A Smart Core-Crosslinked Supramolecular Drug Delivery System (SDDS) Enabled by Pendant Cyclodextrins Encapsulation of Drug Dimers via Host-Guest Interaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. General Procedure of Preparation of Copolymer MPEG-PHA
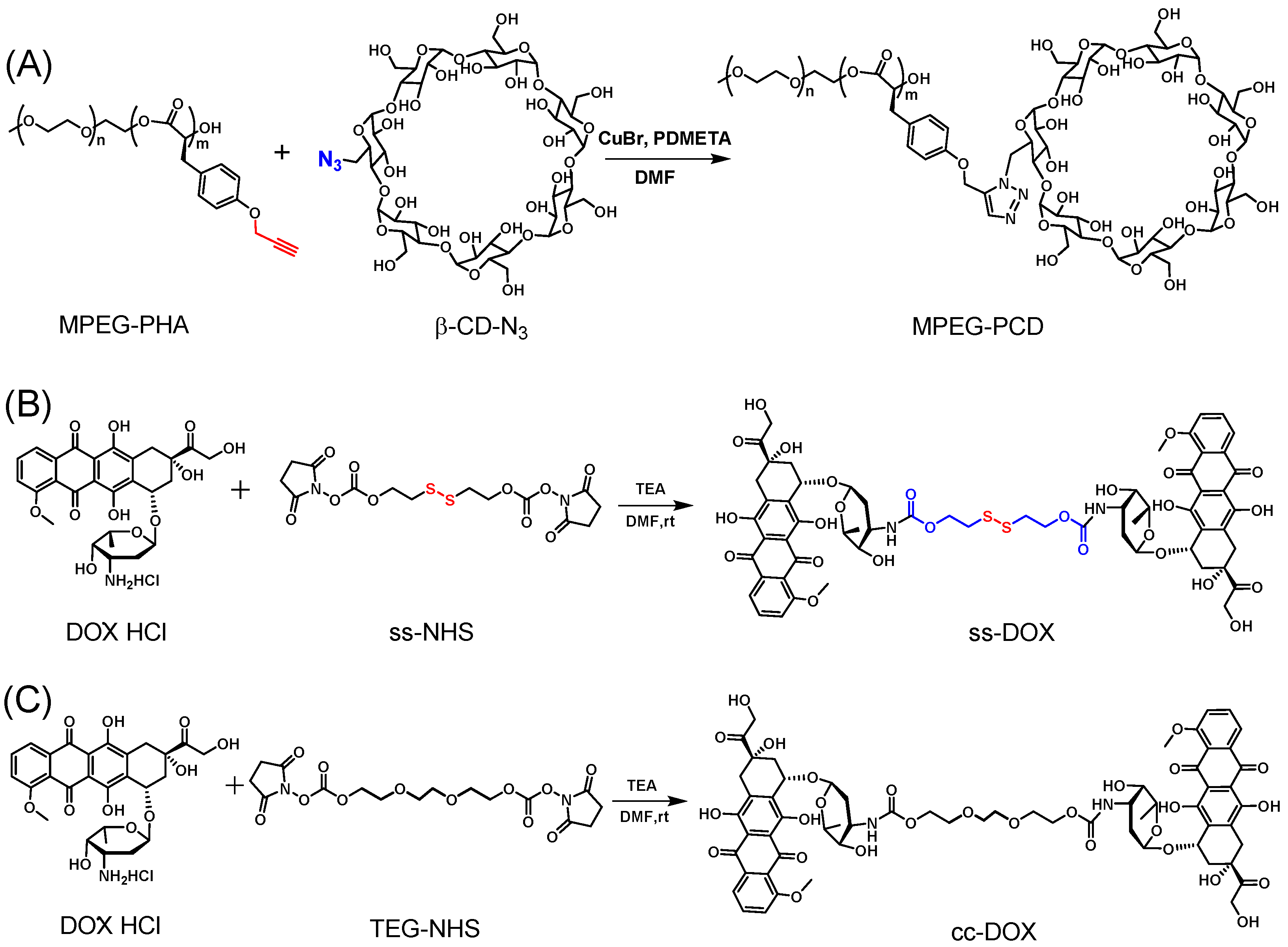
2.3. Synthesis of MPEG-PCD
2.4. Synthesis of the Cleavable DOX Dimer (ss-DOX)
2.5. Synthesis of the Uncleavable DOX Dimer (cc-DOX)
2.6. Preparation of DOX-Loaded and DOX Dimers Cross-Linked Micelles
2.7. Characterization of Materials
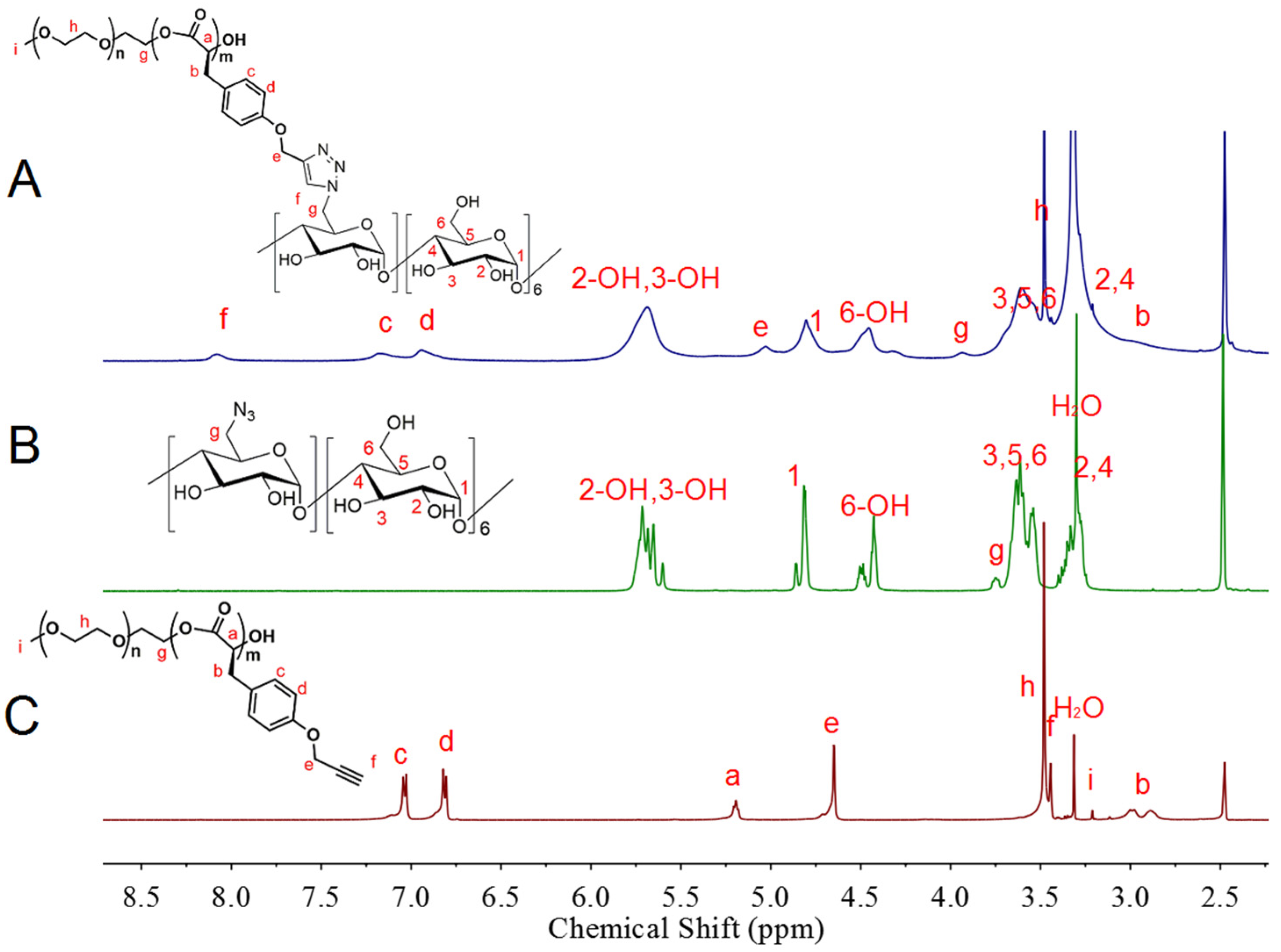
2.7.1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Experiments
2.7.2. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Measurements
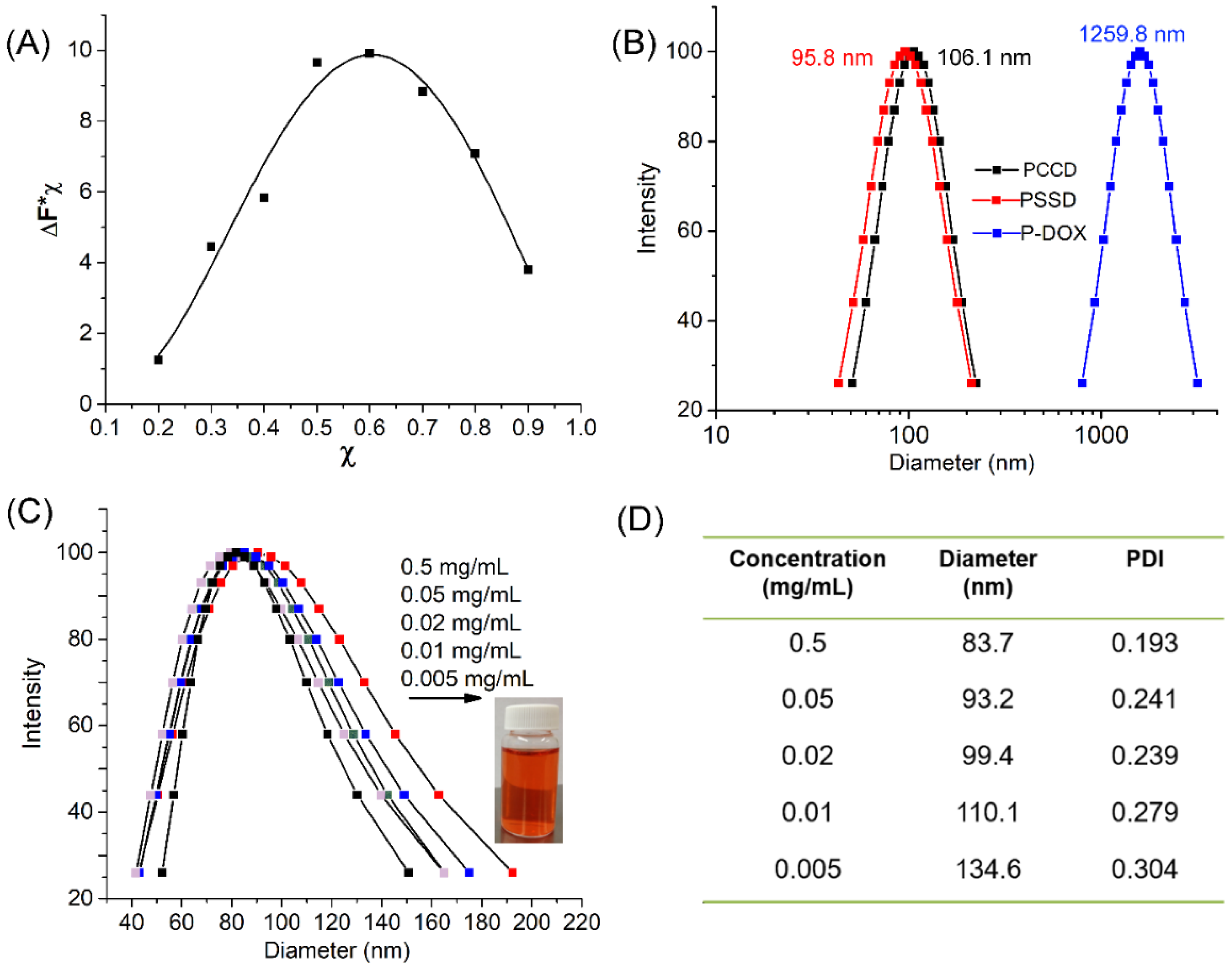
2.7.3. Study of the Stoichiometry of the Complex
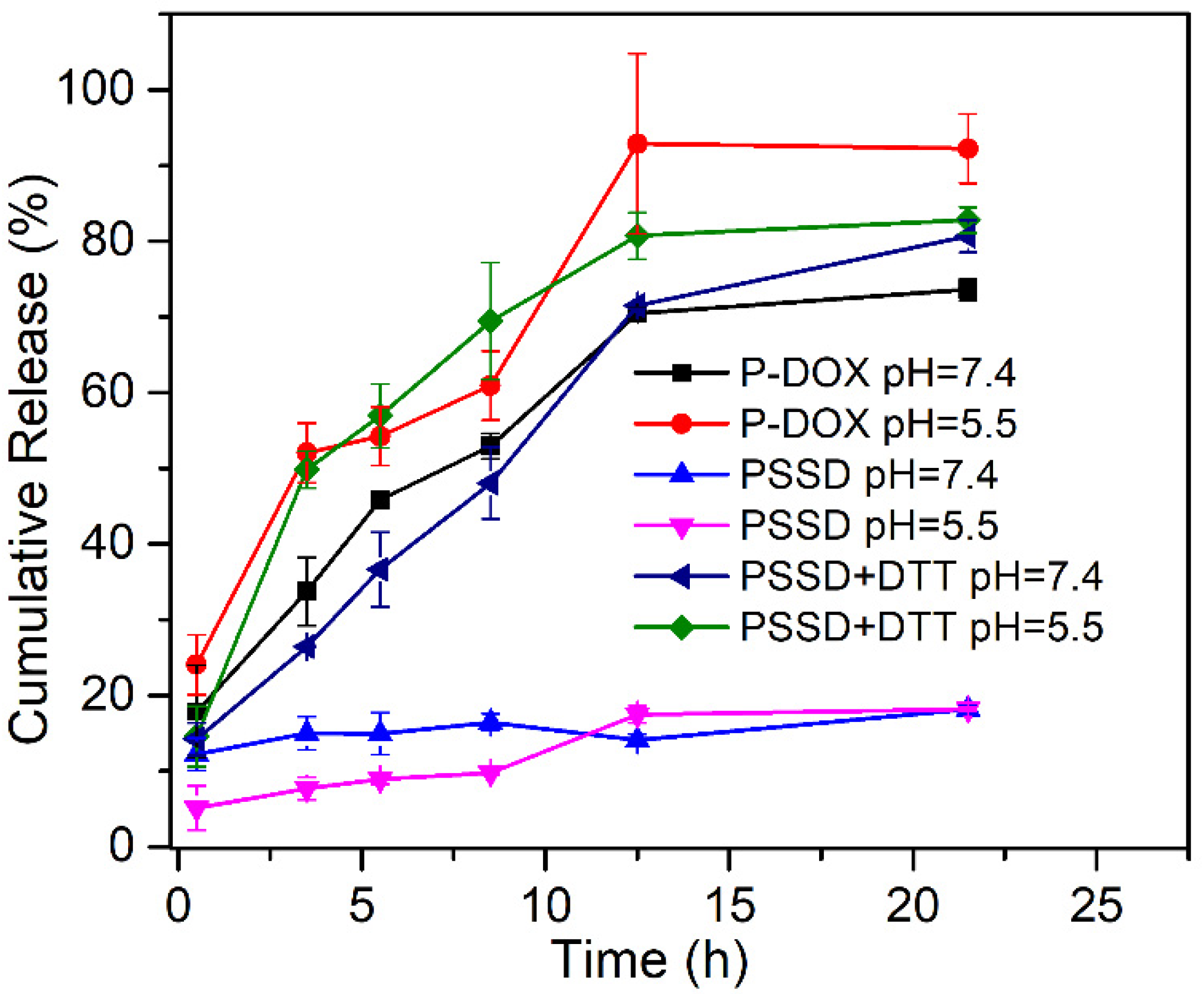
2.7.4. Drug Release Experiments
2.7.5. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurements
2.7.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7.7. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
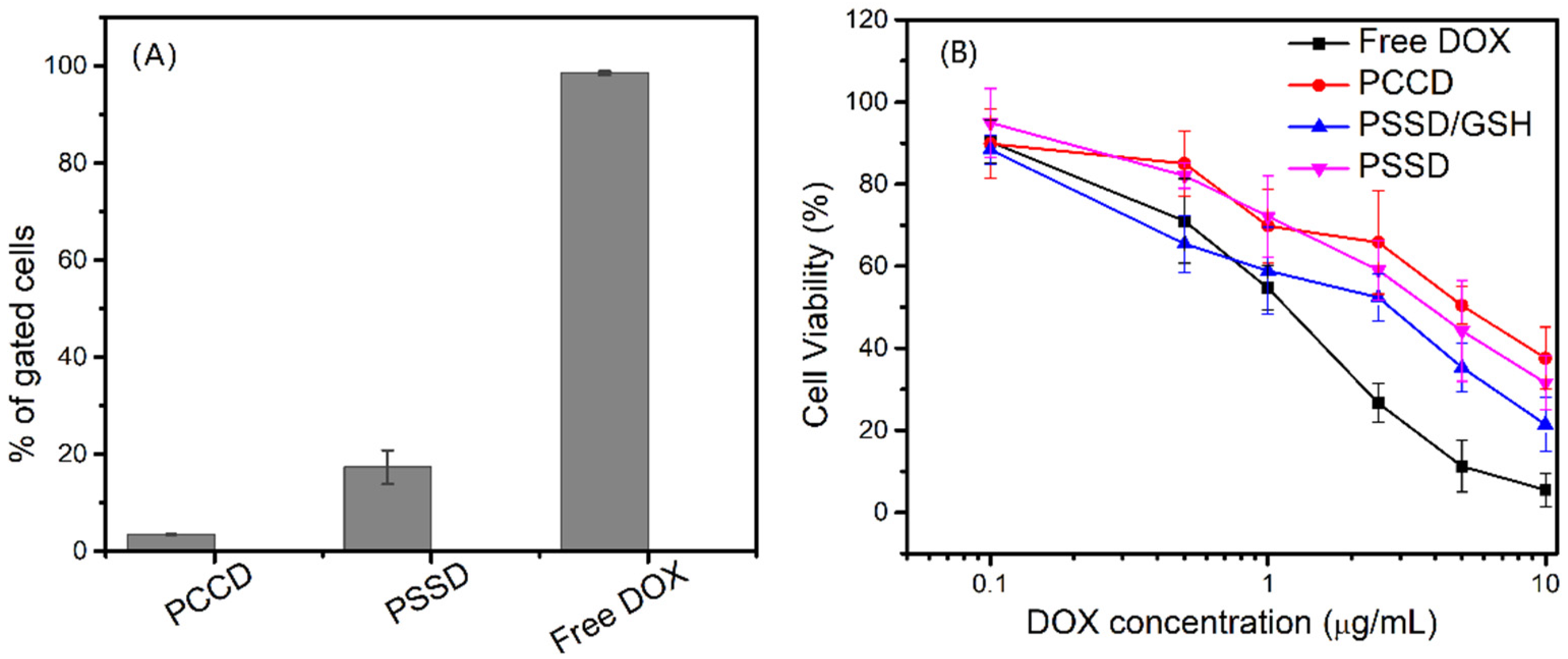
2.7.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.7.9. In Vitro Anticancer Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Copolymer MPEG-PCD and DOX Dimers
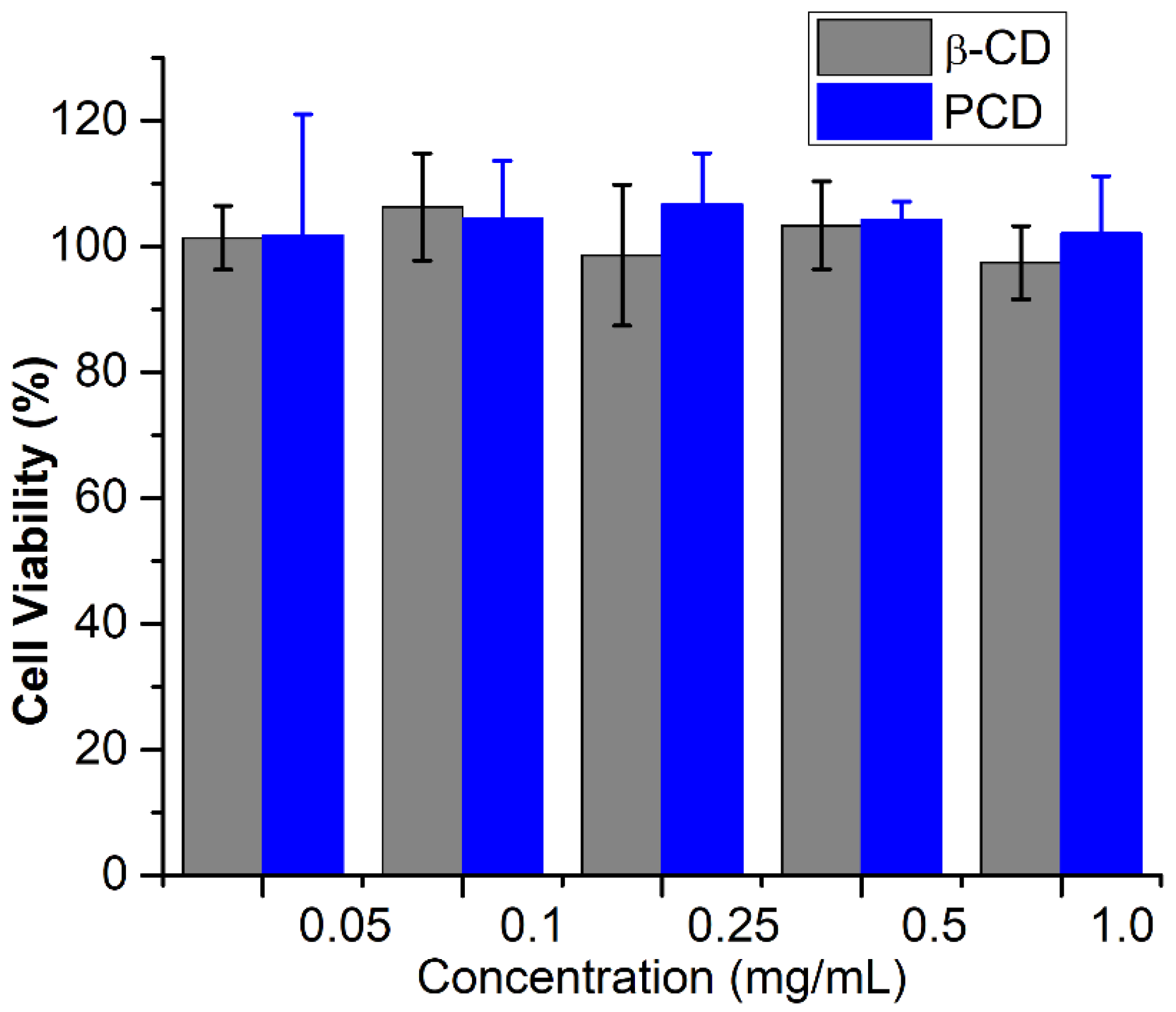
3.2. Physical Properties of MPEG-PHA, MPEG-PCD, PSSD and PCCD
3.3. Drug Release Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, C.Y.; Ju, D.T.; Chang, C.F.; Reddy, P.M.; Velmurugan, B.K. A Review on the Effects of Current Chemotherapy Drugs and Natural Agents in Treating Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Biomedicine 2017, 7, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabner, B.A.; Jr Roberts, T.G. Chemotherapy and the War on Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewin, V. Designing nano-sized chemotherapy. Nature 2021, 593, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, S.; Hossain, M.K.; Basher, M.K.; Mia, M.N.H.; Rahman, M.T.; Uddin, M.J. Smart Nanocarrier-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy and Toxicity Studies: A Review. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, F.; Xiong, F.; Gu, N. The Smart Drug Delivery System and Its Clinical Potential. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1306–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sawy, H.S.; Al-Abd, A.M.; Ahmed, T.A.; El-Say, K.M.; Torchilin, V.P. Stimuli-Responsive Nano-Architecture Drug-Delivery Systems to Solid Tumor Micromilieu: Past, Present, and Future Perspectives. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10636–10664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, T.; Ruttala, H.B.; Gupta, B.; Poudel, B.K.; Choi, H.G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Smart Chemistry-Based Nanosized Drug Delivery Systems for Systemic Applications: A Comprehensive Review. J. Control. Release 2017, 258, 226–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbitt, M.W.; Dahlman, J.E.; Langer, R. Emerging Frontiers in Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavitehrani, I.; Fathi, A.; Badr, H.; Daly, S.; Shirazi, N.A.; Dehghani, F. Biomedical Applications of Biodegradable Polyesters. Polymers 2016, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, C.K.; Law, W.C.; Weinheimer, E.; Sengupta, S.; Prasad, P.N.; Cheng, C. Polylactide-graft-doxorubicin Nanoparticles with Precisely Controlled Drug Loading for pH-Triggered Drug Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitenbach, A.; Li, Y.X.; Kissel, T. Branched Biodegradable Polyesters for Parenteral Drug Delivery Systems. J. Control. Release 2000, 64, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zou, Y.; Jia, J.; Meng, F.; Cheng, R.; Deng, C.; Feijen, J.; Zhong, Z. Functional Poly(ε-caprolactone)s via Copolymerization of ε-Caprolactone and Pyridyl Disulfide-Containing Cyclic Carbonate: Controlled Synthesis and Facile Access to Reduction-Sensitive Biodegradable Graft Copolymer Micelles. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, L.; Xu, Y.; Ren, J.; Cheng, J. Facile Functionalization of Polyesters through Thiol-yne Chemistry for the Design of Degradable, Cell‒Penetrating and Gene Delivery Dual‒Functional Agents. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3456–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Zou, J.; Cheng, C. Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of Functional Poly(α-hydroxyl acid)s. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 5854–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmada, Z.; Shah, A.; Siddiqa, M.; Kraatz, H.B. Polymeric Micelles as Drug Delivery Vehicles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 17028–17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagel, M.; Tesan, F.C.; Bernabeu, E.; Salgueiro, M.J.; Zubillaga, M.B.; Moretton, M.A.; Chiappetta, D.A. Polymeric Mixed Micelles as Nanomedicines: Achievements and Perspectives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 113, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambles, M.T.; Fan, B.; Borecki, A.; Gillies, E.R. Hybrid Polyester Self-Immolative Polymer Nanoparticles for Controlled Drug Release. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5002–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Patel, A.; Gaharwar, A.K.; Mihaila, S.M.; Iviglia, G.; Mukundan, S.; Ba, H.; Yang, H.; Khademhosseini, A. Hyperbranched Polyester Hydrogels with Controlled Drug Release and Cell Adhesion Properties. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molavi, F.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Hamishehkar, H. Polyester Based Polymeric Nnano and Microparticles for Pharmaceutical Purposes: A Review on Formulation Approaches. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wankar, J.; Kotla, N.G.; Gera, S.; Rasala, S.; Pandit, A.; Rochev, Y.A. Recent Advances in Host–Guest Self-Assembled Cyclodextrin Carriers: Implications for Responsive Drug Delivery and Biomedical Engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. Smart stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems based on cyclodextrin: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Yu, C. Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Polymers as Drug Carriers for Cancer Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, H.; Wang, J.; Phan, C.U.; Chen, Q.; Hu, X.; Shao, G.; Zhou, J.; Lai, L.; Tang, G. Cyclodextrin-based host-guest complexes loaded with regorafenib for colorectal cancer treatment. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgung, R.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Jang, Y.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, I.S.; Sokkar, P.; Rhee, Y.M.; Hoffman, A.S.; Kim, W.J. Poly-cyclodextrin and poly-paclitaxel nano-assembly for anticancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2014, 37, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Ng, D.Y.W.; Wu, Y.; Thomas, J.; TamTran, T.; Weil, T. Bis-Sulfide Bioconjugates for Glutathione Triggered Tumor Responsive Drug Release. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1116–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Ju, X.; Ding, L.S.; Zhang, S.; Li, B.J. Reactive Oxygen Species and Glutathione Dual Redox-Responsive Supramolecular Assemblies with Controllable Release Capability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 4475–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, Y. Cyclodextrin-Based Multistimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Assemblies and Their Biological Functions. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1806158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, L.; Tu, C.; Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tong, R.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, J.; Cheng, J. Redox-Responsive, Core Cross-Linked Polyester Micelles. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Ng, S.C. Facile synthesis of mono-6-amino-6-deoxy-α-, β-, γ-cyclodextrin hydrochlorides for molecular recognition, chiral separation and drug delivery. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollis, C.P.; Weiss, H.L.; Leggas, M.; Evers, B.M.; Gemeinhart, R.A.; Li, T. Biodistribution and bioimaging studies of hybrid paclitaxel nanocrystals: Lessons learned of the EPR effect and image-guided drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, X.; Guo, Z.; Su, Y.; Yang, Z.; Qian, J.; Tu, C.; Zhu, L.; Xu, F. A Smart Core-Crosslinked Supramolecular Drug Delivery System (SDDS) Enabled by Pendant Cyclodextrins Encapsulation of Drug Dimers via Host-Guest Interaction. Biosensors 2021, 11, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090306
Xing X, Guo Z, Su Y, Yang Z, Qian J, Tu C, Zhu L, Xu F. A Smart Core-Crosslinked Supramolecular Drug Delivery System (SDDS) Enabled by Pendant Cyclodextrins Encapsulation of Drug Dimers via Host-Guest Interaction. Biosensors. 2021; 11(9):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090306
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Xin, Zhijun Guo, Yue Su, Zhen Yang, Jiwen Qian, Chunlai Tu, Lijuan Zhu, and Feng Xu. 2021. "A Smart Core-Crosslinked Supramolecular Drug Delivery System (SDDS) Enabled by Pendant Cyclodextrins Encapsulation of Drug Dimers via Host-Guest Interaction" Biosensors 11, no. 9: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090306
APA StyleXing, X., Guo, Z., Su, Y., Yang, Z., Qian, J., Tu, C., Zhu, L., & Xu, F. (2021). A Smart Core-Crosslinked Supramolecular Drug Delivery System (SDDS) Enabled by Pendant Cyclodextrins Encapsulation of Drug Dimers via Host-Guest Interaction. Biosensors, 11(9), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios11090306




