Biosensors for Biogenic Amines: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
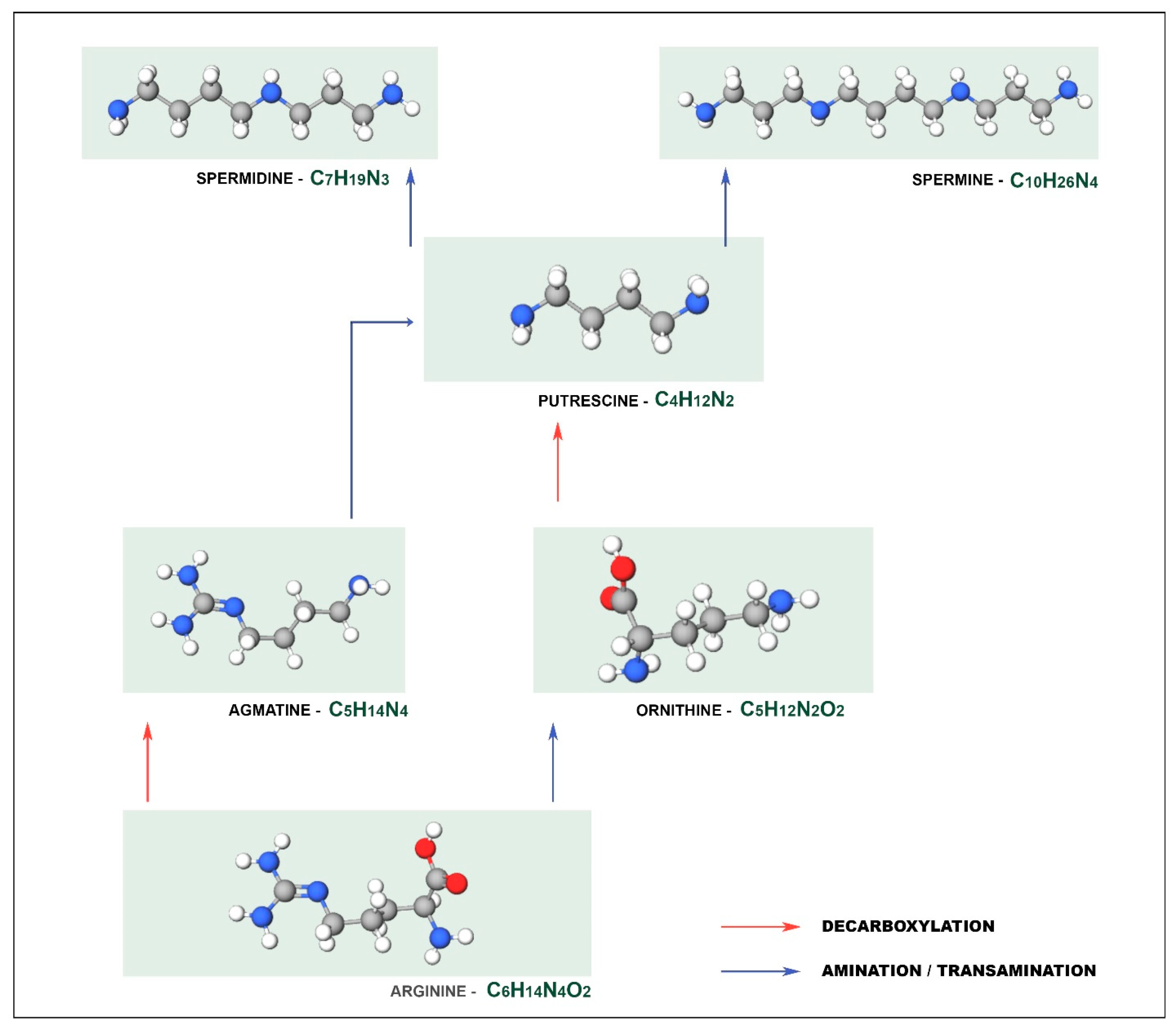
2. Biogenic Amines
3. Biosensors
3.1. Biosensor Main Characteristics
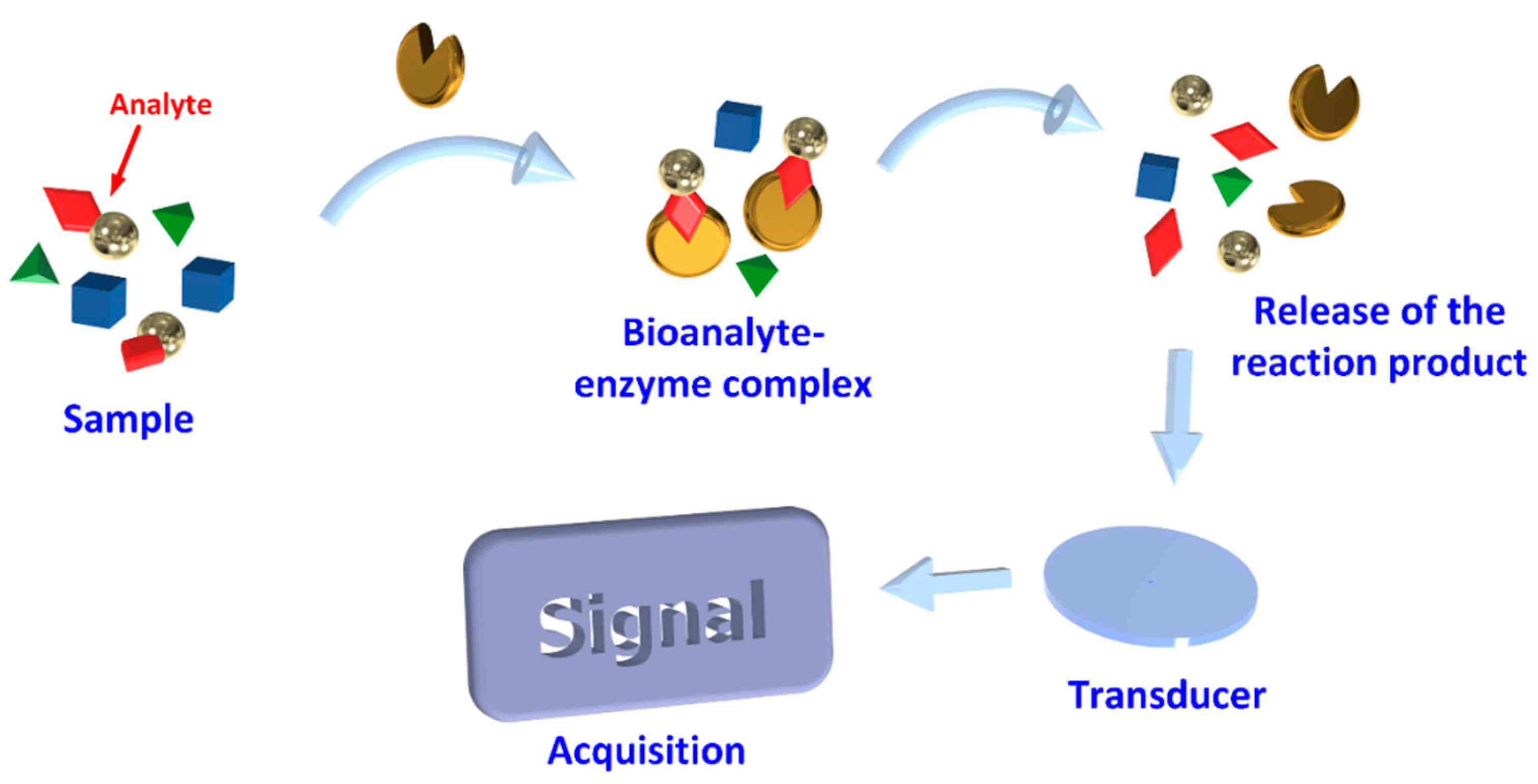
3.2. Biological Element
3.2.1. Enzymes
3.2.2. Microorganisms
3.2.3. Antibodies
3.2.4. Nucleic Acids
3.3. Immobilization of the Biological Element
3.3.1. Adsorption
3.3.2. Self-Assembled Monolayer
3.3.3. Covalent Binding
3.3.4. Entrapment
3.3.5. Cross-Linked
4. Transducing Methods
4.1. Electrochemical Transducing
4.1.1. Amperometric Sensors
4.1.2. Conductometric Sensors
4.1.3. Impedimetric Sensors
4.1.4. Potentiometric Sensors
4.2. Piezoelectric Sensors
5. Optical Transducing
5.1. Surface Plasmon Resonance
5.2. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
5.3. Fiber Optic Biosensors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lara, R.R.; Fallas-lópez, M. Aspects Associated on Food Safety; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Foodborne Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/foodborne-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Ruiz-capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Biogenic Amines on Food Safety; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladero, V.; Calles-Enriquez, M.; Fernandez, M.; Alvarez, M.A. Toxicological Effects of Dietary Biogenic Amines. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2010, 6, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaid, M.; Saad, B.; Ali, A.S.M.; Saleh, M.I.; Basheer, C.; Lee, H.K. In Situ Derivatization Hollow Fibre Liquid-Phase Microextraction for the Determination of Biogenic Amines in Food Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 5165–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neofotistos, A.-D.G.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Danezis, G.P.; Proestos, C. Emerging Trends in Biogenic Amines Analysis. Biog. Amin. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, N.; Hooda, V.; Gahlaut, A.; Gothwal, A.; Hooda, V. Enzymatic Biosensors for the Quantification of Biogenic Amines: A Literature Update. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landete, J.M.; de las Rivas, B.; Marcobal, A.; Muñoz, R. Molecular Methods for the Detection of Biogenic Amine-Producing Bacteria on Foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naila, A.; Flint, S.; Fletcher, G.; Bremer, P.; Meerdink, G. Control of Biogenic Amines in Food—Existing and Emerging Approaches. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biji, K.B.; Ravishankar, C.N.; Venkateswarlu, R.; Mohan, C.O.; Gopal, T.K.S. Biogenic Amines in Seafood: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Önal, A.; Tekkeli, S.E.K.; Önal, C. A Review of the Liquid Chromatographic Methods for the Determination of Biogenic Amines in Foods. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özogul, Y.; Özogul, F. Chapter 1: Biogenic Amines Formation, Toxicity, Regulations in Food. In Food Chemistry, Function and Analysis; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlichová, L.; Buňková, L.; Koutný, M.; Jančová, P.; Buňka, F. Formation, Degradation, and Detoxification of Putrescine by Foodborne Bacteria: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1012–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prester, L. Biogenic Amines in Fish, Fish Products and Shellfish: A Review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2011, 28, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Bulushi, I.; Poole, S.; Deeth, H.C.; Dykes, G.A. Biogenic Amines in Fish: Roles in Intoxication, Spoilage, and Nitrosamine Formation-A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordóñez, J.L.; Troncoso, A.M.; García-Parrilla, M.D.C.; Callejón, R.M. Recent Trends in the Determination of Biogenic Amines in Fermented Beverages—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 939, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Impact of Biogenic Amines on Food Quality and Safety. Foods 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buňková, L.; Buňka, F.; Klčovská, P.; Mrkvička, V.; Doležalová, M.; Kráčmar, S. Formation of Biogenic Amines by Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from Poultry Skin. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardini, F.; Özogul, Y.; Suzzi, G.; Tabanelli, G.; Özogul, F. Technological Factors Affecting Biogenic Amine Content in Foods: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nayak, M.; Kotian, A.; Marathe, S.; Chakravortty, D. Detection of Microorganisms Using Biosensors-A Smarter Way towards Detection Techniques. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, M.G.; García, Y.P.; Alberto, J.; Gonzalez, S.; Vanessa, C.; Bañuelos, O.; Escareño, P.L.; Balagurusamy, N. Biosensors for Food Quality and Safety Monitoring: Fundamentals and Applications; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.A.; Halpern, J.M. Guide to Selecting a Biorecognition Element for Biosensors. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeumner, A.J. Biosensors for Environmental Pollutants and Food Contaminants. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Leblanc, R.M. Biosensors Based on β-Galactosidase Enzyme: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, T.J.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Kubota, L.T. Amperometric Biosensor Based on Horseradish Peroxidase for Biogenic Amine Determinations in Biological Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 37, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, S.; Campàs, M. Electrochemical Enzyme Sensor Arrays for the Detection of the Biogenic Amines Histamine, Putrescine and Cadaverine Using Magnetic Beads as Immobilisation Supports. Microchim. Acta 2016, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, S.; Bartrolí, J.; Fàbregas, E. Amperometric Biosensor for the Determination of Histamine in Fish Samples. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4066–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Prabhakar, N. Current Scenario in Organophosphates Detection Using Electrochemical Biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 62–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Cázares, A.S.; Aristoy, M.C.; Toldrá, F. Reprint of: An Enzyme Sensor for the Determination of Total Amines in Dry-Fermented Sausages Q. J. Food Eng. 2012, 110, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omanovic-Miklicanin, E.; Valzacchi, S. Development of New Chemiluminescence Biosensors for Determination of Biogenic Amines in Meat. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi-xian, W.; Zun-zhong, Y.E.; Cheng-yan, S.I.; Yi-bin, Y. Application of Aptamer Based Biosensors for Detection of Pathogenic Microorganisms. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 40, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, V.; Hashim, U. Advances in Biosensors: Principle, Architecture and Applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2014, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertürk, G.; Lood, R. Bacteriophages as Biorecognition Elements in Capacitive Biosensors: Phage and Host Bacteria Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaree, J.M.; Chen, I.-H.; Horikawa, S.; Riggs, R.; Bryant, K.; Chin, B.A. Bacterial Assessment of Phage Magnetoelastic Sensors for Salmonella Enterica Typhimurium Detection in Chicken Meat. Food Control 2016, 71, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felix, F.S.; Angnes, L. Electrochemical Immunosensors—A Powerful Tool for Analytical Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adányi, N.; Székács, I.; Szendro, I.; Székács, A. Determination of Histamine Content in Vegetable Juices by Using Direct and Competitive Immunosensors. Food Agric. Immunol. 2014, 25, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Song, B.; Zhang, J.; Shi, H. Highly Sensitive and Simultaneous Detection of Melamine and Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Products by Multiplexed Planar Waveguide Fluorescence Immunosensor (MPWFI). Food Chem. 2016, 197, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teepoo, S.; Promta, A.; Phapugrangkul, P. A Competitive Colorimetric Immunosensor for Detection of Tyramine in Fish Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 1886–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, N.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, W.; Muhammd, N.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Z. Online Coupling of Tandem Liquid-Phase Extraction with HPLC-UV for the Determination of Trace: N -Nitrosamines in Food Products. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, R.B.; De-Los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Noronha, J.P.; Sales, M.G.F. A Label-Free DNA Aptamer-Based Impedance Biosensor for the Detection of E. Coli Outer Membrane Proteins. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, L.; Marques Martins de Almeida, J.M.; Santos, J.L.; da Silva Jorge, P.A.; Martins, M.C.L.; Viegas, D.; Queirós, R.B. Aptamer-Based Fiber Sensor for Thrombin Detection. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 087005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Wang, W.F.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.L.; Shi, Y.P. Highly Selective Colorimetric Detection of Putrescine in Fish Products Using O-Phthalaldehyde Derivatization Reaction. Food Chem. 2018, 259, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairal Lerga, T.; Jauset-Rubio, M.; Skouridou, V.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O’Sullivan, C.K. High Affinity Aptamer for the Detection of the Biogenic Amine Histamine. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7104–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerga, T.M.; Skouridou, V.; Bermudo, M.C.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Gold Nanoparticle Aptamer Assay for the Determination of Histamine in Foodstuffs. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwidar, M.; Yokobayashi, Y. Development of a Histamine Aptasensor for Food Safety Monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzano, S.; De Girolamo, A.; DeRosa, M.C.; McKeague, M.; Schena, R.; Catucci, L.; Pascale, M. Screening and Identification of DNA Aptamers to Tyramine Using in Vitro Selection and High-Throughput Sequencing. ACS Comb. Sci. 2016, 18, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. Selection and Application of SsDNA Aptamers against Spermine Based on Capture-SELEX. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1081, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D. Immobilization Strategies to Develop Enzymatic Biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.M.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.P. Advances on Methods and Easy Separated Support Materials for Enzymes Immobilization. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneha, H.P.; Beulah, K.C.; Murthy, P.S. Enzyme Immobilization Methods and Applications in the Food Industry; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.H.A.; Van Ginkel, S.W.; Hussein, M.A.M.; Abskharon, R.; Oh, S.E. Toxicity Assessment Using Different Bioassays and Microbial Biosensors. Environ. Int. 2016, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, J.I.A.; Yusof, N.A. The Strategies of DNA Immobilization and Hybridization Detection Mechanism in the Construction of Electrochemical DNA Sensor: A Review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Fujii, Y.; Nakano, T.; Arimoto, T.; Murata, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Yoshiura, Y.; Ohnuki, H.; Endo, H. Development of a Novel Enhanced Biosensor System for Real-Time Monitoring of Fish Stress Using a Self-Assembled Monolayer. Sensors 2019, 19, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaki, N.K.; Vijayamohanan, K. Self-Assembled Monolayers as a Tunable Platform for Biosensor Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.S.; Khan, F.; Micklefield, J. Selective Covalent Protein Immobilization: Strategies and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4025–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Ren, S.; Sun, B.; Jia, S. Optimization Protocols and Improved Strategies for Metal-Organic Frameworks for Immobilizing Enzymes: Current Development and Future Challenges. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, H.; Aman, A.; Qader, S.A.U. Agar-Agar Immobilization: An Alternative Approach for the Entrapment of Protease to Improve the Catalytic Efficiency, Thermal Stability and Recycling Efficiency. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, N.R.; Marzuki, N.H.C.; Buang, N.A.; Huyop, F.; Wahab, R.A. An Overview of Technologies for Immobilization of Enzymes and Surface Analysis Techniques for Immobilized Enzymes. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2015, 29, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Christena, L.R.; Rajaram, Y.R.S. Enzyme Immobilization: An Overview on Techniques and Support Materials. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thangaraj, B.; Solomon, P.R. Immobilization of Lipases—A Review. Part I: Enzyme Immobilization. ChemBioEng Rev. 2019, 6, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.M.; Thapliyal, N.; Hussain, K.K.; Goyal, R.N.; Shim, Y.B. Conducting Polymer-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Neurotransmitters: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepeli, Y.; Ülkü, A. Electrochemical Biosensors for Influenza Virus a Detection: The Potential of Adaptation of These Devices to POC Systems. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivaldi, F.; Santalucia, D.; Poma, N.; Bonini, A.; Salvo, P.; Del Noce, L.; Melai, B.; Kirchhain, A.; Kolivoška, V.; Sokolová, R.; et al. A Voltammetric PH Sensor for Food and Biological Matrices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kathuroju, P.K.; Jampana, N. Polypyrrole Based Amperometric Glucose Biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhi, J. The Application of Boron-Doped Diamond Electrodes in Amperometric Biosensors. Talanta 2009, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henao-Escobar, W.; Domínguez-Renedo, O.; Asunción Alonso-Lomillo, M.; Julia Arcos-Martínez, M. Simultaneous Determination of Cadaverine and Putrescine Using a Disposable Monoamine Oxidase Based Biosensor. Talanta 2013, 117, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carelli, D.; Centonze, D.; Palermo, C.; Quinto, M.; Rotunno, T. An Interference Free Amperometric Biosensor for the Detection of Biogenic Amines in Food Products. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, R.; Costa-Rama, E.; Lopes, P.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Amperometric Enzyme Sensor for the Rapid Determination of Histamine. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, I.M.; Apetrei, C. The Biocomposite Screen-Printed Biosensor Based on Immobilization of Tyrosinase onto the Carboxyl Functionalised Carbon Nanotube for Assaying Tyramine in Fish Products. J. Food Eng. 2015, 149, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradela-Filho, L.A.; Araújo, D.A.G.; Takeuchi, R.M.; Santos, A.L.; Henry, C.S. Thermoplastic Electrodes as a New Electrochemical Platform Coupled to Microfluidic Devices for Tryptamine Determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1147, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, M.E.; Darwish, H.W.; Darwish, I.A.; Saad, A.S. Solid-State Potentiometric Sensor for the Rapid Assay of the Biologically Active Biogenic Amine (Tyramine) as a Marker of Food Spoilage. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentana, A.; Nardiello, D.; Palermo, C.; Centonze, D. Accurate Glutamate Monitoring in Foodstuffs by a Sensitive and Interference-Free Glutamate Oxidase Based Disposable Amperometric Biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1115, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adley, C.C.; Ryan, M.P. Conductometric Biosensors for High Throughput Screening of Pathogens in Food; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzyadevych, S.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Conductometric Biosensors. In Biological Identification: DNA Amplification and Sequencing, Optical Sensing, Lab-On-Chip and Portable Systems; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 153–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvasnička, F.; Voldřich, M. Determination of Biogenic Amines by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis with Conductometric Detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1103, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosovska, O.; Korpan, Y.; Vocanson, F.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Conductometric Chemosensors Based on Calixarenes for Determination of Amines and Amino Acids. Sens. Lett. 2009, 7, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Impedimetric Biosensors. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 97, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodromidis, M.I. Impedimetric Immunosensors-A Review. Electrochim. Acta. 2010, 4227–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, Z.O.; Ertuǧrul Uygun, H.D. A Short Footnote: Circuit Design for Faradaic Impedimetric Sensors and Biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Paniagua López, M.; Redondo-Gómez, E.; López-Ruiz, B. Electrochemical Enzyme Biosensors Based on Calcium Phosphate Materials for Tyramine Detection in Food Samples. Talanta 2017, 175, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundian, M.; Rüter, A.; Shinde, S. Ultratrace Detection of Histamine Using a Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer-Based Voltammetric Sensor. Sensors 2017, 17, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, W.; Ghica, M.E.; Ajayi, R.F.; Iwuoha, E.I.; Brett, C.M.A. Impedimetric Sensor for Tyramine Based on Gold Nanoparticle Doped-Poly(8-Anilino-1-Naphthalene Sulphonic Acid) Modified Gold Electrodes. Talanta 2019, 195, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.; Ghica, M.E.; Ajayi, R.F.; Iwuoha, E.I.; Brett, C.M.A. Tyrosinase Based Amperometric Biosensor for Determination of Tyramine in Fermented Food and Beverages with Gold Nanoparticle Doped Poly(8-Anilino-1-Naphthalene Sulphonic Acid) Modified Electrode. Food Chem. 2019, 282, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John Ho, L.S.; Fogel, R.; Limson, J.L. Generation and Screening of Histamine-Specific Aptamers for Application in a Novel Impedimetric Aptamer-Based Sensor. Talanta 2020, 208, 120474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Qin, W. Applications of Nanomaterials in Potentiometric Sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 51, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratov, A.; Abramova, N.; Ipatov, A. Recent Trends in Potentiometric Sensor Arrays—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koncki, R. Recent Developments in Potentiometric Biosensors for Biomedical Analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basozabal, I.; Guerreiro, A.; Gomez-Caballero, A.; Aranzazu Goicolea, M.; Barrio, R.J. Direct Potentiometric Quantification of Histamine Using Solid-Phase Imprinted Nanoparticles as Recognition Elements. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamiki, T.; Kurita, R. Potentiometric Detection of Biogenic Amines Utilizing Affinity on a 4-Mercaptobenzoic Acid Monolayer. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Sensors and Biosensors Based on Magnetic Nanoparticles. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Overview of Piezoelectric Biosensors, Immunosensors and DNA Sensors and Their Applications. Materials 2018, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.Q.; Luo, J.K.; Nguyen, N.T.; Walton, A.J.; Flewitt, A.J.; Zu, X.T.; Li, Y.; McHale, G.; Matthews, A.; Iborra, E.; et al. Advances in Piezoelectric Thin Films for Acoustic Biosensors, Acoustofluidics and Lab-on-Chip Applications. Progress Mater. Sci. 2017, 31–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tombelli, S. Piezoelectric Biosensors for Medical Applications. In Biosensors for Medical Applications; Elsevier Masson SAS.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, S.; Çökeliler, D.; Shard, A.; Goktas, H.; Ozansoy, B.; Mutlu, M. Preparation and Characterization of Ethylenediamine and Cysteamine Plasma Polymerized Films on Piezoelectric Quartz Crystal Surfaces for a Biosensor. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzyk-Le, A.; Suriyanarayanan, S.; Kutner, W.; Chitta, R.; D’Souza, F. Selective Histamine Piezoelectric Chemosensor Using a Recognition Film of the Molecularly Imprinted Polymer of Bis(Bithiophene) Derivatives. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, M.; Kong, L.; Wang, S. Development and Application of Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor Based on Novel Molecularly Imprinted Sol-Gel Polymer for Rapid Detection of Histamine in Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5269–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J. Optical Biosensors: An Exhaustive and Comprehensive Review. Analyst 2020, 145, 1605–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansili, N.; Rattu, G.; Krishna, P.M. Label-Free Optical Biosensors for Food and Biological Sensor Applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshchenko, A.; Bechelany, M.; Viter, R.; Khranovskyy, V.; Smyntyna, V.; Starodub, N.; Yakimova, R. Optical Biosensors Based on ZnO Nanostructures: Advantages and Perspectives. A Review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lertvachirapaiboon, C.; Baba, A.; Ekgasit, S.; Shinbo, K.; Kato, K.; Kaneko, F. Transmission Surface Plasmon Resonance Techniques and Their Potential Biosensor Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 399–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. Plasmonic Colorimetric Sensors Based on Etching and Growth of Noble Metal Nanoparticles: Strategies and Applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Peng, Y.; Ning, B.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Z. Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Film for Detection of Histamine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Furui, K.; Soh, N.; Nakano, K.; Imato, T. Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunosensor for Histamine Based on an Indirect Competitive Immunoreaction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 576, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hormozi Nezhad, M.R.; Tashkhourian, J.; Khodaveisi, J. Sensitive Spectrophotometric Detection of Dopamine, Levodopa and Adrenaline Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Band of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2010, 7, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Xiao, W.; Sun, D.W. SERS-Microfluidic Systems: A Potential Platform for Rapid Analysis of Food Contaminants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, J.; He, L. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) Combined Techniques for High-Performance Detection and Characterization. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Grant, E.; Lu, X. Determination of Histamine in Canned Tuna by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers-Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 901, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdoš Kljusurić, J.; Vidaček, S.; Janči, T.; Valinger, D.; Ivanda, M.; Mikac, L. Determination of Histamine in Fish by Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Using Silver Colloid SERS Substrates. Food Chem. 2016, 224, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.Q.; Lin, L.; He, Y. Rapid Determination of Histamine Concentration in Fish (Miichthys Miiuy) by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z.; Ding, Y.; Yang, N.; Wu, F. Tuneable Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Hyphenated to Chemically Derivatized Thin-Layer Chromatography Plates for Screening Histamine in Fish. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.; Shankar, P.M.; Mutharasan, R. A Review of Fiber-Optic Biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addanki, S.; Amiri, I.S.; Yupapin, P. Results in Physics Review of Optical Fi Bers-Introduction and Applications in Fi Ber Lasers. Results Phys. 2018, 10, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.-j.; Gu, B.; An, Q.F.; Yang, C.; Guan, Y.L.; Yong, K.T. Recent Development of Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors and Biosensors: Mechanisms, Materials, Micro/Nano-Fabrications and Applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 348–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. A Review: Development of Novel Fiber-Optic Platforms for Bulk and Serface Refractive Index Sensing Applications. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2020, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, H.; Bakar, M.H.A.; Hamzah, A.S.; Salleh, A.B. A Tapered Fibre Optics Biosensor for Histamine Detection. Sens. Rev. 2016, 36, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospiskova, K.; Safarik, I.; Sebela, M.; Kuncova, G. Magnetic Particles—Based Biosensor for Biogenic Amines Using an Optical Oxygen Sensor as a Transducer. Mikrochim. Acta 2013, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biosensor | Biogenic Amine | Recognition Element | Sample | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amperometric | - | Enzyme | rat blood | 17 ng/Ml | [25] |
| PUT and CAD | Enzyme | octopus | 9.9 ± 0.9 µm 19.9 ± 0.9 µm | [66] | |
| HIS, PUT e CAD | Enzyme | fish | 265.1 ± 2.2; 114.2 ± 3.0; 57.5 ± 2.1 (nA/mm) | [67] | |
| HIS | Enzyme | fish extracts | 0.5 mg/L | [68] | |
| HIS | Enzyme | fish | 1.7 × 10−7 M | [27] | |
| TYM | Enzyme | pickled and smoked fish | 0.62 μm | [69] | |
| Impedimetric | TYM | Enzyme | cheese | 4.85 × 10−8 M | [80] |
| HIS | MIP | serum | 7.4 × 10−11 M | [81] | |
| TYM | Gold NPs | dairy products and fermented drinks | 0.04 µm | [82] | |
| TYM | Enzyme | dairy products and fermented drinks | 0.71 µm | [83] | |
| HIS | Aptamer | solution at a physiological pH | 7.80 mmol/L | [84] | |
| Potentiometric | HIS | MIP | fish and wine | 1.12 × 10−6 mol/L | [88] |
| Piezoelectric | HIS | Plasma polymerization | - | 575 ± 34 Hz | [94] |
| HIS | MIP | - | 5 nm | [95] | |
| HIS | MIP | spiked fish products | 7.49 × 10−4 mg/kg | [96] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasconcelos, H.; Coelho, L.C.C.; Matias, A.; Saraiva, C.; Jorge, P.A.S.; de Almeida, J.M.M.M. Biosensors for Biogenic Amines: A Review. Biosensors 2021, 11, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030082
Vasconcelos H, Coelho LCC, Matias A, Saraiva C, Jorge PAS, de Almeida JMMM. Biosensors for Biogenic Amines: A Review. Biosensors. 2021; 11(3):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030082
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasconcelos, Helena, Luís C. C. Coelho, Ana Matias, Cristina Saraiva, Pedro A. S. Jorge, and José M. M. M. de Almeida. 2021. "Biosensors for Biogenic Amines: A Review" Biosensors 11, no. 3: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030082
APA StyleVasconcelos, H., Coelho, L. C. C., Matias, A., Saraiva, C., Jorge, P. A. S., & de Almeida, J. M. M. M. (2021). Biosensors for Biogenic Amines: A Review. Biosensors, 11(3), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030082










