High Volume-Per-Dose and Low Resistivity of Cobalt Nanowires Grown by Ga+ Focused Ion Beam Induced Deposition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Growth Parameters
3.2. TEM
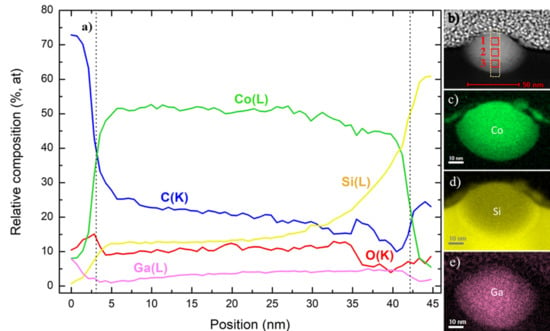
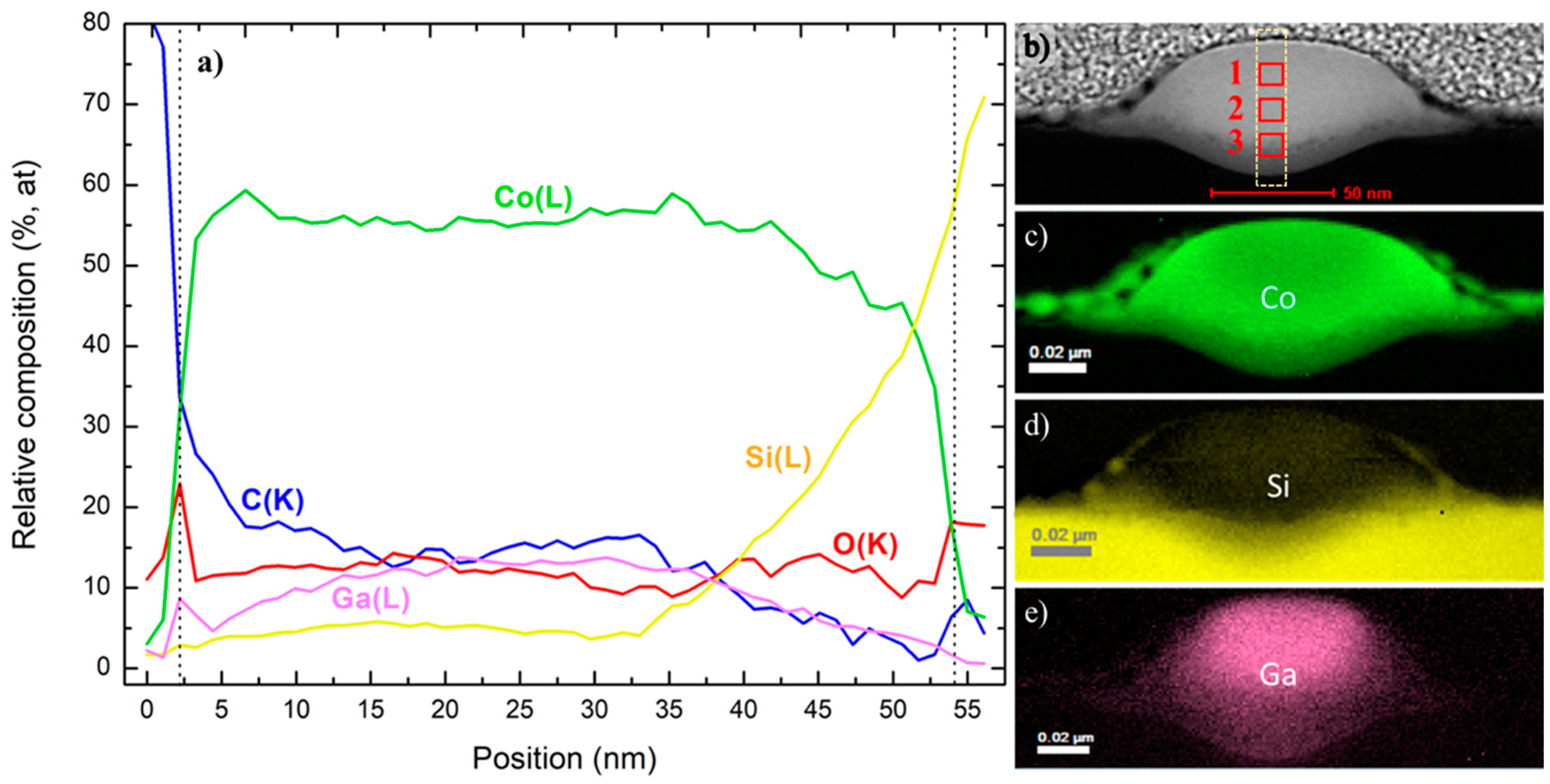
3.2.1. Compositional Analysis by STEM-EELS
3.2.2. Compositional Analysis by STEM-EDS
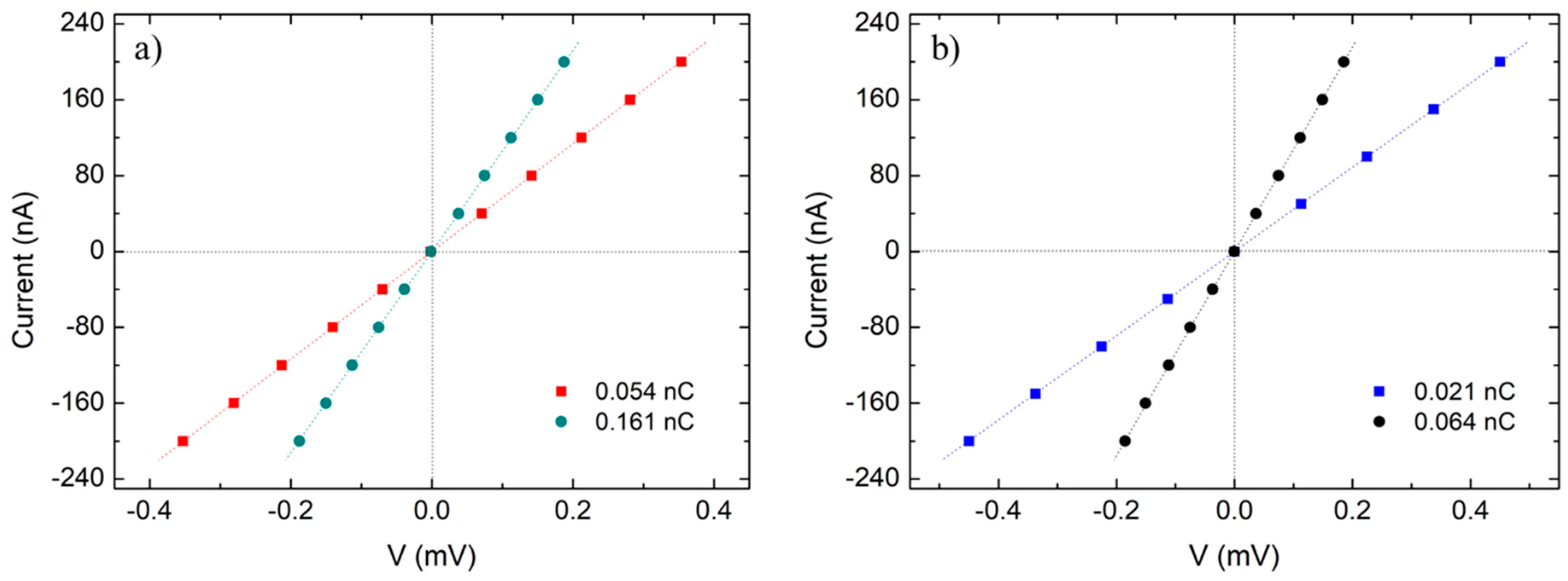
3.3. Analysis of the Transport Properties by Four-Point Electrical Microprobe Measurements
3.4. Analysis of the Magnetization Hysteresis Loops by Magneto-Optical Kerr Effect
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chappert, C.; Fert, A.; Van Dau, F.N. The emergence of spin electronics in data storage. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fert, A. Origin, development, and future of spintronics (Nobel lecture). Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 1517–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Lee, J.S.H.; Zhang, M. Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3995–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrejon, J.; Riou, M.; Araujo, F.A.; Tsunegi, S.; Khalsa, G.; Querlioz, D.; Bortolotti, P.; Cros, V.; Yakushiji, K.; Fukushima, A.; et al. Neuromorphic computing with nanoscale spintronic oscillators. Nature 2017, 547, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, S.D. Colloquium: Opportunities in nanomagnetism. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2006, 78, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, C.A.F.; Bland, J.A.C.; Lauhoff, G. Magnetism in ultrathin film structures. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2008, 71, 056501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Teresa, J.M.; Fernández-Pacheco, A. Present and future applications of magnetic nanostructures grown by FEBID. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Teresa, J.M.; Fernández-Pacheco, A.; Córdoba, R.; Serrano-Ramón, L.; Sangiao, S.; Ibarra, M.R. Review of magnetic nanostructures grown by focused electron beam induced deposition (FEBID). J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. Phys. 2016, 49, 243003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Shimojo, M.; Takeguchi, M.; Mitsuishi, K.; Furuya, K. Formation of iron nano-dot arrays by electron beam-induced deposition using an ultrahigh vacuum transmission electron microscope. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 275, 2361–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Ramón, L.; Córdoba, R.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Magén, C.; Snoeck, E.; Gatel, C.; Serrano, I.; Ibarra, M.R.; De Teresa, J.M. Ultrasmall functional ferromagnetic nanostructures grown by focused electron-beam-induced deposition. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7781–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, Y.M.; Chee, P.C.; Thong, J.T.L.; Ng, V. Properties and applications of cobalt-based material produced by electron-beam-induced deposition. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A Vac. Surf. Films 2002, 20, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pacheco, A.; Serrano-Ramón, L.; Michalik, J.M.; Ibarra, M.R.; De Teresa, J.M.; O’Brien, L.; Petit, D.; Lee, J.; Cowburn, R.P. Three dimensional magnetic nanowires grown by focused electron-beam induced deposition. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangiao, S.; Magén, C.; Mofakhami, D.; de Loubens, G.; De Teresa, J.M. Magnetic properties of optimized cobalt nanospheres grown by focused electron beam induced deposition (FEBID) on cantilever tips. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamoori, M.; Keller, L.; Pieper, J.; Barth, S.; Winkler, R.; Plank, H.; Müller, J.; Huth, M. Magnetic characterization of direct-write free-form building blocks for artificial magnetic 3D lattices. Materials 2018, 11, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utke, I.; Hoffmann, P.; Berger, R.; Scandella, L. High-resolution magnetic Co supertips grown by a focused electron beam. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4792–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavagnin, M.; Wanzenboeck, H.D.; Wachter, S.; Shawrav, M.M.; Persson, A.; Gunnarsson, K.; Svedlindh, P.; Stöger-Pollach, M.; Bertagnolli, E. Free-standing magnetic nanopillars for 3D nanomagnet logic. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20254–20260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belova, L.M.; Hellwig, O.; Dobisz, E.; Dan Dahlberg, E. Rapid preparation of electron beam induced deposition Co magnetic force microscopy tips with 10 nm spatial resolution. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 093711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Belova, L.M.; McMichael, R.D. Spectroscopy and imaging of edge modes in permalloy nanodisks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 017601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavassori, P.; Pancaldi, M.; Perez-Roldan, M.J.; Chuvilin, A.; Berger, A. Remote Magnetomechanical Nanoactuation. Small 2016, 12, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, J.H.; Van Der Heijden, M.A.J.; Ellis, T.H.; Lavrijsen, R.; Daniels, C.; McGrouther, D.; Swagten, H.J.M.; Koopmans, B. Beam-induced Fe nanopillars as tunable domain-wall pinning sites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3508–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boero, G.; Utke, I.; Bret, T.; Quack, N.; Todorova, M.; Mouaziz, S.; Kejik, P.; Brugger, J.; Popovic, R.S.; Hoffmann, P. Submicrometer Hall devices fabricated by focused electron-beam-induced deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 042503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavagnin, M.; Wanzenboeck, H.D.; Belić, D.; Bertagnolli, E. Synthesis of individually tuned nanomagnets for nanomagnet logic by direct write focused electron beam induced deposition. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrovolskiy, O.V.; Huth, M.; Shklovskij, V.A. Anisotropic magnetoresistive response in thin Nb films decorated by an array of Co stripes. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2010, 23, 125014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouco, V.; Córdoba, R.; De Teresa, J.M.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Navau, C.; Del-Valle, N.; Via, G.; Sánchez, A.; Monton, C.; Kronast, F.; et al. Competition between Superconductor-Ferromagnetic stray magnetic fields in YBa2Cu3O7−x films pierced with Co nano-rods. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Pacheco, A.; Streubel, R.; Fruchart, O.; Hertel, R.; Fischer, P.; Cowburn, R.P. Three-dimensional nanomagnetism. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeguchi, M.; Shimojo, M.; Furuya, K. Fabrication of magnetic nanostructures using electron beam induced chemical vapour deposition. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, R.; Sesé, J.; De Teresa, J.M.; Ibarra, M.R. High-purity cobalt nanostructures grown by focused-electron-beam-induced deposition at low current. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 1550–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begun, E.; Dobrovolskiy, O.V.; Kompaniiets, M.; Sachser, R.; Gspan, C.; Plank, H.; Huth, M. Post-growth purification of Co nanostructures prepared by focused electron beam induced deposition. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 075301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puydinger dos Santos, M.V.; Velo, M.F.; Domingos, R.D.; Zhang, Y.; Maeder, X.; Guerra-Nuñez, C.; Best, J.P.; Béron, F.; Pirota, K.R.; Moshkalev, S.; et al. Annealing-Based Electrical Tuning of Cobalt–Carbon Deposits Grown by Focused-Electron-Beam-Induced Deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32496–32503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo-Navarro, J.; Magén, C.; de Teresa, J.M. Purified and Crystalline Three-Dimensional Electron-Beam-Induced Deposits: The Successful Case of Cobalt for High-Performance Magnetic Nanowires. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pablo-Navarro, J.; Winkler, R.; Haberfehlner, G.; Magén, C.; Plank, H.; De Teresa, J.M. In situ real-time annealing of ultrathin vertical Fe nanowires grown by focused electron beam induced deposition. Acta Mater. 2019, 174, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pacheco, A.; De Teresa, J.M.; Córdoba, R.; Ibarra, M.R. Magnetotransport properties of high-quality cobalt nanowires grown by focused-electron-beam-induced deposition. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Stern, L.A.; Xia, D.; Ferranti, D.; Thompson, B.; Klein, K.L.; Gonzalez, C.M.; Rack, P.D. Focused helium ion beam deposited low resistivity cobalt metal lines with 10 nm resolution: Implications for advanced circuit editing. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łapicki, A.; Ahmad, E.; Suzuki, T. Ion beam induced chemical vapor deposition (IBICVD) of cobalt particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 240, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapicki, A.; Kang, K.; Suzuki, T. Fabrication of magnetic dot arrays by ion beam induced chemical vapor deposition (IBICVD). IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 2589–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabureac, M.; Bernau, L.; Utke, I.; Boero, G. Granular Co–C nano-Hall sensors by focused-beam-induced deposition. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 115503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Córdoba, R.; Fernández-Pacheco, R.; Fernández-Pacheco, A.; Gloter, A.; Magén, C.; Stéphan, O.; Ibarra, M.R.; De Teresa, J.M. Nanoscale chemical and structural study of Co-based FEBID structures by STEM-EELS and HRTEM. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peinado, P.; Sangiao, S.; De Teresa, J.M. Focused Electron and Ion Beam Induced Deposition on Flexible and Transparent Polycarbonate Substrates. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 6139–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kötzler, J.; Gil, W. Anomalous Hall resistivity of cobalt films: Evidence for the intrinsic spin-orbit effect. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 060412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakonyi, I.; Kádár, E.T.; Tóth, J.; Kiss, L.F.; Pogány, L.; Cziráki, Á.; Ulhaq-Bouillet, C.; Pierron-Bohnes, V.; Dinia, A.; Arnold, B.; et al. Room temperature electronic transport properties of Co metal and Co(Ru) dilute alloys. Europhys. Lett. 2002, 58, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pacheco, A.; De Teresa, J.M.; Szkudlarek, A.; Córdoba, R.; Ibarra, M.R.; Petit, D.; O’Brien, L.; Zeng, H.T.; Lewis, E.R.; Read, D.E.; et al. Magnetization reversal in individual cobalt micro- and nanowires grown by focused-electron-beam-induced-deposition. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 475704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Current (pA) | Deposit Time (s) | Dose (nC) | Dimensions | Volume Per Dose (µm3/nC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.39 | 3 | 0.004 | 9.78 µm × 879 nm2 | 2.062 |
| 1.39 | 12 | 0.017 | 9.85 µm × 2111 nm2 | 1.247 |
| 1.39 | 233 | 0.324 | 9.85 µm × 4282 nm2 | 0.130 |
| 1.39 | 466 | 0.648 | 9.84 µm × 5167 nm2 | 0.079 |
| 1.39 | 641 | 0.891 | 9.94 µm × 8507 nm2 | 0.095 |
| 1.39 | 926 | 1.287 | 9.94 µm × 9725 nm2 | 0.075 |
| 1.39 | 1156 | 1.607 | 10.1 µm × 13390 nm2 | 0.084 |
| 10.67 | 12 | 0.128 | 9.83 µm × 4037 nm2 | 0.310 |
| 10.67 | 21 | 0.224 | 9.75 µm × 5360 nm2 | 0.233 |
| 10.67 | 48 | 0.512 | 9.90 µm × 6922 nm2 | 0.134 |
| 10.67 | 64 | 0.683 | 9.94 µm × 8160 nm2 | 0.119 |
| 10.67 | 107 | 1.142 | 9.98 µm × 9322 nm2 | 0.081 |
| 10.67 | 132 | 1.408 | 9.78 µm × 9535 nm2 | 0.067 |
| 10.67 | 150 | 1.601 | 9.81 µm × 9758 nm2 | 0.060 |
| 1.5 pA, 0.017 nC | Element (Spectral Line) Atomic% | 9.7 pA, 0.224 nC | Element (Spectral Line) Atomic% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(K) | 33.00 ± 0.90 | C(K) | 11.57 ± 0.33 | ||
| O(K) | 9.89 ± 0.31 | O(K) | 14.34 ± 0.29 | ||
| Region 1 | Si(K) | 2.43 ± 0.15 | Region 1 | Si(K) | 0.28 ± 0.06 |
| Co(K) | 45.59 ± 1.02 | Co(K) | 47.21 ± 0.80 | ||
| Ga(K) | 9.07 ± 0.54 | Ga(K) | 26.57 ± 0.75 | ||
| C(K) | 22.14 ± 0.59 | C(K) | 15.31 ± 0.40 | ||
| O(K) | 8.93 ± 0.28 | O(K) | 11.45 ± 0.28 | ||
| Region 2 | Si(K) | 18.62 ± 0.35 | Region 2 | Si(K) | 2.88 ± 0.12 |
| Co(K) | 41.83 ± 0.90 | Co(K) | 52.63 ± 0.83 | ||
| Ga(K) | 8.45 ± 0.48 | Ga(K) | 17.71 ± 0.59 | ||
| C(K) | 14.94 ± 0.62 | C(K) | 6.66 ± 0.37 | ||
| O(K) | 3.44 ± 0.26 | O(K) | 8.78 ± 0.30 | ||
| Region 3 | Si(K) | 48.32 ± 0.67 | Region 3 | Si(K) | 24.47 ± 0.45 |
| Co(K) | 24.61 ± 0.80 | Co(K) | 48.88 ± 1.06 | ||
| Ga(K) | 8.66 ± 0.63 | Ga(K) | 11.19 ± 0.64 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanz-Martín, C.; Magén, C.; De Teresa, J.M. High Volume-Per-Dose and Low Resistivity of Cobalt Nanowires Grown by Ga+ Focused Ion Beam Induced Deposition. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121715
Sanz-Martín C, Magén C, De Teresa JM. High Volume-Per-Dose and Low Resistivity of Cobalt Nanowires Grown by Ga+ Focused Ion Beam Induced Deposition. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(12):1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121715
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanz-Martín, Carlos, César Magén, and José María De Teresa. 2019. "High Volume-Per-Dose and Low Resistivity of Cobalt Nanowires Grown by Ga+ Focused Ion Beam Induced Deposition" Nanomaterials 9, no. 12: 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121715
APA StyleSanz-Martín, C., Magén, C., & De Teresa, J. M. (2019). High Volume-Per-Dose and Low Resistivity of Cobalt Nanowires Grown by Ga+ Focused Ion Beam Induced Deposition. Nanomaterials, 9(12), 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121715