All-Polymeric Electrode Based on PEDOT:PSS for In Vivo Neural Recording
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Manufacturing of All-Polymeric Electrodes
2.2. Conductivity Measurement
2.3. Impedance Measurement
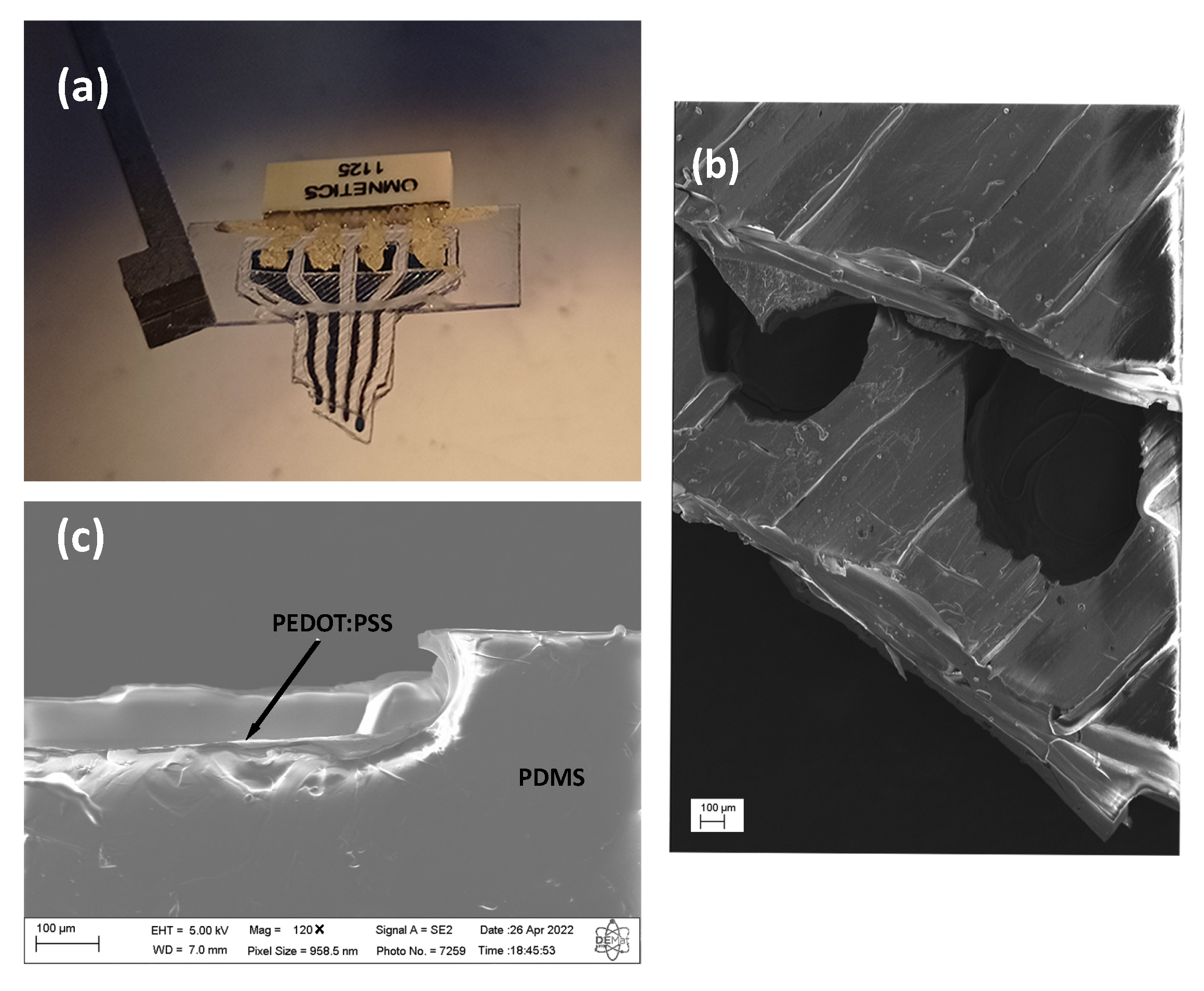
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5. In Vitro Recording
2.6. Animal Handling
2.7. Surgical Implantation
2.8. Neural Recordings
2.9. Euthanasia
2.10. Histological Analysis
2.11. Image Acquisition and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of the All-Polymer Electrode
3.2. Validation In Vitro
3.3. Validation In Vivo
3.4. Progression of the Glial Response


4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sohal, H.S.; Jackson, A.; Jackson, R.; Clowry, G.J.; Vassilevski, K.; O’Neill, A.; Baker, S.N. The sinusoidal probe: A new approach to improve electrode longevity. Front. Neuroeng. 2014, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buzsáki, G.; Anastassiou, C.A.; Koch, C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents—EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikov, V.S.; Tresco, P.A.; Reichert, W.M. Response of brain tissue to chronically implanted neural electrodes. J. Neurosci. Methods 2005, 148, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, M.; Kim, D.; Pané, S.; Santos, S.D.; Pêgo, A.P. Tissue response to neural implants: The use of model systems toward new design solutions of implantable microelectrodes. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubota, Y. Untangling GABAergic wiring in the cortical microcircuit. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2014, 26, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Lieber, C.M. Novel electrode technologies for neural recordings. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Canales, A.; Anikeeva, P. Neural recording and modulation technologies. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Liu, J.; Fu, T.M.; Dai, X.; Zhou, W.; Lieber, C.M. Three-dimensional macroporous nanoelectronic networks as minimally invasive brain probes. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, T.; Hong, G.; Fu, T.M.; Yang, X.; Schuhmann, T.G.; Viveros, R.D.; Lieber, C.M. Syringe-injectable mesh electronics integrate seamlessly with minimal chronic immune response in the brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5894–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hara, S.A.; Kim, B.J.; Kuo, J.T.; Lee, C.D.; Meng, E.; Pikov, V. Long-term stability of intracortical recordings using perforated and arrayed Parylene sheath electrodes. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 066020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Luan, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Potnis, O.; Xie, C. Nanofabricated ultraflexible electrode arrays for high-density intracortical recording. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozai, T.D.Y.; Langhals, N.B.; Patel, P.R.; Deng, X.; Zhang, H.; Smith, K.L.; Lahann, J.; Kotov, N.A.; Kipke, D.R. Ultrasmall implantable composite microelectrodes with bioactive surfaces for chronic neural interfaces. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuk, H.; Lu, B.; Lin, S.; Qu, K.; Xu, J.; Luo, J.; Zhao, X. 3D printing of conducting polymers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girotto, E.M.; Santos, I.A. Medidas de resistividade elétrica DC em sólidos: Como efetuálas corretamente. Química Nova 2002, 25, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillón, R.; Pérez, J.J.; Andrade-Caicedo, H. Electrical performance of PEDOT: PSS-based textile electrodes for wearable ECG monitoring: A comparative study. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozai, T.D.; Catt, K.; Du, Z.; Na, K.; Srivannavit, O.; Razi-ul, M.H.; Seymour, J.; Wise, K.D.; Yoon, E.; Cui, X.T. Chronic in vivo evaluation of PEDOT/CNT for stable neural recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 63, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Suh, K.S. Effects of alcoholic solvents on the conductivity of tosylate-doped poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT-OTs). Polym. Int. 2006, 55, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trantidou, T.; Elani, Y.; Parsons, E.; Ces, O. Hydrophilic surface modification of PDMS for droplet microfluidics using a simple, quick, and robust method via PVA deposition. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2017, 3, 16091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Tharion, J.; Murugan, S.; Kumar, A. ITO-free solution-processed flexible electrochromic devices based on PEDOT: PSS as transparent conducting electrode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 19427–19435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Lei, T.; Kim, Y.; Niu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Foudeh, A.M.; Tok, J.B.H.; et al. Soft and elastic hydrogel-based microelectronics for localized low-voltage neuromodulation. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Pfattner, R.; Yan, H.; Jin, L.; Chen, S.; Molina-Lopez, F.; Lissel, F.; Liu, J.; Rabiah, N.I.; et al. A highly stretchable, transparent, and conductive polymer. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neto, J.P.; Baião, P.; Lopes, G.; Frazão, J.; Nogueira, J.; Fortunato, E.; Barquinha, P.; Kampff, A.R. Does impedance matter when recording spikes with polytrodes? Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Song, S.; Kang, J.; Tsao, Y.; Chen, S.; Mottini, V.; McConnell, K.; Xu, W.; Zheng, Y.Q.; et al. Morphing electronics enable neuromodulation in growing tissue. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garma, L.D.; Ferrari, L.M.; Scognamiglio, P.; Greco, F.; Santoro, F. Inkjet-printed PEDOT:PSS multi-electrode arrays for low-cost in vitro electrophysiology. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 3776–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Perez, A.; Gabriel, G.; Rebollo, B.; Illa, X.; Guimerà-Brunet, A.; Hernández-Ferrer, J.; Martínez, M.T.; Villa, R.; Sanchez-Vives, M.V. Quantification of signal-to-noise ratio in cerebral cortex recordings using flexible MEAs with co-localized platinum black, carbon nanotubes, and gold electrodes. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrenti, V.; Cecchetto, C.; Maschietto, M.; Fortinguerra, S.; Buriani, A.; Vassanelli, S. Understanding the effects of anesthesia on cortical electrophysiological recordings: A scoping review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickert, J.; de Oliveira, S.C.; Vaadia, E.; Aertsen, A.; Rotter, S.; Mehring, C. Encoding of movement direction in different frequency ranges of motor cortical local field potentials. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8815–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferlauto, L.; Vagni, P.; Fanelli, A.; Zollinger, E.G.; Monsorno, K.; Paolicelli, R.C.; Ghezzi, D. All-polymeric transient neural probe for prolonged in-vivo electrophysiological recordings. Biomaterials 2021, 274, 120889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perego, C.; Fumagalli, S.; De Simoni, M.G. Temporal pattern of expression and colocalization of microglia/macrophage phenotype markers following brain ischemic injury in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, A.; Wu, C. Chronically implanted intracranial electrodes: Tissue reaction and electrical changes. Micromachines 2018, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, M.; Sunil, S.; Black, J.; Barkauskas, D.S.; Haung, A.Y.; Miller, R.H.; Selkirk, S.M.; Capadona, J.R. The roles of blood-derived macrophages and resident microglia in the neuroinflammatory response to implanted intracortical microelectrodes. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8049–8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, C.H.; Saxena, A.; Heelan, N.; Salatino, J.; Purcell, E.K. Spatiotemporal patterns of gene expression around implanted silicon electrode arrays. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozai, T.D.; Jaquins-Gerstl, A.S.; Vazquez, A.L.; Michael, A.C.; Cui, X.T. Brain tissue responses to neural implants impact signal sensitivity and intervention strategies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filho, G.; Júnior, C.; Spinelli, B.; Damasceno, I.; Fiuza, F.; Morya, E. All-Polymeric Electrode Based on PEDOT:PSS for In Vivo Neural Recording. Biosensors 2022, 12, 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100853
Filho G, Júnior C, Spinelli B, Damasceno I, Fiuza F, Morya E. All-Polymeric Electrode Based on PEDOT:PSS for In Vivo Neural Recording. Biosensors. 2022; 12(10):853. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100853
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilho, Gilberto, Cláudio Júnior, Bruno Spinelli, Igor Damasceno, Felipe Fiuza, and Edgard Morya. 2022. "All-Polymeric Electrode Based on PEDOT:PSS for In Vivo Neural Recording" Biosensors 12, no. 10: 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100853
APA StyleFilho, G., Júnior, C., Spinelli, B., Damasceno, I., Fiuza, F., & Morya, E. (2022). All-Polymeric Electrode Based on PEDOT:PSS for In Vivo Neural Recording. Biosensors, 12(10), 853. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12100853





