Development of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) to Screen for the Release of the Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A from Polymer Materials and Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of the Hapten–Protein Conjugate
2.3. Antibody Immobilization on Latex Microparticles
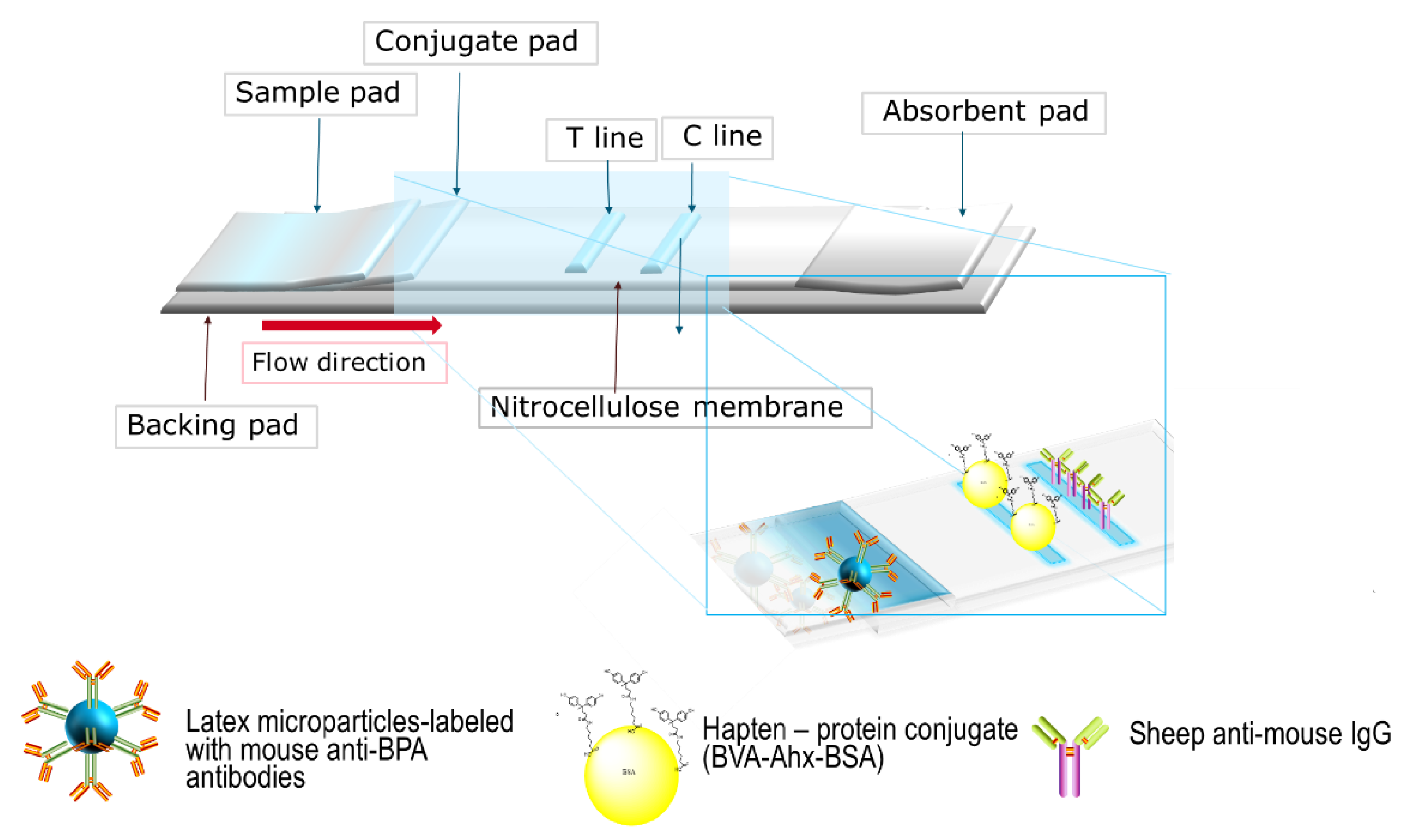
2.4. Assembly of Lateral Flow Test Strips
2.5. Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA)
2.6. Lateral Flow Immunoassay Data Processing
2.7. Competitive indirect ELISA
2.8. Sample Preparation
3. Results
3.1. Analytical Characteristics of the LFIA
3.2. Selectivity of the Antibody
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almeida, S.; Raposo, A.; Almeida-González, M.; Carrascosa, C. Bisphenol A: Food exposure and impact on human health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1503–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben-Jonathan, N. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and breast cancer: The saga of Bisphenol A. Estrogen Recept. Breast Cancer 2019, 343–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, S.C.; Bromfield, J.J. Bisphenol A: A Model endocrine disrupting chemical with a new potential mechanism of action. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1962–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Repr. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ediage, E.N.; Di Mavungu, J.D.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Van Peteghem, C.; De Saeger, S. Multiplex flow-through immunoassay formats for screening of mycotoxins in a variety of food matrices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, S.; Singhal, M.; McKenzie, K.G.; Osborn, J.L.; Arjyal, A.; Dongol, S.; Baker, S.G.; Basnyat, B.; Farrar, J.; Dolecek, C.; et al. A rapid, multiplexed, high-throughput flow-through membrane immunoassay: A convenient alternative to ELISA. Diagnostics 2013, 3, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmistrova, N.A.; Rusanova, T.Y.; Yurasov, N.A.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; De Saeger, S. Multi-detection of mycotoxins by membrane based flow-through immunoassay. Food Control 2014, 46, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damborsky, P.; Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A.; Katrlik, J. Lectin-based lateral flow assay: Proof-of-concept. Analyst 2016, 141, 6444–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.K.; Uzunoglu, A.; Stanciu, L.A. Aminolated and thiolated PEG-covered gold nanoparticles with high stability and antiaggregation for lateral flow detection of bisphenol A. Small 2018, 14, 1702828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemmeli, D.; Mchiri, C.; Dridi, C.; Nasri, H.; Dempsey, E. Development of a new bisphenol A electrochemical sensor based on a cadmium(II) porphyrin modified carbon paste electrode. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 31740–31747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Feng, S.; Wang, S. The development of a photothermal immunochromatographic lateral flow strip for rapid and sensitive detection of bisphenol A in food samples. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, S.; Ren, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z. Magnetic Relaxation Switch Biosensors Based on Self-Assembly of Polystyrene Microspheres and Magnetic Nanoparticles for Detection of Bisphenol A. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 5963–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Liu, S.; Su, L.; Dou, L.; Tao, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Graphite-like carbon nitride-laden gold nanoparticles as signal amplification label for highly sensitive lateral flow immunoassay of 17β-estradiol. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.K.; Stanciu, L.A. Bisphenol A detection using gold nanostars in a SERS improved lateral flow immunochromatographic assay. Sens. Actuators A Chem. 2018, 276, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Kang, L.; Xiang, X.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Luo, R.; Lu, C.; Peng, X. Recent advances and progress in the detection of bisphenol A. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6913–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Song, S.; Park, S.; Joo, C. Recent advances in high-sensitivity detection methods for paper-based lateral-flow assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 152, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre, P.; Gallardo, C.; Monedero, A.; Ruiz, T.; Arias, M.; Sanz, A.; Rueda, P. Development of a novel lateral flow assay for detection of African swine fever in blood. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. A simple, sensitive, rapid and specific detection method for bisphenol A based on fluorescence polarization immunoassay. Immunol. Investig. 2012, 41, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Hanelt, S.; Canitz, C.; Hoffmann, H.; Garbe, L.A.; Schneider, R.J. Synthetic strategies for the modification of diclofenac. Synlett 2017, 28, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raysyan, A.; Moerer, R.; Coesfeld, B.; Eremin, S.A.; Schneider, R.J. Fluorescence polarization immunoassay for the determination of diclofenac in wastewater. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raysyan, A.; Galvidis, I.A.; Schneider, R.J.; Eremin, S.A.; Burkin, M.A. Development of a latex particles-based lateral flow immunoassay for group determination of macrolide antibiotics in breast milk. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 189, 113450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Termo Fischer: Waltham, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Holstein, C.A.; Chevalier, A.; Bennett, S.; Anderson, C.E.; Keniston, K.; Olsen, C.; Li, B.; Bales, B.; Moore, D.R.; Fu, E.; et al. Immobilizing affinity proteins to nitrocellulose: A toolbox for paper-based assay developers. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nečas, D.; Klapetek, P. Gwyddion: An open-source software for SPM data analysis. Open Phys. 2012, 10, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasson, U.; Perret-Liaudet, A.; van Doorn, L.J.C.V.; Blennow, K.; Chiasserini, D.; Engelborghs, S.; Fladby, T.; Genc, S.; Kruse, N.; Kuiperij, H.B.; et al. A practical guide to immunoassay method validation. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, R.A.; Edwards, P.; Ekins, R.P.; Finney, D.J.; McKenzie, I.G.; Raab, G.M.; Rodbard, D.; Rodgers, R.P. Guidelines for immunoassay data processing. Clin. Chem. 1985, 31, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendum, T.; Stoler, E.; VanBenschoten, H.; Warner, J.C. Concentration of bisphenol A in thermal paper. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2021, 1, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Barbato, F.; Grumetto, L. Monitoring of bisphenol A and bisphenol S in thermal paper receipts from the Italian market and estimated transdermal human intake. A pilot study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.K.; Cheng, W.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.R.; Chen, X.P.; Huang, C.J. A novel superparamagnetic surface molecularly imprinted nanoparticle adopting dummy template: An efficient solid-phase extraction adsorbent for bisphenol A. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 720, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, J.P. Standardization of immunoassays for hapten analytes. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1991, 51, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan Maruthamuthu, M.; Selvamani, V.; Eom, G.T.; Hong, S.H. Development of recA promoter based bisphenol-A sensing and adsorption system by recombinant Escherichia coli. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 122, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Bahmani, R.; Ko, J.H.; Hwang, S. Development of bisphenol A (BPA)-sensing indicator Arabidopsis thaliana which synthesizes anthocyanin in response to BPA in leaves. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Kang, L.; Pang, F.; Li, H.; Luo, R.; Luo, X.; Sun, F. A signal-enhanced lateral flow strip biosensor for ultrasensitive and on-site detection of bisphenol A. Food Agric. Immunol. 2018, 29, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dzantiev, B.B.; Taranova, N.A.; Semeykina, A.A.; Zherdev, A.V. Lateral flow immunoassay for bisphenol A: Development of test strips and their application for ecological monitoring. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1172, 012088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñas, P.; Campillo, N.; Martínez-Castillo, N.; Hernández-Córdoba, M. Comparison of two derivatization-based methods for solid-phase microextraction–gas chromatography–mass spectrometric determination of bisphenol A, bisphenol S and biphenol migrated from food cans. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.Y.; Kannan, K. Concentrations and Profiles of bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues in foodstuffs from the United States and their implications for human exposure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Visual Cut-Off, vLOD, µg/L | Instrumental Limit of Detection, cLOD, µg/L |
|---|---|
| 10 | 0.14 |
| Abbr. | Chemical Structure | ELISA | LFIA | Abbr. | Chemical Structure | ELISA | LFIA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPA |  | 100 | 100 | BPF |  | 1.0 | <0.1 |
| BPA-d16 |  | 60 | 52 | BPS |  | 0.13 | <0.1 |
| BVA |  | 13 | 17 | BPB |  | 217 | 105 |
| 4-CP |  | 1.6 | 3.7 | OCP |  | 0.01 | <0.1 |
| BPE |  | 1.0 | 7.5 | 4-NP |  | 0.02 | <0.1 |
| Sample | c (BPA) ± SD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC–MS/MS (µg/L) | LFIA (µg/L) | CV (%) | ELISA (µg/L) | CV (%) | |
| Thermal receipt paper #1 | 0.70 ± 0.03 | <LOD | − | 0.76 ± 0.2 (108) | 18 |
| Thermal receipt paper #2 | <LOD | <LOD | − | <LOD | − |
| Thermal receipt paper #3 | <LOD | <LOD | − | <LOD | − |
| Tickets #1 | 14 ± 1.2 | 15 ± 10 (109) | 6 | 17 ± 2.1 (125) | 12 |
| Tickets #2 | 34 ± 2.3 | 29 ± 10 (83) | 8 | 43 ± 1.6 (126) | 9 |
| Flyers #3 | 47 ± 3.0 | 50 ± 7.1 (105) | 10 | 52 ± 4.4 (110) | 11 |
| Food contact papers | <LOD | <LOD | − | <LOD | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raysyan, A.; Schneider, R.J. Development of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) to Screen for the Release of the Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A from Polymer Materials and Products. Biosensors 2021, 11, 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070231
Raysyan A, Schneider RJ. Development of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) to Screen for the Release of the Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A from Polymer Materials and Products. Biosensors. 2021; 11(7):231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070231
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaysyan, Anna, and Rudolf J. Schneider. 2021. "Development of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) to Screen for the Release of the Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A from Polymer Materials and Products" Biosensors 11, no. 7: 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070231
APA StyleRaysyan, A., & Schneider, R. J. (2021). Development of a Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFIA) to Screen for the Release of the Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A from Polymer Materials and Products. Biosensors, 11(7), 231. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070231






