An Overview of Bio-Inspired Intelligent Imprinted Polymers for Virus Determination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. MIP-Based Virus Sensing Platforms Ordered by Viral Class
2.1. Bacteriophage
2.2. Adenovirus
2.3. Dengue Virus
2.4. Influenza A Virus
2.5. Poliovirus
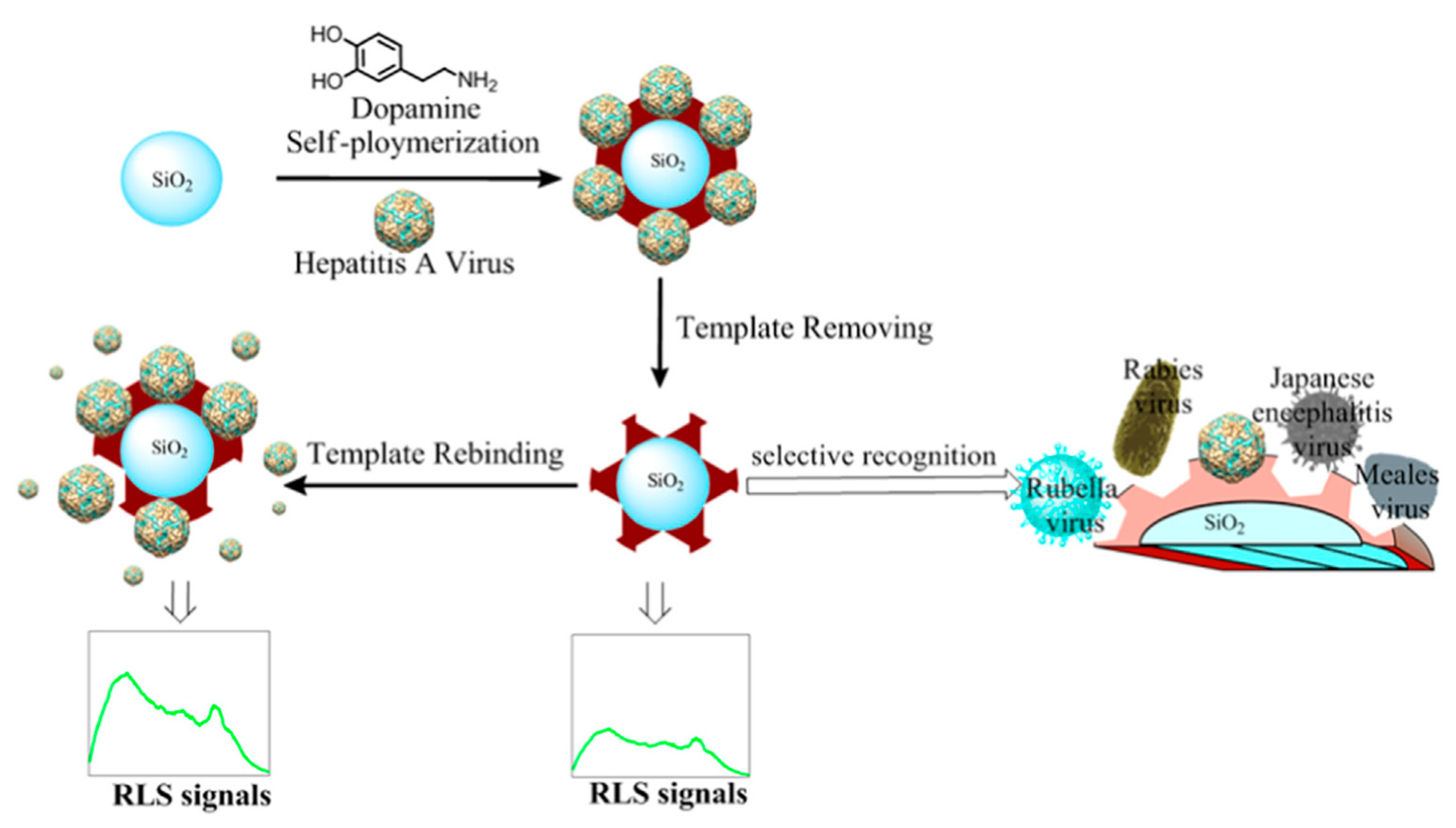
2.6. Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
2.7. Japanese Encephalitis Virus (JEV)
2.8. Apple Stem Pitting Virus (ASPV)
2.9. Picornaviruses
2.10. Turnip Yellow Mosaic Virus (TYMV)
2.11. Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) and Tobacco Necrosis Virus (TNV)
2.12. Norovirus
2.13. Swine Flu Virus
2.14. Zika Virus
3. Challenges and Future Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Rijn, P.; Schirhagl, R. Viruses, artificial viruses and virus-based structures for biomedical applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1386–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singhal, C.; Pundir, C.S.; Narang, J. A genosensor for detection of consensus DNA sequence of Dengue virus using ZnO/Pt-Pd nanocomposites. Biosense. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nidzworski, D.; Siuzdak, K.; Niedziałkowski, P.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Sobaszek, M.; Ryl, J.; Weiher, P.; Sawczak, M.; Wnuk, E.; Iii, W.A.G.; et al. A rapid-response ultrasensitive biosensor for influenza virus detection using antibody modified boron-doped diamond. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.K.R. Monitoring Intact Viruses Using Aptamers. Biosensors 2016, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kizek, R.; Krejcova, L.; Michálek, P.; Rodrigo, M.M.; Heger, Z.; Krizkova, S.; Vaculovicova, M.; Hynek, D.; Adam, V. Nanoscale virus biosensors: State of the art. Nanobiosens. Dis. Diagn. 2015, 4, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Callaway, Z.T.; Lu, H.; Huang, T.J.; Li, Y. A nanowell-based QCM aptasensor for rapid and sensitive de-tection of avian influenza virus. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 17, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clem, A.L.; Sims, J.; Telang, S.; Eaton, J.W.; Chesney, J. Virus detection and identification using random multiplex (RT)-PCR with 3′-locked random primers. Virol. J. 2007, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagar, P.K.; Savargaonkar, D.; Anvikar, A.R. Detection of Dengue Virus-Specific IgM and IgG Antibodies through Peptide Sequences of Envelope and NS1 Proteins for Serological Identification. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ruan, F.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Zhou, J.; Qin, K. Establishment of sandwich ELISA for detecting the H7 sub-type influenza A virus. J. Med. Virol. 2019, 91, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leland, D.S.; Ginocchio, C.C. Role of Cell Culture for Virus Detection in the Age of Technology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 49–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, A.D.; Takemura, K.; Li, T.-C.; Suzuki, T.; Park, E.Y. Electrical pulse-induced electrochemical biosensor for hepatitis E virus detection. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guliy, O.; Kanevskiy, M.; Fomin, A.; Staroverov, S.; Bunin, V. Progress in the use of an electro-optical sensor for virus detection. Opt. Commun. 2020, 465, 125605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caygill, R.L.; Blair, G.E.; Millner, P.A. A review on viral biosensors to detect human pathogens. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 681, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelghani, A. Electrochemical Biosensors for Virus Detection. In Biosensors for Health, Environment and Biosecuri-Ty; Serra, P.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-443-6. [Google Scholar]
- Daaboul, G.G.; Lopez, C.A.; Yurt, A.; Goldberg, B.B.; Connor, J.H.; Unlu, M.S. Label-free optical biosensors for virus detec-tion and characterization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2012, 18, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylan, Y.; Erdem, Ö.; Ünal, S.; Denizli, A. An Alternative Medical Diagnosis Method: Biosensors for Virus Detection. Biosensors 2019, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; He, Q.; Yan, J.; Xiong, H.; Wen, N.; Cai, S.; Peng, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Metal-organic frameworks for virus detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 169, 112604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.A.; Cheong, W.J. Preparation of an open-tubular capillary column with a monolithic layer of S-ketoprofen imprinted and 4-styrenesulfonic acid incorporated polymer and its enhanced chiral separation performance in capillary electrochroma-tography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 2947–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, R.; Kim, K.H.; Zaidi, S.A.; Cheong, W.J.; Moon, M.H. Analysis of phospholipids using an open-tubular capillary col-umn with a monolithic layer of molecularly imprinted polymer in electrochromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2167–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. Dual-templates molecularly imprinted monolithic columns for the evaluation of serotonin and histamine in CEC. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. Molecular imprinted polymers as drug delivery vehicles. Drug Deliv. 2014, 23, 2262–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. Molecular imprinting polymers and their composites: A promising material for diverse applications. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A.; Shin, J.H. Molecularly imprinted polymer electrochemical sensors based on synergistic effect of composites synthe-sized from graphene and other nanosystems. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 4598–4616. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G.; Shinde, S.; Yeung, S.Y.; Jakštaitė, M.; Li, Q.; Wingren, A.Q.; Sellergren, B. An epitope-imprinted biointerface with dy-namic bioactivity for modulating cell-biomaterial interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15959–15963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvolini, G.; Marrazza, G. MIP-Based Sensors: Promising New Tools for Cancer Biomarker Determination. Sensors 2017, 17, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teles, F.S.R.R. Biosensors and rapid diagnostic tests on the frontier between analytical and clinical chemistry for biomolecular diagnosis of dengue disease: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 687, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P. Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: Realising their potential. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieplak, M.; Kutner, W. Artificial Biosensors: How Can Molecular Imprinting Mimic Biorecognition? Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 922–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.S.; Iskierko, Z.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Bioinspired intelligent molecularly imprinted polymers for chemosensing: A mini review. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 50, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eersels, K.; Lieberzeit, P.; Wagner, P. A Review on Synthetic Receptors for Bioparticle Detection Created by Surface-Imprinting Techniques—From Principles to Applications. ACS Sensors 2016, 1, 1171–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Hudson, A.; Foster, C.W.; Eersels, K.; Van Grinsven, B.; Cleij, T.J.; Banks, C.E.; Peeters, M. Recent Advances in Electrosynthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensing Platforms for Bioanalyte Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Diliën, H.; Singla, P.; Peeters, M.; Cleij, T.J.; van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K. MIPs for commercial application in low-cost sensors and assays—An overview of the current status quo. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M. Molecularly imprinted polymers (Mips) for bioanalytical sensors: Strategies for incorporation of Mips into sensing platforms. Austin J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 1, 1011. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Chen, W.; Ma, Y.; Pan, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers as receptor mimics for selective cell recognition. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5574–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, Z.; Gittens, M.; Pocock, J.; Tothill, I.E. Biosensors for waterborne viruses: Detection and removal. Biochimica 2015, 115, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, A.; Mujahid, A.; Schirhagl, R.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Latif, U.; Feroz, S. Gravimetric Viral Diagnostics: QCM Based Biosensors for Early Detection of Viruses. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Nantasenamat, C.; Piacham, T. Molecularly imprinted polymer for human viral pathogen detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankarakumar, N.; Tong, Y.W. Preventing viral infections with polymeric virus catchers: A novel nanotechnological approach to anti-viral therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Liu, Y.-J.; Liu, F.; Luo, M.-F.; Wan, Y.-C.; Huang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Mei, F.-S.; Wang, Z.-C.; Jin, A.-Y.; et al. Bio-inspired virus imprinted polymer for prevention of viral infections. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Z.; Gittens, M.; Guerreiro, A.; Thompson, K.-A.; Walker, J.A.; Piletsky, S.A.; Tothill, I.E. Detection of Waterborne Viruses Using High Affinity Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6801–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, Z.; Pocock, J.; Thompson, K.-A.; Tothill, I.E. Comparative investigations for adenovirus recognition and quantifica-tion: Plastic or natural antibodies? Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gast, M.; Kuehner, S.; Sobek, H.; Walther, P.; Mizaikoff, B. Enhanced Selectivity by Passivation: Molecular Imprints for Viruses with Exceptional Binding Properties. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5576–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gast, M.; Sobek, H.; Mizaikoff, B. Selective virus capture via hexon imprinting. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.-C.; Wu, T.-Z.; Chen, L.-K.; Yang, H.-H.; Tai, D.-F. Development of immunochips for the detection of dengue viral antigens. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 479, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babacan, S.; Pivarnik, P.; Letcher, S.; Rand, A. Evaluation of antibody immobilization methods for piezoelectric biosensor application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.Z.; Su, C.C.; Chen, L.K.; Yang, H.H.; Tai, D.F.; Peng, K.C. Piezoelectric immunochip for the detection of dengue fever in viremia phase. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, D.-F.; Lin, C.-Y.; Wu, T.-Z.; Chen, L.-K. Recognition of Dengue Virus Protein Using Epitope-Mediated Molecularly Imprinted Film. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 5140–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, D.-F.; Lin, C.-Y.; Wu, T.-Z.; Huang, J.-H.; Shu, P.-Y. Artificial Receptors in Serologic Tests for the Early Diagnosis of Dengue Virus Infection. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lieberzeit, P.; Chunta, S.; Navakul, K.; Sangma, C.; Jungmann, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Diagnostics: Sensing High Density Lipoprotein and Dengue Virus. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laconi, A.; Fortin, A.; Bedendo, G.; Shibata, A.; Sakoda, Y.; Awuni, J.A.; Go-Maro, E.; Arafa, A.; Ali, A.S.M.; Terregino, C.; et al. Detection of avian influenza virus: A comparative study of the in silico and in vitro performances of current RT-qPCR assays. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowska, I.; Malecka, K.; Jarocka, U.; Radecki, J.; Radecka, H. Electrochemical biosensors for detection of avian influenza virus—current status and future trends. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2014, 61, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Fan, H.; Ai, S. Electrochemical detection of avian influenza virus H5N1 gene sequence using a DNA ap-tamer immobilized onto a hybrid nanomaterial-modified electrode. Electrochim. Acta. 2011, 56, 6266–6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangchareansak, T.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Chuakheaw, D.; Gleeson, M.P.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Sangma, C. Influenza A virus mo-lecularly imprinted polymers and their application in virus sub-type classification. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangchareansak, T.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Chuakheaw, D.; Gleeson, M.P.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Sangma, C. A novel approach to identify molecular binding to the influenza virus H5N1: Screening using molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs). Med. Chem. Commun. 2014, 5, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karthik, A.; Margulis, K.; Ren, K.; Zare, R.N.; Leung, L.W. Rapid and selective detection of viruses using virus-imprinted polymer films. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 18998–19003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enriquez, C.E.; Abbaszadegan, M.; Pepper, I.L.; Richardson, K.J.; Gerba, C.P. Poliovirus detection in water by cell culture and nucleic acid hybridization. Water Res. 1993, 27, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jain, V.; Yi, J.; Mueller, S.; Sokolov, J.; Liu, Z.; Levon, K.; Rigas, B.; Rafailovich, M.H. Potentiometric sensors based on surface molecular imprinting: Detection of cancer biomarkers and viruses. Sens. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 146, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, T.; Geiss, B.J.; Henry, C.S. Review—Chemical and Biological Sensors for Viral Detection. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. A virus resonance light scattering sensor based on mussel-inspired molecularly imprinted polymers for high sensitive and high selective detection of Hepatitis A Virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Feng, W.; Hu, W.; Chen, C.; Gong, H.; Cai, C. Molecularly imprinted polymer based hybrid structure SiO2@MPS-CdTe/CdS: A novel fluorescence probe for Hepatitis A virus. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2019, 7, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. Molecular imprinting resonance light scattering nanoprobes based on pH-responsive metal-organic framework for determination of hepatitis A virus. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. Visual Simultaneous Detection of Hepatitis A and B Viruses Based on a Multifunctional Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Sensor. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 15748–15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Chen, C.; Liang, C.; Liu, C.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. Highly selective recognition and fluorescent detection of JEV via virus-imprinted magnetic silicon microspheres. Sens. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, H.; He, K.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Gong, H.; Cai, C. A virus-MIPs fluorescent sensor based on FRET for highly sensitive detection of JEV. Talanta 2016, 160, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Feng, W.; Liang, K.; Chen, C.; Cai, C. A novel fluorescence molecularly imprinted sensor for Japanese encephalitis virus detection based on metal organic frameworks and passivation-enhanced selectivity. Talanta 2020, 212, 120744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Liang, K.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, C. Fast and sensitive detection of Japanese encephalitis virus based on a magnetic molecular imprinted polymer–resonance light scattering sensor. Talanta 2019, 202, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Liang, C.; Gong, H.; Cai, C. Sensitive detection of Japanese encephalitis virus by surface molecularly imprinted tech-nique based on fluorescent method. N. J. Chem. 2018, 42, 3503–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
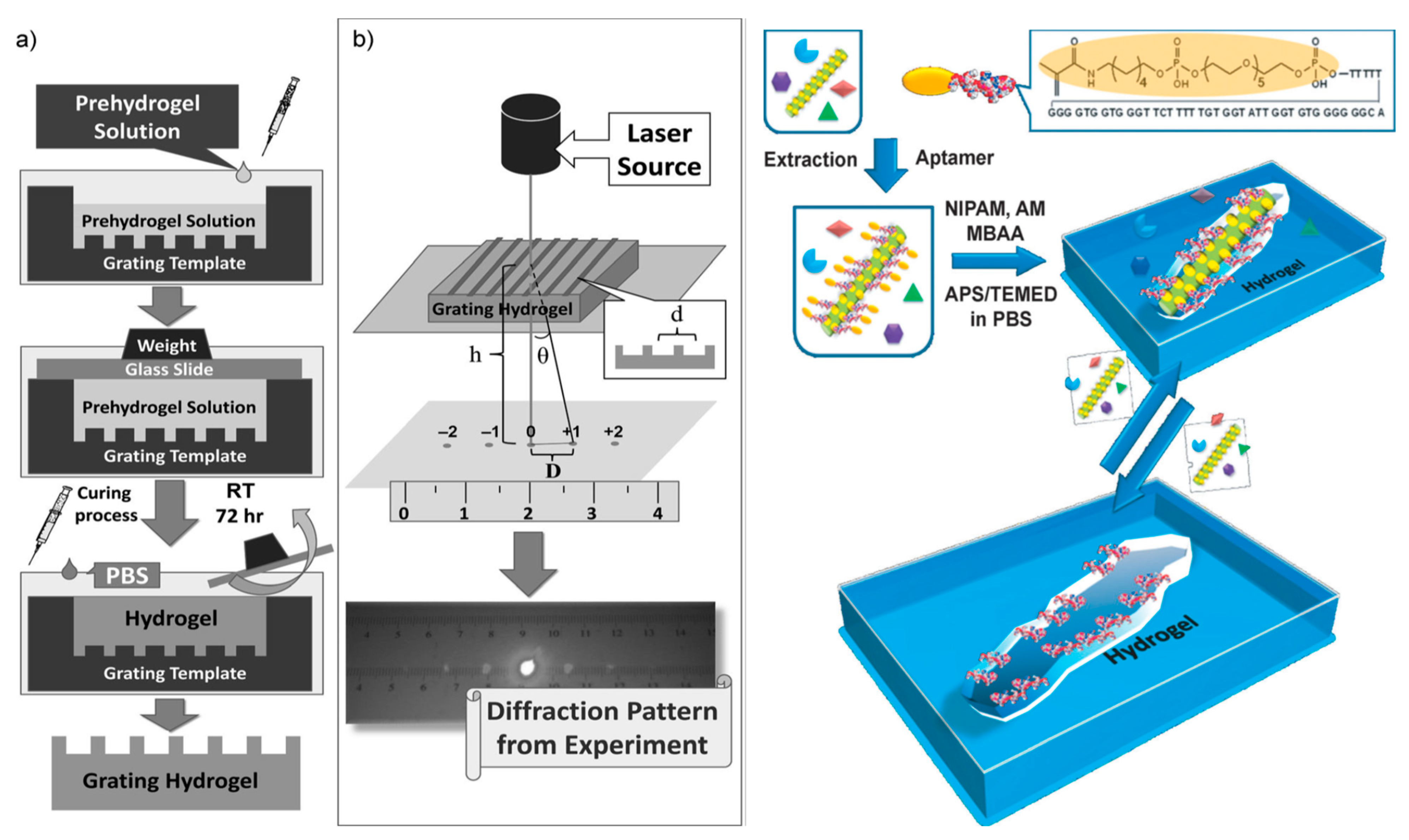
- Bai, W.; Spivak, D.A. A double-imprinted diffraction-grating sensor based on a virus-responsive super-aptamer hydrogel de-rived from an impure extract. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2095–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenik, M.; Schirhagl, R.; Schirk, C.; Hayden, O.; Lieberzeit, P.; Blaas, D.; Paul, G.; Dickert, F.L. Sensing Picornaviruses Using Molecular Imprinting Techniques on a Quartz Crystal Microbalance. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5320–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, H.A.; Hassan, R.; El Nashar, R.M.; Khalil, S.A.; Salem, S.A.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Designing and fabrication of new VIP biosensor for the rapid and selective detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumbo, A.; Lorber, B.; Corvini, P.F.-X.; Meier, W.; Shahgaldian, P. A synthetic nanomaterial for virus recognition produced by surface imprinting. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cumbo, A.; Corvini, P.F.-X.; Shahgaldian, P. A Novel Synthetic Virus Recognition Nanomaterial for Diagnostic and Environ-mental Applications. Chimia 2013, 67, 648–657. [Google Scholar]
- Jablonski, M.; Poghossian, A.; Severins, R.; Keusgen, M.; Wege, C.; Schöning, M.J. Capacitive Field-Effect Biosensor Studying Adsorption of Tobacco Mosaic Virus Particles. Micromachines 2021, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, O.; Bindeus, R.; Haderspock, C.; Mann, K.-J.; Wirl, B.; Dickert, F.L. Mass-sensitive detection of cells, viruses and en-zymes with artificial receptors. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 91, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickert, F.L.; Hayden, O.; Bindeus, R.; Mann, K.-J.; Blaas, D.; Waigmann, E. Bioimprinted QCM sensors for virus detection—Screening of plant sap. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1929–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, O.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Blaas, D.; Dickert, F.L. Artificial antibodies for boanalyte detection-sensing viruses and proteins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolisay, L.D.; Culver, J.N.; Kofinas, P. Molecularly imprinted polymers for tobacco mosaic virus recognition. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4165–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolisay, L.D.; Culver, J.N.; Kofinas, P. Optimization of virus imprinting methods to improve selectivity and reduce nonspecif-ic binding. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 3893–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolisay, L.D.; Kofinas, P. Imprinted Polymer Hydrogels for the Separation of Viruses. Macromol. Symp. 2010, 291–292, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaumer, G.M.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Richter, L.; Schirhagl, R.; Milnera, M.; Dickert, F.L.; Bailey, A.; Ertl, P. Detection of viruses with molecularly imprinted polymers integrated on a microfluidic biochip using contact-less dielectric microsensors. Lab a Chip 2009, 9, 3549–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikawa, T.; Kato, Y.; Yamada, T.; Shiozawa, M.; Narita, M.; Mouri, M.; Hoshino, F.; Watanabe, O.; Tawata, M.; Shimoyama, H. Virus-Templated Photoimprint on the Surface of an Azobenzene-Containing Polymer. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12673–12679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankar, S.; Turner, N.W.; Krupadam, R.J. Polythiophene nanofilms for sensitive fluorescence detection of viruses in drinking water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 82, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DiCaprio, E. Recent advances in human norovirus detection and cultivation methods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 14, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, S.; Cumbo, A.; Belliot, G.; Pothier, P.; Arnal, C.; Dudal, Y.; Corvini, P.F.-X.; Shahgaldian, P. Virus-like particles as virus substitutes to design artificial virus-recognition nanomaterials. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2256–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blome, S.; Staubach, C.; Henke, J.; Carlson, J.; Beer, M. Classical Swine Fever—An Updated Review. Viruses 2017, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klangprapan, S.; Choke-Arpornchai, B.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Choowongkomon, K. Sensing the classical swine fever virus with molecularly imprinted polymer on quartz crystal microbalance. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancharoen, C.; Sukjee, W.; Thepparit, C.; Jaimipuk, T.; Auewarakul, P.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Sangma, C. Electrochemical biosensor based on surface imprinting for Zika virus detection in derum. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Heiden, P.A. Recent Developments in Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles by Surface Imprinting Techniques. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 299, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, P.; Hu, C.; Mao, H. Detecting the Coronavirus (COVID-19). ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 8–2283. [Google Scholar]
- Ekrami, E.; Pouresmaieli, M.; Barati, F.; Asghari, S.; Ziarani, F.R.; Shariati, P.; Mamoudifard, M. Potential Diagnostic Systems for Coronavirus Detection: A Critical Review. Biol. Proced. Online 2020, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, B.A.; Al Mashhadany, Y.; Mokhtar, M.H.H.; Bin Zan, M.S.D.; Arsad, N. An Analysis Review of Detection Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Based on Biosensor Application. Sensors 2020, 20, 6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaidi, S.A. An Overview of Bio-Inspired Intelligent Imprinted Polymers for Virus Determination. Biosensors 2021, 11, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030089
Zaidi SA. An Overview of Bio-Inspired Intelligent Imprinted Polymers for Virus Determination. Biosensors. 2021; 11(3):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030089
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaidi, Shabi Abbas. 2021. "An Overview of Bio-Inspired Intelligent Imprinted Polymers for Virus Determination" Biosensors 11, no. 3: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030089
APA StyleZaidi, S. A. (2021). An Overview of Bio-Inspired Intelligent Imprinted Polymers for Virus Determination. Biosensors, 11(3), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11030089



