Overview on the Design of Magnetically Assisted Electrochemical Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Magnetic-Electrode-Based Electrochemical Biosensors
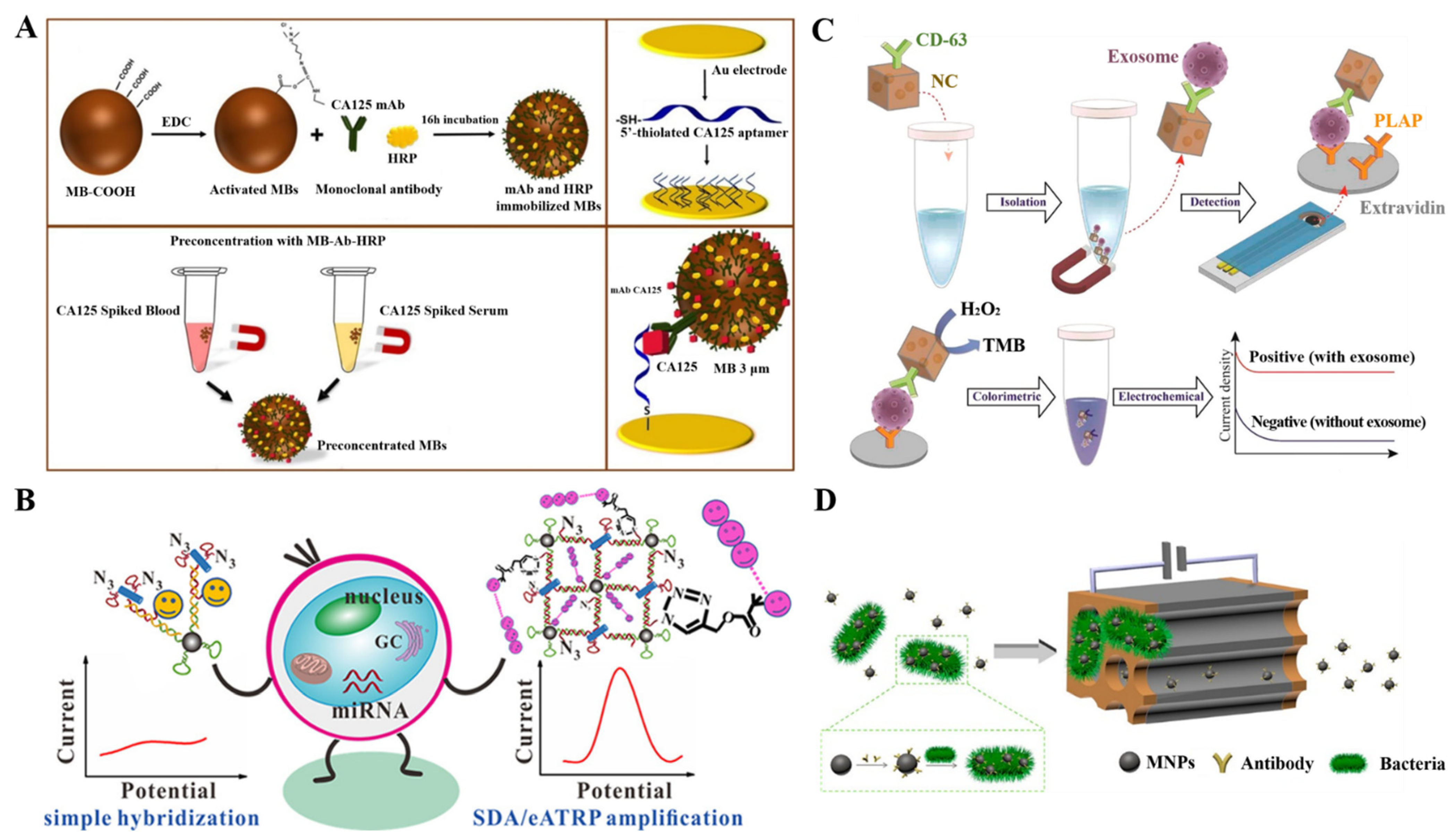
2.1. Electrochemical Immunosensors
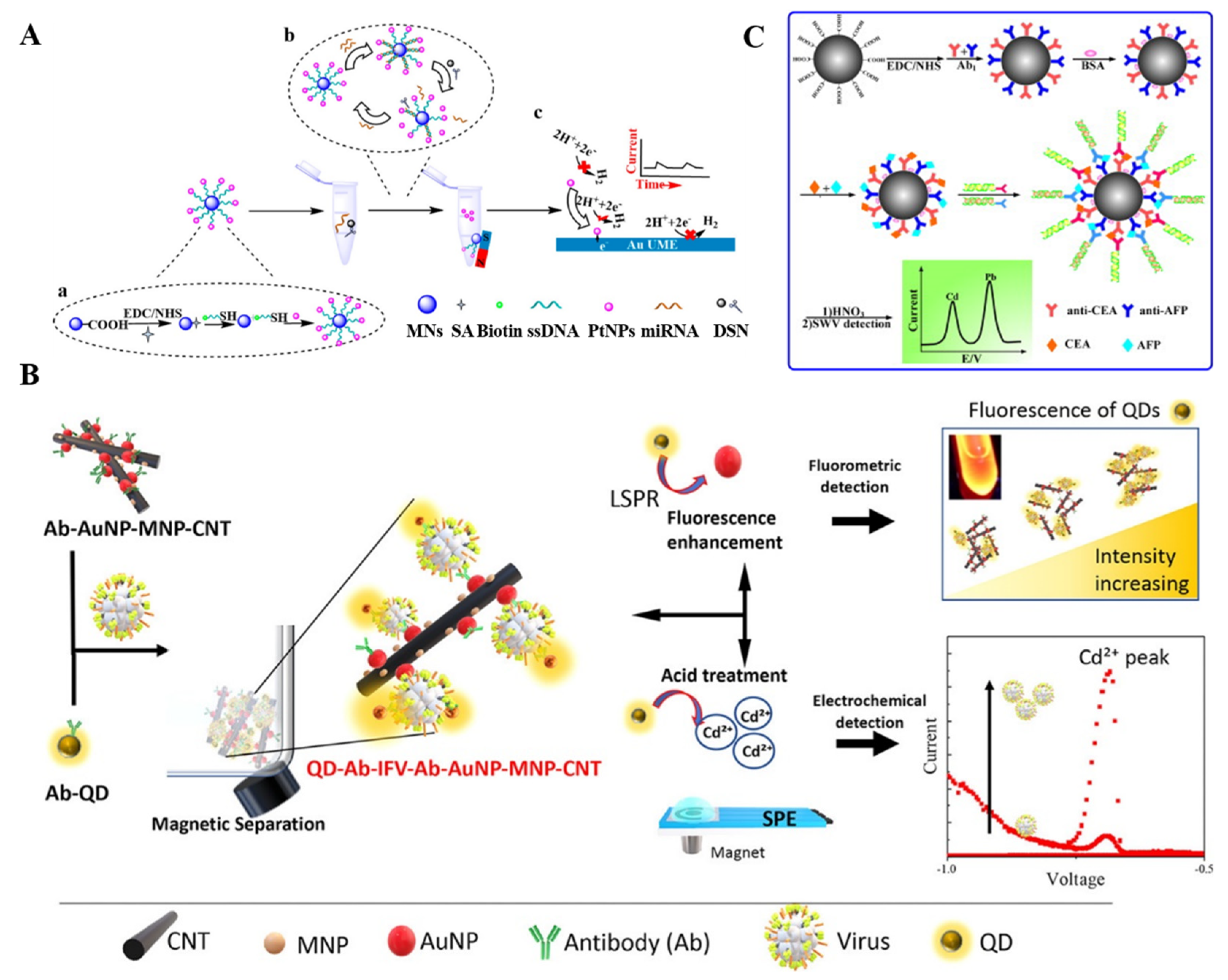
2.1.1. Enzymatic Amplification

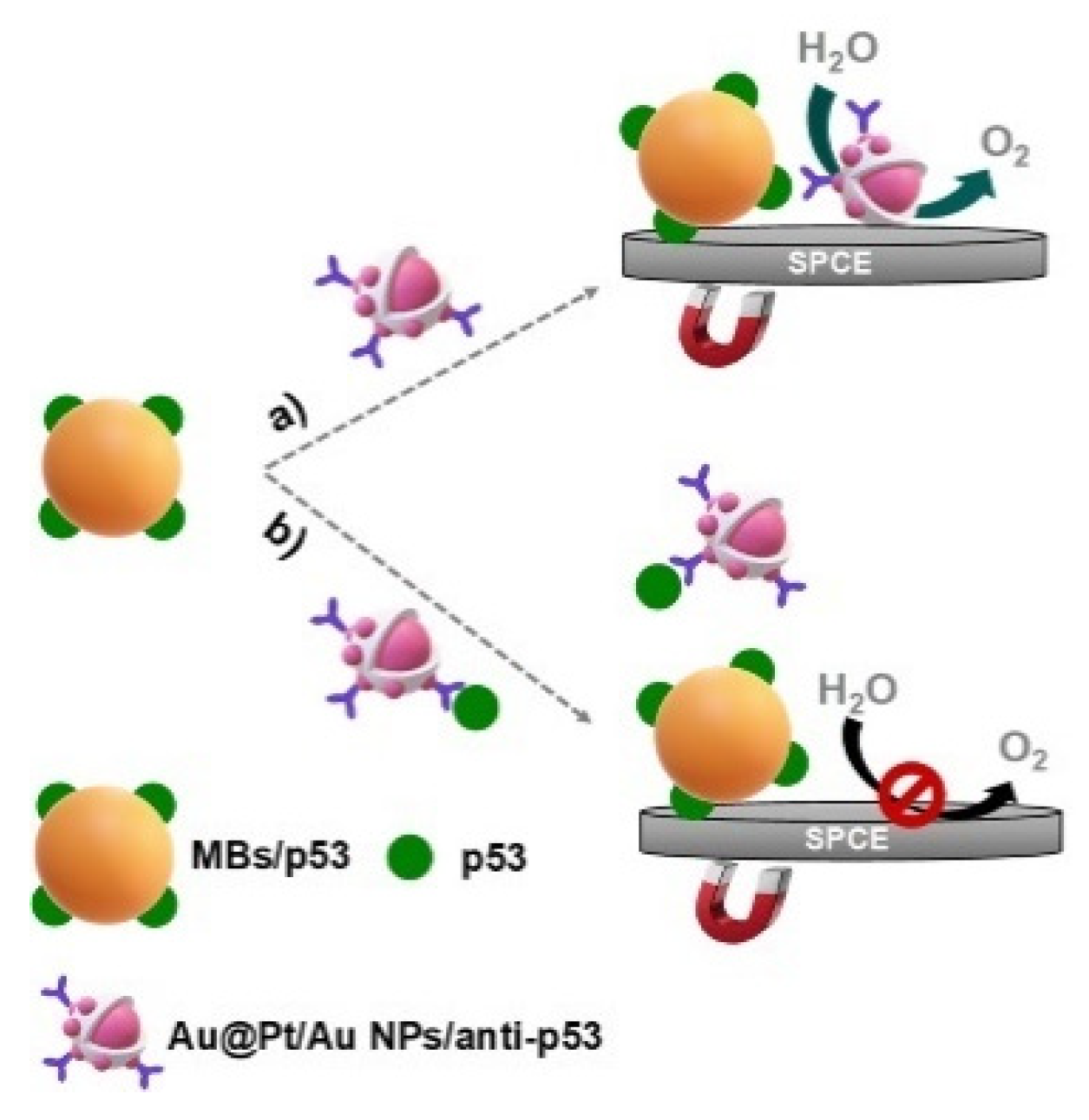
2.1.2. Nanomaterials
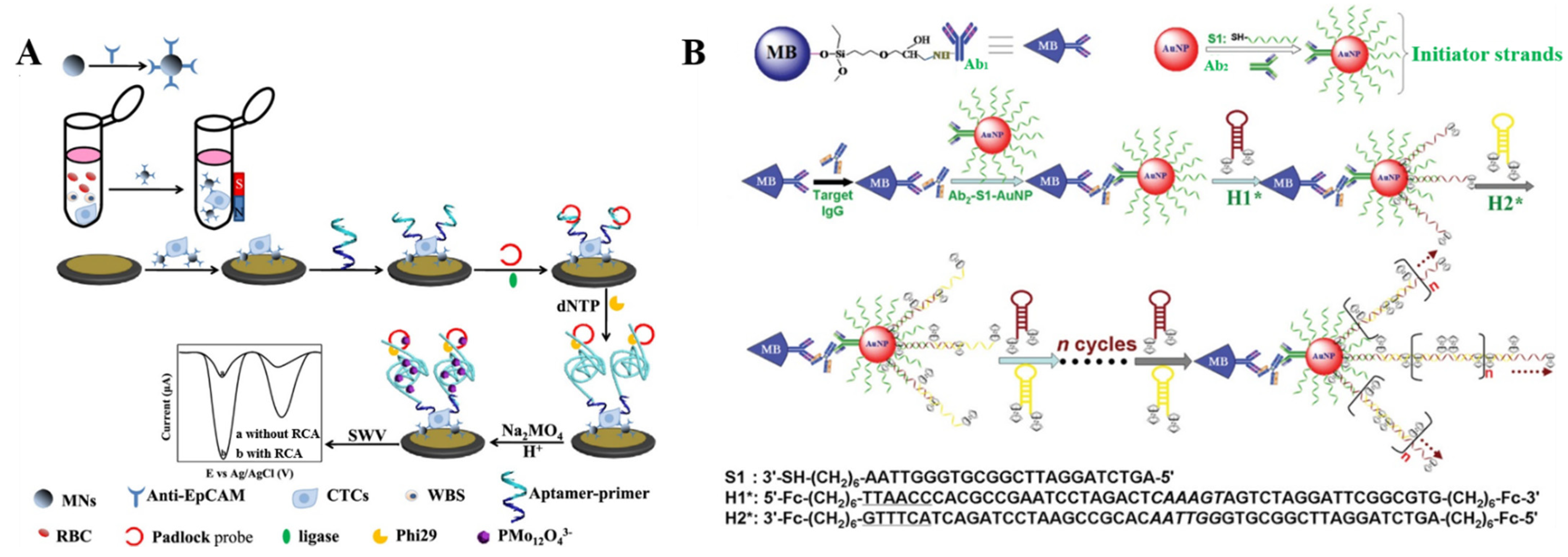
2.1.3. In Situ Assembled DNA Polymers
| Signal Tags | Targets | Linear Range | Detection Limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRP | mRNA and IL-8 | 0.32~7.5 nM for mRNA and 0.0879~5 ng/mL for IL-8 | 0.21 nM for mRNA and 72.4 pg/mL for IL-8 | [49] |
| HRP | HRP2 | 0.36~31.3 ng/mL | 0.36 ng/mL | [58] |
| HRP | Ochratoxin A | 0.01~0 ppb | 0.008 ppb | [59] |
| HRP | HIF-1α | 0.25~10 ng/mL | 76 pg/mL | [52] |
| HRP | 5-mC-MGMT and 5-hmC-MGMT | 4~250 pM for 5-mC-MGMT and 1.44~100 pM for 5-hmC-MGMT | 1.2 pM for 5-mC-MGMT and 0.43 pM for 5-hmC-MGMT | [54] |
| HRP | Cadherin-17 | 4.76~1000 ng/mL | 1.43 ng/mL | [55] |
| HRP | miRNA-205 | 8.2~250 pM | 2.4 pM | [51] |
| HRP | p53-specific autoantibody | 1.1~5 U/mL | 0.34 U/mL | [57] |
| Poly-HRP | MMP-9 | 0.03~2 ng/mL | 13 pg/mL | [61] |
| HRP-AuNPs | CEA | 5~60 ng/mL | 5 ng/mL | [62] |
| HRP-Au@Pt-Gr | Escherichia coli O157:H7 | 4.0 × 102~ 4.0 × 108 CFU/mL | 91 CFU/mL | [63] |
| Thi-HRP-SiNPs | CA 125 | 0.1~450 U/mL | 0.1 U/mL | [64] |
| Thi/Fc-HRP-Fe3O4-GO | CEA and AFP | 0.01~80 and 0.01~200 ng/mL | 1 pg/mL | [65] |
| ALP | MRSA | 1 × 103~1 × 105 CFU/mL | 845 CFU/mL | [67] |
| ALP | HER2 | 5~50 and 50~100 ng/mL | 2.8 ng/mL | [68] |
| Fc@MI-Cu3(PO4)2 | Salmonella typhimurium | 10 to 1 × 107 CFU/mL | 3 CFU/mL | [69] |
| molybdophosphate | CD25 | 1 pg/mL~1 ng/mL | 0.5 pg/mL | [70] |
| AuNPs | Salmonella | 1.5 × 103~1.5 × 105 cells/mL | 143 cells/mL | [74] |
| AuNPs | α-HBsAg IgG antibody | 5~69.2 mIU/mL | 3 mIU/mL | [75] |
| Au@Pt/Au NPs | p53 peptide | 50~1000 nM | 66 nM | [76] |
| Au@Pt NPs | CEA | 5 pg/mL~200 ng/mL | 1.42 pg/mL | [77] |
| AuNPs | IgG | 0.1 fg/mL~100 ng/mL | 0.1 fg/mL | [82] |
2.2. DNA Biosensors
2.2.1. Enzyme Labels
2.2.2. Thermal-Cycle or Isothermal Amplification
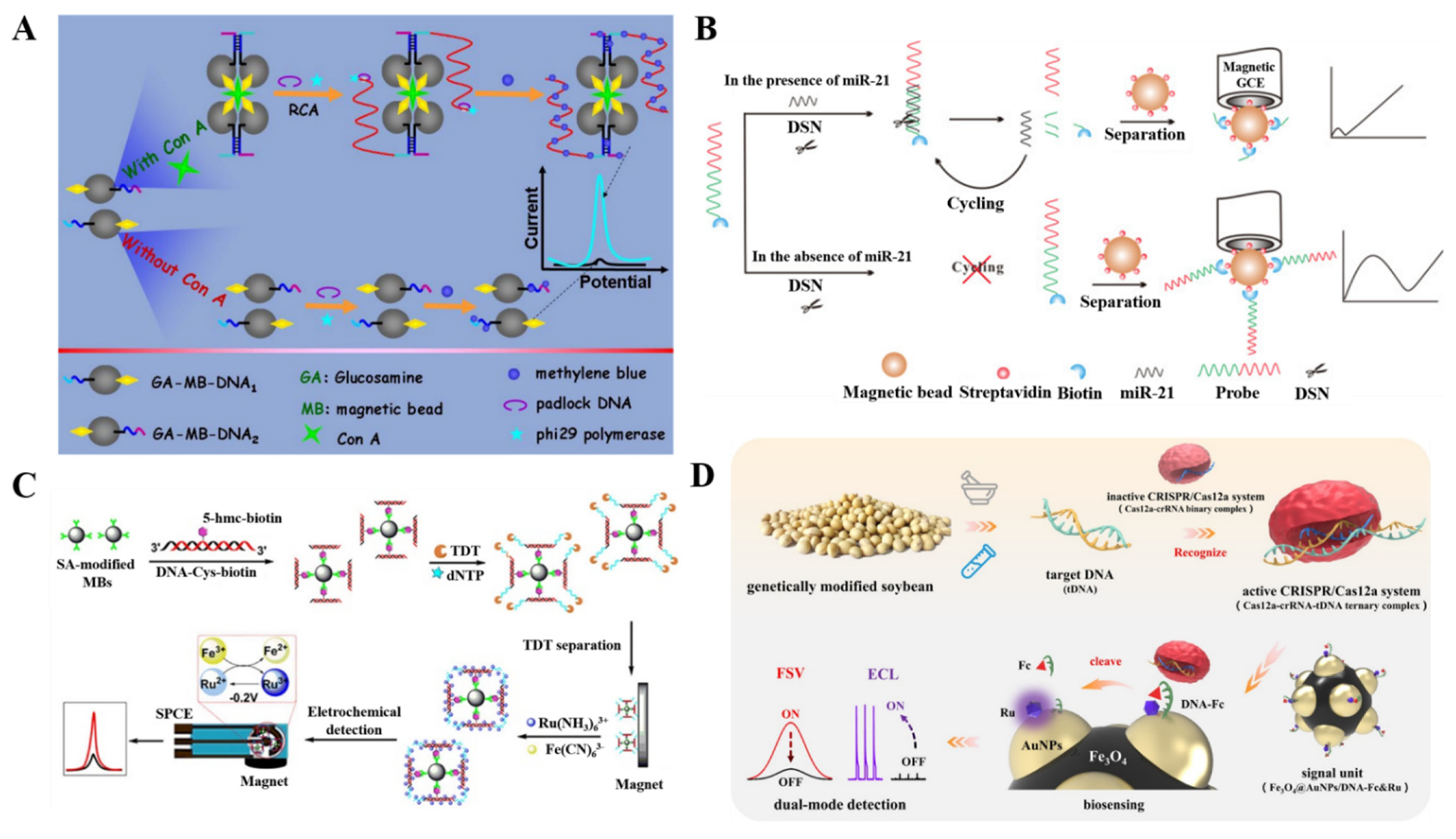
2.2.3. Functional Nanomaterials
| Signal Tags | Targets | Linear Range | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRP | 5-mC | 3.9~500 pM | 1.2 pM | [89] |
| HRP | MTase | 0.5~125 U/mL | 0.2 U/mL | [90] |
| HRP | miR-21 | 0.14~10 nM | 0.04 nM | [91] |
| ProtA-HRP40 | dsDNA | 0.39~75 pM | 0.12 pM | [92] |
| HRP | miRNA | 1 aM~1 fM | 0.22 aM | [94] |
| RCA and methylene blue | Con A | 1.96 pM~98 nM | 1.5 pM | [98] |
| G-quadruplex/hemin | CEA | 0.1~200 ng/mL | 0.4 pg/mL | [99] |
| DSN-assisted target recycling | miR-21 | 0.5~40 fM | 60 aM | [100] |
| TDT enzymaticamplification | 5-mC | 0.01~1000 pM | 9.06 fM | [101] |
| Fc-DNA | SHZD32-1 | 10~1 × 108 fM | 3 fM | [102] |
| HCR and methylene blue | TB | 0.005~50 nM | 1.1 pM | [105] |
| HCR and HRP | miRNA-21 | 0.2~5 nM | 60 pM | [106] |
| HCR and ALP | miRNA-21 | 2.5 fM~25 nM | 0.12 fM | [107] |
| DNAzyme, HCR, and methylene blue | Pb2+ | 50 pM~1 μM | 15 pM | [110] |
| DNAzyme, HCR, and Fc | Pb2+ | 0.1~75 nM | 37 pM | [112] |
| CHA and methylene blue | miRNA | 0.2 fM~1 nM | 0.14 fM | [117] |
| Fc-AuNPs | miRNA-182 | 5~100 fM | 0.14 fM | [118] |
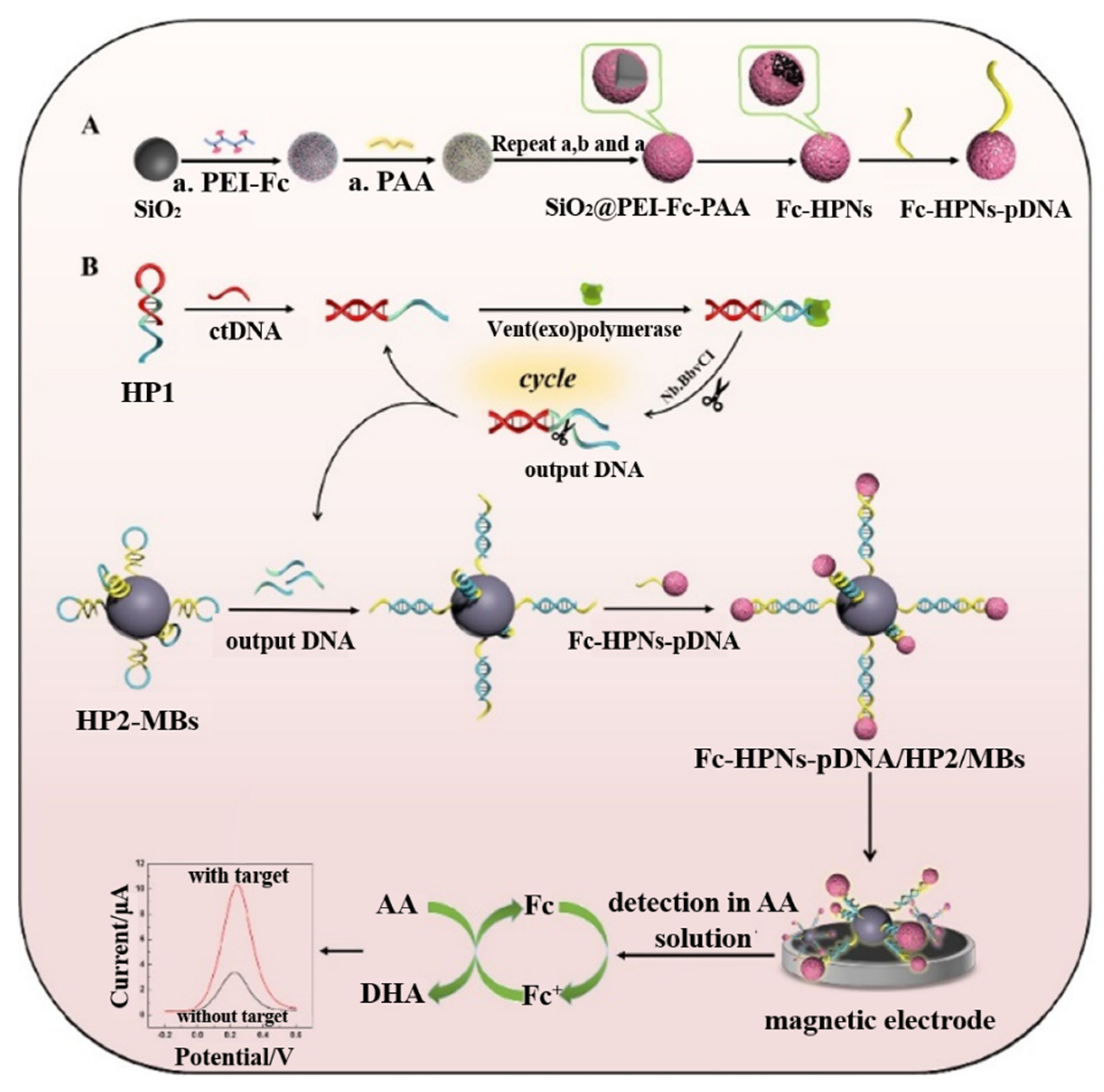
| Fc-HPNs | ctDNA | 10 fM~10 nM | 1.6 fM | [119] |
| AgNPs | HBV DNA | 0~500 pM | 85 pM | [122] |
2.3. Aptasensors

| Signal Tags | Targets | Linear Range | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALP | Thrombin | 0~100 nM | 0.45 nM | [130] |
| HRP | Gliadin | 0.1 ppb~10 ppm | 0.5 ppb | [132] |
| Fc- and Thi-labeled AuNPs | Ramos cells and CCRF-CEM | 5~500 cells/mL | 4 and 3 cells/mL | [134] |
| Ag/CdO NPs | PSA | 0.05~50 ng/mL | 28 pg/mL | [135] |
| DNA nanostructures | Bisphenol A | 0.1~100 nM | 80 pM | [137] |
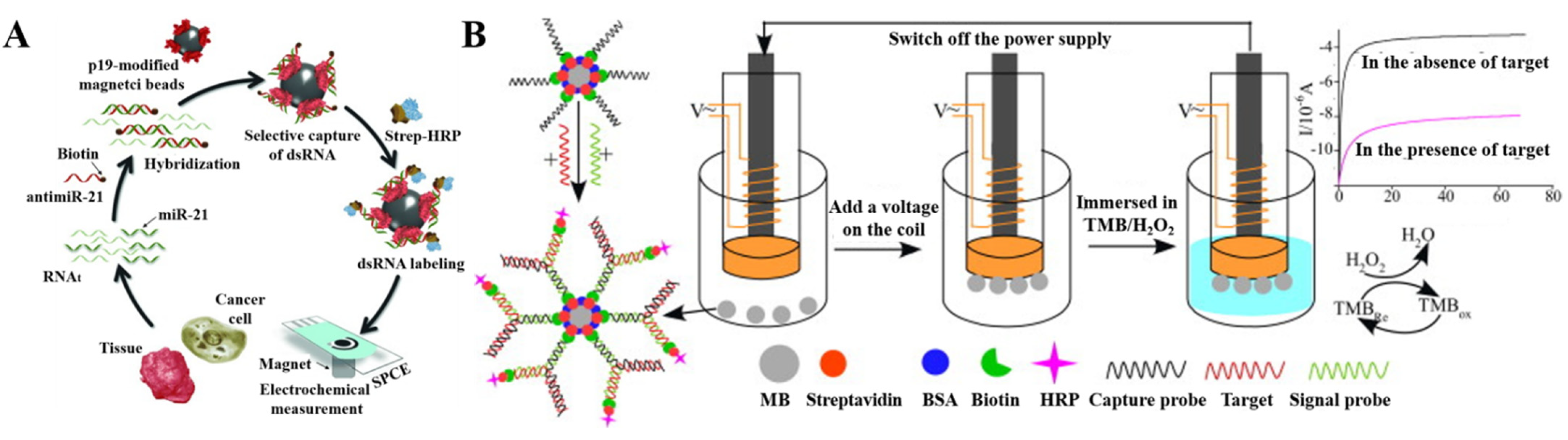
3. MB/MNP-Based Target Conversion
3.1. Stimuli–Response Release of Signal Reporters

3.2. Enzymatic Production of Electroactive Species
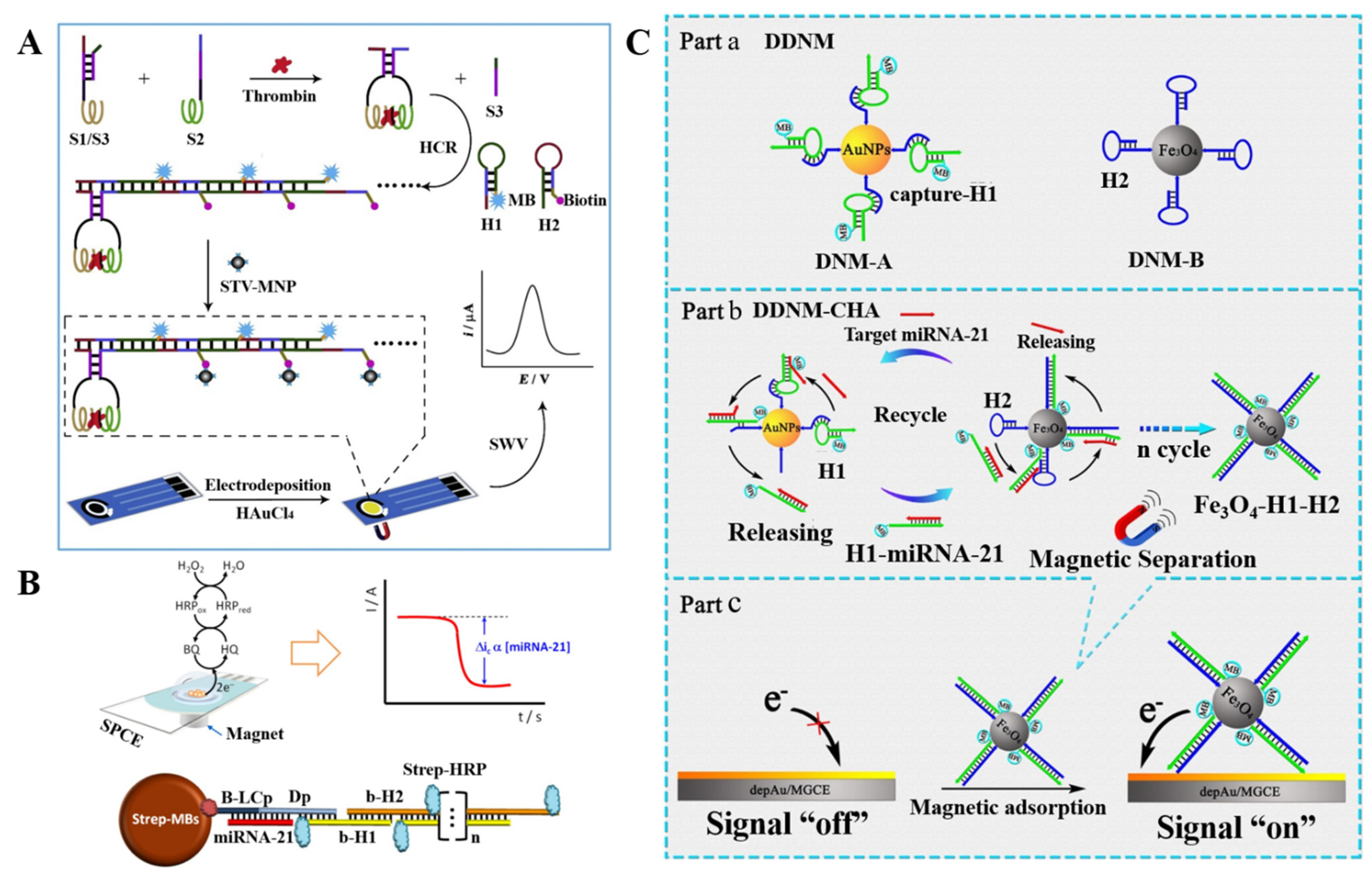
3.3. Target-Induced Generation of Messenger DNA
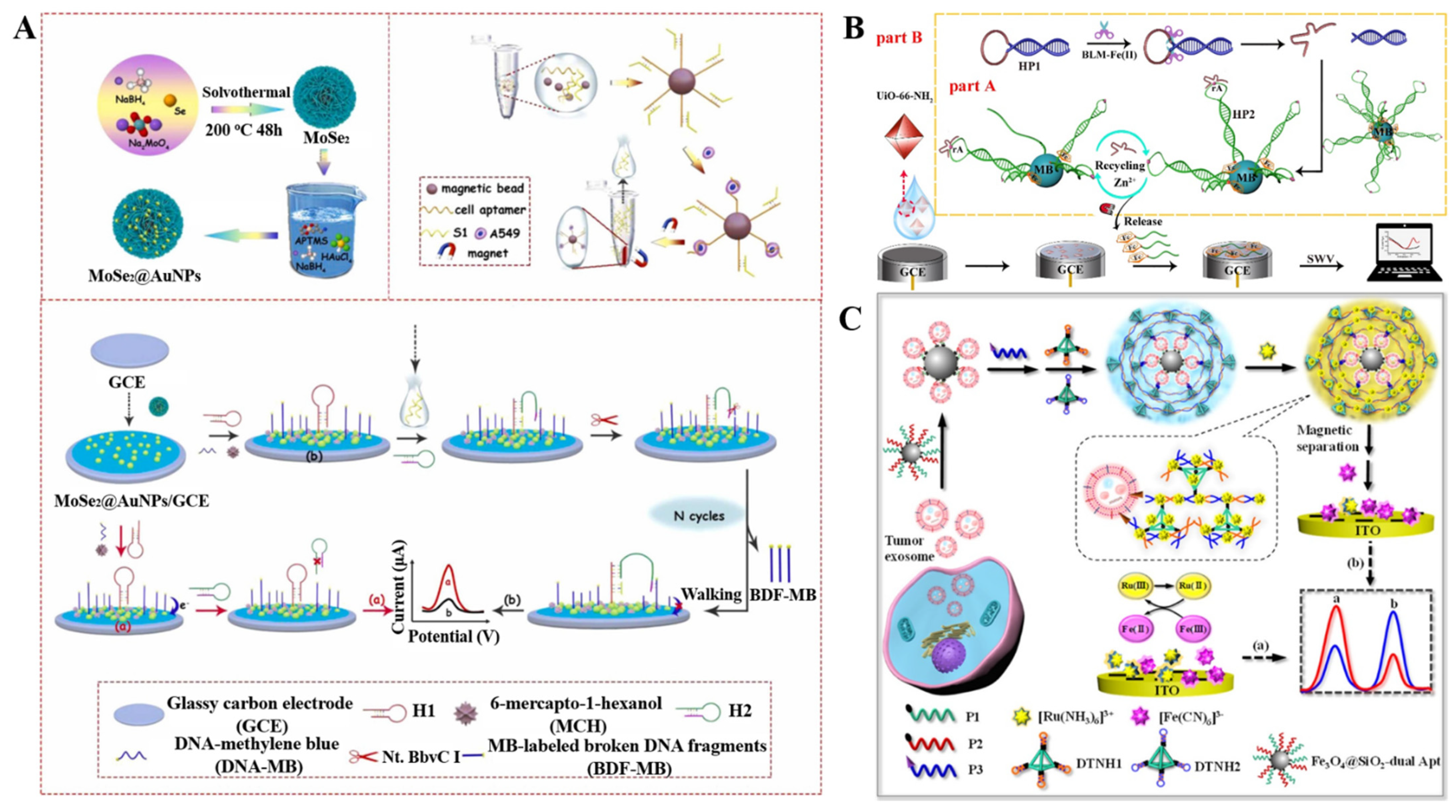
3.4. Other Biosensors with MB/MNP-Based Target Conversion
| Signal Probes | Targets | Linear Range | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V2O5-NP-encapsulated LPs | norovirus | 0.01~10pg/mL | 4.1 fg/mL | [147] |
| Fc-labeled SiO2 NPs | exosomes | 1.2 × 103~1.2 × 107 particles/μL | Not reported | [148] |
| Molybdophosphate | MCF-7 cell | 5~1000 cells/mL | 2 cells/mL | [149] |
| PtNPs | miRNA-21 | 50 aM~5 nM | 47 aM | [150] |
| PtNPs | HIV-DNA | 5 fM~50 nM | 4.86 fM | [151] |
| QDs | BChE | 0.1~20 nM | 0.05 nM | [153] |
| HRP-AuNPs | IgG | 2.5 × 10−6~1µg/mL | 260 pg/mL | [154] |
| QDs | OP-AChE | 0.3~300 ng/mL | 0.15 ng/mL | [157] |
| CdS QDs | mRNA | 1 fM~0.1 nM | 0.48 fM | [158] |
| CdSeTeS QDs | influenza virus A | 1 fg/mL~1 μg/mL | 13.66 fg/mL | [159] |
| QD-PS beads | DNA | 0.5 fM~10 pM | 0.22 fM | [160] |
| CdTe or PbS QDs-coated silica | OTA and FB1 | 0.01~ 10 ng/mL and 0.05~50 ng/mL | 5 and 20 pg/mL | [161] |
| CdS and PbS QDs | CEA and AFP | 0.1~100 ng/mL and 0.5~200 ng/mL | 3.3 and 7.8 pg/mL | [165] |
| AgNPs-aptamer | S. aureus | 10~1 × 106 CFU/mL | 1 CFU/mL | [166] |
| CuNPs-DNA | CD24+ cells | 1 × 102~5 × 106 cells | 42 cells | [167] |
| HAP | thrombin | 0.1 fM~1 nM | 0.40 fM | [169] |
| ALP-AuNPs | thrombin | 1 fM~10 nM | 0.26 fM | [172] |
| dsDNA polymers and Thi | cystatin C | 10 fg/mL~30 ng/mL | 3 fg/mL | [174] |
| Exo III-assisted recycling | exosomes | 1 × 103~1.2 × 105 particles/μL | 70 particles/μL | [175] |
| CHA | Cu2+ | 1 pM~500 nM | 0.33 pM | [176] |
| AgNPs | DNA | 1~100 fM | 0.22 fM | [177] |
| DNA walker | A549 cells | 5~5 × 104 cells/mL | 2 cells/mL | [178] |
| DNAzyme | miR-155 and lysozyme | 0.01 nM~1μM and 1 pM~1μM | 5.2 pM and 0.67 pM | [179] |
| Fc-DNA | bleomycin | 5~2000 pM | 4 pM | [181] |
| Methylene blue-DNA | exosomes | 103~109 particles/mL | 708 particles/mL | [182] |
| DNA superstructure | exosomes | 1 × 105~3.7 × 108 particles/mL | 3.0 × 104 particles/mL | [184] |
| HRP-MBs | CA125 | 2~100 U/mL | 0.08 U/mL | [189] |
| Methylene blue-DNAmodified AuNPs | BNP | 1~1 × 104pg/mL | 0.56 pg/mL | [194] |
| Fc-DNAmodified AuNPs | miRNA-182 | 0.001~2 pM | 0.058 fM | [195] |
| Electroactive polymers | miRNA-21 | 1 aM~1 nM | 0.32 aM | [196] |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongkaew, N.; Simsek, M.; Griesche, C.; Baeumner, A.J. Functional nanomaterials and nanostructures enhancing electrochemical biosensors and lab-on-a-chip performances: Recent progress, applications, and future perspective. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 120–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farka, Z.; Jurik, T.; Kovar, D.; Trnkova, L.; Skladal, P. Nanoparticle-based immunochemical biosensors and assays: Recent advances and challenges. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9973–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Davis, J.J. Electrical biosensors and the label free detection of protein disease biomarkers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5944–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Denno, M.E.; Pyakurel, P.; Venton, B.J. Recent trends in carbon nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors for biomolecules: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 887, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M. Iron and iron-oxide magnetic nanoparticles as signal-amplification elements in electrochemical biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhlband, A.; Kholafazad-Kordasht, H.; Rahimi, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Soleymani, J. Applications of magnetic materials in the fabrication of microfluidic-based sensing systems: Recent advances. Microchem. J. 2022, 173, 107042–107053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Samiei, M.; Davaran, S. Magnetic nanoparticles: Preparation, physical properties, and applications in biomedicine. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beveridge, J.S.; Stephens, J.R.; Williams, M.E. The use of magnetic nanoparticles in analytical chemistry. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2011, 4, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, L.H.; Arias, J.L.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Magnetic nanoparticles: Design and characterization, toxicity and biocompatibility, pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5818–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.H.; Salabas, E.L.; Schuth, F. Magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1222–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, N.; Sun, Z.; Ding, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, L. Protease biosensor by conversion of a homogeneous assay into a surface-tethered electrochemical analysis based on streptavidin-biotin interactions. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, E. Electrochemical biosensors based on magnetic micro/nano particles. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoglu, S.B.; Man, E.; Harmanci, D.; Tozan Ruzgar, S.; Sanli, S.; Keles, N.A.; Ayden, A.; Tuna, B.G.; Duzgun, O.; Ozkan, O.F.; et al. Magnetic nanoparticle-based electrochemical sensing platform using ferrocene-labelled peptide nucleic acid for the early diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Biosensors 2022, 12, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanli, S.; Ghorbani-Zamani, F.; Moulahoum, H.; Gumus, Z.P.; Coskunol, H.; Odaci Demirkol, D.; Timur, S. Application of biofunctionalized magnetic nanoparticles based-sensing in abused drugs diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Han, K.; Li, G. Magnetic nanoparticles applied in electrochemical detection of controllable DNA hybridization. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2447–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguilaz, M.; Villalonga, R.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Pingarron, J.M. Designing electrochemical interfaces with functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and wrapped carbon nanotubes as platforms for the construction of high-performance bienzyme biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7807–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Yu, X.Y.; Xiong, S.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. Electrochemical detection of arsenic(III) completely free from noble metal: Fe3O4 microspheres-room temperature ionic liquid composite showing better performance than gold. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2673–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.H.; Wu, Y.D.; Chi, B.Z.; Wen, S.H.; Liang, R.P.; Qiu, J.D. Simultaneously electrochemical detection of microRNAs based on multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles probe coupling with hybridization chain reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, H.; Yan, T.; Wei, Q. Corallite-like magnetic Fe3O4@MnO2@Pt nanocomposites as multiple signal amplifiers for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18786–18793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Luo, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhang, S.; Che, T.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L. Electrochemical dual-aptamer-based biosensor for nonenzymatic detection of cardiac troponin I by nanohybrid electrocatalysts labeling combined with DNA nanotetrahedron structure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 134, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Sun, D.; Tong, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, Z. DNA nanotetrahedron linked dual-aptamer based voltammetric aptasensor for cardiac troponin I using a magnetic metal-organic framework as a label. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masud, M.K.; Yadav, S.; Islam, M.N.; Nguyen, N.T.; Salomon, C.; Kline, R.; Alamri, H.R.; Alothman, Z.A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Hossain, M.S.A.; et al. Gold-loaded nanoporous ferric oxide nanocubes with peroxidase-mimicking activity for electrocatalytic and colorimetric detection of autoantibody. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11005–11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gunasekaran, D.; Gerchman, Y.; Vernick, S. Electrochemical detection of waterborne bacteria using bi-functional magnetic nanoparticle conjugates. Biosensors 2022, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zha, S.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, G.; Fu, Y. Chemical and electrochemical conversion of magnetic nanoparticles to prussian blue for label-free and refreshment-enhanced electrochemical biosensing of enrofloxacin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1221, 340123–340130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Hu, J.; Li, C.C.; Wang, C.M.; Zhang, C.Y. An electrochemical biosensor based on the enhanced quasi-reversible redox signal of prussian blue generated by self-sacrificial label of iron metal-organic framework. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 122, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Qiao, Z.; Lei, C.; Fu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Yao, S.; Li, Y.; Ying, Y. Electrochemical conversion of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles to electroactive prussian blue analogues for self-sacrificial label biosensing of avian influenza virus H5N1. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12145–12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fan, G.C.; Fan, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Luo, X. Low fouling and ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensors with dual assay methods based on Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5842–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, H.; Fu, Y.; Li, Y. Separation/concentration-signal-amplification in-one method based on electrochemical conversion of magnetic nanoparticles for electrochemical biosensing. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modh, H.; Scheper, T.; Walter, J.G. Aptamer-modified magnetic beads in biosensing. Sensors 2018, 18, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palecek, E.; Fojta, M. Magnetic beads as versatile tools for electrochemical DNA and protein biosensing. Talanta 2007, 74, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiani, G.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; Campàs, M. Magnetic beads in marine toxin detection: A review. Magnetochemistry 2019, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuramitz, H. Magnetic microbead-based electrochemical immunoassays. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.M.; Soda, N.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Magnetic nanomaterial–based electrochemical biosensors for the detection of diverse circulating cancer biomarkers. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 25, 100645–100652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masud, M.K.; Na, J.; Younus, M.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Bando, Y.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Yamauchi, Y. Superparamagnetic nanoarchitectures for disease-specific biomarker detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5717–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garkani Nejad, F.; Tajik, S.; Beitollahi, H.; Sheikhshoaie, I. Magnetic nanomaterials based electrochemical (bio)sensors for food analysis. Talanta 2021, 228, 122075–122097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollarasouli, F.; Zor, E.; Ozcelikay, G.; Ozkan, S.A. Magnetic nanoparticles in developing electrochemical sensors for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Talanta 2021, 226, 122108–122130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, I.M.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, W. Micro- and nano-magnetic particles for applications in biosensing. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfa, J.; Pupin, R.R.; Sotomayor, M.; Pividori, M.I. Magnetic-molecularly imprinted polymers in electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 6141–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barallat, J.; Olive-Monllau, R.; Gonzalo-Ruiz, J.; Ramirez-Satorras, R.; Munoz-Pascual, F.X.; Ortega, A.G.; Baldrich, E. Chronoamperometric magneto immunosensor for myeloperoxidase detection in human plasma based on a magnetic switch produced by 3D laser sintering. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9049–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, R.A.G.; Nicoliche, C.Y.N.; Pasqualeti, A.M.; Shimizu, F.M.; Ribeiro, I.R.; Melendez, M.E.; Carvalho, A.L.; Gobbi, A.L.; Faria, R.C.; Lima, R.S. Low-cost and rapid-production microfluidic electrochemical double-layer capacitors for fast and sensitive breast cancer diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12377–12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, P.; Afkhami, A.; Baradaran, B.; Halabian, R.; Madrakian, T.; Arduini, F.; Nguyen, T.A.; Bagheri, H. Well-orientation strategy for direct immobilization of antibodies: Development of the immunosensor using the boronic acid-modified magnetic graphene nanoribbons for ultrasensitive detection of lymphoma cancer cells. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11405–11412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setterington, E.B.; Alocilja, E.C. Electrochemical biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of magnetically extracted bacterial pathogens. Biosensors 2012, 2, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xue, Z.; Ye, X.; Liang, B. Magnetic immunosensor coupled to enzymatic signal for determination of genomic DNA methylation. Biosensors 2022, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Sun, T.; Liu, L.; Tian, L.; Sun, Z. Heterogeneous sensing of post-translational modification enzymes by integrating the advantage of homogeneous analysis. Talanta 2022, 237, 122949–122957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, Y.; Jin, Z.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.J.; Na, H.B.; Hyeon, T.; Oh, M.K.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.S. Sensitive and high-fidelity electrochemical immunoassay using carbon nanotubes coated with enzymes and magnetic nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3192–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santandreu, M.; Solé, S.; Fàbregas, E.; Alegret, S. Development of electrochemical immunosensing systems with renewable surfaces. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1998, 13, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinero-Fernandez, A.; Moreno-Guzman, M.; Lopez, M.A.; Escarpa, A. Magnetic bead-based electrochemical immunoassays on-drop and on-chip for procalcitonin determination: Disposable tools for clinical sepsis diagnosis. Biosensors 2020, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel, V.; Gamella, M.; Pingarron, J.M. Electrochemical bioplatforms for the simultaneous determination of interleukin (il)-8 mrna and il-8 protein oral cancer biomarkers in raw saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel, V.; Povedano, E.; Vargas, E.; Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Pedrero, M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarron, J.M. Comparison of different strategies for the development of highly sensitive electrochemical nucleic acid biosensors using neither nanomaterials nor nucleic acid amplification. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Campuzano, S.; Farchado-Dinia, M.; Barderas, R.; San Segundo-Acosta, P.; Montoya, J.J.; Pingarron, J.M. Fast electrochemical miRNAs determination in cancer cells and tumor tissues with antibody-functionalized magnetic microcarriers. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-San Martín, C.; Gamella, M.; Pedrero, M.; Montero-Calle, A.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Magnetic beads-based electrochemical immunosensing of hif-1α, a biomarker of tumoral hypoxia. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2020, 307, 127623–127630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel, V.; Povedano, E.; Benede, S.; Mata, L.; Galan-Malo, P.; Gamella, M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarron, J.M. Disposable amperometric immunosensor for the detection of adulteration in milk through single or multiplexed determination of bovine, ovine, or caprine immunoglobulins g. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11266–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povedano, E.; Montiel, V.R.; Valverde, A.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Pedrero, M.; Montero-Calle, A.; Barderas, R.; Pelaez-Garcia, A.; Mendiola, M.; et al. Versatile electroanalytical bioplatforms for simultaneous determination of cancer-related DNA 5-methyl- and 5-hydroxymethyl-cytosines at global and gene-specific levels in human serum and tissues. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Povedano, E.; Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel, V.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Rodriguez, N.; Dominguez, G.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarron, J.M. Determination of cadherin-17 in tumor tissues of different metastatic grade using a single incubation-step amperometric immunosensor. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11161–11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafín, V.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Batlle, M.; García de Frutos, P.; Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Comparative evaluation of the performance of electrochemical immunosensors using magnetic microparticles and nanoparticles. Application to the determination of tyrosine kinase receptor axl. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Guzman-Aranguez, A.; Poves, C.; Fernandez-Acenero, M.J.; Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel, V.; Dominguez, G.; Frutos, L.S.; Rodriguez, N.; Villalba, M.; et al. Toward liquid biopsy: Determination of the humoral immune response in cancer patients using halotag fusion protein-modified electrochemical bioplatforms. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12339–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho Mde, S.; Laube, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Alegret, S.; Pividori, M.I. Magneto immunoassays for plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 related to malaria based on magnetic nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5570–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, P.R.; Arévalo, F.J.; Vettorazzi, N.R.; Zón, M.A.; Fernández, H. Development of a very sensitive electrochemical magneto immunosensor for the direct determination of ochratoxin A in red wine. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2012, 162, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, S.; Gaiani, G.; Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M.; Turquet, J.; Sagrista, N.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Diogene, J.; et al. Addressing the analytical challenges for the detection of ciguatoxins using an electrochemical biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4858–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Vega, G.; Garcia-Robaina, A.; Ben Ismail, M.; Pasamar, H.; Garcia-Berrocoso, T.; Montaner, J.; Zourob, M.; Othmane, A.; Del Campo, F.J.; Baldrich, E. Detection of plasma mmp-9 within minutes. Unveiling some of the clues to develop fast and simple electrochemical magneto-immunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 115, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Wang, P.; Mao, H.; Hu, B.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Bian, X.; Jia, C.; Jing, F.; et al. Multi-nanomaterial electrochemical biosensor based on label-free graphene for detecting cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zhao, G.; Dou, W. Electrochemical sandwich immunoassay for Escherichia coli o157:H7 based on the use of magnetic nanoparticles and graphene functionalized with electrocatalytically active Au@Pt core/shell nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Su, B.; Tang, J.; Ren, J.; Chen, G. Nanoparticle-based sandwich electrochemical immunoassay for carbohydrate antigen 125 with signal enhancement using enzyme-coated nanometer-sized enzyme-doped silica beads. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Tang, D.; Niessner, R.; Chen, G.; Knopp, D. Magneto-controlled graphene immunosensing platform for simultaneous multiplexed electrochemical immunoassay using distinguishable signal tags. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5407–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanso, H.; Barthelmebs, L.; Inguimbert, N.; Noguer, T. Immunosensors for estradiol and ethinylestradiol based on new synthetic estrogen derivatives: Application to wastewater analysis. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemr, C.R.; Smith, S.J.; Liu, W.; Mepham, A.H.; Mohamadi, R.M.; Labib, M.; Kelley, S.O. Nanoparticle-mediated capture and electrochemical detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2847–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Keating, E.; Delerue-Matos, C. High-performance electrochemical immunomagnetic assay for breast cancer analysis. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2020, 308, 127667–127676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.J.; Wang, K.Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Wei, H.G.; Zhang, W.G.; Liu, W.S.; Wan, J.Y. Ferrocene-functionalized nanocomposites as signal amplification probes for electrochemical immunoassay of salmonella typhimurium. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Li, T.; Yang, M. Electrochemical immunoassay for the tumor marker CD25 by coupling magnetic sphere-based enrichment and DNA based signal amplification. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Keating, E.; Fernandes, V.C.; Delerue-Matos, C. Immunomagnetic bead-based bioassay for the voltammetric analysis of the breast cancer biomarker HER2-ecd and tumour cells using quantum dots as detection labels. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, J.C.; Kogan, M.R.; Tsai, Y.-J.; Luo, L.; Richards, I.; Crooks, R.M. Paper-based sensor for electrochemical detection of silver nanoparticle labels by galvanic exchange. ACS Sens. 2015, 1, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scida, K.; Cunningham, J.C.; Renault, C.; Richards, I.; Crooks, R.M. Simple, sensitive, and quantitative electrochemical detection method for paper analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6501–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.S.; Perez-Lopez, B.; Faria, R.C.; Mattoso, L.H.; Hernandez-Herrero, M.; Roig-Sagues, A.X.; Maltez-da Costa, M.; Merkoci, A. Electrochemical detection of salmonella using gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Escosura-Muniz, A.; Maltez-da Costa, M.; Sanchez-Espinel, C.; Diaz-Freitas, B.; Fernandez-Suarez, J.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, A.; Merkoci, A. Gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical magnetoimmunosensor for rapid detection of anti-hepatitis B virus antibodies in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Mayor, A.; Amor-Gutierrez, O.; Novelli, A.; Fernandez-Sanchez, M.T.; Costa-Garcia, A.; de la Escosura-Muniz, A. Bifunctional Au@Pt/Au core@shell nanoparticles as novel electrocatalytic tags in immunosensing: Application for alzheimer’s disease biomarker detection. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 7209–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Xiao, H.; Fang, C.; Zhao, F.; Chen, Z. Electrochemical immunosensor based on binary nanoparticles decorated rGO-tepa as magnetic capture and Au@PtNPs as probe for CEA detection. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yao, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, L. Nanosilver and DNA-functionalized immunosensing probes for electrochemical immunoassay of alpha-fetoprotein. Microchim. Acta 2009, 166, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yuan, R. Fe3o4nps mediated nonenzymatic electrochemical immunosensor for the total protein of nosema bombycis detection without addition of substrate. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7132–7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Wu, J.; Ju, H.; Wu, S. Ultrasensitive enzyme-free electrochemical immunosensor based on hybridization chain reaction triggered double strand DNA@Au nanoparticle tag. Talanta 2014, 120, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Yang, M. Electrochemical detection of circulating tumor cells based on DNA generated electrochemical current and rolling circle amplification. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11614–11619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Tang, D.; Niessner, R.; Chen, G.; Knopp, D. DNA-based hybridization chain reaction for amplified bioelectronic signal and ultrasensitive detection of proteins. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5392–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Gómez, R.; González-Robles, D.; Miranda-Castro, R.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. On the electrochemical detection of alpha-fetoprotein using aptamers: DNA isothermal amplification strategies to improve the performance of weak aptamers. Biosensors 2020, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Z.; Chen, M.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y. Recent advances of functional nucleic acids-based electrochemiluminescent sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 191, 113462–113479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Wu, D.; Sun, T.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhao, F.; Liu, L.; Yi, X. Magnetic bead-based electrochemical and colorimetric methods for the detection of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 with boronic acid derivatives as the signal probes. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2021, 327, 128913–128920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hason, S.; Pivonkova, H.; Vetterl, V.; Fojta, M. Label-free sequence-specific DNA sensing using copper-enhanced anodic stripping of purine bases at boron-doped diamond electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavallaie, R.; McCarroll, J.; Le Grand, M.; Ariotti, N.; Schuhmann, W.; Bakker, E.; Tilley, R.D.; Hibbert, D.B.; Kavallaris, M.; Gooding, J.J. Nucleic acid hybridization on an electrically reconfigurable network of gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles enables microRNA detection in blood. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wu, Y.; Hoque, S.; Tilley, R.D.; Gooding, J.J. Rapid and ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of circulating tumor DNA by hybridization on the network of gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 5196–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povedano, E.; Valverde, A.; Montiel, V.R.; Pedrero, M.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; Barderas, R.; San Segundo-Acosta, P.; Pelaez-Garcia, A.; Mendiola, M.; Hardisson, D.; et al. Rapid electrochemical assessment of tumor suppressor gene methylations in raw human serum and tumor cells and tissues using immunomagnetic beads and selective DNA hybridization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8194–8198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Liu, B.; Leng, J.; Ma, X. Electrochemical determination of the activity of DNA methyltransferase based on the methyl binding domain protein and a customized modular detector. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, S.; Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Lopez-Hernandez, E.; Conzuelo, F.; Granados, R.; Sanchez-Puelles, J.M.; Pingarron, J.M. Magnetobiosensors based on viral protein p19 for microRNA determination in cancer cells and tissues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 6168–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel, V.; Gutierrez, M.L.; Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Povedano, E.; Vargas, E.; Reviejo, A.J.; Linacero, R.; Gallego, F.J.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarron, J.M. Disposable amperometric polymerase chain reaction-free biosensor for direct detection of adulteration with horsemeat in raw lysates targeting mitochondrial DNA. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9474–9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povedano, E.; Ruiz-Valdepenas Montiel, V.; Gamella, M.; Pedrero, M.; Barderas, R.; Pelaez-Garcia, A.; Mendiola, M.; Hardisson, D.; Feliu, J.; Yanez-Sedeno, P.; et al. Amperometric bioplatforms to detect regional DNA methylation with single-base sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 5604–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, W.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Fu, F. A novel electrically magnetic-controllable electrochemical biosensor for the ultra sensitive and specific detection of attomolar level oral cancer-related microRNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojta, M.; Havran, L.; Vojtiskova, M.; Palecek, E. Electrochemical detection of DNA triplet repeat expansion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6532–6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.M.; Trau, M. Direct enhanced detection of multiple circulating tumor DNA variants in unprocessed plasma by magnetic-assisted bioelectrocatalytic cycling. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3217–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, D.; Zhen, S.; Lu, K.; Yi, X.; Sun, Z. Electrochemical detection of telomerase in cancer cells based on the in-situ formation of streptavidin-biotin-DNA-biotin networks for signal amplification. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2021, 334, 129659–129665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Chen, G.; Yang, H.; Tang, D. Proximity ligation assay with three-way junction-induced rolling circle amplification for ultrasensitive electronic monitoring of concanavalin a. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7773–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Weng, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Lu, Q.; Yan, X.; Sakran, M.A.; Hong, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, X. A label-free electrochemical magnetic aptasensor based on exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification for determination of carcinoembryonic antigen. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, D.Z.; Cai, S.X.; Chen, M.; Xia, Y.K.; Wu, F.; Chen, J.H. An immobilization-free electrochemical impedance biosensor based on duplex-specific nuclease assisted target recycling for amplified detection of microRNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Li, C.C.; Zhang, C.Y. Label-free and immobilization-free electrochemical magnetobiosensor for sensitive detection of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in genomic DNA. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Lin, H.; Zhou, H.; Hao, T.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Z. A CRISPR/Cas12a-mediated dual-mode electrochemical biosensor for polymerase chain reaction-free detection of genetically modified soybean. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 14885–14891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
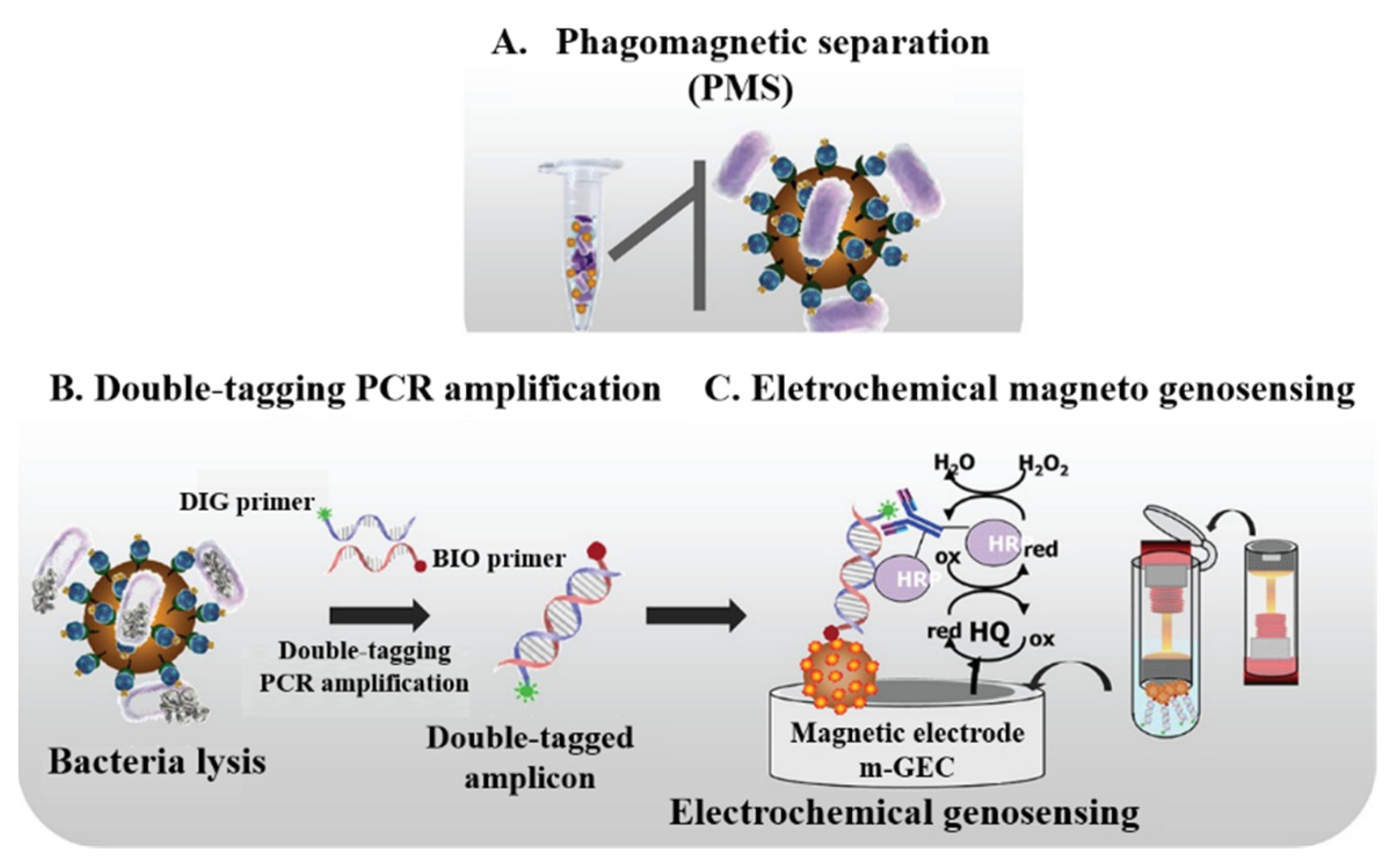
- Liebana, S.; Spricigo, D.A.; Cortes, M.P.; Barbe, J.; Llagostera, M.; Alegret, S.; Pividori, M.I. Phagomagnetic separation and electrochemical magneto-genosensing of pathogenic bacteria. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3079–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebana, S.; Lermo, A.; Campoy, S.; Barbe, J.; Alegret, S.; Pividori, M.I. Magneto immunoseparation of pathogenic bacteria and electrochemical magneto genosensing of the double-tagged amplicon. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5812–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Gan, X.; Jiang, B.; Yuan, R.; Xiang, Y. Electrode immobilization-free and sensitive electrochemical sensing of thrombin via magnetic nanoparticle-decorated DNA polymers. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2021, 331, 129395–129401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Campuzano, S.; Montiel, V.R.; Montoya, J.J.; Pingarron, J.M. Sensitive electrochemical determination of miRNAs based on a sandwich assay onto magnetic microcarriers and hybridization chain reaction amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.J.; Wu, Z.; Yang, X.Y.; Pang, D.W.; Zhang, Z.L. Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 with wide linear dynamic range based on dual signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Burciu, B.; Filipe, C.D.M.; Li, Y.; Dellinger, K.; Didar, T.F. DNAzyme-based biosensors: Immobilization strategies, applications, and future prospective. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 13943–13969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, E.M.; Cozma, I.; Mou, Q.; Brennan, J.D.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y. Biosensing with dnazymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8954–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.; Li, X.; Lu, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, X.; Li, B.; Sakran, M.; Hong, J.; Zhu, W.; et al. A label-free electrochemical biosensor based on magnetic biocomposites with DNAzyme and hybridization chain reaction dual signal amplification for the determination of Pb(2). Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Man, Y.; Li, A.; Jin, X.; Liu, X.; Pan, L. DNAzyme-based biosensor for detection of lead ion: A review. Microchem. J. 2017, 131, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Fu, L.; Xu, M.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, G.; Tang, D. DNAzyme-based magneto-controlled electronic switch for picomolar detection of lead (ii) coupling with DNA-based hybridization chain reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 45, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Purohit, B.; Maurya, P.K.; Pandey, L.M.; Chandra, P. Engineered nanomaterial assisted signal-amplification strategies for enhancing analytical performance of electrochemical biosensors. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1615–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Shorie, M. Nanomaterial based aptasensors for clinical and environmental diagnostic applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 2123–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azzouz, A.; Hejji, L.; Sonne, C.; Kim, K.H.; Kumar, V. Nanomaterial-based aptasensors as an efficient substitute for cardiovascular disease diagnosis: Future of smart biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 193, 113617–113634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H. Functional nanomaterials and nanoprobes for amplified biosensing. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 10, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Yin, Y.; Du, S.-M.; Kong, L.-Q.; Chai, Y.-Q.; Li, Z.-H.; Yuan, R. Dual 3D DNA nanomachine-mediated catalytic hairpin assembly for ultrasensitive detection of MicroRNA. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13952–13959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Tang, H.; Wu, D.; Xia, Y.; Wu, M.; Yi, X.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Amplified voltammetric detection of miRNA from serum samples of glioma patients via combination of conducting magnetic microbeads and ferrocene-capped gold nanoparticle/streptavidin conjugates. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.-P.; Zhao, R.-J.; Feng, Z.; Wang, M.-Y.; Ma, R.-N.; Jia, W.-L.; Shang, L.; Zhang, W.; Xue, Q.-W.; Wang, H.-S. Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of circulating tumor DNA by hollow polymeric nanospheres and dual enzyme assisted target amplification strategy. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2022, 350, 130849–130857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Polsky, R. Magnetically-induced solid-state electrochemical detection of DNA hybridization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4208–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhu, Q. Indium microrod tags for electrochemical detection of DNA hybridization. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6218–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Scida, K.; Crooks, R.M. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA with a paper electrochemical sensor. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9009–9015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, N.; Wu, D.; Yu, H.; Sun, W.; Yi, X.; Liu, L. Magnetic bead-based electrochemical and colorimetric assays of circulating tumor cells with boronic acid derivatives as the recognition elements and signal probes. Talanta 2021, 221, 121640–121647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Battig, M.R.; Wang, Y. Aptamer-based molecular recognition for biosensor development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliuk, A.B.; Hu, L.; Tao, W.A. Aptamer in bioanalytical applications. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4440–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.S.; Raston, N.H.; Gu, M.B. Aptamer-based nanobiosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 2–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, A.K.; Sen, D.; Yu, H.Z. Design and testing of aptamer-based electrochemical biosensors for proteins and small molecules. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 77, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Guo, Z.; Tang, Y. Voltammetric determination of tumor necrosis factor-α based on the use of an aptamer and magnetic nanoparticles loaded with gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 3901–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.; Tang, Y.; Wang, L. DNA modified Fe3O4@Au magnetic nanoparticles as selective probes for simultaneous detection of heavy metal ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3940–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centi, S.; Tombelli, S.; Minunni, M.; Mascini, M. Aptamer-based detection of plasma proteins by an electrochemical assay coupled to magnetic beads. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centi, S.; Messina, G.; Tombelli, S.; Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Different approaches for the detection of thrombin by an electrochemical aptamer-based assay coupled to magnetic beads. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1602–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya-González, S.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.S. Aptamer binding to celiac disease-triggering hydrophobic proteins: A sensitive gluten detection approach. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 2733–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Callaway, Z.; Lum, J.; Wang, R.; Lin, J.; Li, Y. Exploiting enzyme catalysis in ultra-low ion strength media for impedance biosensing of avian influenza virus using a bare interdigitated electrode. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1965–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, B.; Xu, L.; Jiang, B.; Yuan, R.; Xiang, Y. Aptamer-functionalized and gold nanoparticle array-decorated magnetic graphene nanosheets enable multiplexed and sensitive electrochemical detection of rare circulating tumor cells in whole blood. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10792–10799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cui, L.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, F.; Ke, W. Ag/cdo np-engineered magnetic electrochemical aptasensor for prostatic specific antigen detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 3474–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Shen, H.Y.; Su, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, T.; Gan, N. Microfluidic chip for multiplex detection of trace chemical contaminants based on magnetic encoded aptamer probes and multibranched DNA nanostructures as signal tags. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2131–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Gu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Qin, W. DNA nanostructure-based magnetic beads for potentiometric aptasensing. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6465–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
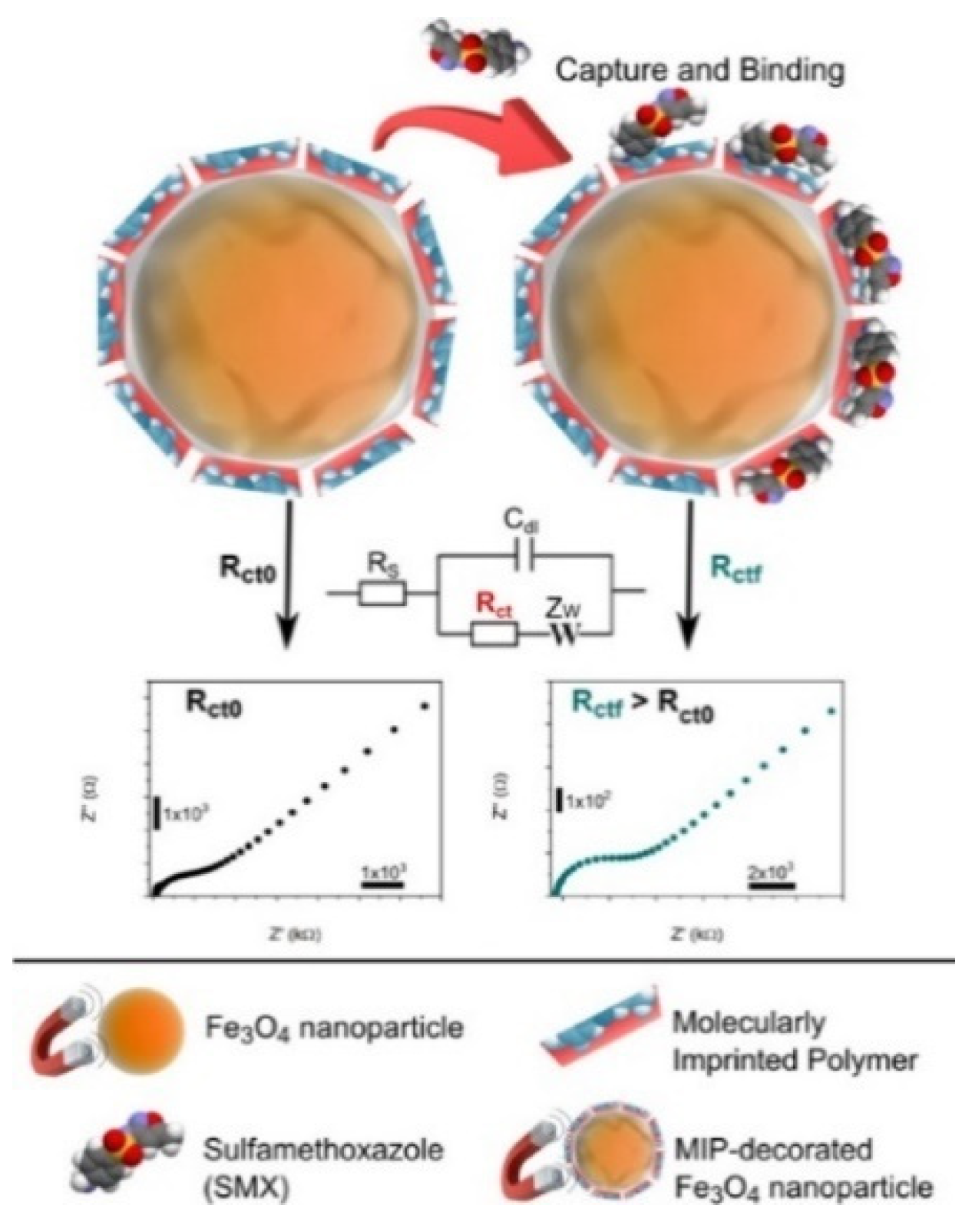
- Dinc, M.; Esen, C.; Mizaikoff, B. Recent advances on core–shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for biomacromolecules. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 114, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S. Application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer as a versatile and highly selective tool in food and environmental analysis: Recent developments and trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 90, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Karimi, M. Recent configurations and progressive uses of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for drug analysis. Talanta 2017, 167, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Galvez, A.; Ait-Lahcen, A.; Mercante, L.A.; Morales-Narvaez, E.; Amine, A.; Merkoci, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer-decorated magnetite nanoparticles for selective sulfonamide detection. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3578–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D. Homogeneous assays using aptamers. Analyst 2011, 136, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-T.; Cai, L.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.-X. Immobilization-free DNA-based homogeneous electrochemical biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Jiao, X.; Chen, D. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for ca 15-3 using thionine-nanoporous gold-graphene as a platform and horseradish peroxidase-encapsulated liposomes as signal amplification. Analyst 2012, 137, 4440–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi-Badiki, T.; Alipour, E.; Hamishehkar, H.; Golabi, S.M. Dopamine-loaded liposome and its application in electrochemical DNA biosensor. J. Biomater. Appl. 2016, 31, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Li, F. Nucleic acid-functionalized metal-organic framework-based homogeneous electrochemical biosensor for simultaneous detection of multiple tumor biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3604–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganganboina, A.B.; Chowdhury, A.D.; Khoris, I.M.; Nasrin, F.; Takemura, K.; Hara, T.; Abe, F.; Suzuki, T.; Park, E.Y. Dual modality sensor using liposome-based signal amplification technique for ultrasensitive norovirus detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 157, 112169–112176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, F.; He, P. Magneto-mediated electrochemical sensor for simultaneous analysis of breast cancer exosomal proteins. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 5404–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, J.; Xie, B.; Li, T.; Yang, M. Electrochemical assay for analysis of circulation tumor cells based on isolation of the cell with magnetic nanoparticles and reaction of DNA with molybdate. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.Y.; Wu, Z.; Xu, C.M.; Zhang, L.; Feng, J.; Pang, D.W.; Zhang, Z.L. One-to-many single entity electrochemistry biosensing for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Chen, F.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wen, W.; Wang, S. Single-particle electrochemical biosensor with DNA walker amplification for ultrasensitive HIV-DNA counting. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4506–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Feng, W.; Lin, L.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, G.; He, P.; Fang, Y. A new amplification strategy for ultrasensitive electrochemical aptasensor with network-like thiocyanuric acid/gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, D.; Smith, J.N.; Timchalk, C.; Lin, Y. Magnetic electrochemical sensing platform for biomonitoring of exposure to organophosphorus pesticides and nerve agents based on simultaneous measurement of total enzyme amount and enzyme activity. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3770–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosi, A.; Castaneda, M.T.; Killard, A.J.; Smyth, M.R.; Alegret, S.; Merkoci, A. Double-codified gold nanolabels for enhanced immunoanalysis. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 5232–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Kawde, A.N.; Polsky, R. Metal nanoparticle-based electrochemical stripping potentiometric detection of DNA hybridization. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5576–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical quantification of single-nucleotide polymorphisms using nanoparticle probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10394–10401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Timchalk, C.; Lin, Y. Magnetic electrochemical immunoassays with quantum dot labels for detection of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase in plasma. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8477–8484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.M.; Wang, L.L.; Luo, J.; Wei, Q.L. A dual-amplified electrochemical detection of mrna based on duplex-specific nuclease and bio-bar-code conjugates. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, K.; Ganganboina, A.B.; Khoris, I.M.; Chowdhury, A.D.; Park, E.Y. Plasmon nanocomposite-enhanced optical and electrochemical signals for sensitive virus detection. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, B.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Quantum dot layer-by-layer assemblies as signal amplification labels for ultrasensitive electronic detection of uropathogens. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4302–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qian, J.; An, K.; Huang, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Q.; Hao, N.; Wang, K. Magneto-controlled aptasensor for simultaneous electrochemical detection of dual mycotoxins in maize using metal sulfide quantum dots coated silica as labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Gan, N.; Zhang, H.; Li, T.; Qiao, L.; Cao, Y.; Su, X.; Jiang, S. Simultaneous electrochemical immunoassay using graphene-Au grafted recombinant apoferritin-encoded metallic labels as signal tags and dual-template magnetic molecular imprinted polymer as capture probes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Merkoci, A. Electrochemical coding technology for simultaneous detection of multiple DNA targets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3214–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Kim, J.; Jan, M.R.; Collins, G.E. Electrochemical coding for multiplexed immunoassays of proteins. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 7126–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.Y.; Xu, B.Y.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Simultaneous electrochemical immunoassay using CdS/DNA and pbs/DNA nanochains as labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, A.; Norouz-Sarvestani, F.; Noori, A.; Soltani, N. Aptamer-conjugated silver nanoparticles for electrochemical dual-aptamer-based sandwich detection of staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yu, X.; Han, B.; Dong, L.; Xu, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, J. In situ programmable DNA circuit-promoted electrochemical characterization of stemlike phenotype in breast cancer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16078–16086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Inoue, K.Y.; Ino, K.; Shiku, H. Highly sensitive electrochemical immunoassay using signal amplification of the coagulation cascade. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 12427–12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q. A dual-channel homogeneous aptasensor combining colorimetric with electrochemical strategy for thrombin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 120, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q. Ultrasensitive label-free homogeneous electrochemical aptasensor based on sandwich structure for thrombin detection. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 267, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dequaire, M.; Degrand, C.; Limoges, B. An immunomagnetic electrochemical sensor based on a perfluorosulfonate-coated screen-printed electrode for the determination of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2571–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.; Deng, R.; Liu, Q.; Xia, J.; Wang, Z. DNA synergistic enzyme-mediated cascade reaction for homogeneous electrochemical bioassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111510–111515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fojta, M.; Kostecka, P.; Trefulka, M.; Havran, L.; Palecek, E. “Multicolor” electrochemical labeling of DNA hybridization probes with osmium tetroxide complexes. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Zhuo, Y.; Yuan, R.; Chai, Y.Q. Highly effective protein converting strategy for ultrasensitive electrochemical assay of cystatin C. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5189–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Chen, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C.; Shen, Q. Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of tumor exosomes based on aptamer recognition-induced multi-DNA release and cyclic enzymatic amplification. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4507–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, M.; Xie, S.; Cai, W.; Tang, D.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, R. Click chemistry reaction-triggered 3D DNA walking machine for sensitive electrochemical detection of copper ion. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11439–11445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.; Miao, P. Bipedal DNA walker based electrochemical genosensing strategy. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4953–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Quan, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H. DNA walker induced “signal off” electrochemical cytosensor strategy for ultrasensitive detection of tumor cells. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2022, 366, 132021–132029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Bi, S.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J.; Zhang, F. In situ growth of three-dimensional graphene films for signal-on electrochemical biosensing of various analytes. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10667–10674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.; Lu, Y.; Osman, E.; Saxena, S.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, S.; Pollinzi, A.; Smieja, M.; Li, Y.; Soleymani, L.; et al. DNAzyme-immobilizing microgel magnetic beads enable rapid, specific, culture-free, and wash-free electrochemical quantification of bacteria in untreated urine. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Q.; Gao, Y.; Gu, H.W.; Meng, X.Z.; Yi, H.C.; Chen, Y.; Sun, W.Y. Target-induced activation of DNAzyme for sensitive detection of bleomycin by using a simple MOF-modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113034–113039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Bo, B.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, J. Programmable DNA-fueled electrochemical analysis of lung cancer exosomes. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 8748–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Qi, H.; Chang, J.; Gai, P.; Li, F. Recent progress in homogeneous electrochemical sensors and their designs and applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 156, 116712–116726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yin, X.; An, B.; Li, F. Precise capture and direct quantification of tumor exosomes via a highly efficient dual-aptamer recognition-assisted ratiometric immobilization-free electrochemical strategy. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lei, C.; Guo, L.; Zhou, Y. Sandwich immunoassay for the prostate specific antigen using a micro-fluxgate and magnetic bead labels. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premaratne, G.; Niroula, J.; Patel, M.K.; Zhong, W.; Suib, S.L.; Kalkan, A.K.; Krishnan, S. Electrochemical and surface-plasmon correlation of a serum-autoantibody immunoassay with binding insights: Graphenyl surface versus mercapto-monolayer surface. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12456–12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, N.; Gonzaga, Z.J.; Chen, S.; Koo, K.M.; Nguyen, N.T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Rehm, B.H.A. Bioengineered polymer nanobeads for isolation and electrochemical detection of cancer biomarkers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 31418–31430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lillehoj, P.B. Ultrafast electrothermal flow-enhanced magneto biosensor for highly sensitive protein detection in whole blood. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200206–e202200214. [Google Scholar]
- Sadasivam, M.; Sakthivel, A.; Nagesh, N.; Hansda, S.; Veerapandian, M.; Alwarappan, S.; Manickam, P. Magnetic bead-amplified voltammetric detection for carbohydrate antigen 125 with enzyme labels using aptamer-antigen-antibody sandwiched assay. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2020, 312, 127985–127993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Guo, W.J.; Bai, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Pang, D.W.; Zhang, Z.L. Digital single virus electrochemical enzyme-linked immunoassay for ultrasensitive h7n9 avian influenza virus counting. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.K.; Vaze, A.; Shen, M.; Rusling, J.F. High-throughput electrochemical microfluidic immunoarray for multiplexed detection of cancer biomarker proteins. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malhotra, R.; Patel, V.; Chikkaveeraiah, B.V.; Munge, B.S.; Cheong, S.C.; Zain, R.B.; Abraham, M.T.; Dey, D.K.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Ultrasensitive detection of cancer biomarkers in the clinic by use of a nanostructured microfluidic array. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 6249–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fapyane, D.; Nielsen, J.S.; Ferapontova, E.E. Electrochemical enzyme-linked sandwich assay with a cellulase label for ultrasensitive analysis of synthetic DNA and cell-isolated rna. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Huang, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, H. Magnetic gold nanocomposite and aptamer assisted triple recognition electrochemical immunoassay for determination of brain natriuretic peptide. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Hailin, T.; Yi, X.; Wang, J. Three-dimensional DNA nanomachine combined with toehold-mediated strand displacement reaction for sensitive electrochemical detection of mirna. Langmuir 2020, 36, 10708–10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yan, H.; Wu, Z.; Wen, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Magnetic nanobeads and de novo growth of electroactive polymers for ultrasensitive microRNA detection at the cellular level. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriachek, K.; Masud, M.K.; Palma, C.; Phan, H.P.; Yamauchi, Y.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Nguyen, N.T.; Salomon, C.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Avoiding pre-isolation step in exosome analysis: Direct isolation and sensitive detection of exosomes using gold-loaded nanoporous ferric oxide nanozymes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3827–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reta, N.; Michelmore, A.; Saint, C.; Prieto-Simon, B.; Voelcker, N.H. Porous silicon membrane-modified electrodes for label-free voltammetric detection of ms2 bacteriophage. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, L.; Shao, X.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y. An electrochemical biosensor based on nucleic acids enzyme and nanochannels for detecting copper (ii) ion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 120, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, Y.; He, Y.; Fang, W.; Ying, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y. Cooperation mode of outer surface and inner space of nanochannel: Separation-detection system based on integrated nanochannel electrode for rapid and facile detection of salmonella. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xing, Y.; Li, G.; Deng, D.; Liu, L. Overview on the Design of Magnetically Assisted Electrochemical Biosensors. Biosensors 2022, 12, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110954
Chang Y, Wang Y, Zhang J, Xing Y, Li G, Deng D, Liu L. Overview on the Design of Magnetically Assisted Electrochemical Biosensors. Biosensors. 2022; 12(11):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110954
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yong, Yanyan Wang, Jingyi Zhang, Yuejiao Xing, Gang Li, Dehua Deng, and Lin Liu. 2022. "Overview on the Design of Magnetically Assisted Electrochemical Biosensors" Biosensors 12, no. 11: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110954
APA StyleChang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Xing, Y., Li, G., Deng, D., & Liu, L. (2022). Overview on the Design of Magnetically Assisted Electrochemical Biosensors. Biosensors, 12(11), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12110954






