Fabrication, Characterization and Application of Biomolecule Micropatterns on Cyclic Olefin Polymer (COP) Surfaces with Adjustable Contrast
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Micropatterned Peptide Surfaces
2.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.4. Fluorescence Microscopy and Assay Readout
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of Micropatterned COP Foils Using Photolithography Followed by the Immobilization of Biomolecules
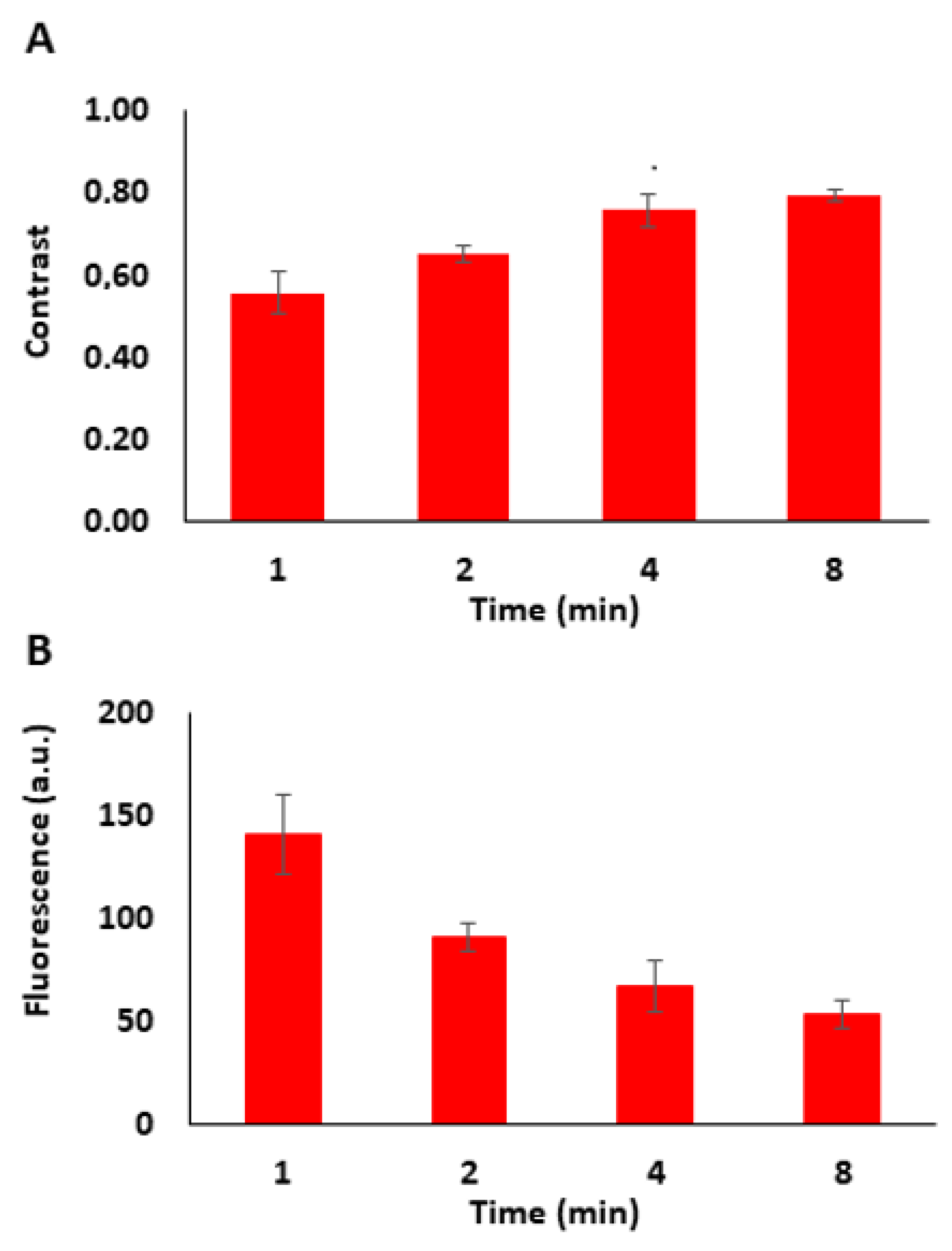
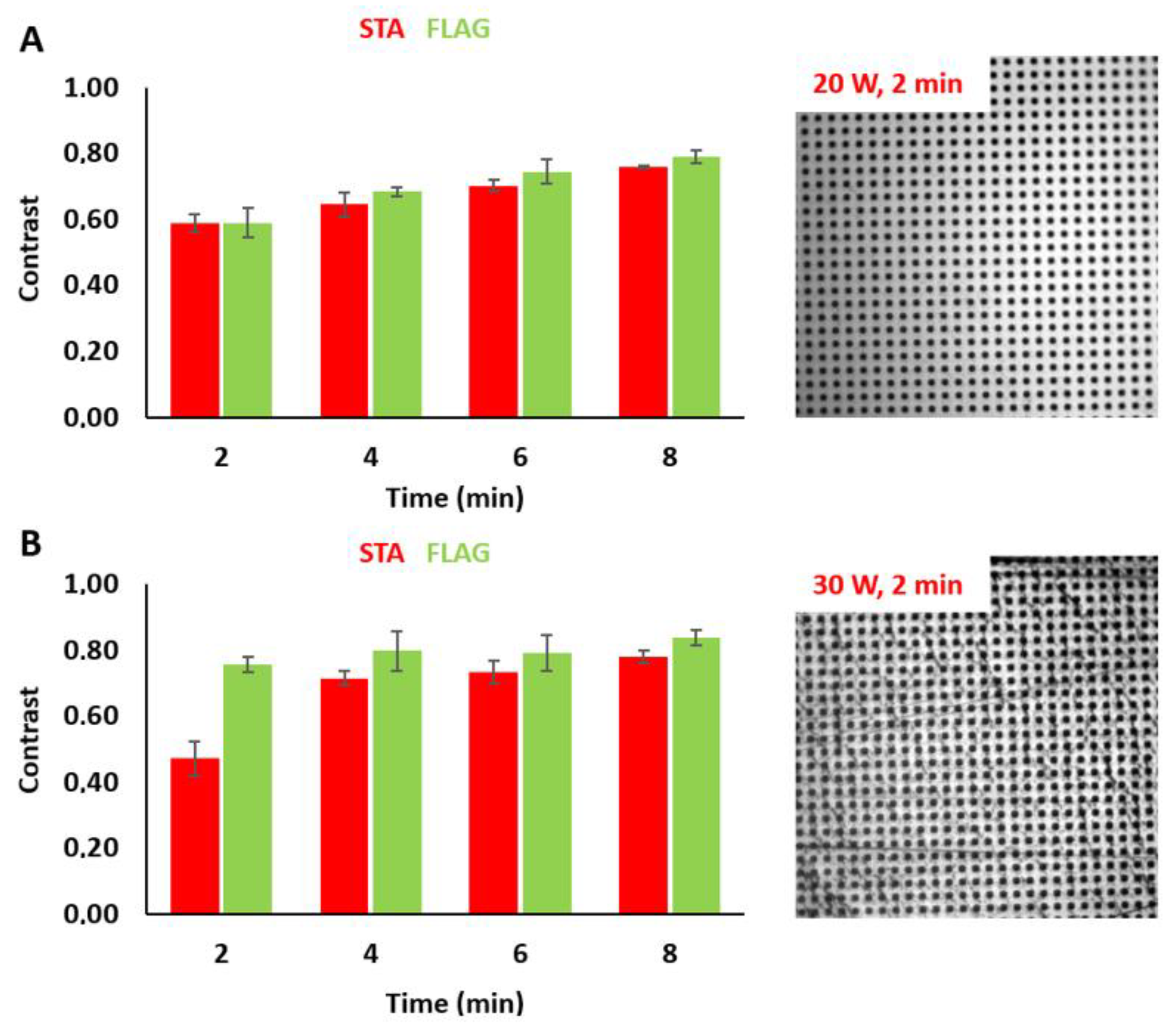
3.2. Tuning the Fluorescence Intensity of Immobilized Biomolecules
3.3. Specific Receptor Interactions in a Live-Cell Context
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Hong, H.J.; Koom, W.S.; Koh, W.G. Cell Microarray Technologies for High-Throughput Cell-Based Biosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joos, T.O.; Schrenk, M.; Hopfl, P.; Kroger, K.; Chowdhury, U.; Stoll, D.; Schorner, D.; Durr, M.; Herick, K.; Rupp, S.; et al. A microarray enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for autoimmune diagnostics. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochte, S.; Waichman, S.; Beutel, O.; You, C.; Piehler, J. Live cell micropatterning reveals the dynamics of signaling complexes at the plasma membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 207, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacBeath, G. Protein microarrays and proteomics. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, M.G.; Shackman, J.G.; Dahlgren, G.M.; Kennedy, R.T. Microfluidic chip for continuous monitoring of hormone secretion from live cells using an electrophoresis-based immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4711–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetala, K.K.R.; Vijayalakshmi, M.A. A review on recent developments for biomolecule separation at analytical scale using microfluidic devices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 906, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Ma, W.; Zheng, W. PCR microfluidic devices for DNA amplification. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 243–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focke, M.; Kosse, D.; Muller, C.; Reinecke, H.; Zengerle, R.; von Stetten, F. Lab-on-a-Foil: Microfluidics on thin and flexible films. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1365–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M.; Ostuni, E.; Takayama, S.; Jiang, X.; Ingber, D.E. Soft lithography in biology and biochemistry. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 3, 335–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Piehler, J. Functional protein micropatterning for drug design and discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipponi, L.; Livingston, P.; Kaspar, O.; Tokarova, V.; Nicolau, D.V. Protein patterning by microcontact printing using pyramidal PDMS stamps. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, C.; Sun, Y.; Simmons, C.A. Solving the shrinkage-induced PDMS alignment registration issue in multilayer soft lithography. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2009, 19, 065015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumens, C.V.; Ziai, M.A.; Belsey, K.E.; Batchelor, J.C.; Holder, S.J. Swelling of PDMS networks in solvent vapours; applications for passive RFID wireless sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, A.; Reinhoudt, D.N.; Huskens, J. Microcontact Printing: Limitations and Achievements. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2257–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, R.; Arnold, A.; Sevcsik, E.; Schutz, G.J.; Howorka, S. Tunable DNA Hybridization Enables Spatially and Temporally Controlled Surface-Anchoring of Biomolecular Cargo. Langmuir: ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2018, 34, 15021–15027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipp, A.M.; Ji, B.; Hager, R.; Haas, S.; Schweiggl, S.; Sonnleitner, A.; Haselgrubler, T. Micro-structured peptide surfaces for the detection of high-affinity peptide-receptor interactions in living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piner, R.D.; Zhu, J.; Xu, F.; Hong, S.; Mirkin, C.A. “Dip-Pen” nanolithography. Science 1999, 283, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truskett, V.N.; Watts, M.P. Trends in imprint lithography for biological applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.S.; Ohlsson, P.D.; Ordeig, O.; Kutter, J.P. Cyclic olefin polymers: Emerging materials for lab-on-a-chip applications. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2010, 9, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, R.E.; Sorkin, A. Endocytosis of functional epidermal growth factor receptor-green fluorescent protein chimera. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 35000–35007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.L.; Larsson, A.; Ocklind, A.; Öhrlund, A. Characterization of air plasma-treated polymer surfaces by ESCA and contact angle measurements for optimization of surface stability and cell growth. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 86, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinas, K.; Tsougeni, K.; Petrou, P.S.; Boulousis, G.; Tsoukleris, D.; Pavlatou, E.; Tserepi, A.; Kakabakos, S.E.; Gogolides, E. Three-dimensional plasma micro-nanotextured cyclo-olefin-polymer surfaces for biomolecule immobilization and environmentally stable superhydrophobic and superoleophobic behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langowski, B.A.; Uhrich, K.E. Microscale plasma-initiated patterning (muPIP). Langmuir: ACS J. Surf. colloids 2005, 21, 10509–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsharhan, A.T.; Acevedo, R.; Warren, R.; Sochol, R.D. 3D microfluidics via cyclic olefin polymer-based in situ direct laser writing. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 2799–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisset, F.; Vieillard, J.; Berton, B.; Morin-Grognet, S.; Duclairoir-Poc, C.; Le Derf, F. Surface functionalization of cyclic olefin copolymer with aryldiazonium salts: A covalent grafting method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 329, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.P.; Kang, S.M.; Hong, D.; Lee, H.Y.; Choi, I.S.; Ko, S.; Lee, J.K. Immobilization of Antibody on a Cyclic Olefin Copolymer Surface with Functionalizable, Non-Biofouling Poly[Oligo(Ethylene Glycol) Methacrylate]. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 1767–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.K.; Nikolov, P.M.; Giselbrecht, S.; Niemeyer, C.M. DNA-SMART: Biopatterned Polymer Film Microchannels for Selective Immobilization of Proteins and Cells. Small 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzerstorfer, P.; Borgmann, D.; Schutz, G.; Winkler, S.M.; Hoglinger, O.; Weghuber, J. Quantification and kinetic analysis of Grb2-EGFR interaction on micro-patterned surfaces for the characterization of EGFR-modulating substances. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzerstorfer, P.; Yoneyama, Y.; Hakuno, F.; Muller, U.; Hoglinger, O.; Takahashi, S.; Weghuber, J. Analysis of insulin receptor substrate signaling dynamics on microstructured surfaces. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 987–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbacher, M.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Brameshuber, M.; Hesch, C.; Paster, W.; Weghuber, J.; Heise, B.; Sonnleitner, A.; Stockinger, H.; Schutz, G.J. Micropatterning for quantitative analysis of protein-protein interactions in living cells. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weghuber, J.; Brameshuber, M.; Sunzenauer, S.; Lehner, M.; Paar, C.; Haselgrubler, T.; Schwarzenbacher, M.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Hesch, C.; Paster, W.; et al. Detection of protein-protein interactions in the live cell plasma membrane by quantifying prey redistribution upon bait micropatterning. Methods Enzymol. 2010, 472, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weibel, D.B.; Diluzio, W.R.; Whitesides, G.M. Microfabrication meets microbiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Fernandez, M.L.; Tynan, C.J.; Webb, S.E. A ‘pocket guide’ to total internal reflection fluorescence. J. Microsc. 2013, 252, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laib, S.; MacCraith, B.D. Immobilization of biomolecules on cycloolefin polymer supports. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6264–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zaytseva, N.V.; Wu, Q.; Li, M.; Fang, Y. Microplate-compatible total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy for receptor pharmacology. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 193702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.; Mowlem, M.C.; Morgan, H. Characterisation of an irreversible bonding process for COC–COC and COC–PDMS–COC sandwich structures and application to microvalves. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheicher, S.R.; Krammer, K.; Fian, A.; Kargl, R.; Ribitsch, V.; Köstler, S. Patterned Surface Activation of Cyclo-Olefin Polymers for Biochip Applications. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2014, 58, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holowka, D.; Baird, B. Mechanisms of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling as characterized by patterned ligand activation and mutational analysis. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, T.R. Molecular Events at Tissue-Biomaterial Interface. In Host Response to Biomaterials; Badylak, S.F., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 81–116. [Google Scholar]
- Schutz, G.J.; Weghuber, J.; Lanzerstorfer, P.; Sevcsik, E. Protein Micropatterning Assay: Quantitative Analysis of Protein-Protein Interactions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1550, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, C.; Roeters, S.J.; Franz, J.; Weidner, T.; Bonn, M.; Gonella, G. Repelling and ordering: The influence of poly (ethylene glycol) on protein adsorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2017, 19, 28182–28188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.L.; Schlapak, R.; Hager, R.; Szleifer, I.; Howorka, S. Molecular and Thermodynamic Factors Explain the Passivation Properties of Poly(ethylene glycol)-Coated Substrate Surfaces against Fluorophore-Labeled DNA Oligonucleotides. Langmuir: ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2015, 31, 11491–11501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilek, M.M.; McKenzie, D.R. Plasma modified surfaces for covalent immobilization of functional biomolecules in the absence of chemical linkers: Towards better biosensors and a new generation of medical implants. Biophys. Rev. 2010, 2, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volcke, C.; Gandhiraman, R.P.; Gubala, V.; Raj, J.; Cummins, T.; Fonder, G.; Nooney, R.I.; Mekhalif, Z.; Herzog, G.; Daniels, S.; et al. Reactive amine surfaces for biosensor applications, prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapour modification of polyolefin materials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hager, R.; Haselgrübler, T.; Haas, S.; Lipp, A.-M.; Weghuber, J. Fabrication, Characterization and Application of Biomolecule Micropatterns on Cyclic Olefin Polymer (COP) Surfaces with Adjustable Contrast. Biosensors 2020, 10, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10010003
Hager R, Haselgrübler T, Haas S, Lipp A-M, Weghuber J. Fabrication, Characterization and Application of Biomolecule Micropatterns on Cyclic Olefin Polymer (COP) Surfaces with Adjustable Contrast. Biosensors. 2020; 10(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleHager, Roland, Thomas Haselgrübler, Sandra Haas, Anna-Maria Lipp, and Julian Weghuber. 2020. "Fabrication, Characterization and Application of Biomolecule Micropatterns on Cyclic Olefin Polymer (COP) Surfaces with Adjustable Contrast" Biosensors 10, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10010003
APA StyleHager, R., Haselgrübler, T., Haas, S., Lipp, A.-M., & Weghuber, J. (2020). Fabrication, Characterization and Application of Biomolecule Micropatterns on Cyclic Olefin Polymer (COP) Surfaces with Adjustable Contrast. Biosensors, 10(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10010003




