Electrospun Gelatin Fibers Surface Loaded ZnO Particles as a Potential Biodegradable Antibacterial Wound Dressing
Abstract
1. Introduction
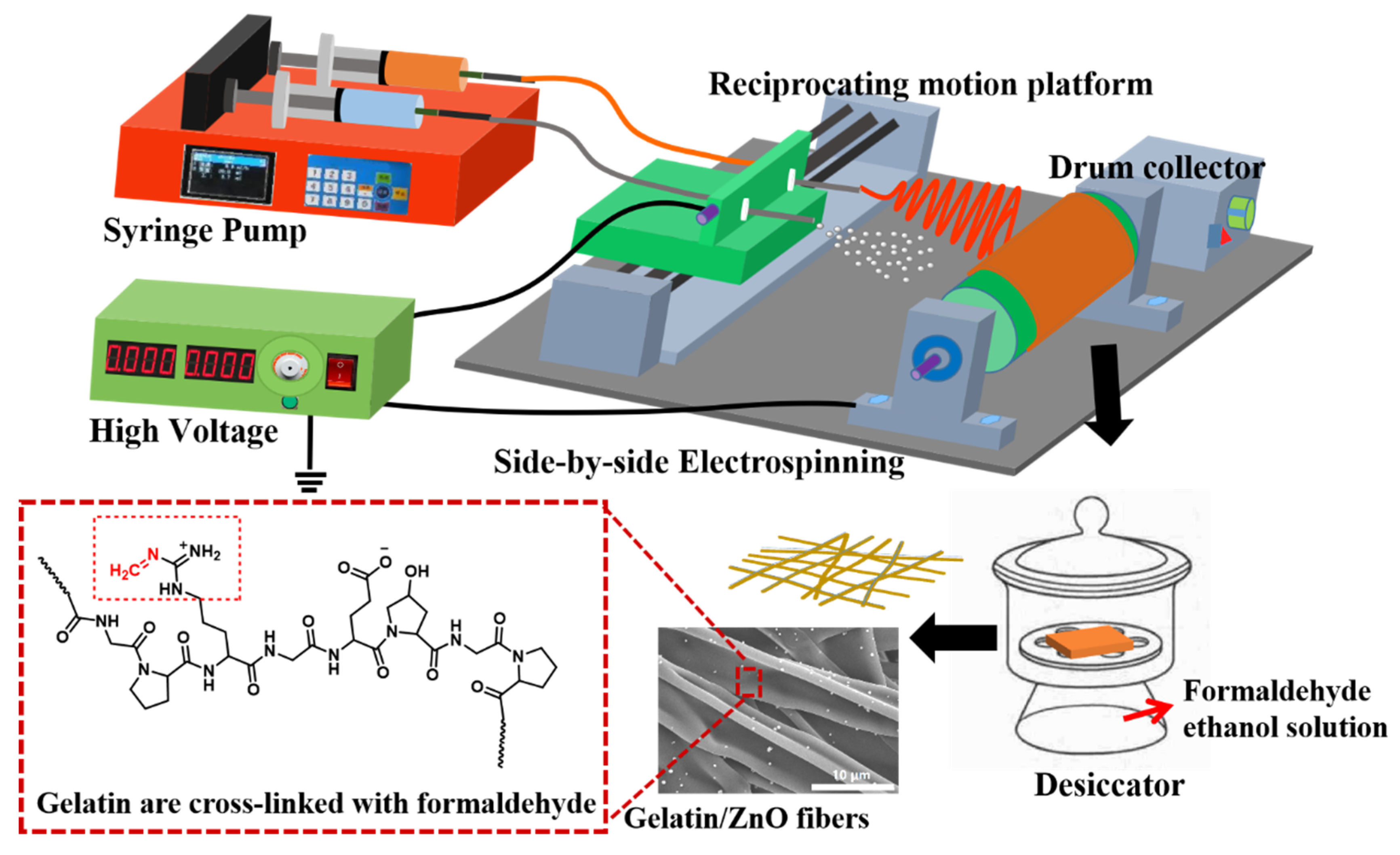
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of ZnO Particles
2.3. Preparation of Gelatin/ZnO Fibers
2.4. Characterization
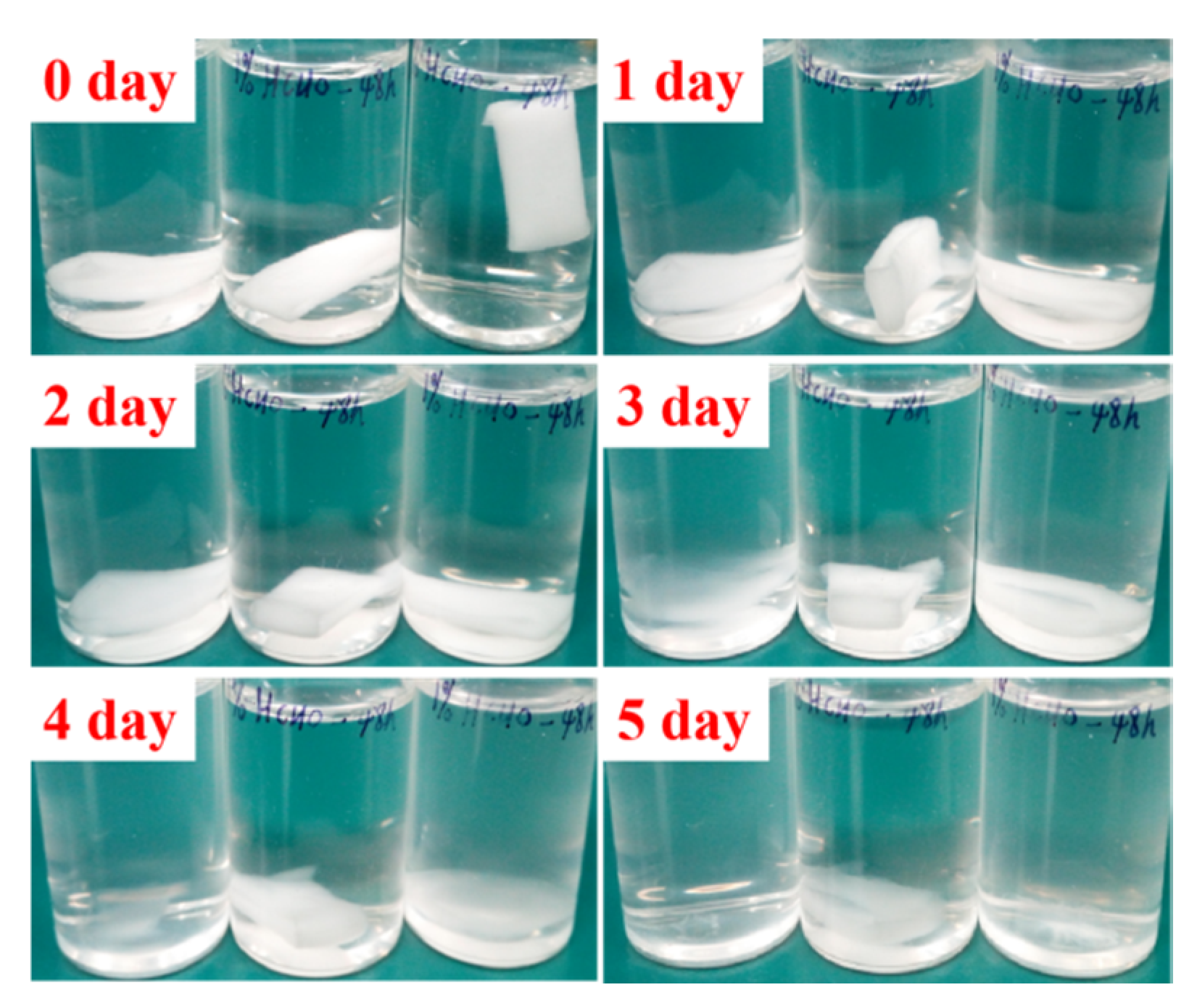
2.5. Stability of GZ2 in Aqueous Solutions
2.6. Cell Culture and Proliferation
2.7. Antibacterial Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
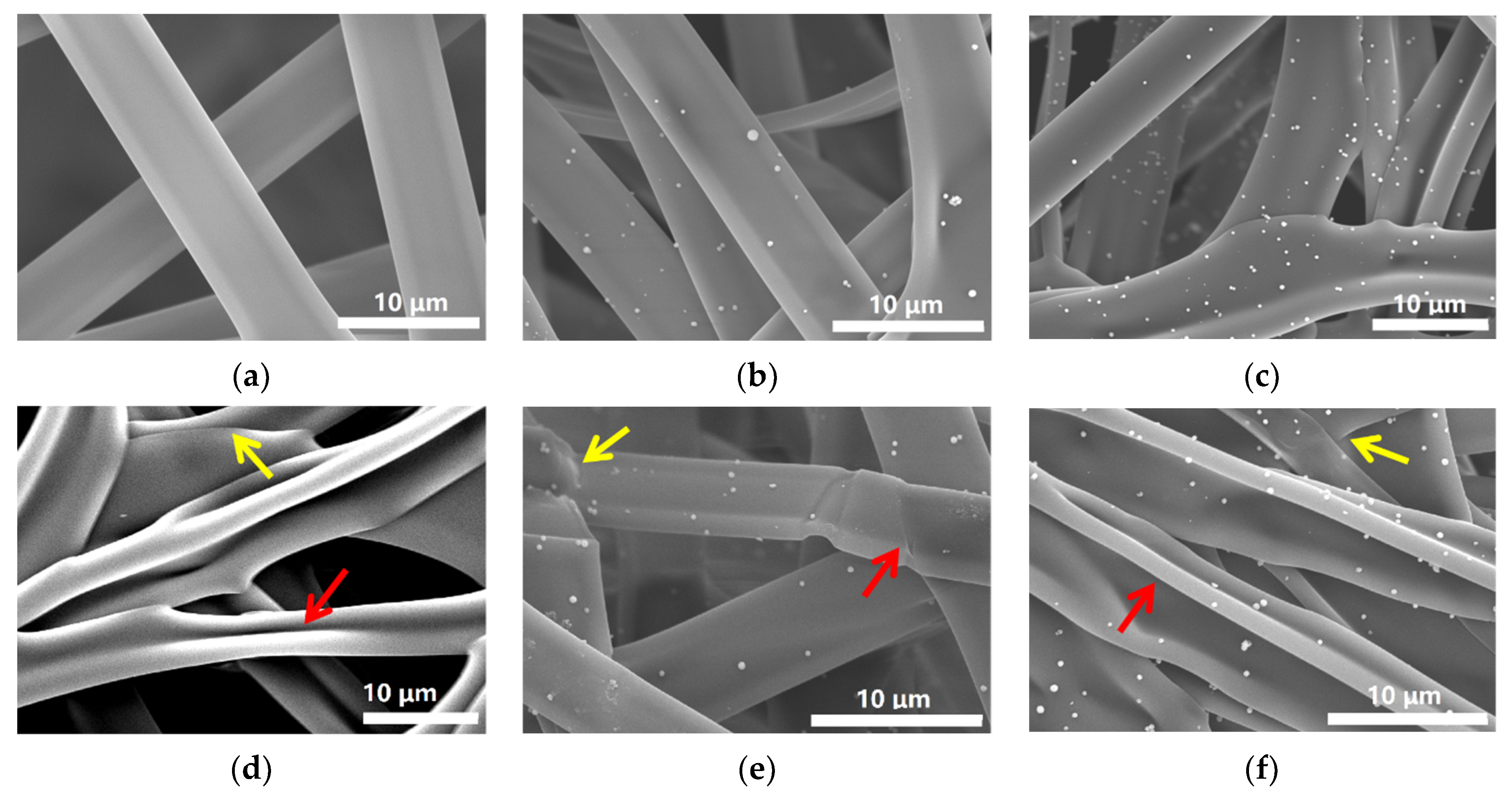
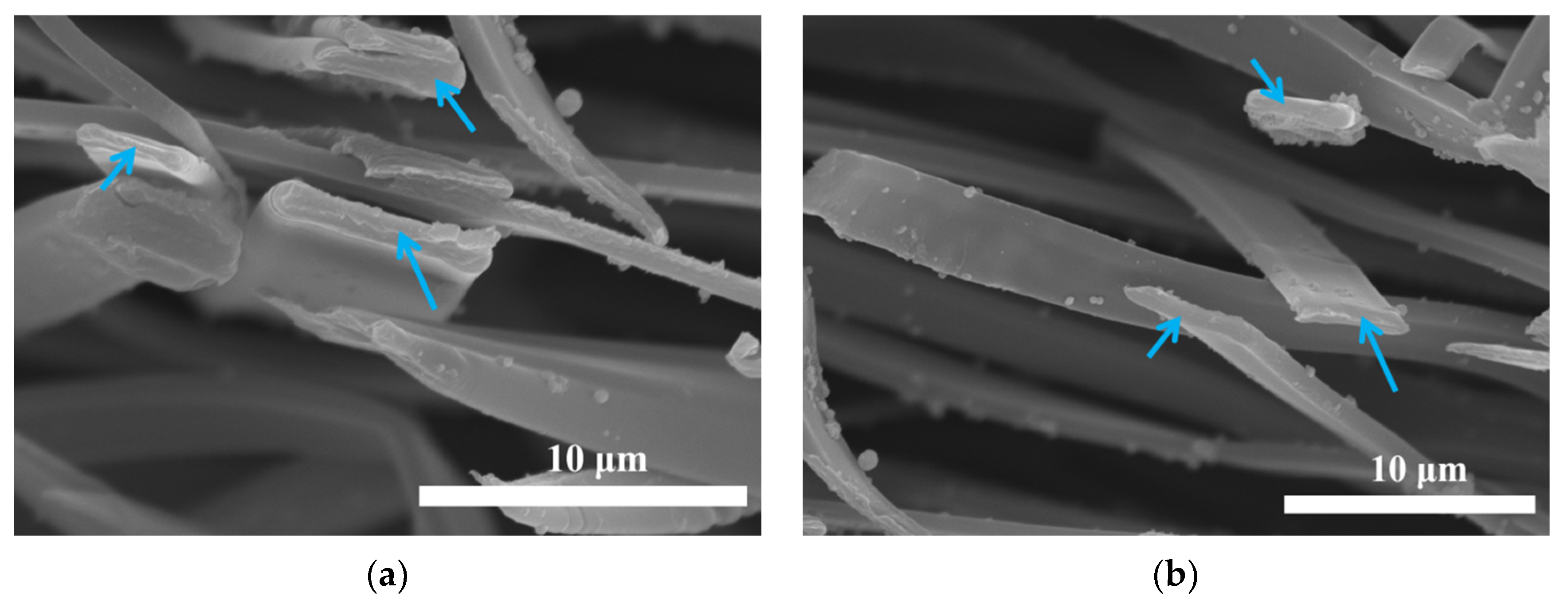
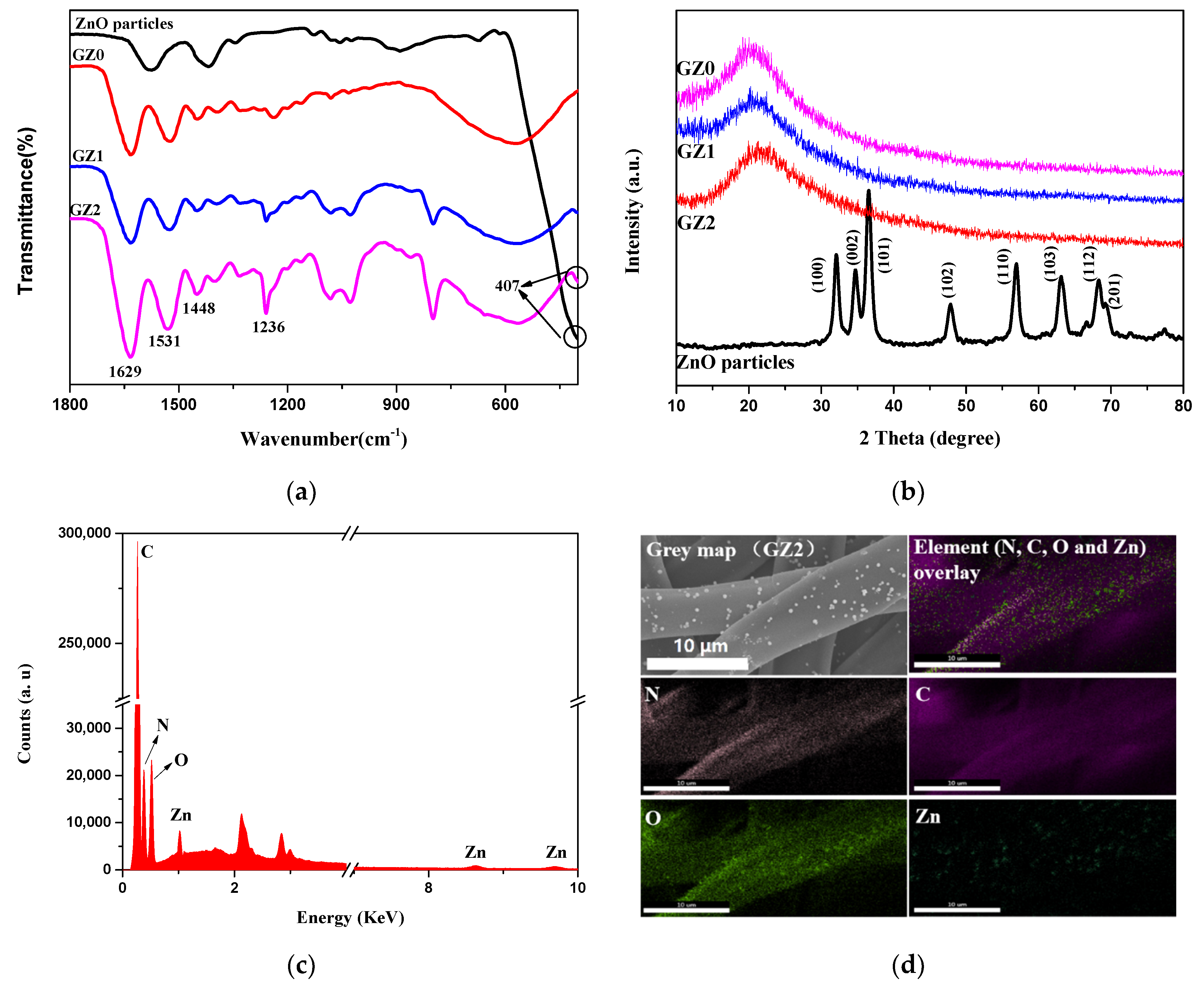
3.1. Morphologies of Gelatin/ZnO Fibers
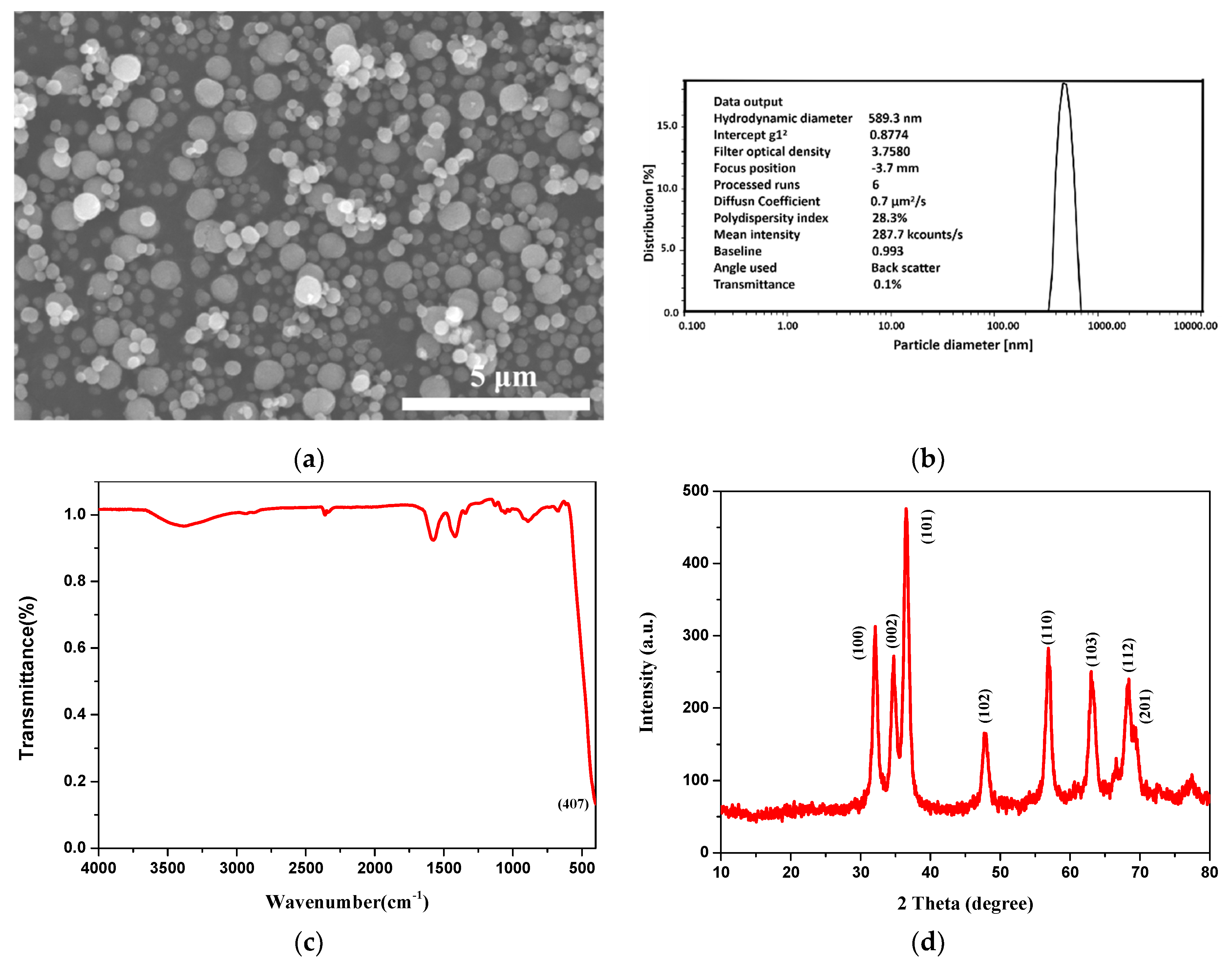
3.1.1. Characterization of ZnO Particles
3.1.2. Characterization of Gelatin/ZnO Fibers
3.2. Bioactivity Studies of Gelatin/ZnO Fibers
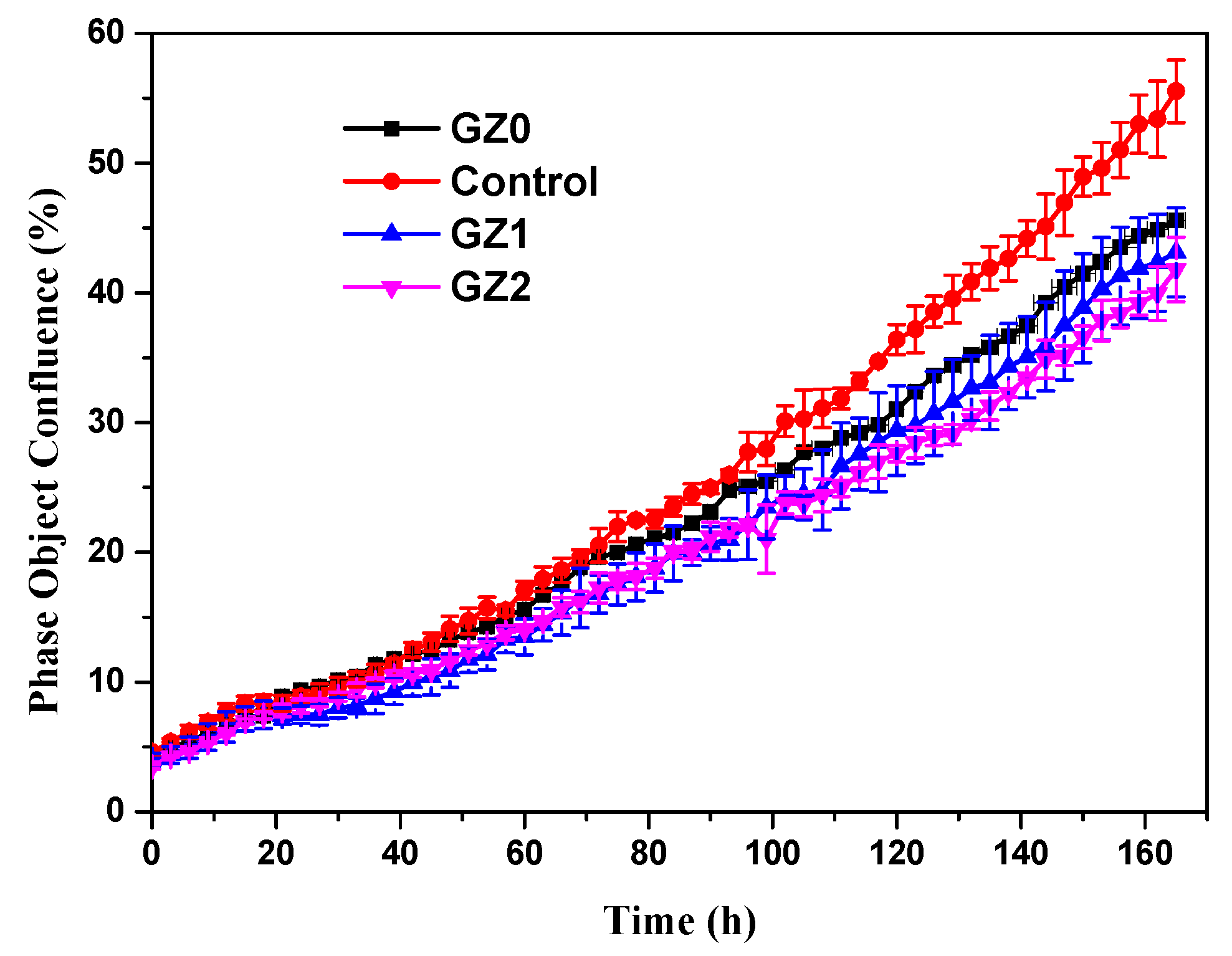
3.2.1. Cell Activity
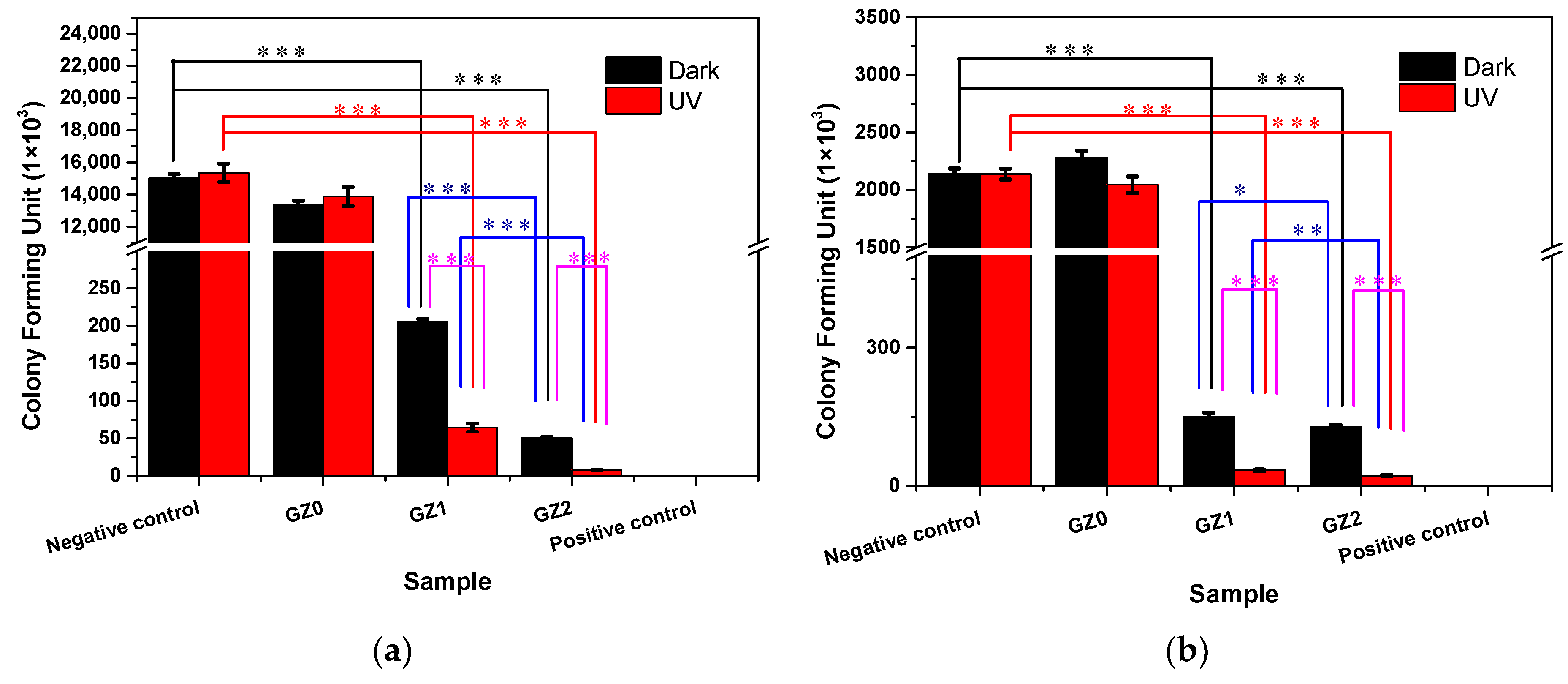
3.2.2. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, D.; Lu, Z.; Yang, H.; Gao, J.; Chen, R. A novel asymmetric wettable agnps/chitosan wound dressing: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3958–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Ye, D.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, W.; Zhang, N.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L. Effectively promoting wound healing with cellulose/gelatin sponges constructed directly from a cellulose solution. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7518–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dou, C.; He, G.; Ban, L.; Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Gong, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P. Biomedical Potential of Ultrafine Ag particles Coated on Poly (Gamma-Glutamic Acid) Hydrogel with Special Reference to Wound Healing. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Pan, S.; Jiang, F.; Wang, E.; Miinea, L.; Marchant, N.; Cakmak, M. Anisotropic swelling wound dressings with vertically aligned water absorptive particles. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 8173–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qu, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, R.; Yu, Q.; Yang, P. Self-assembled proteinaceous wound dressings attenuate secondary trauma and improve wound healing in vivo. J. Mater. Chem B 2018, 6, 4645–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, M.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Fatahi, Y.; Khademhosseini, A.; Kaplan, D.L. Overview of Silk Fibroin Use in Wound Dressings. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldana, A.A.; Malatto, L.; Rehman, M.A.U.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Abraham, G.A. Fabrication of Gelatin Methacrylate (GelMA) Scaffolds with Nano- and Micro-Topographical and Morphological Features. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, H.; Wu, Y. Superhydrophobic coatings on gelatin-based films: Fabrication, characterization and cytotoxicity studies. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 23712–23719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Q.; Miao, Y.; Yang, F.; Lin, X.; Zhang, L.-M.; Wang, Y. Zein/gelatin/nanohydroxyapatite nanofibrous scaffolds are biocompatible and promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Biomater. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppan, P.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M. Fabrication and investigation of nanofibrous matrices as esophageal tissue scaffolds using human non-keratinized, stratified, squamous epithelial cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 26461–26473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, R.; Kumar, P.S.; Sridhar, R.; Sundaramurthy, J.; Venugopal, J.; Mhaisalkar, S.G.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun composite fibers and their multifaceted applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2016, 22, 12953–12971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Shin, K.-H.; Noh, D.-Y.; Jo, I.-H.; Koh, Y.-H.; Choi, W.-Y.; Kim, H.-E. Nanofibrous gelatin-silica hybrid scaffolds mimicking the native extracellular matrix (ECM) using thermally induced phase separation. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14133–14140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, C.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Tunable Physical Properties of Ethylcellulose/Gelatin Composite fibers by Electrospinning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Feng, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Hao, X.; Lv, J.; Ma, N.; Li, W. Surface modification and endothelialization of biomaterials as potential scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5680–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalaja, K.; Sreehari, V.S.; Kumar, P.R.A.; Nirmala, R.J. Graphene oxide decorated electrospun gelatin fibers: Fabrication, properties and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 64, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, M.; Williams, G.R.; Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, L.-M. Electrospun gelatin fibers loaded with vitamins A and E as antibacterial wound dressing materials. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50267–50277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelshtein, I.; Applerot, G.; Perkas, N.; Wehrschetz-Sigl, E.; Hasmann, A.; Guebitz, G.M.; Gedanken, A. Antibacterial Properties of an In Situ Generated and Simultaneously Deposited Nanocrystalline ZnO on Fabrics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2008, 1, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, J.; Begum, G.; Kumar, K.P.; Misra, S.; Rana, R.K. Enabling Antibacterial Coating via Bioinspired Mineralization of Nanostructured ZnO on Fabrics under Mild Conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4457–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.K.; Sharma, P.K.; Bhargava, R.; Kumar, N.; Pandey, A.C. Differential Susceptibility of Escherichia coli Cells toward Transition Metal-Doped and Matrix-Embedded ZnO particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 5594–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, S.; Vaseeharan, B. Antibiofilm, anti cancer and ecotoxicity properties of collagen based ZnO particles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 2331–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Yan, D.; Yin, G.; Liao, X.; Kang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Huang, D.; Hao, B. Toxicological Effect of ZnO particles Based on Bacteria. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4140–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brayner, R.; Dahoumane, S.A.; Yéprémian, C.; Djediat, C.; Meyer, M.; Couté, A.; Fiévet, F. ZnO particles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Ecotoxicological Studies. Langmuir 2010, 26, 6522–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ding, H.; Sun, S. Preparation and Characterization of ZnO particles Supported on Amorphous SiO2. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Zou, L.; Feng, F.; Zhang, H. Hydrophobic Ethylcellulose/Gelatin fibers Containing Zinc Oxide particles for Antimicrobial Packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9498–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, H.; Deshpande, R.; Kanitkar, M.; Jaiswal, A.; Kale, V.P.; Bellare, J.R. A nano zinc oxide doped electrospun scaffold improves wound healing in a rodent model. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münchow, E.A.; Albuquerque, M.T.P.; Zero, B.; Kamocki, K.; Piva, E.; Gregory, R.L.; Bottino, M.C. Development and characterization of novel ZnO-loaded electrospun membranes for periodontal regeneration. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheesh Kumar, P.T.; Lakshmanan, V.-K.; Anilkumar, T.V.; Ramya, C.; Reshmi, P.; Unnikrishnan, A.G.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Flexible and Microporous Chitosan Hydrogel/Nano ZnO Composite Bandages for Wound Dressing: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Shen, C.; Feltis, B.N.; Martin, L.L.; Hughes, A.E.; Wright, P.F.A.; Turney, T.W. Reducing ZnO particle cytotoxicity by surface modification. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, I.-L.; Huang, Y.-J. Titanium Oxide Shell Coatings Decrease the Cytotoxicity of ZnO particles. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.-K.; Tripathy, N.; Son, H.-J.; Ha, K.-T.; Jeong, H.-S.; Hahn, Y.-B. A comprehensive in vitro and in vivo study of ZnO particles toxicity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2985–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chung, J.; Lee, J.; Myoung, J.; Lim, S. Synthesis of ZnO nanospheres with uniform nanopores by a hydrothermal process. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2011, 72, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Pal, U.; Serrano, J.G.; Ucer, K.B.; Williams, R.T. Photoluminesence and ftir study of ZnO particles: The impurity and defect perspective. Phys. Status Solidi 2010, 3, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; He, M.; Li, W.; Cheng, D.; Wang, X. Growing ZnO particles on polydopamine-templated cotton fabrics for durable antimicrobial activity and UV protection. Polymers 2018, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, H.; Song, Y. Environmentally Friendly Gelatin/β-Cyclodextrin Composite Fiber Adsorbents for the Efficient Removal of Dyes from Wastewater. Molecules 2018, 23, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Santhiya, D. In situ mineralization of bioactive glass in gelatin matrix. Mater. Lett. 2017, 188, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomakin, S.M.; Rogovina, S.Z.; Grachev, A.V.; Prut, E.V.; Alexanyan, C.V. Thermal Degradation of Biodegradable Blends of Polyethylene with Cellulose and Ethylcellulose. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 521, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Kim, J.E.; Lee, K.H. Green fabrication of antibacterial gelatin fiber for biomedical application. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 136, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonkar, S.P.; Pillai, V.; Abdala, A. Solvent-free Synthesis of ZnO-Graphene Nanocomposite with Superior Photocatalytic Activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 465, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.P.; Meshram, J.V.; Bohara, R.A.; Nanaware, S.G.; Pawar, S.H. ZnO particle-embedded silk fibroin-polyvinyl alcohol composite film: A potential dressing material for infected wounds. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 14620–14629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Tan, L.; Liu, T.; Meng, X. Solvothermal Synthesis of ZnO particles and Anti-Infection Application in Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghupathi, K.R.; Koodali, R.T.; Manna, A.C. Size-Dependent Bacterial Growth Inhibition and Mechanism of Antibacterial Activity of Zinc Oxide particles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4020–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


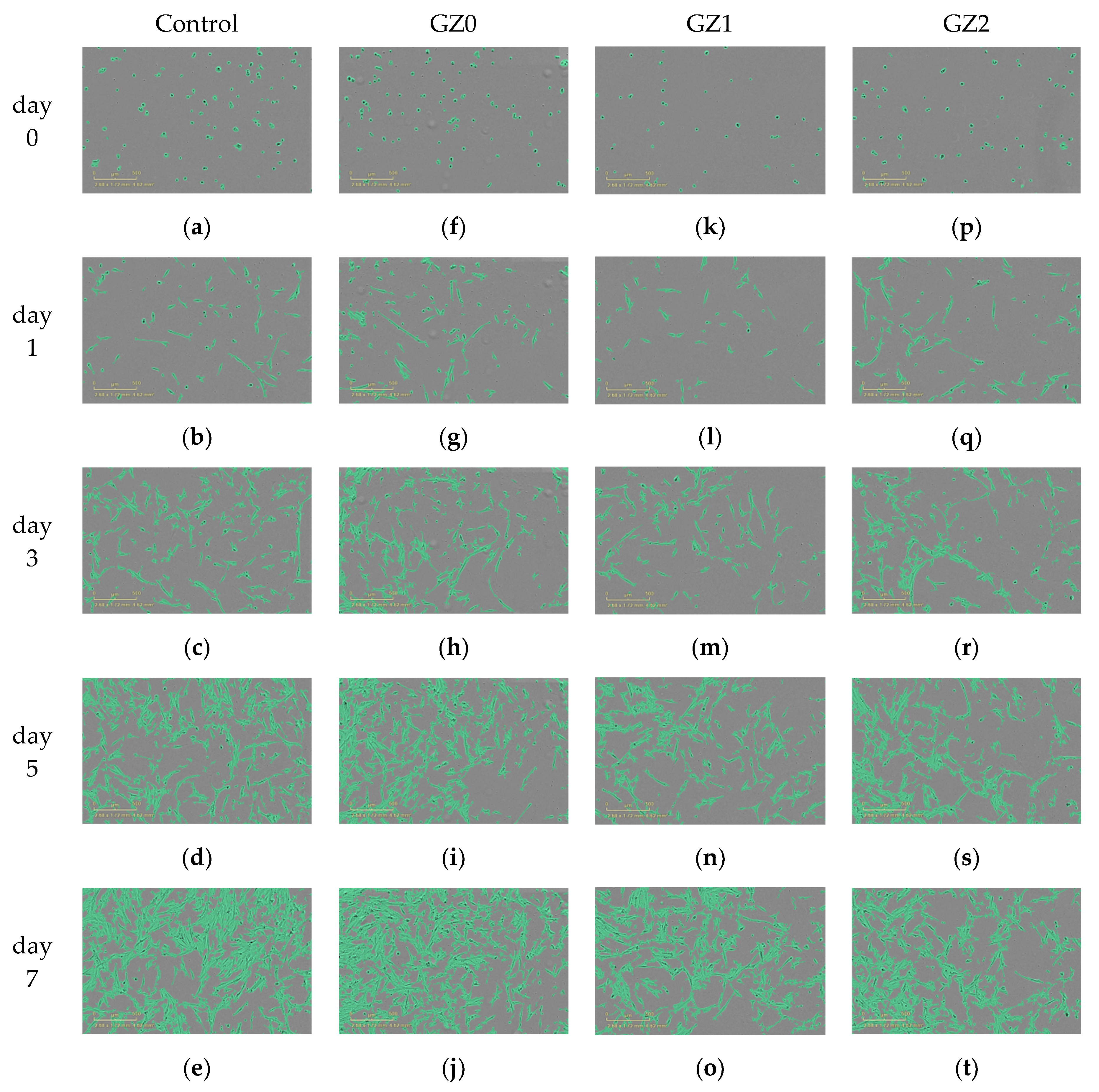

| Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 5 | Day 7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GZ0 | RGR (%) | 105.8 | 95.7 | 85.2 | 82.1 |
| Cytotoxicity level | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| GZ1 | RGR (%) | 84.6 | 81.2 | 80.7 | 77.6 |
| Cytotoxicity level | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| GZ2 | RGR (%) | 92.4 | 84.1 | 75.8 | 75.3 |
| Cytotoxicity level | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Cytotoxicity Level | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGR (%) | >100 | 75–99 | 50–74 | 25–49 | 1–24 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Lu, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y. Electrospun Gelatin Fibers Surface Loaded ZnO Particles as a Potential Biodegradable Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040525
Chen Y, Lu W, Guo Y, Zhu Y, Song Y. Electrospun Gelatin Fibers Surface Loaded ZnO Particles as a Potential Biodegradable Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(4):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040525
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yu, Weipeng Lu, Yanchuan Guo, Yi Zhu, and Yeping Song. 2019. "Electrospun Gelatin Fibers Surface Loaded ZnO Particles as a Potential Biodegradable Antibacterial Wound Dressing" Nanomaterials 9, no. 4: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040525
APA StyleChen, Y., Lu, W., Guo, Y., Zhu, Y., & Song, Y. (2019). Electrospun Gelatin Fibers Surface Loaded ZnO Particles as a Potential Biodegradable Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Nanomaterials, 9(4), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040525





