Nanoelectrode Arrays Fabricated by Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography for Biosensing Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
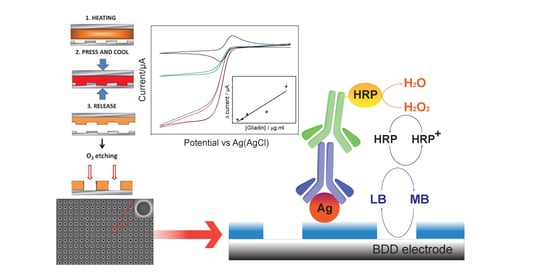
2.2. Stamp Fabrication
2.3. NEA Fabrication
2.4. Surface Functionalization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of NEAs
3.2. Detection of Gliadin Fragment on the Immunosensor Platform
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Electrochemical sensors for clinic analysis. Sensors 2008, 8, 2043–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduini, F.; Cinti, S.; Scognamiglio, V.; Moscone, D. Nanomaterials in electrochemical biosensors for pesticide detection: Advances and challenges in food analysis. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2063–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed.; (the “Gold Book”); Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials and Nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Qin, Y. Electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3965–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Virgilio, F.; Prasciolu, M.; Ugo, P.; Tormen, M. Development of electrochemical biosensors by e-beam lithography for medical diagnostics. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 111, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arrigan, D.W.M. Nanoelectrodes, nanoelectrode arrays and their applications. Analyst 2004, 129, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatore, C.; Pebay, C.; Servant, L.; Sojic, N.; Szunerits, S.; Thouin, L. Mapping electrochemiluminescence as generated at double-band microelectrodes by confocal microscopy under steady state. ChemPhysChem 2006, 7, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley&Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ugo, P.; Moretto, L.M.; Bellomi, S.; Menon, V.P.; Martin, C.R. Ion-exchange voltammetry at polymer film-coated nanoelectrode ensembles. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 4160–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusling, J.F.; Sotzing, G.; Papadimitrakopoulosa, F. Designing nanomaterial-enhanced electrochemical immunosensors for cancer biomarker proteins. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 76, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amatore, C.; Oleinick, A.I.; Svir, I. Numerical simulation of diffusion processes at recessed disk microelectrode arrays using the quasi-conformal mapping approach. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4397–4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Lindner, E. Cyclic voltammograms at coplanar and shallow recessed microdisk electrode arrays: Guidelines for design and experiment. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, Y.L.; Ding, Z.; Zhan, D.; Long, Y.T. Advanced electroanalytical chemistry at nanoelectrodes. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 3338–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatore, C.; Savéant, J.M.; Tessier, D. Charge Transfer at Partially Blocked Surfaces—A Model for the Case of Microscopic Active and Inactive Sites. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1983, 147, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Ugo, P. Recent advances in sensing and biosensing with arrays of nanoelectrodes. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 16, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkin, M.V.; Fan, F.-R.F.; Bard, A.J. Scanning electrochemical Part 13. Evaluation microelectrodes microscopy size of the tip shapes of nanometer. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1992, 328, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Moretto, L.M.; Ugo, P. Nanobiosensing with arrays and ensembles of nanoelectrodes. Sensors 2017, 17, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandison, M.E.; Cooper, J.M. Nanofabrication of electrode arrays by electron-beam and nanoimprint lithographies. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanyon, Y.H.; De Marzi, G.; Watson, Y.E.; Quinn, A.J.; Gleeson, J.P.; Redmond, G.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Fabrication of nanopore array electrodes by focused ion beam milling. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3048–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albonetti, C.; Martinez, J.; Losilla, N.S.; Greco, P.; Cavallini, M.; Borgatti, F.; Montecchi, M.; Pasquali, L.; Garcia, R.; Biscarini, F. Parallel-local anodic oxidation of silicon surfaces by soft stamps. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 435303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albisetti, E.; Petti, D.; Pancaldi, M.; Madami, M.; Tacchi, S.; Curtis, J.; King, W.P.; Papp, A.; Csaba, G.; Porod, W.; et al. Nanopatterning reconfigurable magnetic landscapes via thermally assisted scanning probe lithography. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Losilla, N.S.; Martínez, J.; García, R. Large area nanoscale patterning of silicon surfaces by parallel local oxidation. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 475304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sentic, M.; Virgilio, F.; Zanut, A.; Manojlovic, D.; Arbault, S.; Tormen, M.; Sojic, N.; Ugo, P. Microscopic imaging and tuning of electrogenerated chemiluminescence with boron-doped diamond nanoelectrode arrays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7085–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sotomayor Torres, C.M.; Zankovych, S.; Seekamp, J.; Kam, A.P.; Clavijo Cedeño, C.; Hoffmann, T.; Ahopelto, J.; Reuther, F.; Pfeiffer, K.; Bleidiessel, G.; et al. Nanoimprint lithography: An alternative nanofabrication approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2003, 23, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cefarin, N.; Cian, A.; Sonato, A.; Sovernigo, E.; Suran, F.; Teklu, Z.; Zanut, A.; Pozzato, A.; Tormen, M. Nanostructuring methylammonium lead iodide perovskite by ultrafast nano imprinting lithography. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 176, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauksher, W.J.; Le, N.V.; Ainley, E.S.; Nordquist, K.J.; Gehoski, K.A.; Young, S.R.; Baker, J.H.; Convey, D.; Mangat, P.S. Nano-imprint lithography: Templates, imprinting and wafer pattern transfer. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, I.W.; Cheng, D.F.; Jhaveri, S.B.; Carter, K.R. High-resolution soft lithography of thin film resists enabling nanoscopic pattern transfer. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretto, L.M.; Tormen, M.; De Leo, M.; Carpentiero, A.; Ugo, P. Polycarbonate-based ordered arrays of electrochemical nanoelectrodes obtained by e-beam lithography. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 185305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silvestrini, M.; Fruk, L.; Moretto, L.M.; Ugo, P. Detection of DNA Hybridization by Methylene Blue Electrochemistry at Activated Nanoelectrode Ensembles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 3437–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestrini, M.; Fruk, L.; Ugo, P. Functionalized ensembles of nanoelectrodes as affinity biosensors for DNA hybridization detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Habtamu, H.B.; Not, T.; De Leo, L.; Longo, S.; Moretto, L.M.; Ugo, P. Electrochemical immunosensor based on nanoelectrode ensembles for the serological analysis of IgG-type tissue transglutaminase. Sensors 2019, 19, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bottari, F.; Oliveri, P.; Ugo, P. Electrochemical immunosensor based on ensemble of nanoelectrodes for immunoglobulin IgY detection: Application to identify hen’s egg yolk in tempera paintings. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugo, P.; Moretto, L.M.; Vezzà, F. Ionomer-coated electrodes and nanoelectrode ensembles as electrochemical environmental sensors: Recent advances and prospects. ChemPhysChem 2002, 3, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, I.D.; Dirks, M.H.; Liptak, G.S.; Colletti, R.B.; Fasano, A.; Guandalini, S.; Hoffenberg, E.J.; Horvath, K.; Murray, J.A.; Pivor, M.; et al. Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Celiac Disease in Children: Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, I.S.; Day, A.S.; Shaoul, R. Gluten in celiac disease more or less? Rambam Maimonides Med. J. 2019, 10, e0007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Wang, K.; Weng, S.; Lei, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, W.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y. Development of electrochemical DNA biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; Volpe, G.; Micheli, L.; Palleschi, G. A review on novel developments and applications of immunosensors in food analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 605, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elofsson, U.; Eliasson, A.C.; Wahlgren, M.; Loosveld, A.M.A.; Courtin, C.M.; Delcour, J.A. Adsorption studies of interaction between water-extractable nonstarch polysaccharides and prolamins in cereals. Cereal Chem. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| O2 Plasma | Fluorine-Based Plasma | Plasma Ashing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coil power | 200 W | 400 W | 800 W |
| Platen power | 10 W | 20 W | 20 W |
| Flow | O2 40 sccm | SF6 30 sccm C4F8 60 sccm Ar 10 sccm | O2 50 sccm |
| Pressure | 4 mT | 8 mT | 20 mT |
| BIAS | 35 V | 95 V | 45 V |
| Time | 15 s | 15 s | 15 s |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanut, A.; Cian, A.; Cefarin, N.; Pozzato, A.; Tormen, M. Nanoelectrode Arrays Fabricated by Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography for Biosensing Application. Biosensors 2020, 10, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10080090
Zanut A, Cian A, Cefarin N, Pozzato A, Tormen M. Nanoelectrode Arrays Fabricated by Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography for Biosensing Application. Biosensors. 2020; 10(8):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10080090
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanut, Alessandra, Alessandro Cian, Nicola Cefarin, Alessandro Pozzato, and Massimo Tormen. 2020. "Nanoelectrode Arrays Fabricated by Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography for Biosensing Application" Biosensors 10, no. 8: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10080090
APA StyleZanut, A., Cian, A., Cefarin, N., Pozzato, A., & Tormen, M. (2020). Nanoelectrode Arrays Fabricated by Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography for Biosensing Application. Biosensors, 10(8), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10080090