New Detection Platform for Screening Bacteria in Liquid Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Bacterial Cultures
2.3. Synthesis and Physico-Chemical Characterization of the P(HEMA-AEM) Cryogels
2.4. Surface Characterization
2.5. Adsorption of Bacteria onto P(HEMA-AEM) Cryogels in PBS and Spiked Water Samples
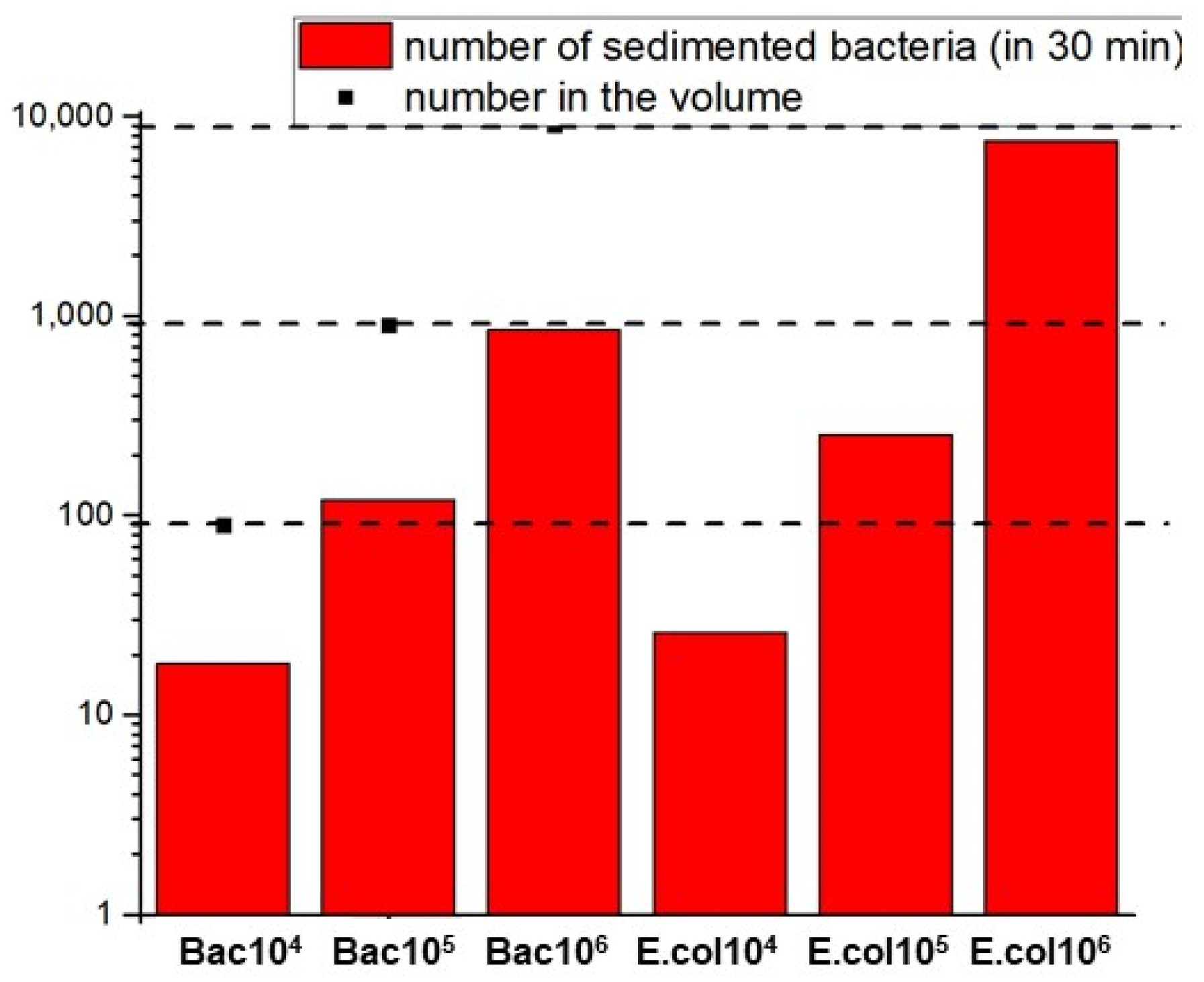
2.6. Quantification of Adsorbed Bacteria onto P(HEMA-AEM)
2.7. Quantification of Adsorbed Bacteria onto P(HEMA-AEM) in Flow Condition
2.8. Elution of Adsorbed Bacteria from P(HEMA-AEM) Cryogel
2.9. Bacterial Motility Measurements
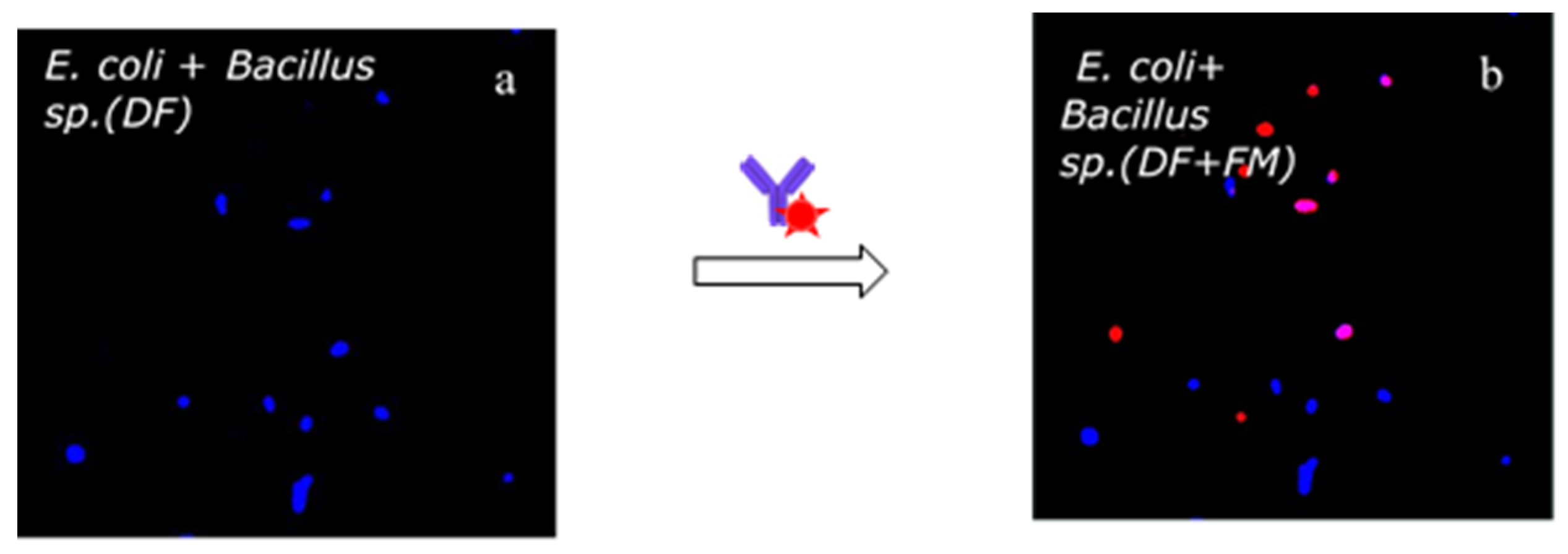
2.10. Bacteria Identification Test with Labeled Antibodies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physico-Chemical Characterization of P(HEMA-AEM) Cryogel
3.1.1. Adsorption of Bacteria in PBS and Spiked Water Samples
3.1.2. Elution of Adsorbed Bacteria from P(HEMA-AEM) Cryogel
3.2. Detection and Identification of Bacteria
3.2.1. Bioreceptor Immobilization
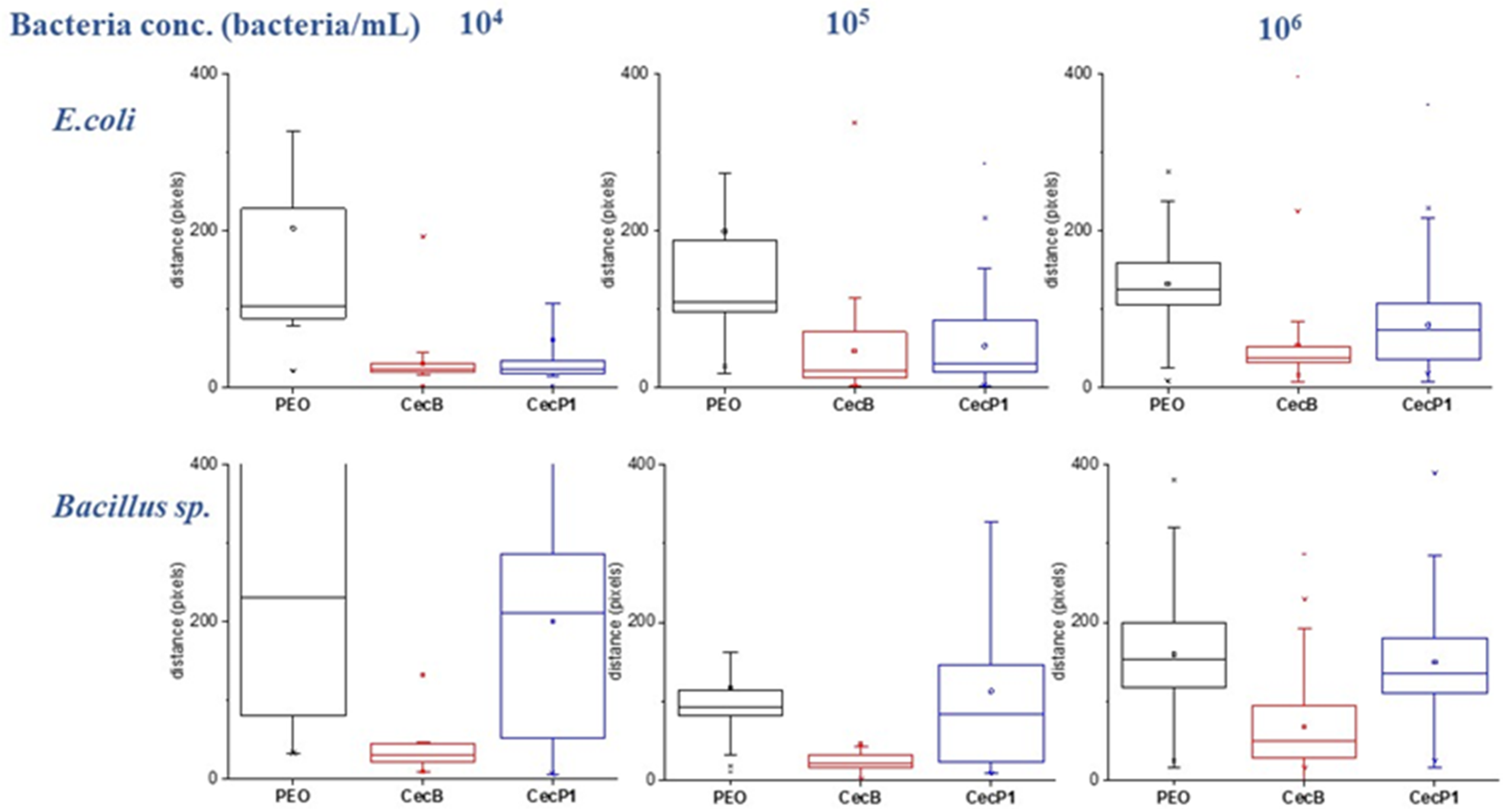
3.2.2. Determination of Bacteria Affinity toward AMPs by Motility Measurement
3.2.3. Bacterial Motility Measurements
3.3. Bacteria Identification by Labelled Antibodies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alahi, M.E.E.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Detection methodologies for pathogen and toxins: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurliyana, M.R.; Sahdan, M.Z.; Wibowo, K.M.; Muslihati, A.; Saim, H.; Ahmad, S.A.; Sari, Y.; Mansor, Z. The detection method of Escherichia coli in water resources: A review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 995, 12065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rock, C.M.; Brassill, N.; Dery, J.L.; Carr, D.; McLain, J.E.; Bright, K.R.; Gerba, C.P. Review of water quality criteria for water reuse and risk-based implications for irrigated produce under the FDA Food Safety Modernization Act, produce safety rule. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappier, S.P.; Ichida, A.; Jaglo, K.; Haugland, R.; Jones, K.R. Advancements in mitigating interference in quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) for microbial water quality monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabinger, S.; Rödiger, S.; Kriegner, A.; Vierlinger, K.; Weinhäusel, A. A survey of tools for the analysis of quantitative PCR (qPCR) data. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2014, 1, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriksson, E.; Aspan, A. Comparison of culture, ELISA and PCR techniques for Salmonella detection in faecal samples for cattle, pig and poultry. BMC Vet. Res. 2007, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heijnen, L.; Medema, G. Quantitative detection of E. coli, E. coli O157 and other shiga toxin producing E. coli in water samples using a culture method combined with real-time PCR. J. Water Health 2006, 4, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, B.Y.; Jung, S.C.; Kweon, C.H. Development of a rapid immunochromatographic strip for detection of Escherichia coli O157. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2140–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Y. Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium using quantum dots as fluorescence labels. Analyst 2006, 131, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Chang, H.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, M.; Wu, T.; Hu, X.; Xu, Z.J.; Xu, C. Detection of Bacteria in Water with β-Galactosidase-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles. SLAS Technol. Transl. Life Sci. Innov. 2018, 23, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.-H.; Bhandari, P.; Patel, P.; Irudayaraj, J. Membrane filter-assisted surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy for the rapid detection of E. coli O157: H7 in ground beef. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammes, F.; Egli, T. Cytometric methods for measuring bacteria in water: Advantages, pitfalls and applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von der Ehe, C.; Busś, T.; Weber, C.; Stumpf, S.; Bellstedt, P.; Hartlieb, M.; Schubert, U.S.; Gottschaldt, M. Glycopolymer-functionalized cryogels as catch and release devices for the pre-enrichment of pathogens. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsebom, H.; Mattiasson, B. Cryostructuration as a tool for preparing highly porous polymer materials. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoux, É.; Roux, A.; Mathey, R.; Boturyn, D.; Roupioz, Y. Antimicrobial peptide arrays for wide spectrum sensing of pathogenic bacteria. Talanta 2019, 203, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoux, É.; Boturyn, D.; Roupioz, Y. Antimicrobial peptides as probes in biosensors detecting whole bacteria: A review. Molecules 2020, 25, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyos-Nogués, M.; Gil, F.J.; Mas-Moruno, C. Antimicrobial peptides: Powerful biorecognition elements to detect bacteria in biosensing technologies. Molecules 2018, 23, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soares, J.W.; Kirby, R.; Morin, K.M.; Mello, C.M. Antimicrobial peptide preferential binding of E. Coli o157: H7. Protein Pept. Lett. 2008, 15, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malanovic, N.; Lohner, K. Gram-positive bacterial cell envelopes: The impact on the activity of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kulagina, N.V.; Lassman, M.E.; Ligler, F.S.; Taitt, C.R. Antimicrobial peptides for detection of bacteria in biosensor assays. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6504–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brétagnol, F.; Lejeune, M.; Papadopoulou-Bouraoui, A.; Hasiwa, M.; Rauscher, H.; Ceccone, G.; Colpo, P.; Rossi, F. Fouling and non-fouling surfaces produced by plasma polymerization of ethylene oxide monomer. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Ceriotti, L.; Buzanska, L.; Hasiwa, M.; Bretagnol, F.; Ceccone, G.; Gilliland, D.; Rauscher, H.; Coecke, S.; Colpo, P. Controlled micropatterning of biomolecules for cell culturing. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 1733–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X52-120, F.S.A.N. Methodology for Testing of Technique for the Detection and Identification of Biological Agents and Pathogens. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/55832.html (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Tuson, H.H.; Weibel, D.B. Bacteria–surface interactions. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 4368–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thwala, J.M.; Li, M.; Wong, M.C.Y.; Kang, S.; Hoek, E.M.; Mamba, B.B. Bacteria–polymeric membrane interactions: Atomic force microscopy and XDLVO predictions. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13773–13782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wei, H.; Xia, B.; Liu, F.; Li, N. Counting bacteria using functionalized gold nanoparticles as the light-scattering reporter. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9721–9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.-Y.; Chowdhury, M.; Huang, Y.-D.; Yu, X.-Q. Insect antimicrobial peptides and their applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5807–5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Hu, T.Y. A low cost mobile phone dark-field microscope for nanoparticle-based quantitative studies. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orth, A.; Wilson, E.R.; Thompson, J.G.; Gibson, B.C. A dual-mode mobile phone microscope using the onboard camera flash and ambient light. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La Spina, R.; António, D.C.; Bombera, R.; Lettieri, T.; Lequarré, A.-S.; Colpo, P.; Valsesia, A. New Detection Platform for Screening Bacteria in Liquid Samples. Biosensors 2021, 11, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050142
La Spina R, António DC, Bombera R, Lettieri T, Lequarré A-S, Colpo P, Valsesia A. New Detection Platform for Screening Bacteria in Liquid Samples. Biosensors. 2021; 11(5):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050142
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa Spina, Rita, Diana C. António, Radoslaw Bombera, Teresa Lettieri, Anne-Sophie Lequarré, Pascal Colpo, and Andrea Valsesia. 2021. "New Detection Platform for Screening Bacteria in Liquid Samples" Biosensors 11, no. 5: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050142
APA StyleLa Spina, R., António, D. C., Bombera, R., Lettieri, T., Lequarré, A.-S., Colpo, P., & Valsesia, A. (2021). New Detection Platform for Screening Bacteria in Liquid Samples. Biosensors, 11(5), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11050142




