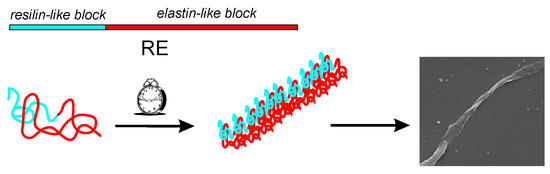
Fibrillar Self-Assembly of a Chimeric Elastin-Resilin Inspired Engineered Polypeptide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Production of rel and eln DNA Genes
2.1.2. Construction of Re (Rel + Eln) Gene
2.1.3. Expression and Purification of the Recombinant RE Polypeptide
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Peptide Purification
2.2.2. Amino Acid Analysis
2.2.3. ESI–MS Analyses
2.2.4. CD-Spectroscopy
2.2.5. UV-Spectroscopy
2.2.6. AFM
2.2.7. SEM
2.2.8. Sample Preparation of RE Polypeptide in Aggregated State
2.2.9. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
2.2.10. Near Edge X-ray Fine Structure (NEXAFS) Spectroscopy
2.3. Biological Studies
2.3.1. Materials for Biological Characterization
2.3.2. Cell Cultures
2.3.3. Treatments
2.3.4. MTT Assay
2.3.5. Evaluation of Living and Dead Cells by Trypan Blue Staining
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Resilin-Elastin (RE) Polypeptide Design
3.2. Polypeptide Characterization
3.2.1. Amino Acid Analysis
3.2.2. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.3. Circular Dichroism
3.4. Self-Aggregation
3.5. Morphological Characterization
3.6. Chemical and Electronic Structure Characterization
3.7. Biological Characterization
3.7.1. Cell Viability Evaluation
3.7.2. Evaluation of Dead and Living Cells by Trypan Blue Staining
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bochicchio, B.; Bracalello, A.; Pepe, A. Characterization of a Crosslinked Elastomeric-Protein Inspired Polypeptide. Chirality 2016, 28, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbrana, F.; Fotia, C.; Bracalello, A.; Baldini, N.; Marletta, G.; Ciapetti, G.; Bochicchio, B.; Vassalli, M. Multiscale characterization of a chimeric biomimetic polypeptide for stem cell culture. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2012, 4, 046007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.; Harmon, T.S.; Schaal, J.L.; Miao, V.; Li, K.J.; Hunt, A.; Wen, Y.; Oas, T.G.; Collier, J.H.; Pappu, R.V.; et al. Injectable tissue integrating networks from recombinant polypeptides with tunable order. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochicchio, B.; Pepe, A.; Tamburro, A.M. Investigating by CD the molecular mechanism of elasticity of elastomeric proteins. Chirality 2008, 20, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balu, R.; Whittaker, J.; Dutta, N.K.; Elvin, C.M.; Choudhury, N.R. Multi-responsive biomaterials and nanobioconjugates from resilin-like protein polymers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5936–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvin, C.M.; Carr, A.G.; Huson, M.G.; Maxwell, J.M.; Pearson, R.D.; Vuocolo, T.; Liyou, N.E.; Wong, D.C.C.; Merritt, D.J.; Dixon, N.E. Synthesis and properties of crosslinked recombinant pro-resilin. Nature 2005, 437, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis-Fogh, T. A rubber-like protein in insect cuticle. J. Exp. Biol. 1960, 37, 889–907. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, G.; Rivkin, A.; Lapidot, S.; Hu, X.; Preis, I.; Arinus, S.; Dgany, O.; Shoseyov, O.; Kaplan, D.L. Recombinant exon-encoded resilins for elastomeric biomaterials. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9231–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charati, M.B.; Ifkovits, J.L.; Burdick, J.A.; Linhardt, J.G.; Kiick, K.L. Hydrophilic elastomeric biomaterials based on resilin-like polypeptides. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3412–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, R.E.; Elvin, C.M.; Taylor, K.; Lekieffre, N.; Ramshaw, J.A.M. Purification of recombinant protein by cold-coacervation of fusion constructs incorporating resilin-inspired polypeptides. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2947–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, J.N.; Cherry, K.M.; Su, R.S.C.; Liu, J.C. Characterization of resilin-based materials for tissue engineering applications. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3678–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, J.N.; Kim, Y.; Cherry, K.M.; Liu, J.C. Modular cloning and protein expression of long, repetitive resilin-based proteins. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzhandler, I.; Dzuricky, M.; Hoffmann, I.; Garcia Quiroz, F.; Gradzielski, M.; Chilkoti, A. Micellar Self-Assembly of Recombinant Resilin-/Elastin-Like Block Copolypeptides. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzuricky, M.; Xiong, S.; Weber, P.; Chilkoti, A. Avidity and Cell Uptake of Integrin-Targeting Polypeptide Micelles is Strongly Shape-Dependent. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 6124–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecham, R.P. Elastin Synthesis and Fiber Assembly. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 624, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburro, A.M.; Panariello, S.; Santopietro, V.; Bracalello, B.; Bochicchio, B.; Pepe, A. Molecular and Supramolecular Structural Studies on Significant Repetitive Sequences of Resilin. ChemBioChem 2010, 11, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Eden, P., Ed.; Physical Electronics Inc.: Eden Prairie, MI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shirley, D.A. High-resolution X-ray photoemission spectrum of the valence bands of gold. Phys. Rev. B 1972, 5, 4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamson, G.; Briggs, D. High Resolution XPS of Organic Polymers. In The Scienta ESCA300 Database; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bracalello, A.; Santopietro, V.; Vassalli, M.; Marletta, G.; Del Gaudio, R.; Bochicchio, B.; Pepe, A. Design and Production of a Chimeric Resilin-, Elastin-, and Collagen-Like Engineered Polypeptide. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2957–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochicchio, B.; Pepe, A.; Crudele, M.; Belloy, N.; Baud, S.; Dauchez, M. Tuning self-assembly in elastin-derived peptides. Soft Matter 2015, 7, 3385–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostuni, A.; Bochicchio, B.; Armentano, M.F.; Bisaccia, F.; Tamburro, A.M. Molecular and Supramolecular Structural Studies on Human Tropoelastin Sequences. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 3640–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, G.C.; Keeley, F.W.; Weiss, A.S. Coacervation of tropoelastin. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressan, G.M.; Castellani, I.; Giro, M.G.; Volpin, D.; Fornieri, C.; Pasquali Ronchetti, I. Banded fibers in tropoelastin coacervates at physiological temperatures. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1983, 82, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali-Ronchetti, I.; Fornieri, C. The ultrastructural organization of the elastin fiber. In Electron Microscopy in Biology and Medicine; Ruggeri, A., Motta, P.M., Eds.; Martin Njioff Publ.: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 126–139. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquali-Ronchetti, I.; Fornieri, C.; Baccarani Contri, M.; Quaglino, D. Ultrastructure of elastin. Ciba Found. Symp. 1995, 192, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ruoslahti, E. Variants of the cell recognition site of fibronectin that retain attachment-promoting activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 5985–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ruoslahti, E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature 1984, 309, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.C.; Heilshorn, S.C.; Tirrell, D.A. Comparative cell response to artificial extracellular matrix proteins containing the RGD and CS5 cell-binding domains. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 297–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.C.; Tirrell, D.A. Cell response to RGD density in cross-linked artificial extracellular matrix protein films. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2984–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isotopident. Available online: http://education.expasy.org/student_projects/isotopident/htdocs/ (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Wingfield, P.T. N-terminal methionine processing. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2017, 88, 6.14.1–6.14.3. [Google Scholar]
- Bochicchio, B.; Pepe, A. Role of polyproline II conformation in human tropoelastin structure. Chirality 2011, 23, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburro, A.M.; Bochicchio, B.; Pepe, A. Dissection of Human Tropoelastin: Exon-By-Exon Chemical Synthesis and Related Conformational Studies. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 13347–13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodkin, M.J.; Goodfellow, J.M. Hydrophobic solvation in aqueous trifluoroethanol solution. Biopolymers 1996, 39, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, M. Trifluoroethanol and colleagues: Cosolvents come of age. Recent studies with peptides and proteins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1998, 31, 297–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiersen, H.; Rees, A.R. Trifluoroethanol may form a solvent matrix for assisted hydrophobic interactions between peptide side chains. Protein Eng. 2000, 13, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perczel, A.; Hollosi, M.; Sandor, P.; Fasman, G.D. The Evaluation of Type I and Type II beta-turn Mixtures. Circular Dichroism, NMR and Molecular Dynamic Studies. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1993, 41, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburro, A.M.; Guantieri, V.; Scopa, A.; Drabble, J.M. Polypeptide models of elastin: CD and NMR studies on synthetic poly(X-Gly-Gly). Chirality 1991, 3, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiersen, H.; Clarke, A.R.; Rees, A.R. Short elastin-like peptides exhibit the same temperature-induced structural transitions as elastin polymers: Implications for protein engineering. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 283, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Guerra, D.; Bochicchio, B.; Quaglino, D.; Gheduzzi, D.; Pasquali Ronchetti, I.; Tamburro, A.M. Dissection of human tropoelastin: Supramolecular organization of polypeptide sequences coded by particular exons. Matrix Biol. 2005, 24, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamia, R.; Salvi, A.M.; D’Alessio, L.; Castle, J.E.; Tamburro, A.M. Transformation of amyloid-like fibres, formed from an elastin-based biopolymer, into hydrogel: An XPS and AFM study. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secchi, V.; Franchi, S.; Fioramonti, M.; Polzonetti, G.; Iucci, G.; Bochicchio, B.; Battocchio, C. Nanofibers of Human Tropoelastin-inspired peptides: Structural characterization and biological properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzilotto, V.; Silva, J.L.; Zhang, T.; Stredansky, M.; Grazioli, C.; Simonov, K.; Giangrisostomi, E.; Ovsyannikov, R.; De Simone, M.; Coreno, M.; et al. Spectroscopic Fingerprints of Intermolecular H-Bonding Interactions in Carbon Nitride Model Compounds. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 14198–14206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database; Version 4.1; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. Available online: http://srdata.nist.gov/xps/ (accessed on 2 October 2019).
- Monti, S.; Carravetta, V.; Battocchio, C.; Iucci, G.; Polzonetti, G. Peptide/TiO2 surface in teraction: A theoretical and experimental study on the structure of adsorbed ALA- GLU and ALA-LYS. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3205–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polzonetti, G.; Battocchio, C.; Iucci, G.; Dettin, M.; Gambaretto, R.; Di Bello, C.; Carravetta, V. Thin films of a self-assembling peptide on TiO2 and Au studied by NEXAFS, XPS and IR spectroscopies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2006, 26, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, G.; Romeo, M.; Stener, M.; Fronzoni, G.; Cvetko, D.; Cossaro, A.; Dell’Angela, M.; Kladni, G.; Venkataraman, L.; Morgante, A. Computational Study of Amino Mediated Molecular Interaction Evidenced in N 1s NEXAFS: 1,4-Diaminobenzene on Au (111). J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamia, R.; Zhdan, P.A.; Martino, M.; Castle, J.E.; Tamburro, A.M. AFM Study of the Elastin-like Biopolymer (ValGlyGlyValGly). Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburro, A.M.; Pepe, A.; Bochicchio, B.; Quaglino, D.; Pasquali Ronchetti, I. Supramolecular amyloid-like assembly of the polypeptide sequence coded by exon 30 of human tropoelastin. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bracalello, A.; Secchi, V.; Mastrantonio, R.; Pepe, A.; Persichini, T.; Iucci, G.; Bochicchio, B.; Battocchio, C. Fibrillar Self-Assembly of a Chimeric Elastin-Resilin Inspired Engineered Polypeptide. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111613
Bracalello A, Secchi V, Mastrantonio R, Pepe A, Persichini T, Iucci G, Bochicchio B, Battocchio C. Fibrillar Self-Assembly of a Chimeric Elastin-Resilin Inspired Engineered Polypeptide. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(11):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111613
Chicago/Turabian StyleBracalello, Angelo, Valeria Secchi, Roberta Mastrantonio, Antonietta Pepe, Tiziana Persichini, Giovanna Iucci, Brigida Bochicchio, and Chiara Battocchio. 2019. "Fibrillar Self-Assembly of a Chimeric Elastin-Resilin Inspired Engineered Polypeptide" Nanomaterials 9, no. 11: 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111613
APA StyleBracalello, A., Secchi, V., Mastrantonio, R., Pepe, A., Persichini, T., Iucci, G., Bochicchio, B., & Battocchio, C. (2019). Fibrillar Self-Assembly of a Chimeric Elastin-Resilin Inspired Engineered Polypeptide. Nanomaterials, 9(11), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111613