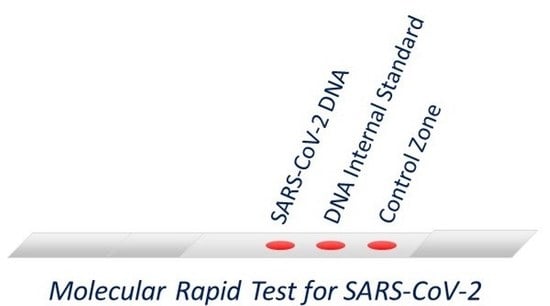
A Molecular Lateral Flow Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Quantitative Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Samples
2.2. Synthesis of Polystyrene Microsphere Conjugates
2.3. Preparation of Anti-Biotin Antibody-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles (Antibiotin–AuNPs)
2.4. Tailing of Complementary Probes with dA
2.5. Reverse Transcription
2.6. Competitive Quantitative PCR
2.7. Hybridization of the PCR Products to the Complementary Probes
2.8. Molecular Strip Test—Lateral Flow Assay
3. Results
3.1. Detectability of the Molecular Lateral Flow Assay
3.2. Clinical Samples
3.3. Specificity of the Molecular Lateral Flow Assay
3.4. Repeatability of the Molecular Lateral Flow Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicola, M.; Alsafi, Z.; Sohrabi, C.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, M.; Agha, R. The Socio-Economic Implications of the Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19): A Review. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 78, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.R.; Allerton, C.M.N.; Anderson, A.S.; Aschenbrenner, L.; Avery, M.; Berritt, S.; Boras, B.; Cardin, R.D.; Carlo, A.; Coffman, K.J.; et al. An Oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science 2021, 3, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Fact Sheet for Healthcare Providers Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for Paxlovid. 2021; pp. 1–36. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/155050/download (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Ilkhani, H.; Hedayat, N.; Farhad, S. Novel Approaches for Rapid Detection of COVID-19 during the Pandemic: A Review. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 634, 114362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ding, L.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Point-of-Care COVID-19 Diagnostics Powered by Lateral Flow Assay. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindeirinho, J.M.; Pinho, E.; Azevedo, N.F.; Almeida, C. SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostics Based on Nucleic Acids Amplification: From Fundamental Concepts to Applications and Beyond. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2022.
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Qin, Z.; Sackrison, J.; Bischof, J.C. Ultrasensitive and Highly Specific Lateral Flow Assays for Point-of-Care Diagnosis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3593–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, W.W.W.; Le, T.N.; Pham, D.M.; Ko, H.H.; Chang, H.C.; Lee, C.C.; Sharma, N.; Lee, C.K.; Chiang, W.H. Recent Advances in Novel Lateral Flow Technologies for Detection of COVID-19. Biosensors 2021, 11, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Nimse, S.B.; Kim, J.; Song, K.S.; Kim, T. Development of a Lateral Flow Strip Membrane Assay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of the SARS-CoV-2. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14139–14144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wei, H.; Rong, Z.; Wang, S. Tetra-Primer ARMS-PCR Combined with Dual-Color Fluorescent Lateral Flow Assay for the Discrimination of SARS-CoV-2 and its Mutations with a Handheld Wireless Reader. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 1531–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Li, S.; He, L.; Fu, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Multiplex Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Combined with Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor for the Diagnosis of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 166, 112437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, S.; Yan, H.; Chang, B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, S. Rapid and Visual Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Multiplex Reverse Transcription Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Linked With Gold Nanoparticle-Based Lateral Flow Biosensor. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 581239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Warmt, C.; Henkel, J.; Schrick, L.; Nitsche, A.; Bier, F.F. Lateral Flow–Based Nucleic Acid Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Using Enzymatic Incorporation of Biotin-Labeled dUTP for POCT Use. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 3177–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Huang, X.; Liang, J.; Qiu, L.; Han, D.; Tan, W. Rapid One-Pot Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Based on a Lateral Flow Assay in Clinical Samples. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 3325–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Suo, C.; Brown, T.; Wang, T.; Teichmann, S.A.; Bassett, A.R. INSIGHT: A Population-Scale COVID-19 Testing Strategy Combining Point-of-Care Diagnosis with Centralized High-Throughput Sequencing. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.Z.; Chen, J.T.; Li, J.; Wu, X.J.; Wen, J.Z.; Liu, X.Z.; Lin, L.Y.; Liang, X.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Zha, G.C.; et al. Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay With Lateral Flow Dipstick Assay for Rapid Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 613304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelite, T.R.; Uscanga-Palomeque, A.C.; Castellanos-Gonzalez, A.; Melby, P.C.; Travi, B.L. Isothermal Recombinase Polymerase Amplification-Lateral Flow Detection of SARS-CoV-2, the Etiological Agent of COVID-19. J. Virol. Methods 2021, 296, 114227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chaput, J.C. REVEALR: A Multicomponent XNAzyme-Based Nucleic Acid Detection System for SARS-CoV-2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 8957–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Y.L.; Ismail, I.; Mustapa, N.I.B.; Lai, M.Y.; Soh, T.S.T.; Hassan, A.H.; Peariasamy, K.M.; Lee, Y.L.; Kahar, M.K.B.A.; Chong, J.; et al. Development of a Reverse Transcription Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Rapid and Direct Visual Detection of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyani, R.; Sharma, K.; Kojima, K.; Biyani, M.; Sharma, V.; Kumawat, T.; Juma, K.M.; Yanagihara, I.; Fujiwara, S.; Kodama, E.; et al. Development of Robust Isothermal RNA Amplification Assay for Lab-Free Testing of RNA Viruses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Dandy, D.S.; Geiss, B.J.; Henry, C.S. Padlock Probe-Based Rolling Circle Amplification Lateral Flow Assay for Point-of-Need Nucleic Acid Detection. Analyst 2021, 146, 4340–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchsung, M.; Jantarug, K.; Pattama, A.; Aphicho, K.; Suraritdechachai, S.; Meesawat, P.; Sappakhaw, K.; Leelahakorn, N.; Ruenkam, T.; Wongsatit, T.; et al. Clinical Validation of a Cas13-Based Assay for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Huo, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, S.; Luo, X.; Hou, C. Automated, Portable, and High-Throughput Fluorescence Analyzer (APHF-Analyzer) and Lateral Flow Strip Based on CRISPR/Cas13a for Sensitive and Visual Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Talanta 2022, 248, 123594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, J.P.; Deng, X.; Yu, G.; Fasching, C.L.; Servellita, V.; Singh, J.; Miao, X.; Streithorst, J.A.; Granados, A.; Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A.; et al. CRISPR–Cas12-Based Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, J.; Ren, L.; Jiang, W.; Wang, M.; Zhuang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, R.; Zeng, Y.; Luu, L.D.W.; et al. A One-Step, One-Pot CRISPR Nucleic Acid Detection Platform (CRISPR-Top): Application for the Diagnosis of COVID-19. Talanta 2021, 233, 122591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Smith, B.M.; Jain, P.K. Enhancement of Trans-Cleavage Activity of Cas12a with Engineered crRNA Enables Amplified Nucleic Acid Detection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Luo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Yu, S.; Tai, J.; Wang, Y. Rapid, Ultrasensitive, and Highly Specific Diagnosis of COVID-19 by CRISPR-Based Detection. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, C.S.; Park, K.H.; Ahn, W.C.; Kim, Y.S.; Kwon, O.S.; Yong, D.; Kang, T.; Woo, E. Detection of Infectious Viruses Using CRISPR-Cas12-Based Assay. Biosensors 2021, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogan, D.J.; Chaverra-Rodriguez, D.; Lin, C.P.; Smidler, A.L.; Yang, T.; Alcantara, L.M.; Antoshechkin, I.; Liu, J.; Raban, R.R.; Belda-Ferre, P.; et al. Development of a Rapid and Sensitive CasRX-Based Diagnostic Assay for SARS-CoV-2. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 3957–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, E.; Jiang, L.; Tian, T.; Hu, M.; Yue, H.; Huang, M.; Lin, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, X. Simultaneous Dual-Gene Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 Based on CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Lateral Flow Assay. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5307–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, M.; Phutela, R.; Kumar, M.; Ansari, A.H.; Rauthan, R.; Gulati, S.; Sharma, N.; Sinha, D.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; et al. Rapid and Accurate Nucleobase Detection Using FnCas9 and Its Application in COVID-19 Diagnosis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 183, 113207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, S.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, S.; Lei, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, L.; et al. Rapid Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Fluorescence Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, K.; Moitra, P.; Alafeef, M.; Gunaseelan, N.; Pan, D. A Rapid RNA Extraction-Free Lateral Flow Assay for Molecular Point-of-Care Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Augmented by Chemical Probes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 200, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Su, F.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, H.; Yan, X.J.; Yang, C.; Fan, X.; Wu, G. Rapid Point-of-Care Testing for SARS-CoV-2 Virus Nucleic Acid Detection by an Isothermal and Nonenzymatic Signal Amplification System Coupled with a Lateral Flow Immunoassay Strip. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2021, 342, 129899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalligosfyri, P.; Nikou, S.; Bravou, V.; Kalogianni, D.P. Liquid Biopsy Genotyping by a Simple Lateral Flow Strip Assay with Visual Detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1163, 338470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dust, K.; Hedley, A.; Nichol, K.; Stein, D.; Adam, H.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Bullard, J.; Van Caeseele, P.; Alexander, D.C. Comparison of Commercial Assays and Laboratory Developed Tests for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 285, 113970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalligosfyri, P.M.; Nikou, S.; Karteri, S.; Kalofonos, H.P.; Bravou, V.; Kalogianni, D.P. Rapid Multiplex Strip Test for the Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA Mutations for Liquid Biopsy Applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toubanaki, D.K.; Christopoulos, T.K.; Ioannou, P.C.; Flordellis, C.S. Identification of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms by the Oligonucleotide Ligation Reaction: A DNA Biosensor for Simultaneous Visual Detection of Both Alleles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnes, J.; Deeks, J.J.; Adriano, A.; Berhane, S.; Davenport, C.; Dittrich, S.; Emperador, D.; Takwoingi, Y.; Cunningham, J.; Beese, S.; et al. Rapid, Point-of-Care Antigen and Molecular-Based Tests for Diagnosisof SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 7, CD013705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Name | DNA Sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|
| PCR Primers | |
| SARS-CoV-2 Forward | GACCCCAAAATCAGCGAAAT |
| SARS-CoV-2 Reverse | Biotin-TCTGGTTACTGCCAGTTGAATCTG |
| Synthetic Targets | |
| SARS-CoV-2 amplified DNA sequence | GACCCCAAAATCAGCGAAATGCACCCCGCATTACGTTTGGTGGACCCTCAGATTCAACTGGCAGTAACCAGA |
| IS double-stranded | GACCCCAAAATCAGCGAAATGCGTTAGTTAGATTATTGTTAGTTAGCTCAGATTCAACTGGCAGTAACCAGA |
| Complementary probes | |
| SARS-CoV-2 probe | ACCCCGCATTACGTTTGGTGGACC |
| IS probe | GTTAGTTAGATTATTGTTAGTTAG |
| Complementary tag-probes | |
| SARS-CoV-2 tag-probe | ACGTCACCATCCGAACTTAAAACGCCGAATTCTCTCACCCCGCATTACGTTTGGTGGACC |
| IS tag-probe | AGTCGTAGTCAGAAGTTCAGCAAGCCGAATTCTCTCGTTAGTTAGATTATTGTTAGTTAG |
| Anti-tag sequences | |
| anti-tag for SARS-CoV-2 | NH2-CGTTTTAAGTTCGGATGGTGACGT |
| anti-tag for IS | NH2-CTTGCTGAACTTCTGACTACGACT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maglaras, P.; Lilis, I.; Paliogianni, F.; Bravou, V.; Kalogianni, D.P. A Molecular Lateral Flow Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Quantitative Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110926
Maglaras P, Lilis I, Paliogianni F, Bravou V, Kalogianni DP. A Molecular Lateral Flow Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Quantitative Detection. Biosensors. 2022; 12(11):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110926
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaglaras, Panagiotis, Ioannis Lilis, Fotini Paliogianni, Vasiliki Bravou, and Despina P. Kalogianni. 2022. "A Molecular Lateral Flow Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Quantitative Detection" Biosensors 12, no. 11: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110926
APA StyleMaglaras, P., Lilis, I., Paliogianni, F., Bravou, V., & Kalogianni, D. P. (2022). A Molecular Lateral Flow Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Quantitative Detection. Biosensors, 12(11), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110926