Folic Acid-Modified Fluorescent-Magnetic Nanoparticles for Efficient Isolation and Identification of Circulating Tumor Cells in Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
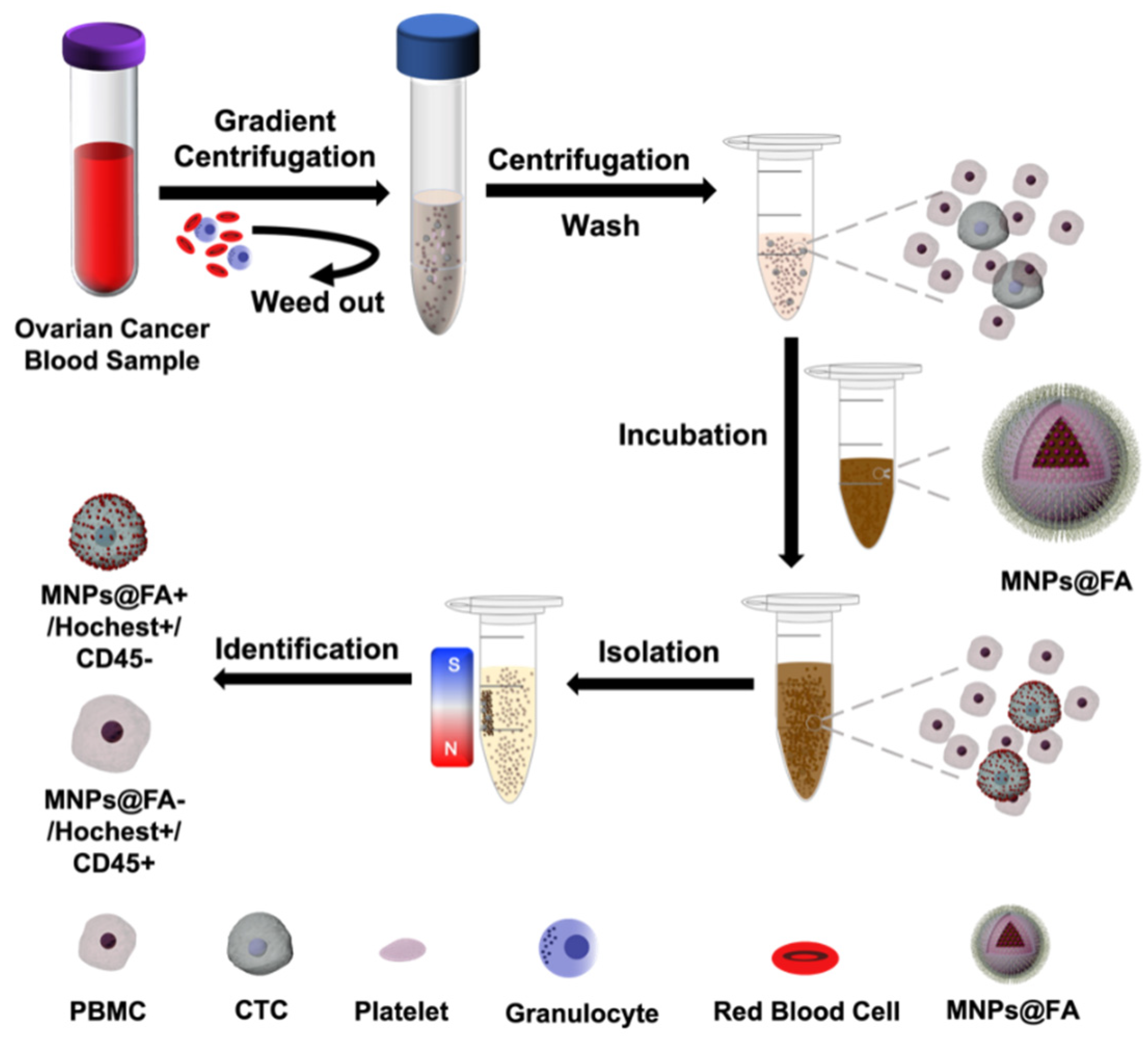
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Cells Culture
2.2. Preparation of FA-Modified Fluorescent-Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.2.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles (MNPs)
2.2.2. Preparation of Fluorescent-Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs@QD)
2.2.3. Fabrication of Functionalized Hydrogel MNPs (MNPs@hydrogel)
2.2.4. Synthesis of MNPs@FA
2.3. Characterization of Nanoparticles and Captured Cells
2.4. Exploration of Capture Performance
2.4.1. Investigation of Optimum Capture Conditions
2.4.2. Flow Cytometric Analysis and Western Blotting
2.4.3. Verification of Capture Specificity
2.4.4. Cell Viability Analyses of Captured Tumor Cells
2.4.5. Capture of Rare Cells
2.5. CTC Isolation of Ovarian Cancer Patient Peripheral Blood Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of MNPs@FA
3.2. Cell Capture Performance of MNPs@FA
3.3. Capture Sensitivity Test of MNPs@FA
3.4. CTC Detection from OC Patient Blood Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asante, D.B.; Calapre, L.; Ziman, M.; Meniawy, T.M.; Gray, E.S. Liquid biopsy in ovarian cancer using circulating tumor DNA and cells: Ready for prime time? Cancer Lett. 2020, 468, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lheureux, S.; Gourley, C.; Vergote, I.; Oza, A.M. Epithelial ovarian cancer. Lancet 2019, 393, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pokhriyal, R.; Hariprasad, R.; Kumar, L.; Hariprasad, G. Chemotherapy resistance in advanced ovarian cancer patients. Biomark. Cancer 2019, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Wu, A.; Chen, X. Current detection technologies for circulating tumor cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2038–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankó, P.; Lee, S.Y.; Nagygyörgy, V.; Zrínyi, M.; Chae, C.H.; Cho, D.H.; Telekes, A. Technologies for circulating tumor cell separation from whole blood. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franses, J.W.; Philipp, J.; Missios, P.; Bhan, I.; Liu, A.; Yashaswini, C.; Tai, E.; Zhu, H.; Ligorio, M.; Nicholson, B.; et al. Pancreatic circulating tumor cell profiling identifies LIN28B as a metastasis driver and drug target. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Meng, Q.F.; Huang, Q.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Yu, G.T.; Li, A.; Ma, W.J.; Zhang, N.G.; Guo, S.S.; Zhao, X.Z.; et al. Platelet-leukocyte hybrid membrane-coated immunomagnetic beads for highly efficient and highly specific isolation of circulating tumor cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, A.; Bott, H.; Malek, N.P.; Zengerle, R.; Maucher, T.; Hoffmann, J. Real-time detection of tumor cells during capture on a filter element significantly enhancing detection rate. Biosensors 2021, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, E.; Rothwell, D.G.; Brady, G.; Dive, C. Liquid biopsy-based biomarkers of treatment response and resistance. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Yu, V.; Garon, E.B.; Goldman, J.W.; Di Carlo, D. Biophysical isolation and identification of circulating tumor cells. Lab. Chip 2017, 17, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, Z.; He, R.; Wen, D.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y. A 3D graphene oxide microchip and an Au-enwrapped silica nanocomposite-based supersandwich cytosensor toward capture and analysis of circulating tumor cells. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16354–16360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Wang, S.Q.; Ou, G.Y.; Li, Y.; Ruan, H.M.; Li, Z.H.; Ma, Y.Y.; Zou, R.F.; Qiu, J.Y.; Shen, Z.Y.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells based on improved SERS-active magnetic nanoparticles. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 2918–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Wang, Y.; Oliver, C.R.; Thamm, D.H.; Cooling, L.; Paoletti, C.; Smith, K.J.; Nagrath, S.; Hayes, D.F. A temporary indwelling intravascular aphaeretic system for in vivo enrichment of circulating tumor cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Wuethrich, A.; Wang, J.; Korbie, D.; Lin, L.L.; Trau, M. Dynamic monitoring of EMT in CTCs as an indicator of cancer metastasis. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16787–16795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Ding, P.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Q.; Pei, R. Isolation of DNA aptamers targeting N-cadherin and high-efficiency capture of circulating tumor cells by using dual aptamers. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 22574–22585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Abafogi, A.T.; Ponnuvelu, D.V.; Song, I.; Ko, K.; Park, S. Enhanced luminescent detection of circulating tumor cells by a 3D printed immunomagnetic concentrator. Biosensors 2021, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamloo, A.; Ahmad, S.; Momeni, M. Design and parameter study of integrated microfluidic platform for CTC isolation and enquiry; A Numerical Approach. Biosensors 2018, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Li, R.; Huang, B.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wei, X.; Heng, C.; Liu, W.; Yu, M.; Guo, S.S.; et al. TiO2 nanopillar arrays coated with gelatin film for efficient capture and undamaged release of circulating tumor cells. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 335101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ge, C.; Liang, W.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Ma, W.; Shi, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. In vivo enrichment and elimination of circulating tumor cells by using a black phosphorus and antibody functionalized intravenous catheter. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Feng, X.; Yang, S.; Xu, H.; Yin, X.; Yu, Y. Capture, detection, and simultaneous identification of rare circulating tumor cells based on a rhodamine 6G-loaded metal-organic framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 52406–52416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Fan, C.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Y. Bioinspired DNA nanointerface with anisotropic aptamers for accurate capture of circulating tumor cells. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Samy, S.; Oliveira, M.I.; Pereira-Veiga, T.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; Carvalho, S.; Gaspar, J.; Freitas, P.P.; López-López, R.; Costa, C.; Diéguez, L. Fast and efficient microfluidic cell filter for isolation of circulating tumor cells from unprocessed whole blood of colorectal cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, C.; Levermann, J.; Neves, R.P.L.; Liffers, S.T.; Kuhlmann, J.D.; Buderath, P.; Kimmig, R.; Kasimir-Bauer, S. Image-based identification and genomic analysis of single circulating tumor cells in high grade serous ovarian cancer patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Han, L.; Yang, L.; Xu, T.; He, J.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yu, X.; Jia, L. Natural Fish Trap-Like Nanocage for Label-Free Capture of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2002259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.W.; Sun, H.; Jiang, W.N.; Xu, T.; Song, B.; Peng, R.L.; Han, L.L.; Jia, L.Y. A Chemical Method for Specific Capture of Circulating Tumor Cells Using Label-Free Polyphenol-Functionalized Films. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 4372–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, N.; Liu, H.; Chen, C.; Ding, P.; Yue, X.; Zou, H.; Xing, C.; Pei, R. High-efficiency isolation and rapid identification of heterogeneous circulating tumor cells (CTCs) using dual-antibody-modified fluorescent-magnetic nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 39586–39593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Sun, N.; Cao, Y.; Cai, X.; Yuan, F.; Zou, H.; Xing, C.; Pei, R. Antifouling hydrogel-coated magnetic nanoparticles for selective isolation and recovery of circulating tumor cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Hu, M.; Zhu, W.; Sun, N.; Pei, R. Tannic acid (TA)-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for EpCAM-independent circulating tumor cell (CTC) isolation from patients with different cancers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 3694–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Li, F.; Huang, X.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Wang, Y.A.; Xiong, Y.; Fu, F.; Xu, H. Folic acid targeting for efficient isolation and detection of ovarian cancer CTCs from human whole blood based on two-step binding strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14055–14062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhao, Y.W.; Cao, Y.; Ding, P.; Liu, H.; Su, N.; Pei, R.J. A folic acid modified polystyrene nanosphere surface for circulating tumor cell capture. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 5718–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C. Folate based radiopharmaceuticals for imaging and therapy of cancer and inflammation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1058–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, C.; Palaia, I.; Giorgini, M.; De Medici, C.; Iadarola, R.; Vertechy, L.; Domenici, L.; Di Donato, V.; Tomao, F.; Muzii, L.; et al. Targeted drug delivery via folate receptors in recurrent ovarian cancer: A review. OncoTargets Ther. 2014, 7, 1223–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Yu, M.; Ma, W.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. Fe3O4/PVIM-Ni2+ magnetic composite microspheres for highly specific separation of histidine-rich proteins. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 8836–8844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ding, P.; Gao, T.; Li, Q.; Hu, M.; Zhu, W.; Pei, R. A PLGA nanofiber microfluidic device for highly efficient isolation and release of different phenotypic circulating tumor cells based on dual aptamers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2212–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Low, P.S. Immunotherapy of folate receptor-expressing tumors: Review of recent advances and future prospects. J. Control Release 2003, 91, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Diao, Z.; Shu, D.; Guo, P.; Shen, G. Evaluation of specific delivery of chimeric phi29 pRNA/siRNA nanoparticles to multiple tumor cells. Mol. Biosyst. 2009, 5, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viola-Villegas, N.; Rabideau, A.E.; Cesnavicious, J.; Zubieta, J.; Doyle, R.P. Targeting the folate receptor (FR): Imaging and cytotoxicity of ReI conjugates in FR-overexpressing cancer cells. Chem. Med. Chem. 2008, 3, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.E.; Karve, S.; Sukumar, R.; Cummings, N.D.; Copp, J.A.; Chen, R.C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, A.Z. Folate-targeted nanoparticle delivery of chemo- and radiotherapeutics for the treatment of ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8548–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.E.; Pinkney, M.; Piggott, N.H.; Calvert, H.; Milton, I.D.; Lunec, J. A novel monoclonal antibody for detection of folate receptor alpha in paraffin-embedded tissues. Hybridoma 2007, 26, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.L.; Xu, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.F. Magnetic particles as promising circulating tumor cell catchers assisting liquid biopsy in cancer diagnosis: A review. Trend. Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, M.; Cai, H.; He, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Nondestructive capture, release, and detection of circulating tumor cells with cystamine-mediated folic acid decorated magnetic nanospheres. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 9971–9979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Bardia, A.; Aceto, N.; Bersani, F.; Madden, M.W.; Donaldson, M.C.; Desai, R.; Zhu, H.; Comaills, V.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Ex vivo culture of circulating breast tumor cells for individualized testing of drug susceptibility. Science 2014, 345, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Amidi, E.; Zhu, Q. Photoacoustic tomography reconstruction using lag-based delay multiply and sum with a coherence factor improves in vivo ovarian cancer diagnosis. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 2250–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhou, T.; Wu, Z.; Ding, P.; Sun, N.; Liu, L.; Pei, R.; Zhu, W. Folic Acid-Modified Fluorescent-Magnetic Nanoparticles for Efficient Isolation and Identification of Circulating Tumor Cells in Ovarian Cancer. Biosensors 2022, 12, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030184
Pan Y, Wang Z, Ma J, Zhou T, Wu Z, Ding P, Sun N, Liu L, Pei R, Zhu W. Folic Acid-Modified Fluorescent-Magnetic Nanoparticles for Efficient Isolation and Identification of Circulating Tumor Cells in Ovarian Cancer. Biosensors. 2022; 12(3):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030184
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yue, Zhili Wang, Jialing Ma, Tongping Zhou, Zeen Wu, Pi Ding, Na Sun, Lifen Liu, Renjun Pei, and Weipei Zhu. 2022. "Folic Acid-Modified Fluorescent-Magnetic Nanoparticles for Efficient Isolation and Identification of Circulating Tumor Cells in Ovarian Cancer" Biosensors 12, no. 3: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030184
APA StylePan, Y., Wang, Z., Ma, J., Zhou, T., Wu, Z., Ding, P., Sun, N., Liu, L., Pei, R., & Zhu, W. (2022). Folic Acid-Modified Fluorescent-Magnetic Nanoparticles for Efficient Isolation and Identification of Circulating Tumor Cells in Ovarian Cancer. Biosensors, 12(3), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12030184




