Polystyrene Microsphere-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Maize
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
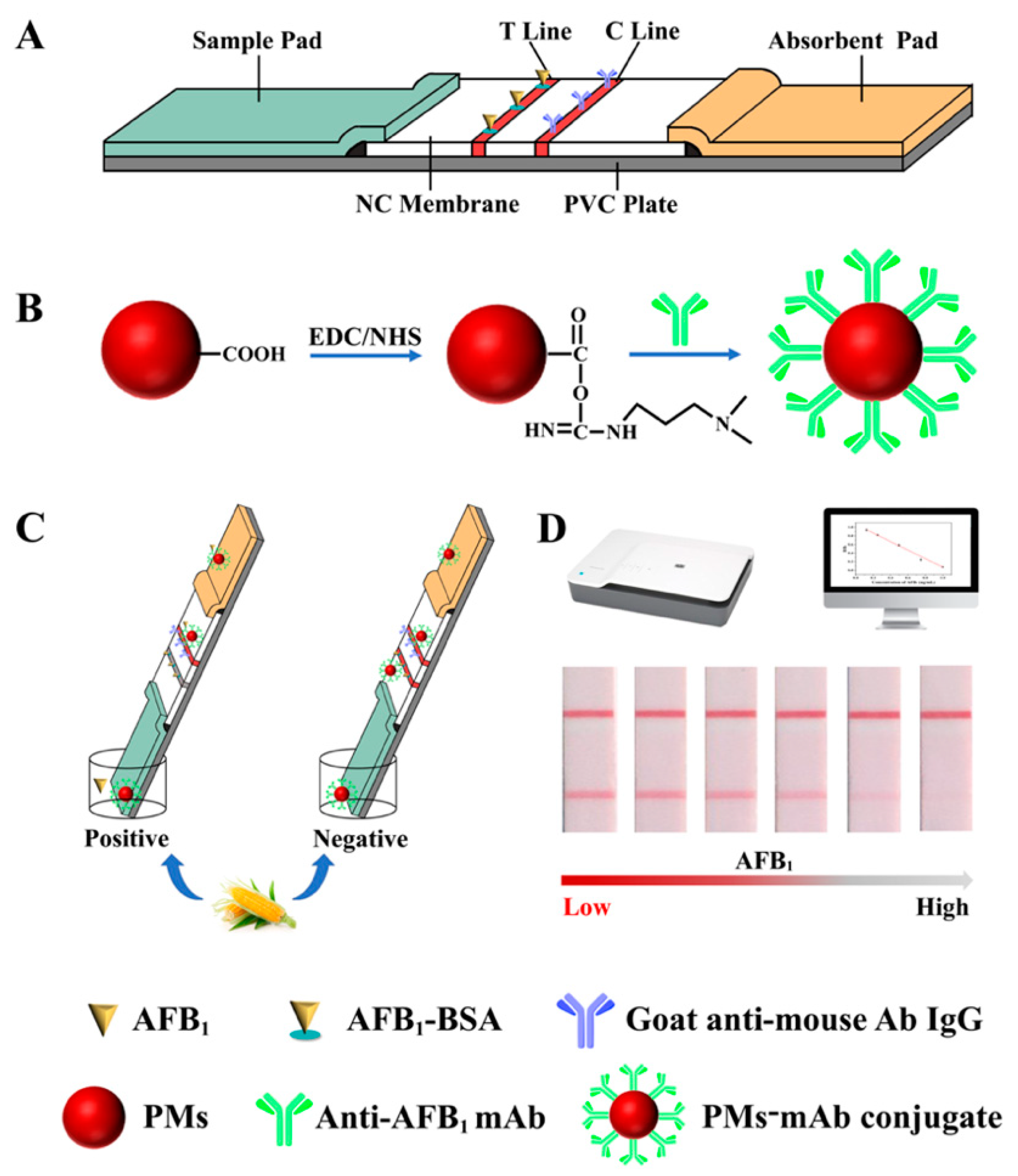
2.2. Labeling of mAbs with PMs
2.3. Fabrication of PMs-ICA Strips
2.4. Optimization of Key Parameters
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.6. Test Procedure
2.7. Sensitivity and Specificity of PMs-ICA
2.8. Accuracy and Precision
2.9. Detection of Real Maize Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Principle of PMs-ICA
3.2. Optimization of Key Parameters of PMs-ICA
3.2.1. The Amount of PMs
3.2.2. The Condition for Activating Carboxyl Groups of PMs
3.2.3. The Amounts of mAb
3.2.4. The Immune Probe Amount
3.3. Sensitivity and Specificity of PMs-ICA
3.4. Accuracy and Precision
3.5. Detection of Real Maize Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beizaei, A.; O’Kane, S.L.; Kamkar, A.; Misaghi, A.; Henehan, G.; Cahill, D.J. Highly sensitive toxin microarray assay for aflatoxin B1 detection in cereals. Food Control 2015, 57, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Ok, H.E.; Hwang, J.-B.; Chung, D.-H. Determination of aflatoxin levels in nuts and their products consumed in South Korea. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawal, S.; Kim, J.E.; Coulombe, R., Jr. Aflatoxin B1 in poultry: Toxicology, metabolism and prevention. Res. Vet. Sci. 2010, 89, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, Q. Direct fluorescence anisotropy approach for aflatoxin B1 detection and affinity binding study by using single tetramethylrhodamine labeled aptamer. Talanta 2018, 189, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Groopman, J.D.; Pestka, J.J. Public health impacts of foodborne mycotoxins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bedard, L.L.; Massey, T.E. Aflatoxin B1-induced DNA damage and its repair. Cancer Lett. 2006, 241, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Fu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. A water-stable luminescent metal–organic framework for effective detection of aflatoxin B1 in walnut and almond beverages. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 364, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Khodaei, D.; Javanmardi, F.; Khaneghah, A.M. The global overview of the occurrence of mycotoxins in Cereals: A three-year survey. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.N.; Jaiswal, P.; Kaur, J.; Ramya, H. Rapid Detection and Quantification of Aflatoxin B1 in Milk Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. A 2021, 102, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakin, F.; Tekeli, İ.O.; Yipel, M.; Kürekci, C. Occurrence and health risk assessment of aflatoxins and ochratoxin a in Sürk, a Turkish dairy food, as studied by HPLC. Food Control 2018, 90, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangampalli Adi, P.; Matcha, B. Analysis of aflatoxin B1 in contaminated feed, media, and serum samples of Cyprinus carpio L. by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Quality Saf. 2018, 2, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Schrunk, D.E.; Imerman, P.M.; Smith, L.; Francis, K.; Tahara, J.; Tkachenko, A.; Reimschuessel, R.; Rumbeiha, W.K. Evaluation of a diagnostic method to quantify aflatoxins B1 and M1 in animal liver by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhjavan, B.; Ahmed, N.S.; Khosravifard, M. Development of an improved method of sample extraction and quantitation of multi-mycotoxin in feed by LC-MS/MS. Toxins 2020, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, T.A.; Ekwomadu, T.I.; Mwanza, M. Multi mycotoxin determination in dried beef using liquid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Toxins 2020, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, T.; de la Guardia, M.; Baradaran, B. Lateral flow assays towards point-of-care cancer detection: A review of current progress and future trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnasko, R.M.; Jackson, E.S.; Lin, A.V.; Haff, R.P.; McGarvey, J.A. A Rapid and Sensitive Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) for the Detection of Gluten in Foods. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, J.; Fu, S.; Zhang, J.; Mei, Q.; Zhang, Y. Single-Line Flow Assay Platform Based on Orthogonal Emissive Upconversion Nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3010–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, L.; Lv, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, P.; Yu, J. DNAzyme-triggered visual and ratiometric electrochemiluminescence dual-readout assay for Pb (II) based on an assembled paper device. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3874–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Chung, D.-R.; Kang, M. A new point-of-care test for the diagnosis of infectious diseases based on multiplex lateral flow immunoassays. Analyst 2019, 144, 2460–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiong, E.; Tian, T.; Cheng, M.; Lin, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/Cas9-mediated lateral flow nucleic acid assay. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2497–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, G.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Ren, S.; Gao, Z.; Chen, A. Dual-competitive lateral flow aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin B1 in food and feedstuffs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.; Song, Y.; Shi, Q.; Du, D.; Liu, D.; Luo, Y.; Xu, W.; Lin, Y. Au@ Pd nanopopcorn and aptamer nanoflower assisted lateral flow strip for thermal detection of exosomes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13986–13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razo, S.C.; Panferov, V.G.; Safenkova, I.V.; Varitsev, Y.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Double-enhanced lateral flow immunoassay for potato virus X based on a combination of magnetic and gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1007, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzantiev, B.B.; Byzova, N.A.; Urusov, A.E.; Zherdev, A.V. Immunochromatographic methods in food analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 55, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.-Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Xiong, Q.-R.; Xu, H.-Y.; Xiong, Y.-H.; Liu, K.; Jin, Y.; Lai, W.-H. Advantages of fluorescent microspheres compared with colloidal gold as a label in immunochromatographic lateral flow assays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Hua, Q.; Liang, J.; Shen, X.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H.; Sun, Y. Latex microsphere immunochromatography for quantitative detection of dexamethasone in milk and pork. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borse, V.; Srivastava, R. Fluorescence lateral flow immunoassay based point-of-care nanodiagnostics for orthopedic implant-associated infection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 280, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-J.; Sheng, W.; Wen, W.; Gu, Y.; Wang, J.-P.; Wang, S. Three kinds of lateral flow immunochromatographic assays based on the use of nanoparticle labels for fluorometric determination of zearalenone. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taranova, N.; Berlina, A.; Zherdev, A.; Dzantiev, B. ‘Traffic light’immunochromatographic test based on multicolor quantum dots for the simultaneous detection of several antibiotics in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panferov, V.G.; Safenkova, I.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Urchin peroxidase-mimicking Au@ Pt nanoparticles as a label in lateral flow immunoassay: Impact of nanoparticle composition on detection limit of Clavibacter michiganensis. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Yao, X.; Wang, Z.; Dou, L.; Su, L.; Zhao, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Developing a Simple Immunochromatography Assay for Clenbuterol with Sensitivity by One-Step Staining. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15509–15515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Wen, K.; Li, C.; Mujtaba Mari, G.; Jiang, H.; Shi, W.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Multiplex lateral flow immunoassays based on amorphous carbon nanoparticles for detecting three fusarium mycotoxins in maize. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8063–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Liu, N.; Zhao, Z.; Njumbe Ediage, E.; Wu, S.; Sun, C.; De Saeger, S.; Wu, A. Multiplex lateral flow immunoassay for mycotoxin determination. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4995–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hua, Q.; Wang, J.; Liang, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. A smartphone-based dual detection mode device integrated with two lateral flow immunoassays for multiplex mycotoxins in cereals. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 158, 112178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Yi, C.; Jiang, L.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Shen, X.; Sun, Y.; Lei, H. A smartphone-based quantitative detection device integrated with latex microsphere immunochromatography for on-site detection of zearalenone in cereals and feed. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 290, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Han, M.; Zhou, J.; Gong, L.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, L. Development and optimization of a multiplex lateral flow immunoassay for the simultaneous determination of three mycotoxins in corn, rice and peanut. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Liao, X.; Sun, C.; Fang, L.; Zhou, L.; Kong, W. Development of a quantum dot nanobead-based fluorescent strip immunosensor for on-site detection of aflatoxin B1 in lotus seeds. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Lai, W. Rapid detection method for aflatoxin B1 in soybean sauce based on fluorescent microspheres probe. Food Control 2015, 50, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Lu, Z.; Tao, X. Comparative Study of Time-Resolved Fluorescent Nanobeads, Quantum Dot Nanobeads and Quantum Dots as Labels in Fluorescence Immunochromatography for Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Grains. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Nanoparticles | Cut-Off Value (ng/mL) | Result Judging | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colloidal gold | 10 | Naked eye | [37] |
| Quantum dot | 1 | Reader | [38] |
| Fluorescent microspheres | 2.5 | Reader | [39] |
| Time-resolved fluorescent Nanobeads | >1 | Reader | [40] |
| PMs | 1 | Naked eye | this work |
| Mycotoxin | IC50 | CR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| AFB1 | 0.57 | 100 |
| AFB2 | 2.56 | 22.3 |
| AFG1 | 3.90 | 14.6 |
| AFG2 | 15.83 | 3.6 |
| AFM1 | 1.34 | 42.5 |
| OTA | >10,000 | <0.1 |
| DON | >10,000 | <0.1 |
| FB1 | >10,000 | <0.1 |
| T-2 | >10,000 | <0.1 |
| Samples | Added (µg/kg) | Found (µg/kg) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maize | 1 | 1.05 | 105.0 | 8.4 |
| 3 | 2.88 | 96.0 | 3.2 | |
| 5 | 5.38 | 107.6 | 2.5 | |
| 12 | + 1 | / 2 | / |
| Sample Number | PMs-ICA (µg/kg) | LC–MS/MS |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ND 1 | ND |
| 2 | ND | ND |
| 3 | ND | ND |
| 4 | ND | ND |
| 5 | ND | ND |
| 6 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| 7 | ND | ND |
| 8 | ND | ND |
| 9 | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| 10 | ND | ND |
| 11 | ND | ND |
| 12 | ND | ND |
| 13 | ND | ND |
| 14 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| 15 | ND | ND |
| 16 | ND | ND |
| 17 | 1.9 | 1.8 |
| 18 | ND | ND |
| 19 | ND | ND |
| 20 | ND | ND |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Li, X.; Shen, X.; Zhang, A.; Liu, J.; Lei, H. Polystyrene Microsphere-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Maize. Biosensors 2021, 11, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060200
Wang J, Li X, Shen X, Zhang A, Liu J, Lei H. Polystyrene Microsphere-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Maize. Biosensors. 2021; 11(6):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060200
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jin, Xiangmei Li, Xing Shen, Ang Zhang, Jinxiu Liu, and Hongtao Lei. 2021. "Polystyrene Microsphere-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Maize" Biosensors 11, no. 6: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060200
APA StyleWang, J., Li, X., Shen, X., Zhang, A., Liu, J., & Lei, H. (2021). Polystyrene Microsphere-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Maize. Biosensors, 11(6), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11060200







