Portable Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Assay Platform for the Detection of Cortisol in Human Serum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Design of the LFA Readout Device
2.4. Preparation of the Europium Chelate Nanoparticle Conjugates
2.5. Preparation and Characterization of AuNP Probes
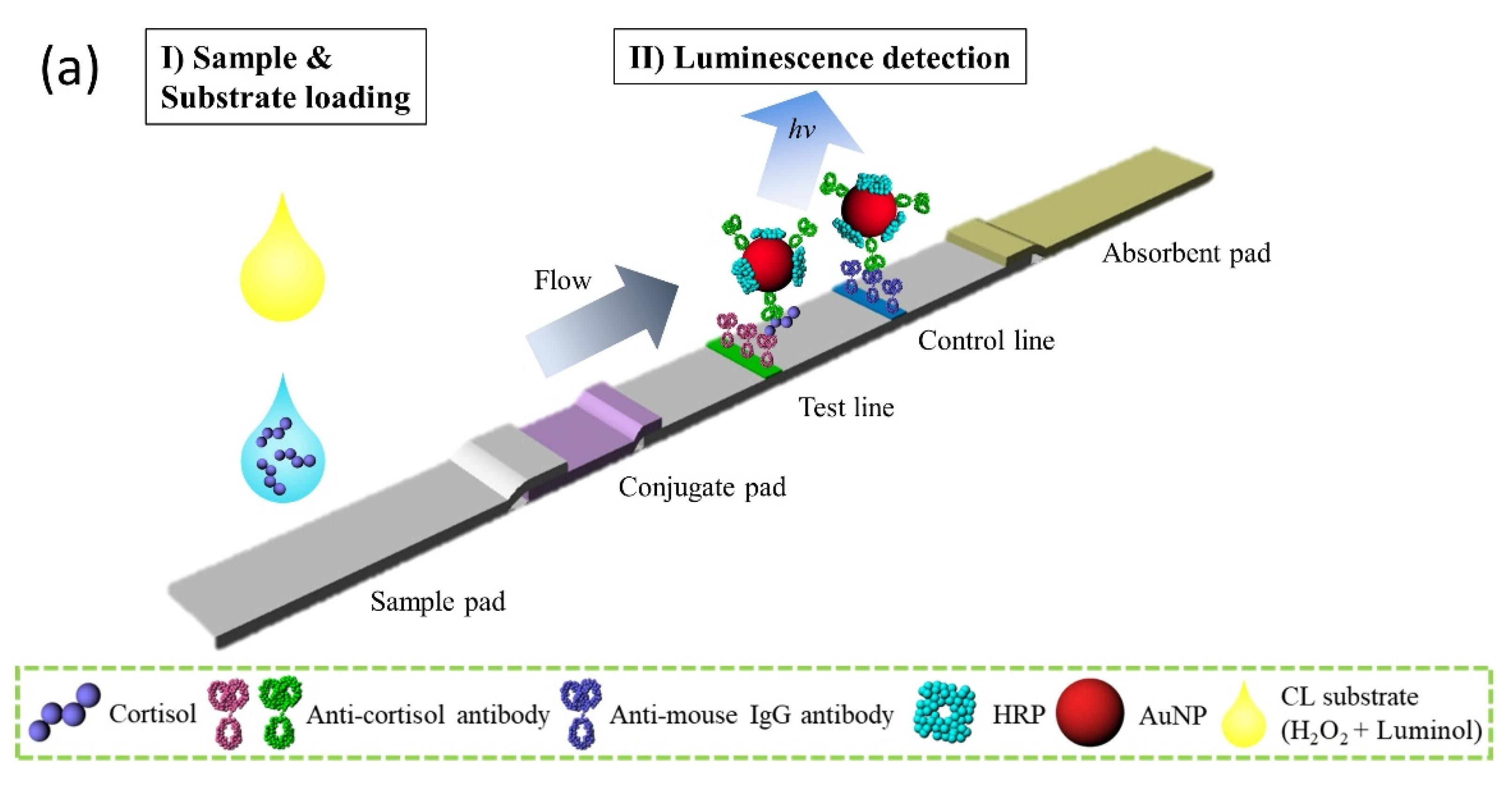
2.6. Preparation of Lateral Flow Assay Strip
2.7. Cortisol Lateral Flow Assay Using the Platform
3. Results and Discussion
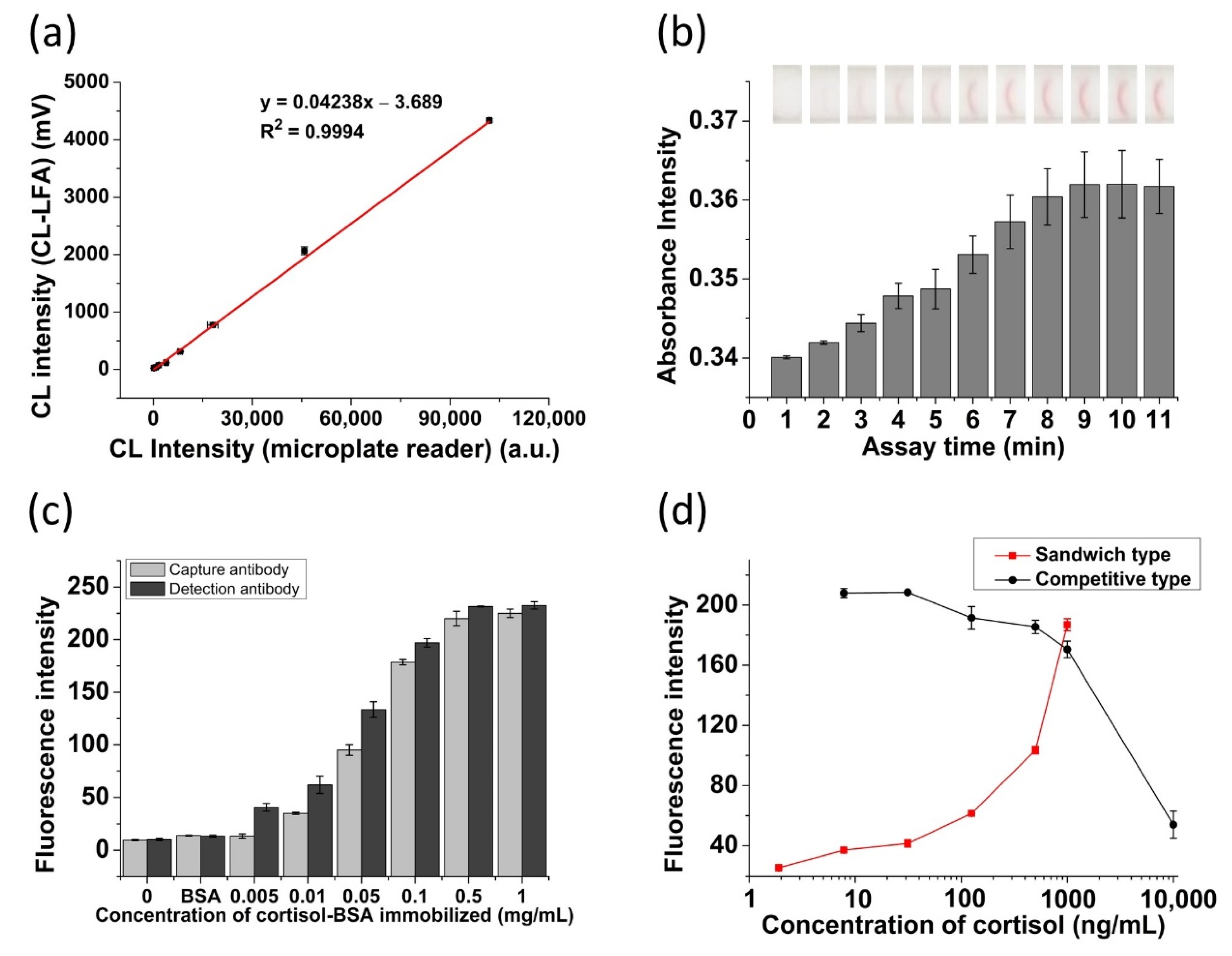
3.1. Evaluation of the LFA Platform
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of AuNP Probes
3.3. Optimization of Cortisol Lateral Flow Assay
3.4. Clinical Serum Sample Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.-H.; Hwang, Y.; Cheon, K.-A.; Jung, H.-I. Emotion-on-a-chip (EOC): Evolution of biochip technology to measure human emotion using body fluids. Med. Hypotheses 2012, 79, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarejo, M.V.; Zapirain, B.G.; Zorrilla, A.M. A stress sensor based on Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) controlled by ZigBee. Sensors 2012, 12, 6075–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Chew, W.M.; Feinstein, Y.; Skeath, P.; Sternberg, E.M. Quantification of cortisol in human eccrine sweat by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Analyst 2016, 141, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, G.; Smitha, K.G. EEG Based Stress Level Identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Budapest, Hungary, 9 October 2016; pp. 003270–003274. [Google Scholar]
- Munla, N.; Khalil, M.; Shahin, A.; Mourad, A. Driver stress level detection using HRV analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Advances in Biomedical Engineering (ICABME), Madrid, Spain, 20 July 2015; pp. 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Steckl, A.J.; Ray, P. Stress biomarkers in biological fluids and their point-of-use detection. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 2025–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, J.A.; Brown, M.A.; Kelly, J.J.; Williamson, P.M. Mechanisms of cortisol-induced hypertension in humans. Steroids 1995, 60, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Bartak, N.A.; Baiomy, A.; Habra, M.A.; Mukhi, S.V.; Morani, A.C.; Korivi, B.R.; Waguespack, S.G.; Elsayes, K.M. Cushing syndrome: Diagnostic workup and imaging features, with clinical and pathologic correlation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiksdal, A.; Hanlin, L.; Kuras, Y.; Gianferante, D.; Chen, X.; Thoma, M.V.; Rohleder, N. Associations between symptoms of depression and anxiety and cortisol responses to and recovery from acute stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 102, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erichsen, M.M.; Husebye, E.S.; Michelsen, T.M.; Dahl, A.A.; Løvås, K. Sexuality and fertility in women with Addison’s disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouanes, S.; Popp, J. High cortisol and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: A review of the literature. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apilux, A.; Rengpipat, S.; Suwanjang, W.; Chailapakul, O. Paper-based immunosensor with competitive assay for cortisol detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 178, 112925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, L.; Ducroq, D.H.; Fraser, H.L.; Gillingwater, S.; Evans, C.; Pickett, A.J.; Rees, D.W.; John, R.; Turkes, A. Measurement of urinary free cortisol by tandem mass spectrometry and comparison with results obtained by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and two commercial immunoassays. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 45, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.S.; Lowe, T.E.; Ingram, J.R. Rapid ultrasensitive measurement of salivary cortisol using nano-linker chemistry coupled with surface plasmon resonance detection. Analyst 2009, 134, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Ramgir, N.; Bhansali, S. An immunoelectrochemical sensor for salivary cortisol measurement. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 133, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Rong, Y.; Lai, W.; Chen, T. A remarkable sensitivity enhancement in a gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 45092–45097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthuma-Trumpie, G.A.; Korf, J.; van Amerongen, A. Lateral flow (immuno) assay: Its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirasoli, M.; Buragina, A.; Dolci, L.S.; Guardigli, M.; Simoni, P.; Montoya, A.; Maiolini, E.; Girotti, S.; Roda, A. Development of a chemiluminescence-based quantitative lateral flow immunoassay for on-field detection of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 721, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.G.; Nordman, E.S.; Johnson, M.D.; Oldham, M.F. A low-cost, high-performance system for fluorescence lateral flow assays. Biosensors 2013, 3, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jia, Q.; Yang, C.; Qiao, R.; Jing, L.; Wang, L.; Xu, C.; Gao, M. Lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for sensitive pesticide detection by using Fe3O4 nanoparticle aggregates as color reagents. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6778–6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinawang, P.D.; Rai, V.; Ionescu, R.E.; Marks, R.S. Electrochemical lateral flow immunosensor for detection and quantification of dengue NS1 protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X. A self-contained chemiluminescent lateral flow assay for point-of-care testing. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9132–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Yang, H.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Wen, T.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Mei, Q.; Xu, F. Improved analytical sensitivity of lateral flow assay using sponge for HBV nucleic acid detection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavis, L.D.; Raines, R.T. Bright building blocks for chemical biology. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.-B.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.-X.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Xiang, Z.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.-B. A general method to increase stokes shift by introducing alternating vibronic structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7716–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Li, H.; Lin, J.-M. Development of a highly sensitive magnetic particle-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for thyroid stimulating hormone and comparison with two other immunoassays. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2010, 411, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Lin, J.-M.; Wang, X.; Xin, T.-B.; Liang, S.-X.; Li, Z.-J.; Hu, G.-M. Magnetic particle-based chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for free thyroxine in human serum. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Loh, K.Y.; Peng, M.; Chen, C.; Cui, Y. The improved sensitive detection of C-reactive protein based on the chemiluminescence immunoassay by employing monodispersed PAA-Au/Fe3O4 nanoparticles and zwitterionic glycerophosphoryl choline. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3919–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesay, A.M.; Micheli, L.; Tervo, P.; Palleschi, G.; Virtanen, V. Development of a competitive immunoassay for the determination of cortisol in human saliva. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 434, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.-K.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, M.-G. High sensitive and broad-range detection of cortisol in human saliva using a trap lateral flow immunoassay (trapLFI) sensor. Analyst 2018, 143, 3883–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak, O.; Keene, S.T.; Marais, A.; Curto, V.F.; Salleo, A. Molecularly selective nanoporous membrane-based wearable organic electrochemical device for noninvasive cortisol sensing. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupica, S.J.; Turner, J.W., Jr. Validation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for measurement of faecal cortisol in fish. Aquac. Res. 2009, 40, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grewal, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Alhussien, M.N. Seasonal alterations in the expression of inflammatory cytokines and cortisol concentrations in periparturient Sahiwal cows. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, G.; Varambally, S.; Thirthalli, J.; Rao, M.; Christopher, R.; Gangadhar, B. Serum cortisol and BDNF in patients with major depression—Effect of yoga. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2016, 28, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinitha, T.; Ghosh, S.; Milleman, A.; Nguyen, T.; Ahn, C.H. A new polymer lab-on-a-chip (LOC) based on a microfluidic capillary flow assay (MCFA) for detecting unbound cortisol in saliva. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fill, C.; Nugen, S.R. Development of chemiluminescent lateral flow assay for the detection of nucleic acids. Biosensors 2012, 2, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangheri, M.; Di Nardo, F.; Mirasoli, M.; Anfossi, L.; Nascetti, A.; Caputo, D.; De Cesare, G.; Guardigli, M.; Baggiani, C.; Roda, A. Chemiluminescence lateral flow immunoassay cartridge with integrated amorphous silicon photosensors array for human serum albumin detection in urine samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 8869–8879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G. Nano-Inspired Biosensors for Protein Assay with Clinical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bastús, N.G.; Comenge, J.; Puntes, V. Kinetically controlled seeded growth synthesis of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: Size focusing versus Ostwald ripening. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11098–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.P.; Ibaraki, Y.; Gupta, S.D. Estimation of the chlorophyll content of micropropagated potato plants using RGB based image analysis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2010, 100, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangheri, M.; Di Nardo, F.; Anfossi, L.; Giovannoli, C.; Baggiani, C.; Roda, A.; Mirasoli, M. A multiplex chemiluminescent biosensor for type B-fumonisins and aflatoxin B1 quantitative detection in maize flour. Analyst 2015, 140, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, H.-A.; Oh, Y.K.; Kim, M.-G. An automatic enzyme immunoassay based on a chemiluminescent lateral flow immunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 53, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Xianyu, Y.; Yin, B.; Niu, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X. A dual-readout chemiluminescent-gold lateral flow test for multiplex and ultrasensitive detection of disease biomarkers in real samples. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 15205–15212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangheri, M.; Cevenini, L.; Anfossi, L.; Baggiani, C.; Simoni, P.; Di Nardo, F.; Roda, A. A simple and compact smartphone accessory for quantitative chemiluminescence-based lateral flow immunoassay for salivary cortisol detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Table | Linear Range | Limit of Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aflatoxins B1 | 0.15–50 μg/L | 0.15 μg/L | [41] |
| Fumonisin B1 | 0.6–1500 μg/L | 0.6 μg/L | [41] |
| α-fetoprotein | 1–200 ng/mL | 0.27 ng/mL | [22] |
| Folic acid | 0.5–50 ng/mL | 0.22 ng/mL | [22] |
| 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene | --- | 0.2 μg/mL | [18] |
| hs-CRP | 1–10,000 ng/mL | 1.05 ng/mL | [42] |
| Carcino embryonic antigen | 5–200 ng/mL | 0.17 ng/mL | [43] |
| Procalcitonin | 1–1000 pg/mL | 0.02 pg/mL | [43] |
| Salivary cortisol | 0.1–60 ng/mL | 0.1 ng/mL | [44] |
| Serum cortisol | 0.78–12.5 μg/dL | 0.342 μg/dL | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.T.; Jin, E.; Lee, M.-H. Portable Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Assay Platform for the Detection of Cortisol in Human Serum. Biosensors 2021, 11, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060191
Kim HT, Jin E, Lee M-H. Portable Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Assay Platform for the Detection of Cortisol in Human Serum. Biosensors. 2021; 11(6):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060191
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyun Tae, Enjian Jin, and Min-Ho Lee. 2021. "Portable Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Assay Platform for the Detection of Cortisol in Human Serum" Biosensors 11, no. 6: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060191
APA StyleKim, H. T., Jin, E., & Lee, M.-H. (2021). Portable Chemiluminescence-Based Lateral Flow Assay Platform for the Detection of Cortisol in Human Serum. Biosensors, 11(6), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060191





