Facile Fabrication of Fluorescent Inorganic Nanoparticles with Diverse Shapes for Cell Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Instrument
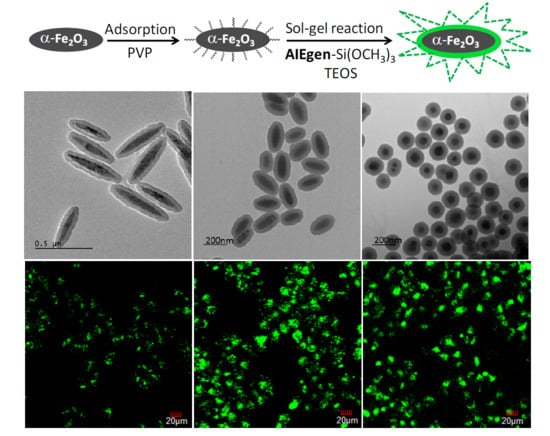
2.2. Synthesis of HNPs with Different Shapes
2.3. Adsorption of PVP
2.4. Fabrication of Fluorescent HNPs
2.5. Cell Viability
2.6. Cell Imaging
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of HNPs with Different Shapes
3.2. Reaction Condition Optimization
3.3. Preparation of Fluorescent HNPs with Different Shapes
3.4. Cell Viability
3.5. Cell Imaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Champion, J.A.; Katare, Y.K.; Mitragotri, S. Particle shape: A new design parameter for micro-and nanoscale drug delivery carriers. J. Control. Release 2007, 121, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitragotri, S.; Lahann, J. Physical approaches to biomaterial design. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canelas, D.A.; Herlihy, K.P.; DeSimone, J.M. Top-down particle fabrication: Control of size and shape for diagnostic imaging and drug delivery. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2009, 1, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champion, J.A.; Mitragotri, S. Shape induced inhibition of phagocytosis of polymer particles. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartczak, D.; Muskens, O.L.; Nitti, S.; Sanchez-Elsner, T.; Millar, T.M.; Kanaras, A.G. Interactions of human endothelial cells with gold nanoparticles of different morphologies. Small 2012, 8, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ito, Y.; Pradeep, B.; Valiyaveettil, S. Shape sensitivity on toxicity of gold nanoplates in breast cancer cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 9520–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Teng, X.; Chen, D.; Tang, F.; He, J. The effect of the shape of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on cellular uptake and cell function. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Yang, S.; Li, Z.; Xia, T.; Chen, J.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, S.; Huang, C.; et al. Aspect ratio determines the quantity of mesoporous silica nanoparticle uptake by a small gt pase-dependent macropinocytosis mechanism. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4434–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Hao, N.; Liu, H.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. The shape effect of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on biodistribution, clearance, and biocompatibility in vivo. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5390–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Tang, F.; Li, L. The shape effect of PEGylated mesoporous silica nanoparticles on cellular uptake pathway in Hela cells. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 162, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safi, M.; Yan, M.; Guedeau-Boudeville, M.-A.; Conjeaud, H.; Garnier-Thibaud, V.; Boggetto, N.; Baeza-Squiban, A.; Niedergang, F.; Averbeck, D.; Berret, J.-F. Interactions between magnetic nanowires and living cells: Uptake, toxicity, and degradation. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5354–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardillo, D.; Tehei, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Islam, M.M.; Bogusz, K.; Shi, D.; Mitchell, D.; Lerch, M.; Rosenfeld, A.; Corde, S.; et al. Synthesis-dependent surface defects and morphology of hematite nanoparticles and their effect on cytotoxicity in vitro. ACS Appl. Mater. Interace 2016, 8, 5867–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonrungsiman, S.; Suchaoin, W.; Chetprayoon, P.; Viriya-Empikul, N.; Aueviriyavit, S.; Maniratanachote, R. Shape and surface properties of titanate nanomaterials influence differential cellular uptake behavior and biological responses in THP-1 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 9, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Dalhaimer, P.; Cai, S.; Tsai, R.; Tewari, M.; Minko, T.; Discher, D.E. Shape effects of filaments versus spherical particles in flow and drug delivery. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Tian, W.; Xie, Z. Tailoring the morphology of AIEgen fluorescent nanoparticles for optimal cellular uptake and imaging efficacy. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Eber, F.J.; Nagarajan, A.S.; DiFranco, N.A.; Schmidt, N.; Wen, A.M.; Eiben, S.; Twyman, R.M.; Wege, C.; Steinmetz, N.F. The impact of aspect ratio on the biodistribution and tumor homing of rigid soft-matter nanorods. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, J.; Luehmann, T.; Hall, H.; Vogel, V. The race to the pole: How high-aspect ratio shape and heterogeneous environments limit phagocytosis of filamentous escherichia coli bacteria by macrophages. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2901–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickson, J. In vivo optical imaging: Preclinical applications and considerations. Urol. Oncol. 2009, 27, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Shi, H.; Huang, J.; Huo, X. Fluorescent nanoparticles for chemical and biological sensing. Sci. China Chem. 2011, 54, 1157–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ding, D.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, J.; Tang, B.Z.; Liu, B. Biocompatible organic dots with aggregation-induced emission for in vitro and in vivo fluorescence imaging. Sci. China Chem. 2013, 56, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, A.; Wojcik, T.; Malek, K.; Kwolek, U.; Kepczynski, M.; Ansary, A.A.; Chlopicki, S.; Baranska, M. Rhodamine 6G conjugated to gold nanoparticles as labels for both SERS and fluorescence studies on live endothelial cells. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjubaashini, N.; Thangadurai, T.D.; Bharathi, G.; Nataraj, D. Rhodamine capped gold nanoparticles for the detection of Cr3+ ion in living cells and water samples. J. Lumin. 2018, 202, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.K.; Tapadia, K.; Maharana, T.; Sharma, A. Convenient and ultra-sensitive fluorescence detection of bovine serum albumin by using Rhodamine-6G modified gold nanoparticles in biological samples. J. Biol. Chem. Lumin. 2018, 33, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, M.; Lim, J.M.; Kang, D.; Yoon, J.; Jung, J.H. Fluorescein-functionalized silica nanoparticles as a selective fluorogenic chemosensor for Cu2+ in living cells. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Park, J.Y.; Kattel, K.; Ahmad, M.W.; Bony, B.A.; Heo, W.C.; Jin, S.; Park, J.W.; Chang, Y.; Kim, T.J.; et al. Fluorescein-polyethyleneimine coated gadolinium oxide nanoparticles as T-1 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-cell labeling (CL) dual agents. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 10907–10915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Son, H.; Lim, J.M.; Oh, J.; Kang, D.; Han, W.S.; Jung, J.H. BODIPY-functionalized gold nanoparticles as a selective fluoro-chromogenic chemosensor for imaging Cu2+ in living cells. Analyst 2010, 135, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Jia, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Qin, W. Synthesis and photochemical properties of BODIPY-functionalized silica nanoparticles for imaging Cu2+ in living cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 23571–23579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, S.; Puvvada, N.; Kumar, B.N.P.; Rajput, S.; Pathak, A.; Mandal, M.; Singh, N.D.P. Photoresponsive coumarin-tethered multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for release of anticancer drug. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 5232–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Pudavar, H.E.; Bonoiu, A.; Prasad, P.N. Aggregation-enhanced fluorescence in organically modified silica nanoparticles: A novel approach toward high-signal-output nanoprobes for two-photon fluorescence bioimaging. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3791–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; Hong, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Qin, A.; Lu, P.; Tang, B.Z. Fabrication of fluorescent silica nanoparticles hybridized with aie luminogens and exploration of their applications as nanobiosensors in intracellular imaging. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 4266–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtab, F.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yuan, W.; Lu, P.; Tang, B.Z. Covalent immobilization of aggregation-induced emission luminogens in silica nanoparticles through click reaction. Small 2011, 7, 1448–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahtab, F.; Yu, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Lu, P.; Zhang, X.; Tang, B.Z. Fabrication of silica nanoparticles with both efficient fluorescence and strong magnetization, and exploration of their biological applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 1733–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Li, M.; Peng, T.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, J.; Hu, Q.; Song, Z.; Zheng, Q. In vitro cytotoxicity of fluorescent silica nanoparticles hybridized with aggregation-induced emission luminogens for living cell imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Liu, M.; Xu, D.; Wan, Q.; Huang, Q.; Jiang, R.; Shi, Y.; Deng, F.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Synthesis, surface modification and biological imaging of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) dye doped silica nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 403, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Ren, L.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Yu, J. AIE gen-functionalised mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a FRET donor for monitoring drug delivery. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; Yu, J. Fluorescent sensors based on AIE gen-functionalised mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the detection of explosives and antibiotics. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 2183–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-L.; Wang, D.; Cui, Y.; Fan, Z.; Ren, L.; Li, D.; Yu, J. AIEgen-functionalized mesoporous silica gated by cyclodextrin-modified CuS for cell imaging and chemo-photothermal cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 12155–12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Synthesis and cellular internalization of spindle hematite/polymer hybrid nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 5454–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiner, P.; Ferric, E. Hydrous oxide sols: III. Preparation of uniform particles by hydrolysis of Fe (III)-chloride,-nitrate, and-perchlorate solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1978, 63, 509–524. [Google Scholar]
- Ocana, M.; Morales, M.P.; Serna, C.J. Homogeneous precipitation of uniform alpha-Fe2O3 particles from iron salts solutions in the presence of urea. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 212, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, C.; Vossen, D.L.J.; Imhof, A.; van Blaaderen, A. A general method to coat colloidal particles with silica. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6693–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Xia, Y. Synthesis and self-assembly of Au@SiO2 core−shell colloids. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. Preparation and thermal stability of the spindle α-Fe2O3@SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 2014, 211, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, D.T.; Ramos-Romero, S.; Shankar, B.H.; Garrido, C.; Rubio, N.; Sanchez-Cid, L.; Borros Gomez, S.; Blanco, J.; Ramaiah, D. In vitro and in vivo demonstration of photodynamic activity and cytoplasm imaging through TPE nanoparticles. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Nieves, A.; Nieves, F.J.D. The role of zeta potential in the colloidal stability of different TiO2/electrolyte solution interfaces. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 148, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglia, S.; Ledda, M.; Fioretti, D.; Iucci, G.; Papi, M.; Capellini, G.; Lolli, M.G.; Grimaldi, S.; Rinaldi, M.; Lisi, A. In vitro biocompatibility study of sub-5 nm silica-coated magnetic iron oxide fluorescent nanoparticles for potential biomedical application. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratton, S.E.A.; Ropp, P.A.; Pohlhaus, P.D.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, V.J.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, C.; Oehring, H.; Herrmann, R.; Foerster, M.; Reller, A.; Hilger, I. Fate of cerium dioxide nanoparticles in endothelial cells: Exocytosis. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Entry | Sample Name | TEOS (mL) | AIEgens (mg) | Thickness of SiO2 Shell (nm) b | Aspect Ratio b | λemc | ΦFd (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SNP-1 | 0.05 | 10 | 26 | 3.51–3.76 | 520 | 3.12 |
| 2 | SNP-2 | 0.10 | 10 | 32 | 3.41–3.71 | 514 | 4.74 |
| 3 | SNP-3 | 0.20 | 10 | 54 | 2.68–2.89 | 504 | 6.42 |
| 4 | SNP-4 | 0.10 | 4.5 | 30 | 3.18–3.53 | 506 | 2.56 |
| 5 | SNP-5 | 0.10 | 20 | 40 | 3.35–3.75 | 518 | 9.94 |
| Sample | Thickness of SiO2 Shell (nm) b | Aspect Ratio b | Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) c | Zeta Potential (mV) c | λemd | ΦFe (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | 32 | 3.41–3.71 | 258 | −24.3 | 514 | 4.74 |
| ENP | 39 | 1.65–1.81 | 221 | −26.1 | 507 | 5.77 |
| QSNP | 43 | 1.05–1.07 | 217 | −29.6 | 507 | 2.87 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Y. Facile Fabrication of Fluorescent Inorganic Nanoparticles with Diverse Shapes for Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020154
Wang G, Wang J, Zhao L, Zhang Q, Lu Y. Facile Fabrication of Fluorescent Inorganic Nanoparticles with Diverse Shapes for Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020154
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Guifang, Jing Wang, Linlin Zhao, Qiang Zhang, and Yan Lu. 2019. "Facile Fabrication of Fluorescent Inorganic Nanoparticles with Diverse Shapes for Cell Imaging" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020154
APA StyleWang, G., Wang, J., Zhao, L., Zhang, Q., & Lu, Y. (2019). Facile Fabrication of Fluorescent Inorganic Nanoparticles with Diverse Shapes for Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020154