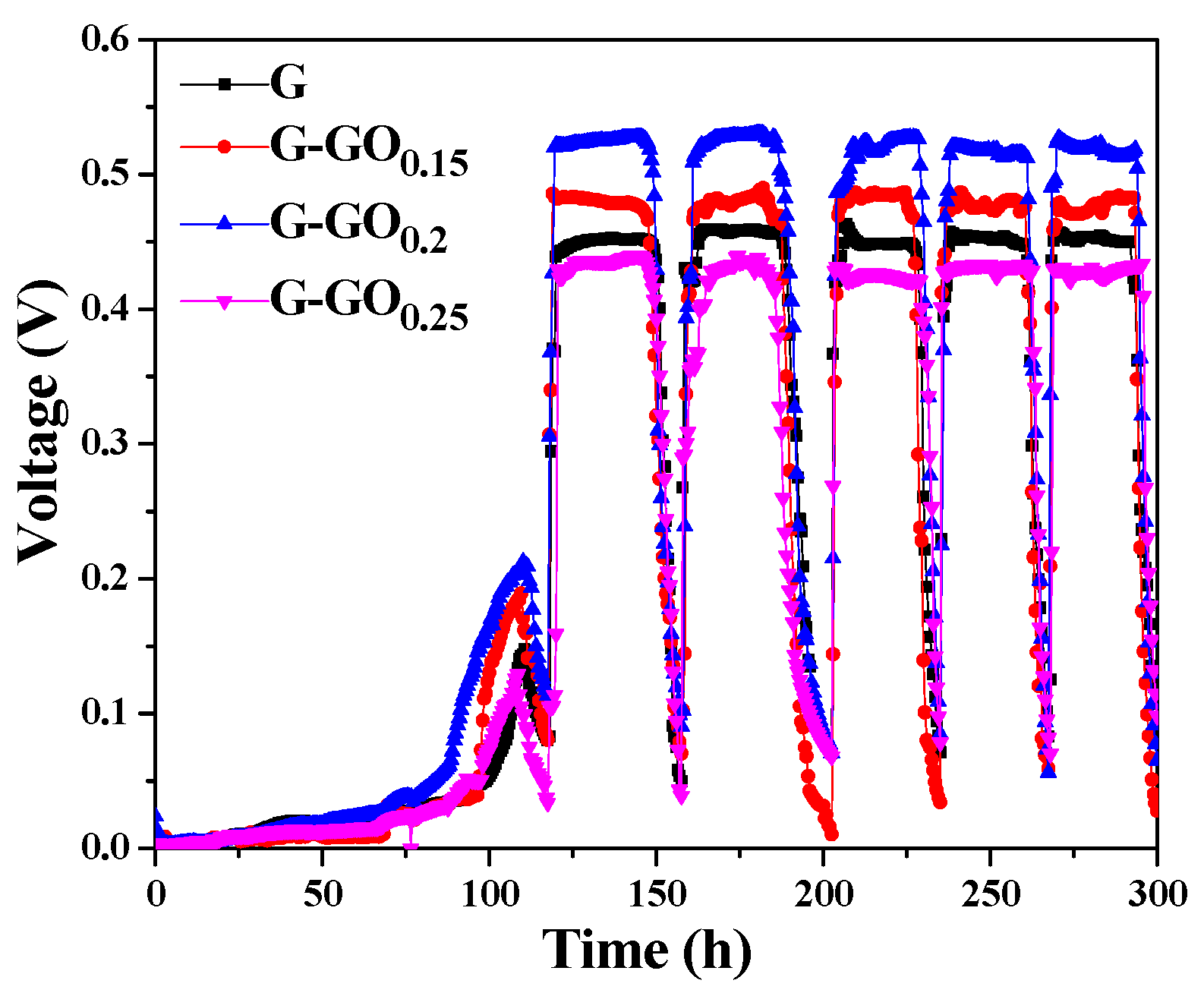
3.2. Performance of G-GO Anodes
3.3. Substrate Utilization and Coulombic Recovery
3.4. Electrochemical Characterization of G and GO Anodes
3.5. Anode Biomass
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Logan, B.E.; Regan, J.M. Microbial fuel cells-challenges and applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5172–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.W.; Yu, H.Q.; He, Z. Towards sustainable wastewater treatment by using microbial fuel cells-centered technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullen, R.A.; Arnot, T.C.; Lakeman, J.B.; Walsh, F.C. Biofuel cells and their development. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 2015–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, M.V.; Kumar, G.G. Current status, key challenges and its solutions in the design and development of graphene based ORR catalysts for the microbial fuel cell applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Yang, N.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Hua, Z.; Wang, X. Effect of binder-free graphene-cetyltrimethylammonium bromide anode on the performance of microbial fuel cells. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commault, A.S.; Barrière, F.; Lapinsonnière, L.; Lear, G.; Bouvier, S.; Weld, R.J. Influence of inoculum and anode surface properties on the selection of Geobacter-dominated biofilms. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 195, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, K.; Freguia, S.; Dennis, P.G.; Chen, X.; Donose, B.C.; Keller, J.; Gooding, J.J.; Rabaey, K. Effects of surface charge and hydrophobicity on anodic biofilm formation, community composition, and current generation in bioelectrochemical systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7563–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Mo, G.Q.; Li, X.W.; Zhang, W.D.; Zhang, J.Q.; Ye, J.S.; Huang, X.D.; Yu, C.Z. A graphene modified anode to improve the performance of microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 5402–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.T.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, C.Y.; Tai, N.H.; Chang, H.Y. Highly durable anodes of microbial fuel cells using a reduced graphene oxide/carbon nanotube-coated scaffold. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.W.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.W.; Li, X.S.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and graphene oxide: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.-L.; Christoph, G.S. A simple and mild chemical oxidation route to high-purity nano-graphene oxide. Carbon 2016, 106, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Marcano, D.C.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Berlin, J.M.; Sinitskii, A.; Sun, Z.Z.; Slesarev, A.; Alemany, L.B.; Lu, W.; Tour, J.M. Improved synthesis of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4806–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.F.; Zhou, B.M.; Zhu, T.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z.W.; Hu, C.S.; Wang, J.J. Facile and low-cost approach towards a PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with enhanced hydrophilicity and antifouling performance via graphene oxide/water-bath coagulation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 7880–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, B.M.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F. Enhanced hydrophilicity and salt rejection study of graphene oxide-polysulfone mixed matrix membrane. Desalination 2013, 313, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Navaneethaiyer, U.; Mohan, R.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.-J. Graphene oxide nanostructures modified multifunctional cotton fabrics. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 2, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Yu, H.B.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.X.; Feng, J.L. A novel structure of scalable air-cathode without Nafion and Pt by rolling activated carbon and PTFE as catalyst layer in microbial fuel cells. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5777–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Logan, B.E. Electricity generation using an air-cathode single chamber microbial fuel cell in the presence and absence of a proton exchange membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4040–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Cheng, S.A.; Pant, D.; Van Bogaert, G.; Logan, B.E. Power generation using an activated carbon and metal mesh cathode in a microbial fuel cell. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 2177–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.L.; Ibrahim, S.; Pichiah, S. Synergetic effect of conductive polymer poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) with different structural configuration of anode for microbial fuel cell application. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.X.; Liu, Z.L.; Zhang, P.Y. A new method for fabrication of graphene/polyaniline nanocomplex modified microbial fuel cell anodes. J. Power Sources 2013, 224, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.C.; Liang, P.; Cao, X.X.; Huang, X. A new insight into potential regulation on growth and power generation of Geobacter sulfurreducens in microbial fuel cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3187–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.K.; Ziegler, C.; Oszcipok, M.; Zobel, M.; Hebling, C. Hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity study of catalyst layers in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Li, K.X.; Zhang, P.; Pu, L.T.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Z. The performance of activated carbon treated with H3PO4 at 80 °C in the air-cathode microbial fuel cell. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Liang, P.; Yang, X.F.; Jiang, Y.; Bian, Y.H.; Chen, C.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, X. Binder-free graphene and manganese oxide coated carbon felt anode for high-performance microbial fuel cell. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.R.; Deng, L.F.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y. MnO2/Polypyrrole/MnO2 multi-walled-nanotube-modified anode for high-performance microbial fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 196, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, Z.A.; An, N.; Yang, Y.Y.; Li, Z.M.; Wu, H.Y. Facile synthesis of MnO2/CNTs composite for supercapacitor electrodes with long cycle stability. J. Phys. Chem. 2014, 118, 22865–22872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katuri, K.P.; Kavanagh, P.; Rengaraj, S.; Leech, D. Geobacter sulfurreducens biofilms developed under different growth conditions on glassy carbon electrodes: Insights using cyclic voltammetry. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4758–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsili, E.; Rollefson, J.B.; Baron, D.B.; Hozalski, R.M.; Bond, D.R. Microbial biofilm voltammetry: Direct electrochemical characterization of catalytic electrode-attached biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7329–7337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, K.J.; Choi, M.J.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, I.S. Effect of different substrates on the performance, bacterial diversity, and bacterial viability in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3518–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.P.; Yates, M.D.; Logan, B.E. Set potential regulation reveals additional oxidation peaks of Geobacter sulfurreducens anodic biofilms. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 22, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, A.K.; Bretschger, O.; Nealson, K.H.; Mansfeld, F. The polarization behavior of the anode in a microbial fuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3508–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, A.K.; Mansfeld, F. The internal resistance of a microbial fuel cell and its dependence on cell design and operating conditions. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhai, L.F.; Li, W.W.; Yu, H.Q. Harvest and utilization of chemical energy in wastes by microbial fuel cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2847–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Anodes | G | G-GO0.15 | G-GO0.2 | G-GO0.25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phospholipid concentration (μg·cm−2) | 6.68 ± 0.57 | 6.86 ± 0.56 | 7.07 ± 0.56 | 6.11 ± 0.57 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, N.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Effect of Graphene-Graphene Oxide Modified Anode on the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6090174
Yang N, Ren Y, Li X, Wang X. Effect of Graphene-Graphene Oxide Modified Anode on the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(9):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6090174
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Na, Yueping Ren, Xiufen Li, and Xinhua Wang. 2016. "Effect of Graphene-Graphene Oxide Modified Anode on the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell" Nanomaterials 6, no. 9: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6090174
APA StyleYang, N., Ren, Y., Li, X., & Wang, X. (2016). Effect of Graphene-Graphene Oxide Modified Anode on the Performance of Microbial Fuel Cell. Nanomaterials, 6(9), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6090174