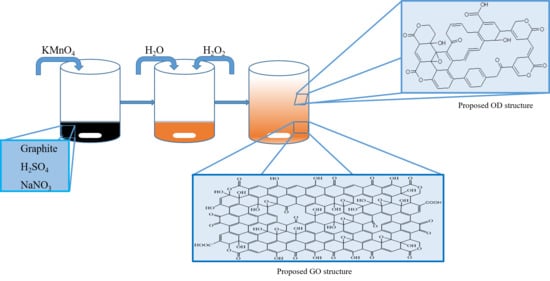
Structural Characterization of Graphene Oxide: Surface Functional Groups and Fractionated Oxidative Debris
Abstract
Share and Cite
Aliyev, E.; Filiz, V.; Khan, M.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Abetz, C.; Abetz, V. Structural Characterization of Graphene Oxide: Surface Functional Groups and Fractionated Oxidative Debris. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081180
Aliyev E, Filiz V, Khan MM, Lee YJ, Abetz C, Abetz V. Structural Characterization of Graphene Oxide: Surface Functional Groups and Fractionated Oxidative Debris. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(8):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081180
Chicago/Turabian StyleAliyev, Elvin, Volkan Filiz, Muntazim M. Khan, Young Joo Lee, Clarissa Abetz, and Volker Abetz. 2019. "Structural Characterization of Graphene Oxide: Surface Functional Groups and Fractionated Oxidative Debris" Nanomaterials 9, no. 8: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081180
APA StyleAliyev, E., Filiz, V., Khan, M. M., Lee, Y. J., Abetz, C., & Abetz, V. (2019). Structural Characterization of Graphene Oxide: Surface Functional Groups and Fractionated Oxidative Debris. Nanomaterials, 9(8), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9081180