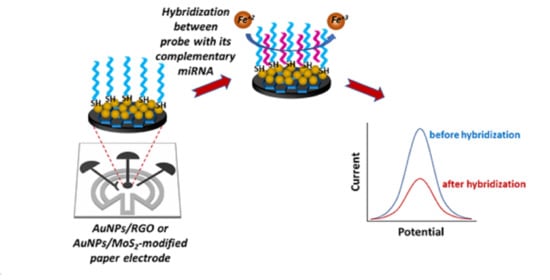
Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Voltammetric Detection of miRNA Biomarkers Using Reduced Graphene Oxide or MoS2 Nanosheets Decorated with Gold Nanoparticle Electrodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Generation and Modification of Paper Electrode
2.4. Preparation of a Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheet (MoS2)-Modified Paper Electrode
2.5. Electrodeposition of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) on an RGO- or MoS2-Modified Paper Electrode
2.6. miRNA Detection with AuNP/RGO- or AuNP/MoS2-Modified Paper Electrodes
2.7. Voltammetric Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
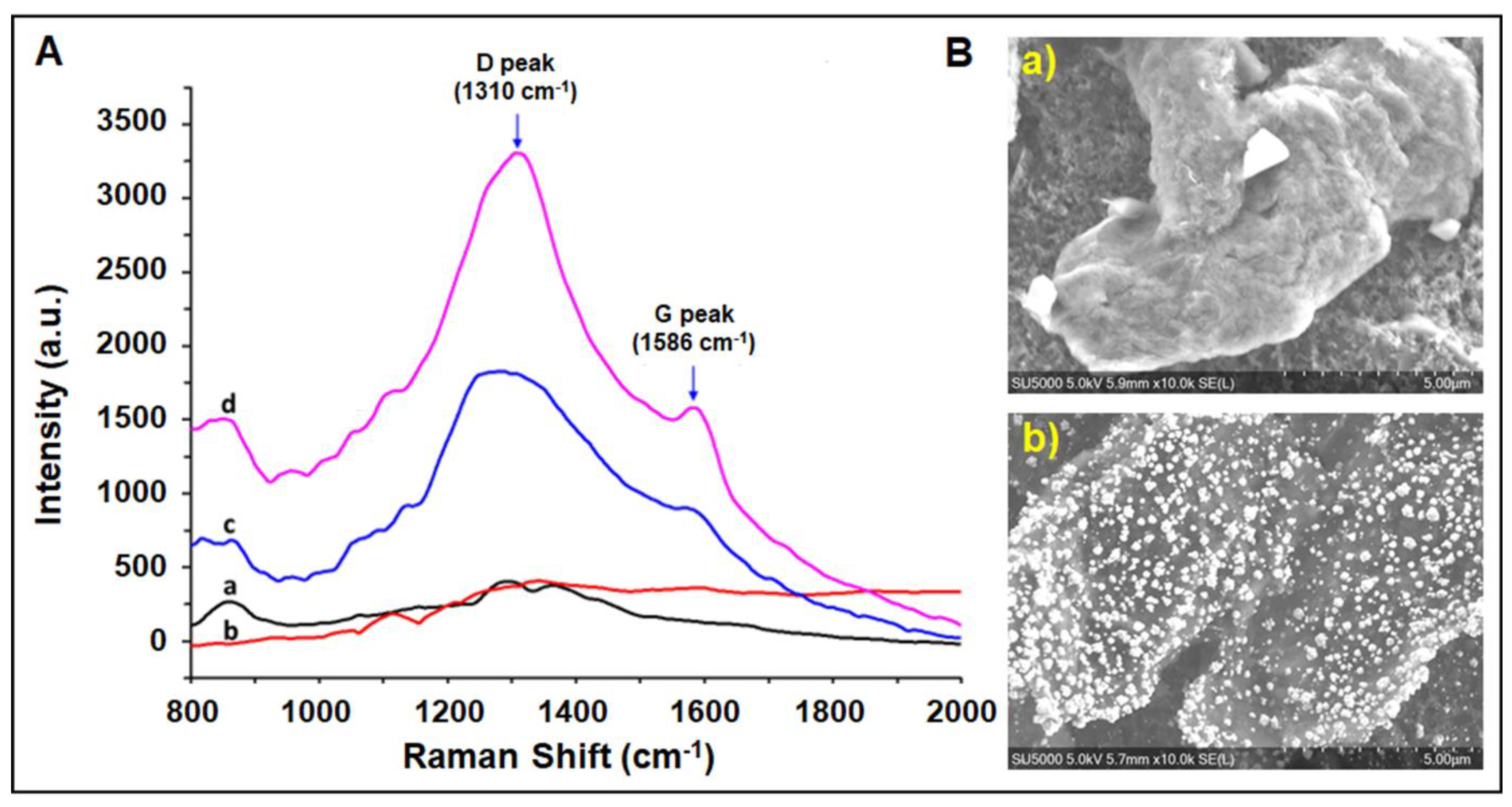
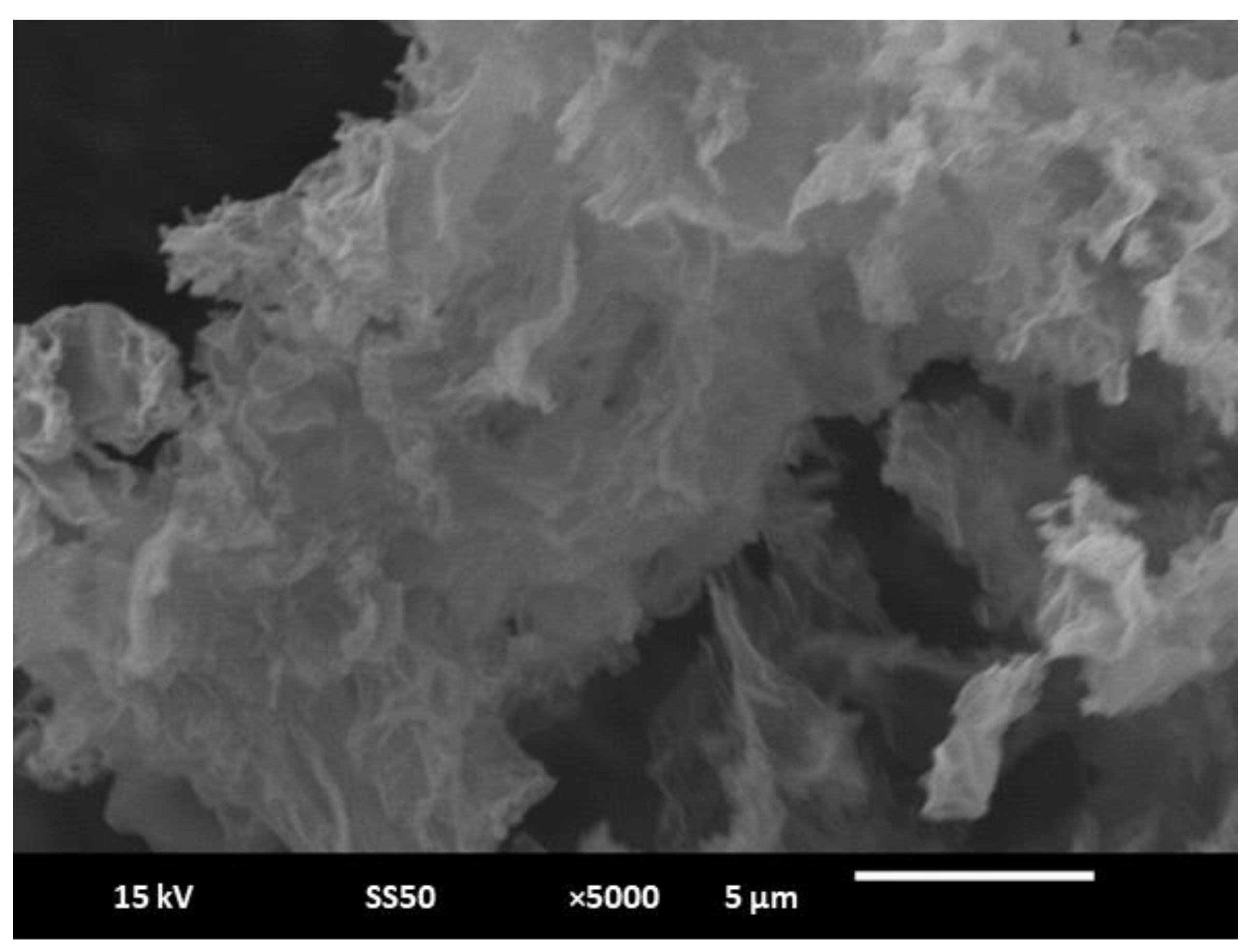
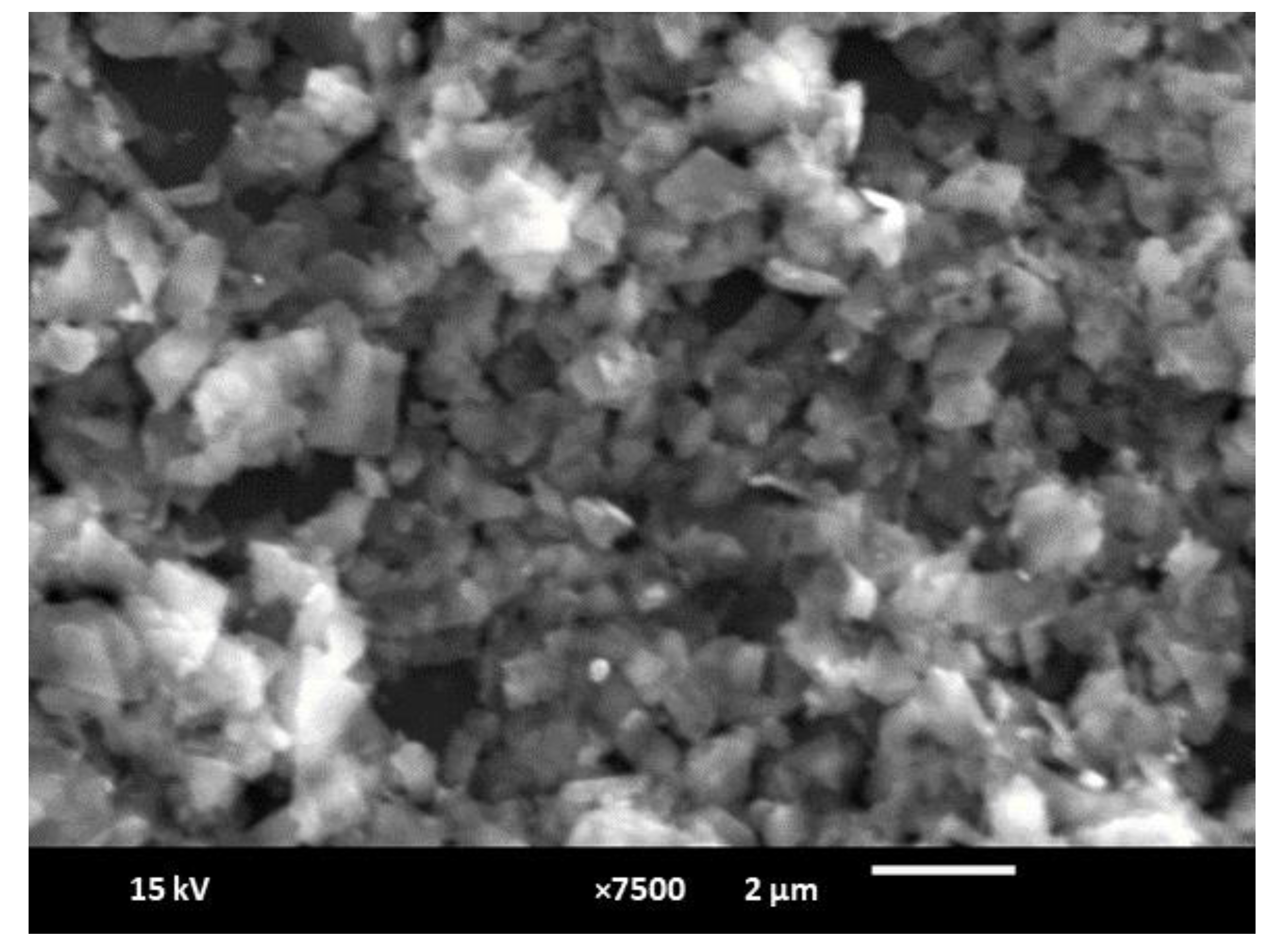
3.1. Characterization Studies of the Paper Electrode Modified with Gold Nanoparticles/Reduced Graphene Oxide (AuNPs/RGO)
3.2. Voltammetric Detection of miRNA-155 and miRNA-21 by a AuNP/RGO-Modified Paper Electrode
3.3. Selectivity of the Assay on the Voltammetric Detection of miRNA-155 by the AuNP/RGO-Modified Paper Electrode
3.4. Selectivity of the Assay on the Detection of miRNA-21 by Differential Pulse Voltammetry Using an AuNP/RGO-Modified Paper Electrode
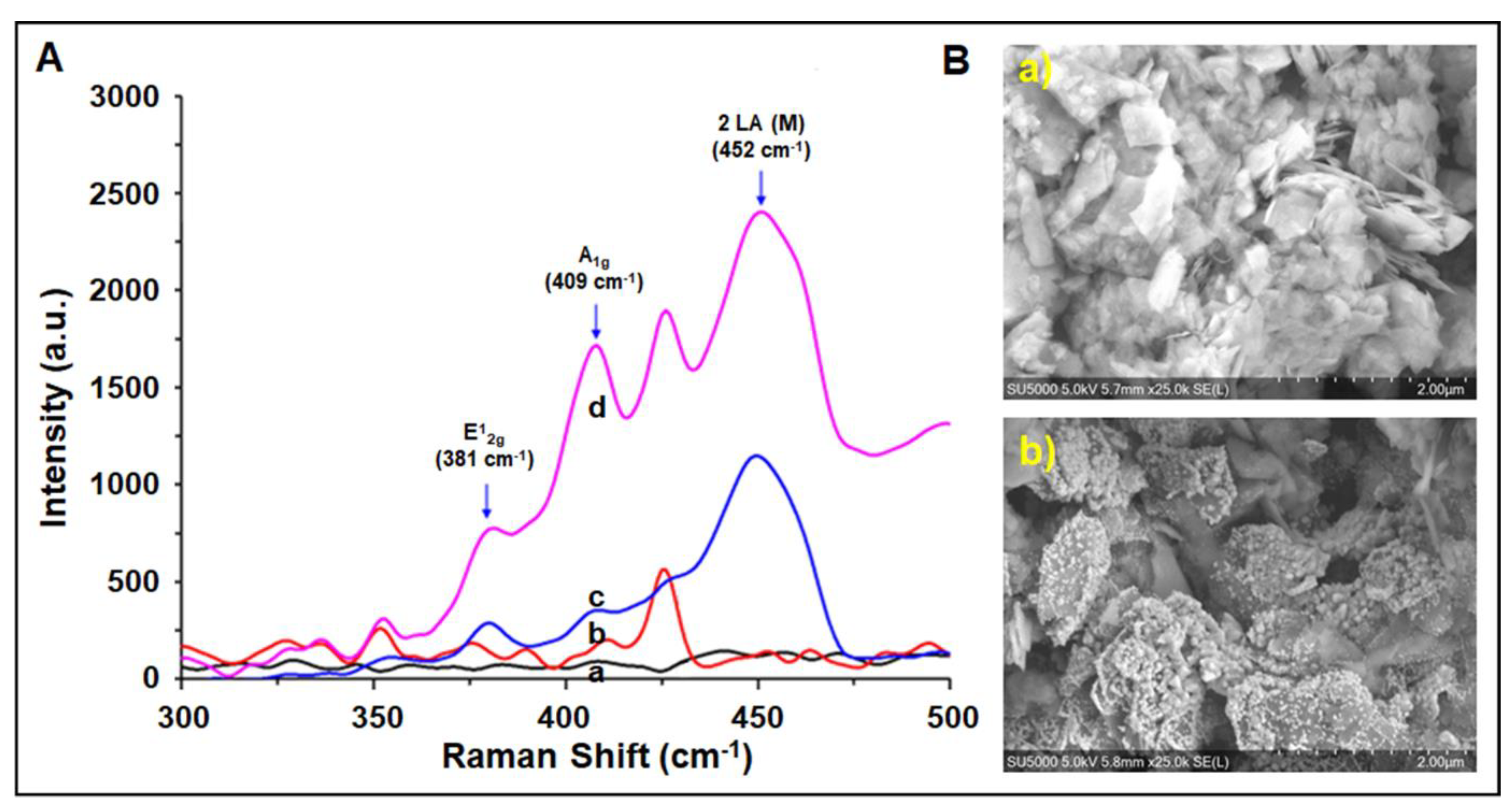
3.5. Characterization Studies of the Paper Electrode Modified with Gold Nanoparticle–Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheets (AuNP/MoS2)
3.6. Voltammetric Detection of miRNA-155 and miRNA-21 by the AuNP- and MoS2-Modified Paper Electrodes
3.7. Selectivity of the Assay on the Detection of miRNA-155 by Differential Pulse Voltammetry Using the AuNP- and MoS2-Modified Paper Electrodes
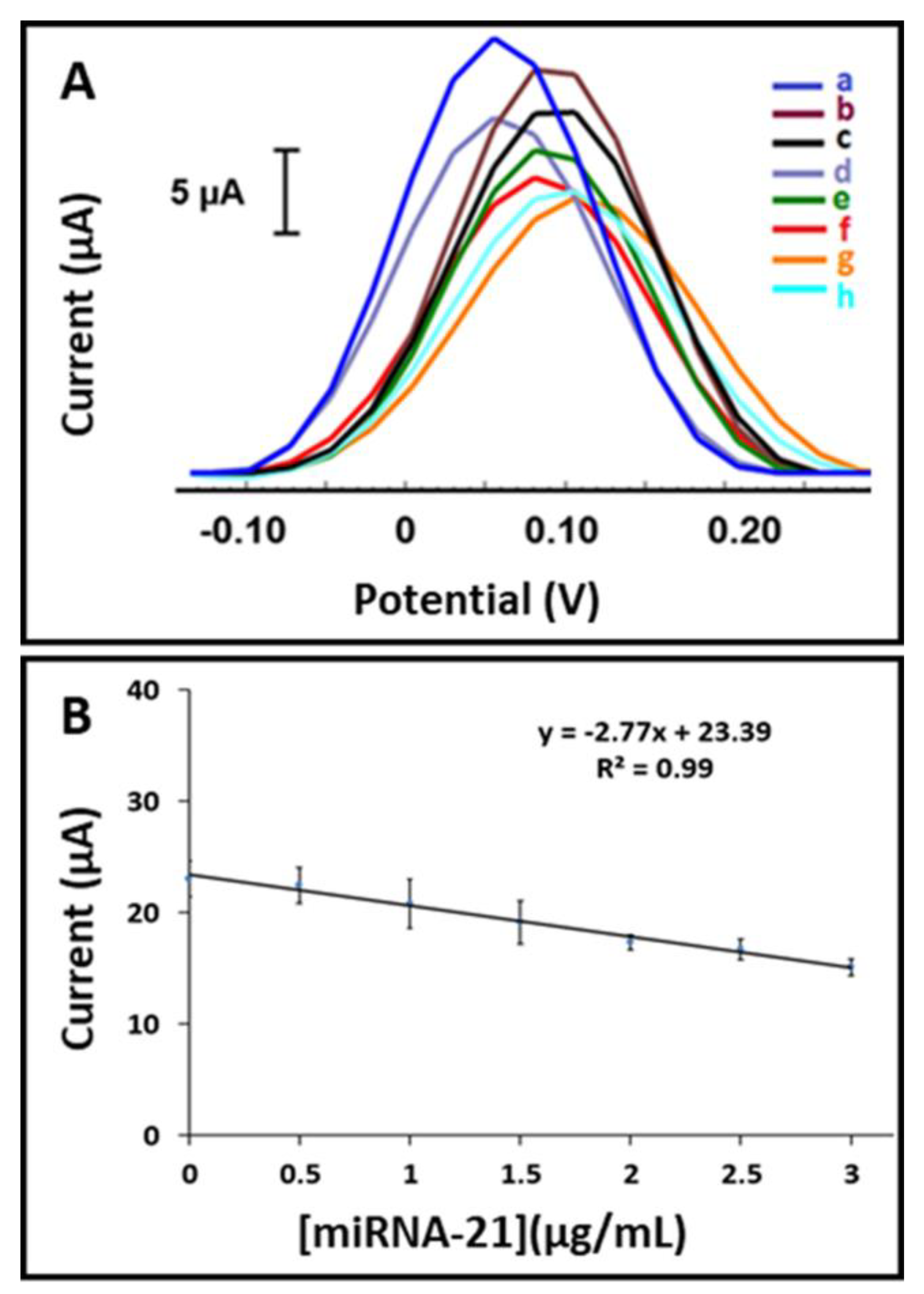
3.8. Selectivity of the Assay on the Detection of miRNA-21 by Differential Pulse Voltammetry Using the AuNP- and MoS2-Modified Paper Electrodes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yagoda, H. Applications of confined spot tests in analytical chemistry. Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 1937, 9, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.H.; Clegg, D.L. Automatic paper chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1949, 21, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comer, J.P. Semiquantitative specific test paper for glucose in urine. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 1748–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Phillips, S.T.; Butte, M.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, L.M.; Wang, Y.N. Detection methods and applications of microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 107, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Si, J.; Li, Z. Fabrication techniques for microfluidic paper-based analytical devices and their applications for biological testing: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilghaz, A.; Guan, L.; Tan, W.; Shen, W. Advances of Paper-Based Microfluidics for Diagnostics—The Original Motivation and Current Status. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1382–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torul, H.; Ciftci, H.; Cetin, D.; Suludere, Z.; Boyaci, I.H.; Tamer, U. Paper membrane-based SERS platform for the determination of glucose in blood samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 8243–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dungchai, W.; Chailapakul, O.; Henry, C.S. Electrochemical detection for paper-based microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5821–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Ino, K.; Lin, Z.; Shiku, H.; Chen, G.; Matsue, T. Amperometric detection of DNA hybridization using a multi-point, addressable electrochemical device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Nijhuis, C.A.; Gong, J.; Chen, X.; Kumachev, A.; Martinez, A.W.; Narovlyansky, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Electrochemical sensing in paper-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sjöberg, P.; Määttänen, A.; Vanamo, U.; Novell, M.; Ihalainen, P.; Andrade, F.J.; Bobacka, J.; Peltonen, J. Paper-based potentiometric ion sensors constructed on ink-jet printed gold electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.J.; Xie, Y.; Yan, Y.F.; Yang, H.; Gu, H.Y.; Bao, N. Paper-based analytical devices for direct electrochemical detection of free IAA and SA in plant samples with the weight of several milligrams. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 247, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, W.; He, Z.; Lin, J.M. Recent advances in microfluidic 3D cellular scaffolds for drug assays. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 87, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, J.M.C.C.; Tayo, L.L.; Liu, C.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Fu, L.M. Rapid microfluidic paper-based platform for low concentration formaldehyde detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 3623–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Yu, J.; Ge, S.; Song, X.; Yan, M. Paper-based biosensor for noninvasive detection of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, G.; Bhat, M.P.; Patil, P.; Uthappa, U.T.; Jung, H.Y.; Altalhi, T.; Kumeria, T.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Pai, R.K.; Madhuprasad; et al. Paper-based microfluidic analytical devices for colorimetric detection of toxic ions: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 93, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, F.; Micheli, L.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Piermarini, S.; Ricci, F.; Volpe, G. Electrochemical biosensors based on nanomodified screen-printed electrodes: Recent applications in clinical analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, W.C.; Beni, V.; Turner, A.P.F. Lateral-flow technology: From visual to instrumental. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M. Portable biosensing devices for point-of-care diagnostics: Recent developments and applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, R.; Céspedes, F.; Gabriel, D.; Baeza, M. Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip platforms for environmental monitoring. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 95, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Dutta, A. MicroRNAs in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2009, 4, 199–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.; Feinbaum, R.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans Heterochronic Gene lin-4 Encodes Small RNAs with Antisense Complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, L.-A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.N.; Masud, M.K.; Haque, M.H.; Al Hossain, M.S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. RNA Biomarkers: Diagnostic and Prognostic Potentials and Recent Developments of Electrochemical Biosensors. Small Methods 2017, 1, 1700131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, M.; Ferracin, M.; Sabbioni, S.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in human cancer: From research to therapy. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eis, P.S.; Tam, W.; Sun, L.; Chadburn, A.; Li, Z.; Gomez, M.F.; Lund, E.; Dahlberg, J.E. Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3627–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.A.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6029–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kilic, T.; Erdem, A.; Ozsoz, M.; Carrara, S. microRNA biosensors: Opportunities and challenges among conventional and commercially available techniques. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, A.; Congur, G.; Eksin, E. Multi channel screen printed array of electrodes for enzyme-linked voltammetric detection of MicroRNAs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isin, D.; Eksin, E.; Erdem, A. Graphene oxide modified single-use electrodes and their application for voltammetric miRNA analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosik, M.; Trefulka, M.; Hrstka, R.; Vojtesek, B.; Palecek, E. Os(VI)bipy-based electrochemical assay for detection of specific microRNAs as potential cancer biomarkers. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 33, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.K.; Umer, M.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Nanoarchitecture Frameworks for Electrochemical miRNA Detection. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, A.T.; Besant, J.D.; Lam, B.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Ultrasensitive electrochemical biomolecular detection using nanostructured microelectrodes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2417–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Tran, V.K.; Ko, E.; Park, C.H.; Chung, W.S.; Seong, G.H. Determination of acetaminophen using functional paper-based electrochemical devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 232, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Fiedoruk-Pogrebniak, M.; Pokrzywnicka, M.; Koncki, R.; Bobacka, J.; Lisak, G. Solid reference electrode integrated with paper-based microfluidics for potentiometric ion sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 323, 128680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukird, J.; Soum, V.; Kwon, O.S.; Shin, K.; Chailapakul, O.; Rodthongkum, N. 3D paper-based microfluidic device: A novel dual-detection platform of bisphenol A. Analyst 2020, 145, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eksin, E.; Torul, H.; Yarali, E.; Tamer, U.; Papakonstantinou, P.; Erdem, A. Paper-based electrode assemble for impedimetric detection of miRNA. Talanta 2021, 225, 122043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, J.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Papakonstantinou, P. Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Edges of a Few Layer Molybdenum Disulfide Nanodots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 14113–14122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yang, L.X.; Yang, Z.G. Nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide intertwined with V2O3 nanoflakes as self-supported electrodes for flexible all-solid-state supercapacitors. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 25732–25739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, A.; Kar, S.; Debnath, A.K.; Aswal, D.K.; Bindal, R.C.; Tewari, P.K. Reinforcement of nanostructured reduced graphene oxide: A facile approach to develop high-performance nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes minimizing the trade-off between flux and selectivity. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46801–46816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasuja, K.; Berry, V. Implantation and growth of dendritic gold nanostructures on graphene derivatives: Electrical property tailoring and Raman enhancement. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2358–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ju, X.M.; Yang, H.X.; Chen, Y.X.; Sun, Z.F. Electrodeposited graphene and gold nanoparticle modified carbon ionic liquid electrode for sensitive detection of rutin. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 41, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Hou, L.; Zhang, T.; Han, Y.; Kong, C. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on a gold nanoparticle/carbon nanotube hybrid material for the sensitive detection of isoniazid. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 9121–9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Hou, S. A glassy carbon electrode modified with gold nanoparticle-encapsulated graphene oxide hollow microspheres for voltammetric sensing of nitrite. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, T.E.; Elving, P.J. Determination of the Electrochemically Effective Electrode Area. Anal. Chem. 1978, 50, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, H.B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.M. Sub-femtomolar DNA detection based on layered molybdenum disulfide/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites, au nanoparticle and enzyme multiple signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, T.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Jiao, K. Conductive architecture of Fe2O3 microspheres/self-doped polyaniline nanofibers on carbon ionic liquid electrode for impedance sensing of DNA hybridization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Benson, J.; Papakonstantinou, P. Sensitive chronocoulometric detection of miRNA at screen-printed electrodes modified by gold-decorated MoS2 nanosheets. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 6th ed.; Pearson: Harlow, UK, 2010; ISBN 0273730428/9780273730422. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, T.S.; Mitra, S. Exfoliated MoS2 Sheets and Reduced Graphene Oxide-An Excellent and Fast Anode for Sodium-ion Battery. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Tronganh, N.; Lu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, B. MoS2/graphene nanocomposite with enlarged interlayer distance as a high performance anode material for lithium-ion battery. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 3151–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavallaie, R.; McCarroll, J.; Le Grand, M.; Ariotti, N.; Schuhmann, W.; Bakker, E.; Tilley, R.D.; Hibbert, D.B.; Kavallaris, M.; Gooding, J.J. Nucleic acid hybridization on an electrically reconfigurable network of gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles enables microRNA detection in blood. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal Masud, M.; Islam, M.N.; Haque, M.H.; Tanaka, S.; Gopalan, V.; Alici, G.; Nguyen, N.T.; Lam, A.K.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Yamauchi, Y.; et al. Gold-loaded nanoporous superparamagnetic nanocubes for catalytic signal amplification in detecting miRNA. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8231–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, K.M.; Carrascosa, L.G.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Trau, M. Poly(A) Extensions of miRNAs for Amplification-Free Electrochemical Detection on Screen-Printed Gold Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.N.; Masud, M.K.; Nguyen, N.T.; Gopalan, V.; Alamri, H.R.; Alothman, Z.A.; Al Hossain, M.S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Lam, A.K.Y.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Gold-loaded nanoporous ferric oxide nanocubes for electrocatalytic detection of microRNA at attomolar level. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 101, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, D.; Liu, W.; Zhao, D.; Hao, Q.; Li, J.; Huang, J.; Shi, J.; Chao, J.; Su, S.; Wang, L. Label-Free Electrochemical Sensing Platform for MicroRNA-21 Detection Using Thionine and Gold Nanoparticles Co-Functionalized MoS2 Nanosheet. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35597–35603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.J.; Wu, Z.; Yang, X.Y.; Pang, D.W.; Zhang, Z.L. Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 with wide linear dynamic range based on dual signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Qian, K.; Qi, J.; Liu, Q.; Yao, C.; Song, W.; Wang, Y. Gold nanoparticles superlattices assembly for electrochemical biosensor detection of microRNA-21. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Cao, W.; Liu, W.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, D.; Chao, J.; Weng, L.; Wang, L.; Fan, C.; Wang, L. Dual-mode electrochemical analysis of microRNA-21 using gold nanoparticle-decorated MoS2 nanosheet. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Dong, S.; Zhu, N.; Gyimah, E.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. An ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor for detection of microRNA-21 based on redox reaction of ascorbic acid/iodine and duplex-specific nuclease assisted target recycling. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Gyimah, E.; Yakubu, S.; Wang, K.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z. Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Tetrahedral DNA Nanostructures and G-Quadruplex-Hemin Conformation for the Ultrasensitive Detection of MicroRNA-21 in Serum. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 7353–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Ou, D.; Sun, D.; Tong, Y.; Luo, H.; Chen, Z. Ultrasensitive biosensor for microRNA-155 using synergistically catalytic nanoprobe coupled with improved cascade strand displacement reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 146, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, R. An electrochemical biosensor for sensitive detection of microRNA-155: Combining target recycling with cascade catalysis for signal amplification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R.; Su, H.; Han, J. A novel label-free electrochemical microRNA biosensor using Pd nanoparticles as enhancer and linker. Analyst 2013, 138, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimzadeh, M.; Rahaie, M.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Ashtari, K.; Naderi-Manesh, H. An electrochemical nanobiosensor for plasma miRNA-155, based on graphene oxide and gold nanorod, for early detection of breast cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| miRNA | Electrode | Method | Analysis Time | Sample Volume | Concentration Range | DL | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA-107 | SPGE | DPV | 75 min | 30 µL | 5 fM−5 pM | 10 fM | [55] |
| Au-NPFe2O3NC/SPCE | CC | 45 min | - | 100 aM–1 nM | 100 aM | [56] | |
| miRNA-21 | MoS2/Thi/AuNPs nanocomposite/GCE | SWV | 18 h | 5 µL | 1 pM–10 nM | 0.26 pM | [57] |
| Au@NPFe2O3NC/GCE | CC | - | - | 100 fM–1 µM | 100 fM | [54] | |
| AuNPs/ITO | ASV | 17 h | 100 µL | 2.5 fM–25 nM | 0.12 fM | [58] | |
| AuNPs/GCE | DPV | 3.5 h | 40 µL | 100 aM–1 nM | 78.0 aM | [59] | |
| AuNPs@MoS2/GCE | DPV EIS | 17 h | 20 µL | 10 fM–1 nM | 0.78 fM 0.45 fM | [60] | |
| MWCNTs@GONRs/AuNPs/GCE | DPV | 14 h | 6 µL | 0.1 fM–0.1 nM | 0.034 fM | [61] | |
| AuE | DPV | 14 h | 2 µL | 0.1 fM–1 nM | 0.04 fM | [62] | |
| AuNPs@MoS2/SPGE AuNPs@/SPGE | CC | 22 h | 10 µL | 100 aM–1 pM 10 fM–10 pM | 100.0 aM 10.0 fM | [49] | |
| AuNPs/RGO/PE | DPV | 35 min | 5 µL | 37.5 nM–150 nM | 12 nM | This study | |
| AuNPs/MoS2/PE | 71.7 nM–430.2 nM | 51.7 nM | |||||
| miRNA-155 | AuE | SWV | 8 h | - | 0.5 pM–0.1 µM | 0.13 fM | [63] |
| GO/Au/GCE | CV, DPV | 21 h | 10 µL | 0.8 fM–1 nM | 0.37 fM | [64] | |
| nano-Pd/Thi/GCE | CV | 17 h | 20 µL | 5.6 pM–5.6 µM | 1.87 pM | [65] | |
| AuNRs/GO/GCE | DPV | 4 h | 5 µL | 2 fM–8 pM | 0.6 fM | [66] | |
| AuNPs/RGO/PE | DPV | 35 min | 5 µL | 33.8 nM–135.3 nM | 25.7 nM | This study | |
| AuNPs/MoS2/PE | 135.6 nM–406.8 nM | 59.7 nM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torul, H.; Yarali, E.; Eksin, E.; Ganguly, A.; Benson, J.; Tamer, U.; Papakonstantinou, P.; Erdem, A. Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Voltammetric Detection of miRNA Biomarkers Using Reduced Graphene Oxide or MoS2 Nanosheets Decorated with Gold Nanoparticle Electrodes. Biosensors 2021, 11, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070236
Torul H, Yarali E, Eksin E, Ganguly A, Benson J, Tamer U, Papakonstantinou P, Erdem A. Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Voltammetric Detection of miRNA Biomarkers Using Reduced Graphene Oxide or MoS2 Nanosheets Decorated with Gold Nanoparticle Electrodes. Biosensors. 2021; 11(7):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070236
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorul, Hilal, Ece Yarali, Ece Eksin, Abhijit Ganguly, John Benson, Ugur Tamer, Pagona Papakonstantinou, and Arzum Erdem. 2021. "Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Voltammetric Detection of miRNA Biomarkers Using Reduced Graphene Oxide or MoS2 Nanosheets Decorated with Gold Nanoparticle Electrodes" Biosensors 11, no. 7: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070236
APA StyleTorul, H., Yarali, E., Eksin, E., Ganguly, A., Benson, J., Tamer, U., Papakonstantinou, P., & Erdem, A. (2021). Paper-Based Electrochemical Biosensors for Voltammetric Detection of miRNA Biomarkers Using Reduced Graphene Oxide or MoS2 Nanosheets Decorated with Gold Nanoparticle Electrodes. Biosensors, 11(7), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11070236