Electrospun Filaments Embedding Bioactive Glass Particles with Ion Release and Enhanced Mineralization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioactive Glass Synthesis and Characterization
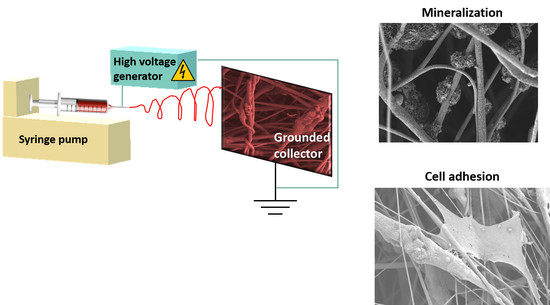
2.2. Electrospinning
2.3. Morphology and Mechanical Properties of PLLA-SBA2 Fibres
2.4. Degradation studies
2.5. Acellular Bioactivity
2.6. Cell Cultures
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutmacher, D.W. Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2529–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, J.; Woodruff, M.A.; Epari, D.R.; Steck, R.; Glatt, V.; Dickinson, I.C.; Choong, P.F.M.; Schuetz, M.A.; Hutmacher, D.W. Bone Regeneration Based on Tissue Engineering Conceptions—A 21st Century Perspective. Bone Res. 2013, 1, 216–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M. Developing bioactive composite materials for tissue replacement. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2133–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezwan, K.; Chen, Q.Z.; Blaker, J.J.; Boccaccini, A.R. Biodegradable and bioactive porous polymer/inorganic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3413–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamayol, A.; Akbari, M.; Annabi, N.; Paul, A.; Khademhosseini, A.; Juncker, D. Fiber-based tissue engineering: Progress, challenges, and opportunities. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, H.; Jo, S.; Mikos, A.G. Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4353–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miola, M.; Fucale, G.; Maina, G.; Verné, E. Antibacterial and bioactive composite bone cements containing surface silver-doped glass particles. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 10, 055014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, A.; Güldal, N.S.; Boccaccini, A.R. A review of the biological response to ionic dissolution products from bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xynos, I.D.; Edgar, A.J.; Buttery, L.D.K.; Hench, L.L.; Polak, J.M. Gene-expression profiling of human osteoblasts following treatment with the ionic products of Bioglass® 45S5 dissolution. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 55, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.M.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Shurey, S.; Roether, J.A.; Forbes, A.; Hench, L.L.; Gabe, S.M. Assessment of polyglycolic acid mesh and bioactive glass for soft-tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5857–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguez-Pacheco, V.; Hench, L.L.; Boccaccini, A.R. Bioactive glasses beyond bone and teeth: Emerging applications in contact with soft tissues. Acta Biomater. 2015, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaker, J.J.; Gough, J.E.; Maquet, V.; Notingher, I.; Boccaccini, A.R. In vitro evaluation of novel bioactive composites based on Bioglass®-filled polylactide foams for bone tissue engineering scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2003, 67A, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maquet, V.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Pravata, L.; Notingher, I.; Jérôme, R. Porous poly(α-hydroxyacid)/Bioglass® composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. I: Preparation and in vitro characterisation. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4185–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Francis, L.F. Processing and properties of porous poly(l-lactide)/bioactive glass composites. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2489–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allo, B.A.; Rizkalla, A.S.; Mequanint, K. Synthesis and Electrospinning of ε-Polycaprolactone-Bioactive Glass Hybrid Biomaterials via a Sol–Gel Process. Langmuir 2010, 26, 18340–18348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gönen, S.Ö.; Taygun, M.E.; Küçükbayrak, S. Fabrication of Bioactive Glass Containing Nanocomposite Fiber Mats For Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Compos. Struct. 2016, 138, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baino, F.; Verné, E.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Feasibility, tailoring and properties of polyurethane/bioactive glass composite scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, W.-T.; Zhang, X.; Luo, S.-H.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.-H.; Rahaman, M.N.; Day, D.E.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Xie, Z.-P.; Wang, J.-Q. Novel borate glass/chitosan composite as a delivery vehicle for teicoplanin in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Ginebra, M.P.; Planell, J.A.; Zeppetelli, S.; Ambrosio, L. Development and cell response of a new biodegradable composite scaffold for guided bone regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Aparicio, C.; Charles-Harris, M.; Ginebra, M.P.; Engel, E.; Planell, J.A. Development of a Biodegradable Composite Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering: Physicochemical, Topographical, Mechanical, Degradation, and Biological Properties. In Ordered Polymeric Nanostructures at Surfaces; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 209–231. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Aligned biodegradable nanofibrous structure: A potential scaffold for blood vessel engineering. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Murugan, R.; Wang, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospinning of nano/micro scale poly(l-lactic acid) aligned fibers and their potential in neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Thomopoulos, S.; Xia, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers for Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, H.; Shin, Y.M.; Terai, H.; Vacanti, J.P. A biodegradable nanofiber scaffold by electrospinning and its potential for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2077–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo Pitaluga, L.; Trevelin Souza, M.; Dutra Zanotto, E.; Santocildes Romero, M.E.; Hatton, P.V. Electrospun F18 Bioactive Glass/PCL—Poly (ε-caprolactone)—Membrane for Guided Tissue Regeneration. Materials 2018, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camposeo, A.; Greenfeld, I.; Tantussi, F.; Moffa, M.; Fuso, F.; Allegrini, M.; Zussman, E.; Pisignano, D. Conformational Evolution of Elongated Polymer Solutions Tailors the Polarization of Light-Emission from Organic Nanofibers. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 4704–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bognitzki, M.; Frese, T.; Steinhart, M.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H.; Schaper, A.; Hellwig, M. Preparation of fibers with nanoscaled morphologies: Electrospinning of polymer blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2001, 41, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megelski, S.; Stephens, J.S.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Micro-and Nanostructured Surface Morphology on Electrospum Polymer Fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.-E.; Yong, T.; Ma, Z.; Ramaseshan, R. Electrospun nanofibers: Solving global issues. Mater. Today 2006, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liverani, L.; Roether, J.A.; Boccaccini, A.R. Nanofiber composites in bone tissue engineering. In Nanofiber Composite Materials for Biomedical Applications; Ramalingam, M., Ramakrishna, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 301–323. [Google Scholar]
- Miola, M.; Bruno, M.; Maina, G.; Fucale, G.; Lucchetta, G.; Vernè, E. Antibiotic-free composite bone cements with antibacterial and bioactive properties. A preliminary study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 43, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miola, M.; Fucale, G.; Maina, G.; Verné, E. Composites bone cements with different viscosities loaded with a bioactive and antibacterial glass. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 5133–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.K.; Mohn, D.; Brunner, T.J.; Stark, W.J.; Philip, S.E.; Roy, I.; Salih, V.; Knowles, J.C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Comparison of nanoscale and microscale bioactive glass on the properties of P(3HB)/Bioglass® composites. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.H.; Lee, E.J.; Shin, D.S.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, H.W.; Koh, Y.H.; Jang, J.H. In vitro/in vivo biocompatibility and mechanical properties of bioactive glass nanofiber and poly(ε-caprolactone) composite materials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 91, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, J.R.; Low, S.; Choon, A.T.; Bharath Kumar, A.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanobioengineered electrospun composite nanofibers and osteoblasts for bone regeneration. Artif. Organs 2008, 32, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patlolla, A.; Collins, G.; Livingston Arinzeh, T. Solvent-dependent properties of electrospun fibrous composites for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Meth 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricotti, L.; Polini, A.; Genchi, G.G.; Ciofani, G.; Iandolo, D.; Vazão, H.; Mattoli, V.; Ferreira, L.; Menciassi, A.; Pisignano, D. Proliferation and Skeletal Myotube Formation Capability of C2C12 and H9c2 Cells on Isotropic and Anisotropic Electrospun Nanofibrous PHB Scaffolds. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liverani, L.; Boccaccini, A.R. Versatile production of poly(Epsilon-caprolactone) fibers by electrospinning using benign solvents. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theron, S.A.; Zussman, E.; Yarin, A.L. Experimental Investigation of the Governing Parameters in the Electrospinning of Polymer Solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 2017–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauricella, M.; Cipolletta, F.; Pontrelli, G.; Pisignano, D.; Succi, S. Effects of Orthogonal Rotating Electric Fields on Electrospinning Process. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 082003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Kaplan, D. Porosity of 3D Biomaterial Scaffolds and Osteogenesis. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5474–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakade, M.V.; Givens, S.; Gardner, K.; Lee, K.H.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Electric Field Induced Orientation of Polymer Chains in Macroscopically Aligned Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2777–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arinstein, A.; Burman, M.; Gendelman, O.; Zussman, E. Effect of Supramolecular Structure on Polymer Nanofibre Elasticity. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliara, S.; Vitiello, M.S.; Camposeo, A.; Polini, A.; Cingolani, R.; Scamarcio, G.; Pisignano, D. Optical Anisotropy in Single Light-Emitting Polymer Nanofibers. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 20399–20405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Lacroix, M.; Pellerin, C. Molecular Orientation in Electrospun Fibers: From Mats to Single Fibers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 9473–9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Yuan, M.; Deng, X. Biodegradable and Biocompatible Nanocomposites of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) with Hydroxyapatite Nanocrystals: Thermal and Mechanical Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerruti, M.; Greenspan, D.; Powers, K. Effect of pH and ionic strength on the reactivity of Bioglass® 45S5. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, R. Ca2+ Signaling, Intracellular pH and Cell Volume in Cell Proliferation. J. Membr. Biol. 2005, 205, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Solodovnyk, A.; Li, W.; Goudouri, O.-M.; Stähli, C.; Nazhat, S.N.; Boccaccini, A.R. Aging Time and Temperature Effects on the Structure and Bioactivity of Gel-Derived 45S5 Glass-Ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 98, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, H.; Serra, J.; González, P.; León, B. Structural Study of Sol–gel Silicate Glasses by IR and Raman Spectroscopies. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, N.; Rahaman, M.N.; Liu, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhang, C. Wound Dressings Composed of Copper-Doped Borate Bioactive Glass Microfibers Stimulate Angiogenesis and Heal Full-Thickness Skin Defects in a Rodent Model. Biomaterials 2015, 53, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, R.M. Bioactive Glass Stimulates the Secretion of Angiogenic Growth Factors and Angiogenesis in Vitro. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, M.N.; Day, D.E.; Bal, B.S.; Fu, Q.; Jung, S.B.; Bonewald, L.F.; Tomsia, A.P. Bioactive Glass in Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2355–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, R.M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Effect of Particulate Bioactive Glasses on Human Macrophages and Monocytesin Vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2005, 73A, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xynos, I.D.; Edgar, A.J.; Buttery, L.D.K.; Hench, L.L.; Polak, J.M. Ionic Products of Bioactive Glass Dissolution Increase Proliferation of Human Osteoblasts and Induce Insulin-like Growth Factor II MRNA Expression and Protein Synthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanò, C.L.; Logoluso, N.; Meani, E.; Romanò, D.; De Vecchi, E.; Vassena, C.; Drago, L. A Comparative Study of the Use of Bioactive Glass S53P4 and Antibiotic-Loaded Calcium-Based Bone Substitutes in the Treatment of Chronic Osteomyelitis. Bone Joint J. 2014, 96, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baino, F.; Novajra, G.; Miguez-Pacheco, V.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Bioactive Glasses: Special Applications Outside the Skeletal System. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2016, 432, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Peng, J.; Dong, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Chang, J. Combined Chemical and Structural Signals of Biomaterials Synergistically Activate Cell-Cell Communications for Improving Tissue Regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busa, W.B.; Nuccitelli, R. Metabolic Regulation via Intracellular PH. Am. J. Physiol. 1984, 246 Pt 2, R409–R438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xynos, I.D.; Hukkanen, M.V.J.; Batten, J.J.; Buttery, L.D.; Hench, L.L.; Polak, J.M. Bioglass®45S5 Stimulates Osteoblast Turnover and Enhances Bone Formation In Vitro: Implications and Applications for Bone Tissue Engineering. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2000, 67, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, M.; Zanardi, L.; Hench, L.; Cannas, M. Type I Collagen Production by Osteoblast-like Cells Cultured in Contact with Different Bioactive Glasses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2003, 64A, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Sample | Average Fibre Diameter (µm) | Minimum Fibre Transversal Size (µm) | Maximum Fibre Transversal Size (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLLA | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 1.0 | 3.9 |
| PLLA-SBA2 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.3 | 2.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serio, F.; Miola, M.; Vernè, E.; Pisignano, D.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Liverani, L. Electrospun Filaments Embedding Bioactive Glass Particles with Ion Release and Enhanced Mineralization. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020182
Serio F, Miola M, Vernè E, Pisignano D, Boccaccini AR, Liverani L. Electrospun Filaments Embedding Bioactive Glass Particles with Ion Release and Enhanced Mineralization. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(2):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020182
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerio, Francesca, Marta Miola, Enrica Vernè, Dario Pisignano, Aldo R. Boccaccini, and Liliana Liverani. 2019. "Electrospun Filaments Embedding Bioactive Glass Particles with Ion Release and Enhanced Mineralization" Nanomaterials 9, no. 2: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020182
APA StyleSerio, F., Miola, M., Vernè, E., Pisignano, D., Boccaccini, A. R., & Liverani, L. (2019). Electrospun Filaments Embedding Bioactive Glass Particles with Ion Release and Enhanced Mineralization. Nanomaterials, 9(2), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020182