Development of a Diagnostic Biosensor Method of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis towards a Point-of-Care Biosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Serum Samples
2.2. Pigeon Antigen Production
2.3. ELISA
2.4. Diagnostic Biosensor Method of Avian-Related Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
2.4.1. Step 1: Beads Functionalization
2.4.2. Step 2: Reaction with IgG Anti-Pigeon Antigen Antibodies (APAA)
2.4.3. Step 3: Reaction with Anti-Human IgG APAA (αHIgG-488)
2.4.4. Confocal Microscopy Detection and Image Analysis
2.4.5. Image Processing
2.5. Microfluidic Chip
2.5.1. Fabrication
2.5.2. Loading of the Microfluidic chip
2.5.3. Control of Bead Displacement Inside the Microfluidic Chip
2.5.4. Optical Detection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
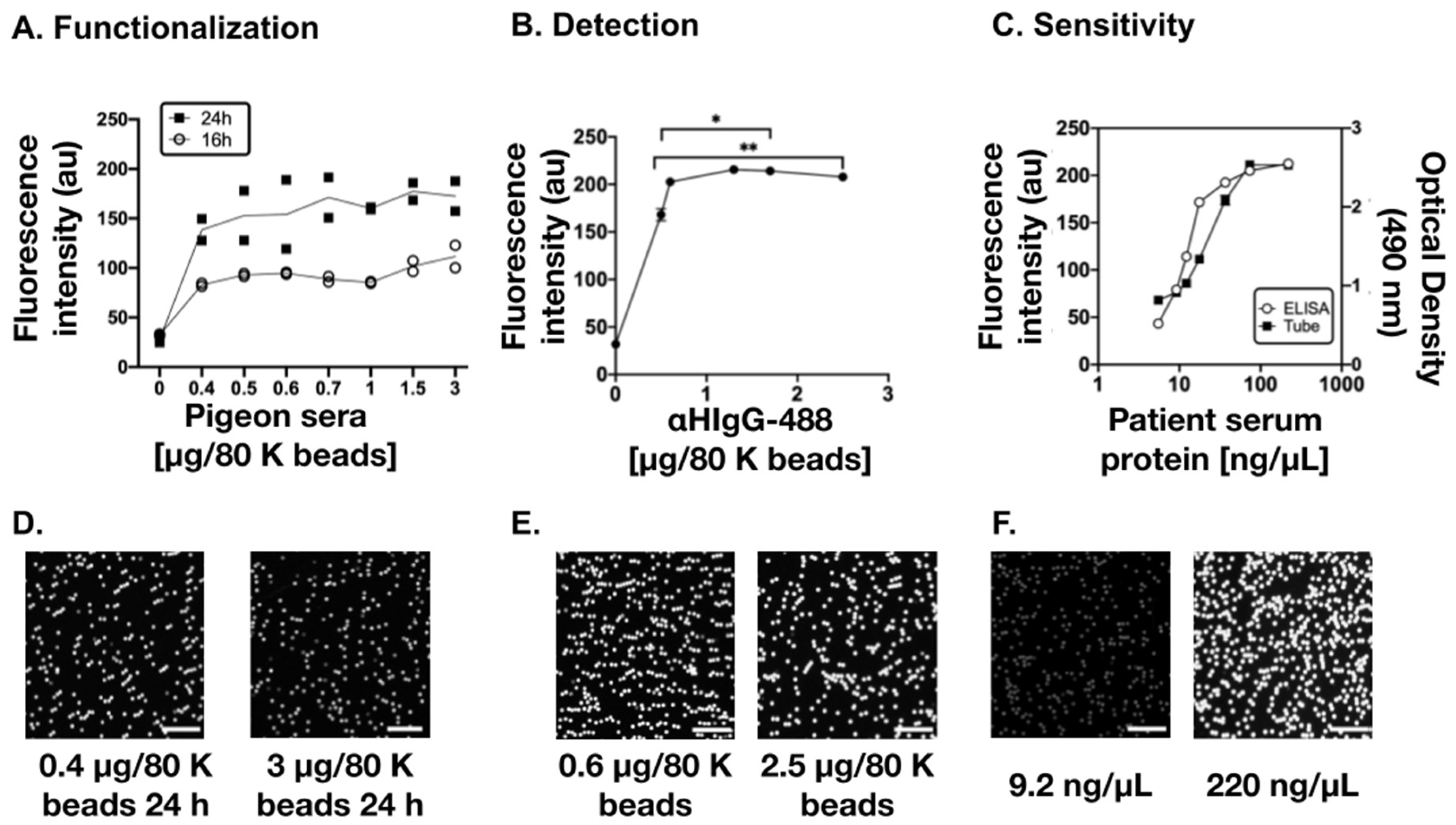
3.1. Optimization of the Diagnostic Biosensor Method
3.2. Detection of Human IgG Anti-Pigeon Antigen Antibodies in Patient’s Sera
4. Discussion and Conclusions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selman, M.; Pardo, A.; King, T.E., Jr. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Insights in diagnosis and pathobiology. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Ryerson, C.J.; Myers, J.L.; Kreuter, M.; Vasakova, M.; Bargagli, E.; Chung, J.H.; Collins, B.F.; Bendstrup, E.; et al. Diagnosis of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis in Adults. An Official ATS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 202, e36–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasakova, M.; Selman, M.; Morell, F.; Sterclova, M.; Molina-Molina, M.; Raghu, G. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: Current Concepts of Pathogenesis and Potential Targets for Treatment. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Rodríguez, J.G.; Sansores, R.H.; Castrejón, A.; Pérez-Padilla, R.; Ramírez-Venegas, A.; Selman, M. Neumonitis por hipersensibilidad en la ciudad de México. Salud Pública Méx. 2000, 42, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krasnick, J.; Meuwissen, H.J.; Nakao, M.A.; Yeldandi, A.; Patterson, R. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: Problems in diagnosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 97, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Pérez, E.R.; Swigris, J.J.; Forssén, A.V.; Tourin, O.; Solomon, J.J.; Huie, T.J.; Olsen, A.L.; Brown, K.K. Identifying an inciting antigen is associated with improved survival in patients with chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chest 2013, 144, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fenoglio, C.-M.; Reboux, G.; Sudre, B.; Mercier, M.; Roussel, S.; Cordier, J.-F.; Piarroux, R.; Dalphin, J.-C. Diagnostic value of serum precipitins to mould antigens in active hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 29, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouzet, A.; Reboux, G.; Dalphin, J.-C.; Gondouin, A.; De Vuyst, P.; Balliau, T.; Millon, L.; Valot, B.; Roussel, S. An immunoproteomic approach revealed antigenic proteins enhancing serodiagnosis performance of bird fancier’s lung. J. Immunol. Methods 2017, 450, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannson, K.A.; Barnes, H.; Bellanger, A.-P.; Dalphin, J.-C.; Pérez, E.R.F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Huang, Y.-C.T.; Jones, K.D.; Kawano-Dourado, L.; Kennedy, K.; et al. Exposure Assessment Tools for Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiroshita, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Furukawa, Y.; Kataoka, Y. Diagnostic accuracy of specific IgG antibodies for bird fancier’s lung: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, F.; Bruch, R.; Bergmann, M.; Partel, S.; Urban, G.A.; Dincer, C. Enhanced Protein Immobilization on Polymers—A Plasma Surface Activation Study. Polymers 2020, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaushik, A.; Mujawar, M.A. Point of Care Sensing Devices: Better Care for Everyone. Sensors 2018, 18, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, C.P.Y.; Mak, W.C.; Cheung, K.Y.; Sin, K.K.; Yu, C.M.; Rainer, T.H.; Renneberg, R. Evidence-Based Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Current Status and Emerging Technologies. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2013, 6, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper, I.C.; Gowers, S.A.N.; Booth, M.A.; Wang, C.; Watts, T.; Phairatana, T.; Vallant, N.; Sandhu, B.; Papalois, V.; Boutelle, M.G. Portable Microfluidic Biosensing System for Real-Time Analysis of Microdialysate in Transplant Kidneys. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 14631–14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Soler, M.; Özdemir, C.I.; Belushkin, A.; Yesilköy, F.; Altug, H. Plasmonic nanohole array biosensor for label-free and real-time analysis of live cell secretion. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 2208–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, C.M.; Augustine, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Nara, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Microfluidics Based Point-of-Care Diagnostics. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 1700047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Zaman, M.H. Low-cost tools for diagnosing and monitoring HIV infection in low-resource settings. Bull. World Health Organ. 2012, 90, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Huang, X.; Guo, J.; Ma, X. Automatic smartphone-based microfluidic biosensor system at the point of care. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.; Papadimitriou, K.I.; Greathead, L.; Vasilakis, N.; Pantelidis, P.; Kelleher, P.; Morgan, H.; Prodromakis, T. An Assay System for Point-of-Care Diagnosis of Tuberculosis using Commercially Manufactured PCB Technology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Sridhara, A.; Melo, R.; Richer, L.; Chee, N.H.; Kim, J.; Linder, V.; Steinmiller, D.; Sia, S.K.; Gomes-Solecki, M. Microfluidics-based point-of-care test for serodiagnosis of Lyme Disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Gaur, G.; Neethirajan, S. Rapid Detection of Food Allergens by Microfluidics ELISA-Based Optical Sensor. Biosensors 2016, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricci, F.; Adornetto, G.; Palleschi, G. A review of experimental aspects of electrochemical immunosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, T.J.; McKenna, W.L.; Shropshire, T.D.; Wride, D.A.; Deschamps, J.D.; Liu, X.; Stamm, R.; Wang, H.; Dunbar, W.B. A handheld platform for target protein detection and quantification using disposable nanopore strips. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; He, Z.; Zhang, A.P.; Tam, H.-Y. Ultrasensitive optofluidic enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay by on-chip integrated polymer whispering-gallery-mode microlaser sensors. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2438–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Rica, R.; Stevens, M.M. Plasmonic ELISA for the ultrasensitive detection of disease biomarkers with the naked eye. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lei, J.; Sun, X.-C.; Lei, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. A Dynabeads-labeled immunoassay based on a fluxgate biosensor for the detection of biomarkers. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 2391–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleček, E.; Fojta, M. Magnetic beads as versatile tools for electrochemical DNA and protein biosensing. Talanta 2007, 74, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, E.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Montiel, V.R.-V.; Povedano, E.; Pedrero, M.; Montoya, J.J.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Magnetic Beads-Based Sensor with Tailored Sensitivity for Rapid and Single-Step Amperometric Determination of miRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, B.; Li, F.; Yang, H.; Yu, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, R.; Hu, Y. Magnetic beads-based enzymatic spectrofluorometric assay for rapid and sensitive detection of antibody against ApxIVA of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coarsey, C.; Coleman, B.; Kabir, A.; Sher, M.; Asghar, W. Development of a flow-free magnetic actuation platform for an automated microfluidic ELISA. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8159–8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mani, V.; Paleja, B.; Larbi, K.; Kumar, P.; Tay, J.A.; Siew, J.Y.; Inci, F.; Wang, S.; Chee, C.; Wang, Y.T.; et al. Microchip-based ultrafast serodiagnostic assay for tuberculosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, F.; Baltazares, M.; Ramirez, A.; Sansores, R.; Nava, A.; Bañales, J.L.; Selman, M. Detection of salivary and seric IgG and IgA antipooled pigeon sera activities in patients with pigeon breeder’s disease. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1996, 10, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckenberger, D.J.; De Groot, T.E.; Wan, A.M.D.; Beebe, D.J.; Young, E.W.K. Micromilling: A method for ultra-rapid prototyping of plastic microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2364–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran, H.H.; Wu, W.; Lee, N.Y. Ethanol and UV-assisted instantaneous bonding of PMMA assemblies and tuning in bonding reversibility. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.-W.; DeVoe, D.L. Bonding of thermoplastic polymer microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2009, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDougall, D.; Crummett, W.B. Guidelines for data acquisition and data quality evaluation in environmental chemistry. Anal. Chem. 1980, 52, 2242–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huergo, L.F.; Selim, K.A.; Conzentino, M.S.; Gerhardt, E.C.M.; Santos, A.R.S.; Wagner, B.; Alford, J.T.; Deobald, N.; Pedrosa, F.O.; de Souza, E.M.; et al. Magnetic Bead-Based Immunoassay Allows Rapid, Inexpensive, and Quantitative Detection of Human SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Moncayo, R.; Cedillo-Alcantar, D.F.; Guevara-Pantoja, P.E.; Chavez-Pineda, O.G.; Hernandez-Ortiz, J.A.; Amador-Hernandez, J.U.; Rojas-Velasco, G.; Sanchez-Muñoz, F.; Manzur-Sandoval, D.; Patino-Lopez, L.D.; et al. A high-throughput multiplexed microfluidic device for COVID-19 serology assays. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Condition | Reactions of the DBM | Fluorescence Intensity (au) | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | Step 2 | Step 3 | |||
| Negative control | PS | PBS | αHIgG-488 | 34.7 | 5.3 |
| Control 1 | PS | PBS | PBS | 39.0 | 2.2 |
| Control 2 | Buffer 1 | PBS | PBS | 40.5 | 1.5 |
| Control 3 | Buffer 1 | Patient sample | PBS | 41.6 | 2.4 |
| Control 4 | Buffer 1 | PBS | αHIgG-488 | 43.9 | 2.5 |
| Control 5 | Buffer 1 | Patient sample | αHIgG-488 | 53.8 | 1.5 |
| Full reaction | PS | Patient sample | αHIgG-488 | 101.6 | 4.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiordelisio, T.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; Hautefeuille, M.; Del-Rio, D.; Ríos-López, D.G.; Zamarrón-Hernández, D.; Amat-Shapiro, S.; Campa-Higareda, A.; Jiménez-Díaz, E.; González-Villa, E.; et al. Development of a Diagnostic Biosensor Method of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis towards a Point-of-Care Biosensor. Biosensors 2021, 11, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060196
Fiordelisio T, Buendia-Roldan I, Hautefeuille M, Del-Rio D, Ríos-López DG, Zamarrón-Hernández D, Amat-Shapiro S, Campa-Higareda A, Jiménez-Díaz E, González-Villa E, et al. Development of a Diagnostic Biosensor Method of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis towards a Point-of-Care Biosensor. Biosensors. 2021; 11(6):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060196
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiordelisio, Tatiana, Ivette Buendia-Roldan, Mathieu Hautefeuille, Diana Del-Rio, Diana G. Ríos-López, Diego Zamarrón-Hernández, Samuel Amat-Shapiro, Andrea Campa-Higareda, Edgar Jiménez-Díaz, Erika González-Villa, and et al. 2021. "Development of a Diagnostic Biosensor Method of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis towards a Point-of-Care Biosensor" Biosensors 11, no. 6: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060196
APA StyleFiordelisio, T., Buendia-Roldan, I., Hautefeuille, M., Del-Rio, D., Ríos-López, D. G., Zamarrón-Hernández, D., Amat-Shapiro, S., Campa-Higareda, A., Jiménez-Díaz, E., González-Villa, E., Nelson-Mora, J., García-Carreño, N., López-Aparicio, J., Montes, E., Santiago-Ruiz, A., Pardo, A., & Selman, M. (2021). Development of a Diagnostic Biosensor Method of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis towards a Point-of-Care Biosensor. Biosensors, 11(6), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060196








