Electrochemical Detection and Capillary Electrophoresis: Comparative Studies for Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Release from Living Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Chemicals and Instruments
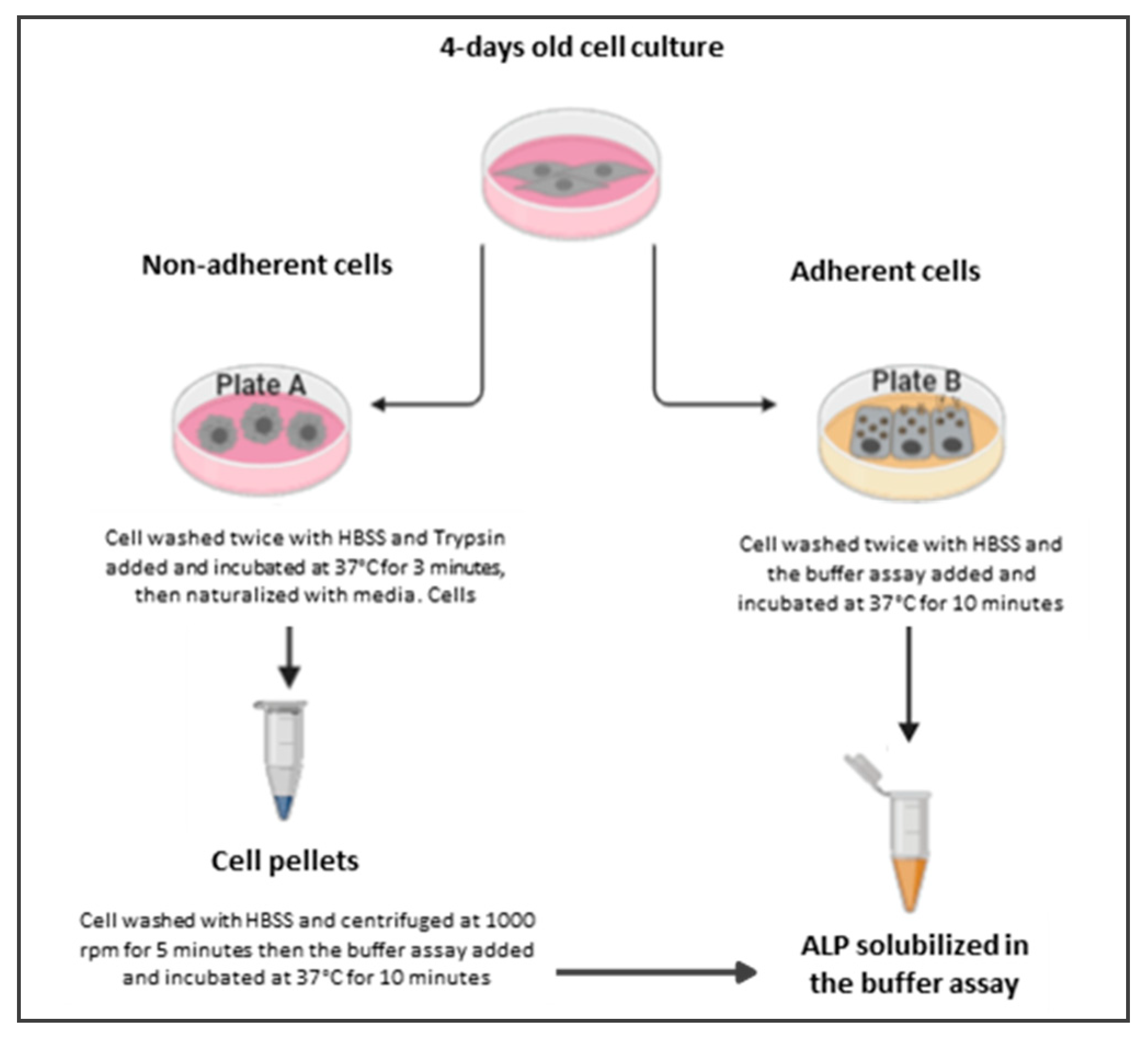
2.2. ALP Release and Cell Culture
2.3. Stabilization of Graphite Screen-Printed Electrodes
2.4. Optimization of Electrochemical Measurement
2.5. Linearity Performance of ALP Release vs. Cell Number
2.6. Concentration of the Substrate pAPP from Adhesion Cells
2.7. Comparative Study of ALP Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stabilization of Graphite Screen-Printed Electrodes
3.2. Optimization of Electrochemical Measurement

3.3. Linearity Performance of ALP Release vs. Cell Number
3.4. Concentration of the Substrate pAPP from Adhesion Cells
3.5. Comparative Study of ALP Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Millán, J.L. Mammalian Alkaline Phosphatases: From Biology to Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tartter, P.I.; Slater, G.; Gelernt, I.; Aufses, A.H. Screening for Liver Metastases from Colorectal Cancer with Carcinoembryonic Antigen and Alkaline Phosphatase. Ann. Surg. 1981, 193, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibali, O.; Petrucci, M.; Santini, D.; Mariani, M.; Pisani, F.; Bongarzoni, V.; Venditti, O.; Rago, A.; Cerchiara, E.; Fiorini, A.; et al. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Levels in Multiple Myeloma (MM) And Cancer With Bone Lesions: Is There any Difference? Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015, 15, e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, E.A.; Said, R.N.; Mosallam, D.S.; Moawad, E.M.; Kamal, N.; Fathallah, M.G.-D. Serial serum alkaline phosphatase as an early biomarker for osteopenia of prematurity. Medicine 2016, 95, e4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Linb, Y. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors Based on Nanomaterials and Nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2014, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.Q.; Barone, G.C.; Halsall, H.; Heineman, W.R. Comparison of methods for following alkaline phosphatase catalysis: Spectrophotometric versus amperometric detection. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 192, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Yamazaki, S.-I.; Kano, K.; Ikeda, T. Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of alkaline phosphatase. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 424, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Wang, K.; Bartling, B.; Liu, C.-C. The Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase Using an Electrochemical Biosensor in a Single-Step Approach. Sensors 2009, 9, 8709–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, S.-P.; Wu, J.; Yi-Bin, Y.; Ji, F. Electrochemical Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase Using Ionic Liquid Modified Carbon Nanotubes Electrode. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 40, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Ma, F.; Zhao, F.; He, Q.; Du, J.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, L. Comparing the performances of electrochemical sensors using p-aminophenol redox cycling by different reductants on gold electrodes modified with self-assembled monolayers. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 109, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, T.; Li, H.; Li, F. A highly sensitive homogeneous electrochemical assay for alkaline phosphatase activity based on single molecular beacon-initiated T7 exonuclease-mediated signal amplification. Analyst 2015, 140, 4030–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Hauber, J.; Hauber, R.; Geiger, R.; Cullen, B.R. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: A powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene 1988, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Athey, D.; McNeil, C. Amperometric detection of alkaline phosphatase activity at a horseradish peroxidase enzyme electrode based on activated carbon: Potential application to electrochemical immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupicault, S.; Linioges, B.; Dcpwncl, C. Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Using a Redox Procationic Labeled Substrate and a Renewable Nafion-Loaded Carbon Paste Electrode. Electroanalysis 1996, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limoges, B.; DeGrand, C. Ferrocenylethyl Phosphate: An Improved Substrate for the Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase by Cathodic Stripping Ion-Exchange Voltammetry. Application to the Electrochemical Enzyme Affinity Assay of Avidin. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 4141–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.G.; Eremenko, A.V.; Ehrentreich-Förster, E.; Bier, F.F.; Makower, A.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R.; Scheller, F.W. Zeptomole-Detecting Biosensor for Alkaline Phosphatase in an Electrochemical Immunoassay for 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 2453–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kain, S.R. Use of Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase as a Reporter of Gene Expression in Mammalian Cells. Recomb. Protein Protoc. 2003, 63, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.-T.; Sinai, P.; Kitts, P.A.; Kain, S.R. Quantification of Gene Expression with a Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase Reporter System. Biotechniques 1997, 23, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettan, M.; Darteil, R.; Scherman, D. Secreted Human Placental Alkaline Phosphatase as a Reporter Gene for in Vivo Gene Transfer. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 271, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, B.R. Utility of the secreted placental alkaline phosphatase reporter enzyme. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 326, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, E.; McLean, J.; Cardosi, M.F. Electrochemical Detection of Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase: Implications to Cell Based Assays. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, B.R.; Malim, M. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase as a eukaryotic reporter gene. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 216, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronin, K.; Zakharchuk, A.; Grinenko, N.; Yurov, G.; Krougliak, V.; Naroditsky, B. Expression of the gene encoding secreted placental alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) by a nondefective adenovirus vector. Gene 1993, 126, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, I.; Fortin, J.J.; Voyta, J.C.; Juo, R.R.; Edwards, B.; E Olesen, C.; Lijam, N.; Kricka, L.J. Chemiluminescent reporter gene assays: Sensitive detection of the GUS and SEAP gene products. Biotechniques 1994, 17, 176–177. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, T.C.; Wang, J.K.; Hung, M.W.; Chiao, C.H.; Tsai, L.C.; Chang, G.G. Regulation of the expression of alkaline phosphatase in a human breast-cancer cell line. Biochem. J. 1994, 303, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Landau, N.R. Use of a novel human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reporter virus expressing human placental alkaline phosphatase to detect an alternative viral receptor. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4587–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murata, T.; Yasukawa, T.; Shiku, H.; Matsue, T. Electrochemical single-cell gene-expression assay combining dielectrophoretic manipulation with secreted alkaline phosphatase reporter system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.Y.; Yasukawa, T.; Shiku, H.; Matsue, T. Cell-Based Electrochemical Assay for Endotoxin Using a Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase Reporter System. Electrochemistry 2008, 76, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şen, M.; Ino, K.; Inoue, K.Y.; Arai, T.; Nishijo, T.; Suda, A.; Kunikata, R.; Shiku, H.; Matsue, T. LSI-based amperometric sensor for real-time monitoring of embryoid bodies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernick, S.; Freeman, A.; Rishpon, J.; Niv, Y.; Vilkin, A.; Shacham-Diamand, Y. Electrochemical Biosensing for Direct Biopsy Slices Screening for Colorectal Cancer Detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, P1–P4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porat-Ophir, C.; Dergachev, V.; Belkin, A.; Vernick, S.; Freynd, G.; Katsnelson, M.; Chetvertnykh, V.; Rishpon, J.; Shacham-Diamand, Y. Chip level agitation effects on the electrochemical sensing of alkaline-phosphatase expressed from integrated liver tissue. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 213, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim-Semerci, C.; Benayahu, D.; Adamovski, M.; Wollenberger, U. An Electrochemical Assay for Monitoring Differentiation of the Osteoblastic Cell Line (MBA-15) on the Sensor Chip. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shacham-Diamand, Y.; Schreiber, D.; Inberg, A.; Berkh, O.; Kósa, G.; Freeman, A.; Shacham-Diamand, Y. Disposable electrochemical sensor prepared using 3D printing for cell and tissue diagnostics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehara, Y.; Mansho, K.; Takahashi, K.; Kato, K. Purification and Characterization of Alkaline Phosphatase from Plasma Membranes of Rat Ascites Hepatoma1. J. Biochem. 1978, 83, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sone, M.; Kishigami, S.; Yoshihisa, T.; Ito, K. Roles of Disulfide Bonds in Bacterial Alkaline Phosphatase. J. Boil. Chem. 1997, 272, 6174–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satou, Y.; Al-Shawafi, H.A.; Sultana, S.; Makita, S.; Sohda, M.; Oda, K. Disulfide bonds are critical for tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase function revealed by analysis of mutant proteins bearing a C201-Y or C489-S substitution associated with severe hypophosphatasia. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA). Mol. Basis Dis. 2012, 1822, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, E.J.; Pravda, M.; Kreuzer, M.P.; Guilbault, G.G. Comparative Study of 4-Aminophenyl Phosphate and Ascorbic Acid 2-Phosphate, as Substrates for Alkaline Phosphatase Based Amperometric Immunosensor. Anal. Lett. 2003, 36, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosén, I.; Rishpon, J. Alkaline phosphatase as a label for a heterogeneous immunoelectrochemical sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1989, 258, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemberton, R.M.; Hart, J.; Stoddard, P.; A Foulkes, J. A comparison of 1-naphthyl phosphate and 4 aminophenyl phosphate as enzyme substrates for use with a screen-printed amperometric immunosensor for progesterone in cows’ milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1999, 14, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, G.; Wu, P.; Cai, C. Real-time fluorescence assay of alkaline phosphatase in living cells using boron-doped graphene quantum dots as fluorophores. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattu, S.; Crihfield, C.; Lu, G.; Bwanali, L.; Veltri, L.M.; Holland, L.A. Advances in enzyme substrate analysis with capillary electrophoresis. Methods 2018, 146, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbaied, T.; Moore, E. Resazurin-Based Assay for Quantifying Living Cells during Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Release. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sappia, L.; Felice, B.; Sanchez, M.; Martì, M.; Madrid, R.; Pividori, M.; Pividori, I. Electrochemical sensor for alkaline phosphatase as biomarker for clinical and in vitro applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, J.-L.; Fluxa, V.S.; Maillard, N. Enzyme assays. Chem. Commun. 2008, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Morita, T.; Kanekiyo, T.; Tamiya, E. On-chip capillary electrophoresis for alkaline phosphatase testing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2001, 16, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodner, B.; Napiórkowska, M. Characterization and inhibition studies of tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase by aminoalkanol derivatives of 1,7-dimethyl-8,9-diphenyl-4-azatricyclo[5.2.1.0 2,6]dec-8-ene-3,5,10-trione, new competitive and non-competitive inhibitors, by capillary electrophoresis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 143, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayanagi, T.; Mine, M.; Mizuguchi, H. Capillary Electrophoresis/Dynamic Frontal Analysis for the Enzyme Assay of 4-Nitrophenyl Phosphate with Alkaline Phosphatase. Anal. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Cell Line | Concentration (×103 Cells/mL) | Media | Supplements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Balb/c 3t3 | 40 | DMEM | 10% NBCS |
| A549 | 40 | DMEM | 10% FBS |
| MCF-7 | 40 | MEME | 10% FBS |
| Ht-29 | 80 | McCoy’s 5A | 10% FBS |
| Scan Rate | a Emid vs. Ag/AgCl | b ∆Ep (mV) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min | 10 min | 20 min | 0 min | 10 min | 20 min | |
| 5 | 0.2285 | 0.0768 | 0.198 | 175 | 146.4 | 76 |
| 10 | 0.2465 | 0.08145 | 0.194 | 207 | 143.1 | 68 |
| 20 | 0.261 | 0.09155 | 0.192 | 230 | 144.9 | 68 |
| 50 | 0.2715 | 0.1163 | 0.192 | 247 | 137.4 | 64 |
| 70 | 0.277 | 0.1225 | 0.191 | 260 | 151 | 62 |
| 100 | 0.282 | 0.1305 | 0.191 | 270 | 153 | 62 |
| 150 | 0.294 | 0.135 | 0.194 | 288 | 162 | 64 |
| 200 | 0.298 | 0.1585 | 0.193 | 300 | 163 | 58 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balbaied, T.; Hogan, A.; Moore, E. Electrochemical Detection and Capillary Electrophoresis: Comparative Studies for Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Release from Living Cells. Biosensors 2020, 10, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10080095
Balbaied T, Hogan A, Moore E. Electrochemical Detection and Capillary Electrophoresis: Comparative Studies for Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Release from Living Cells. Biosensors. 2020; 10(8):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10080095
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalbaied, Thanih, Anna Hogan, and Eric Moore. 2020. "Electrochemical Detection and Capillary Electrophoresis: Comparative Studies for Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Release from Living Cells" Biosensors 10, no. 8: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10080095
APA StyleBalbaied, T., Hogan, A., & Moore, E. (2020). Electrochemical Detection and Capillary Electrophoresis: Comparative Studies for Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Release from Living Cells. Biosensors, 10(8), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10080095





