Temperature Distribution of Vessel Tissue by High Frequency Electric Welding with Combination Optical Measure and Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vessel Tissue Welding Experiment
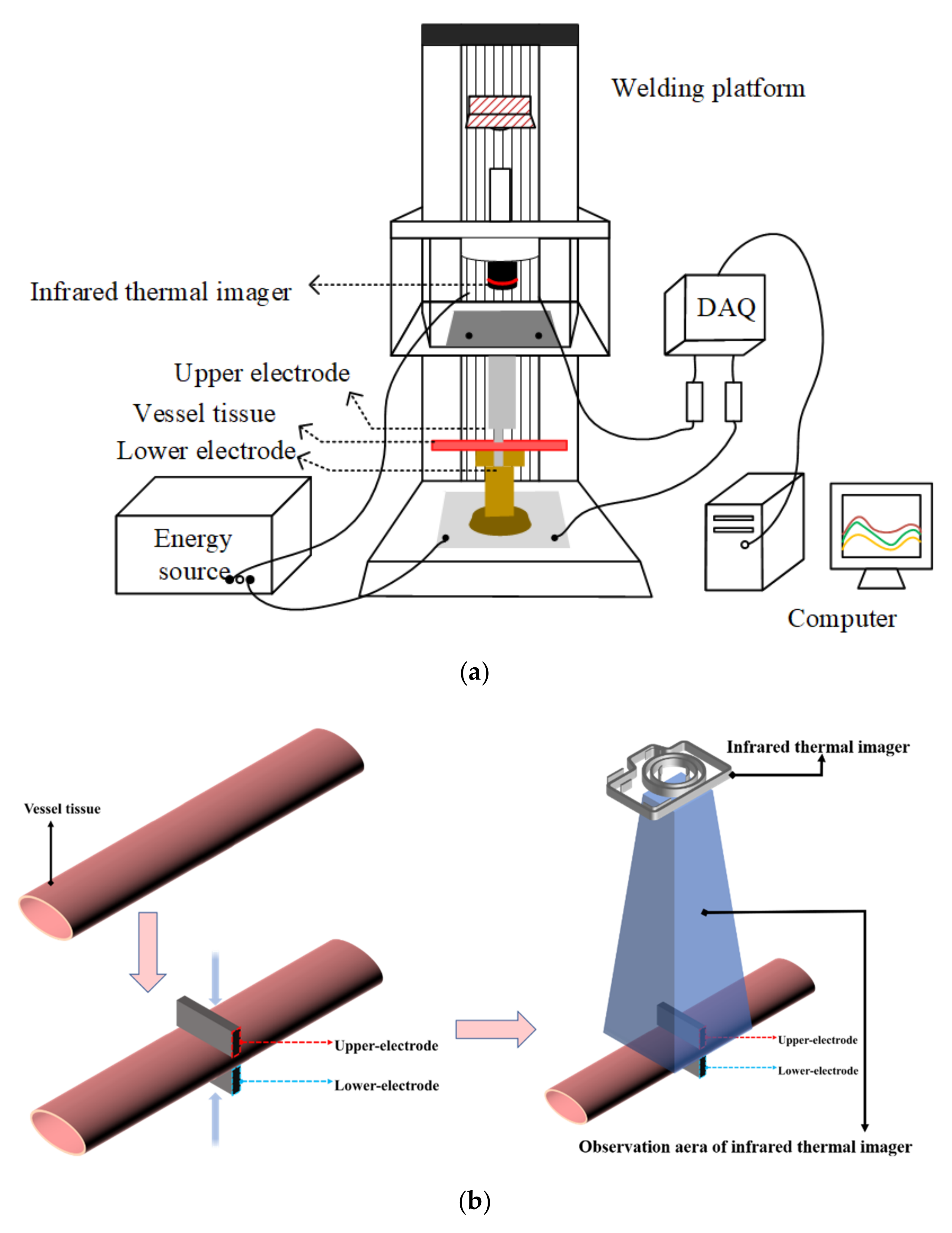
2.1.1. H.F.E.W. Platform Set Up
2.1.2. Vessel Tissue Preparation
2.1.3. Vessel Tissue Welding Process
2.1.4. Temperature Measurement in Welding Process
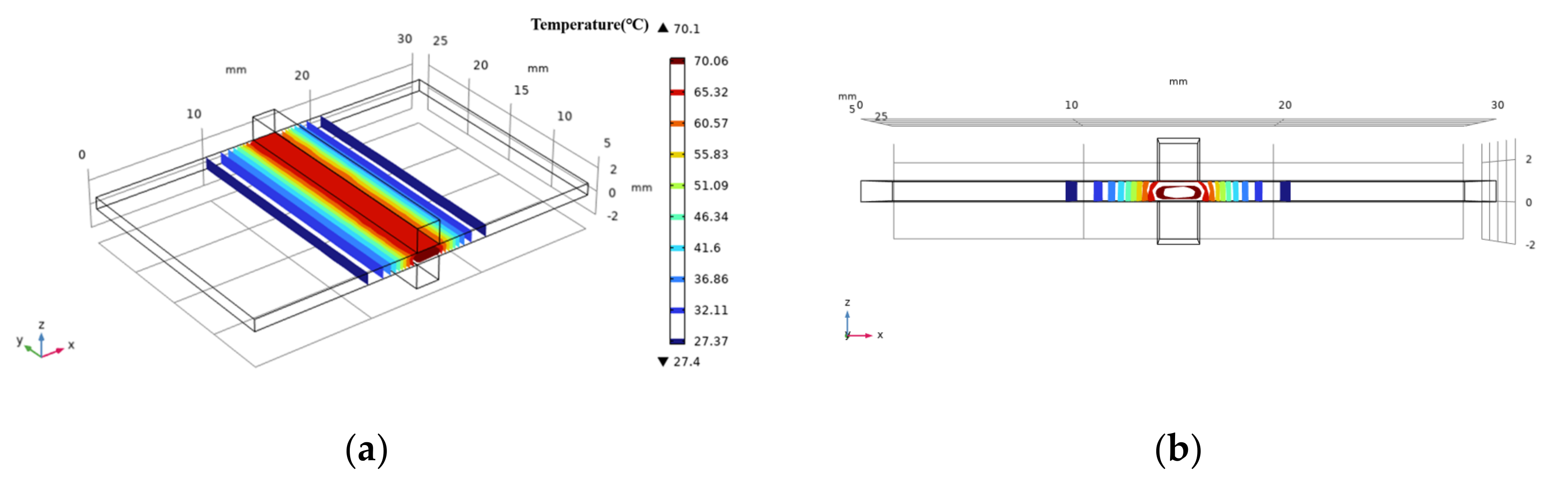
2.2. COMSOL Simulation
2.3. Vessel Tissue Welding Strength Test
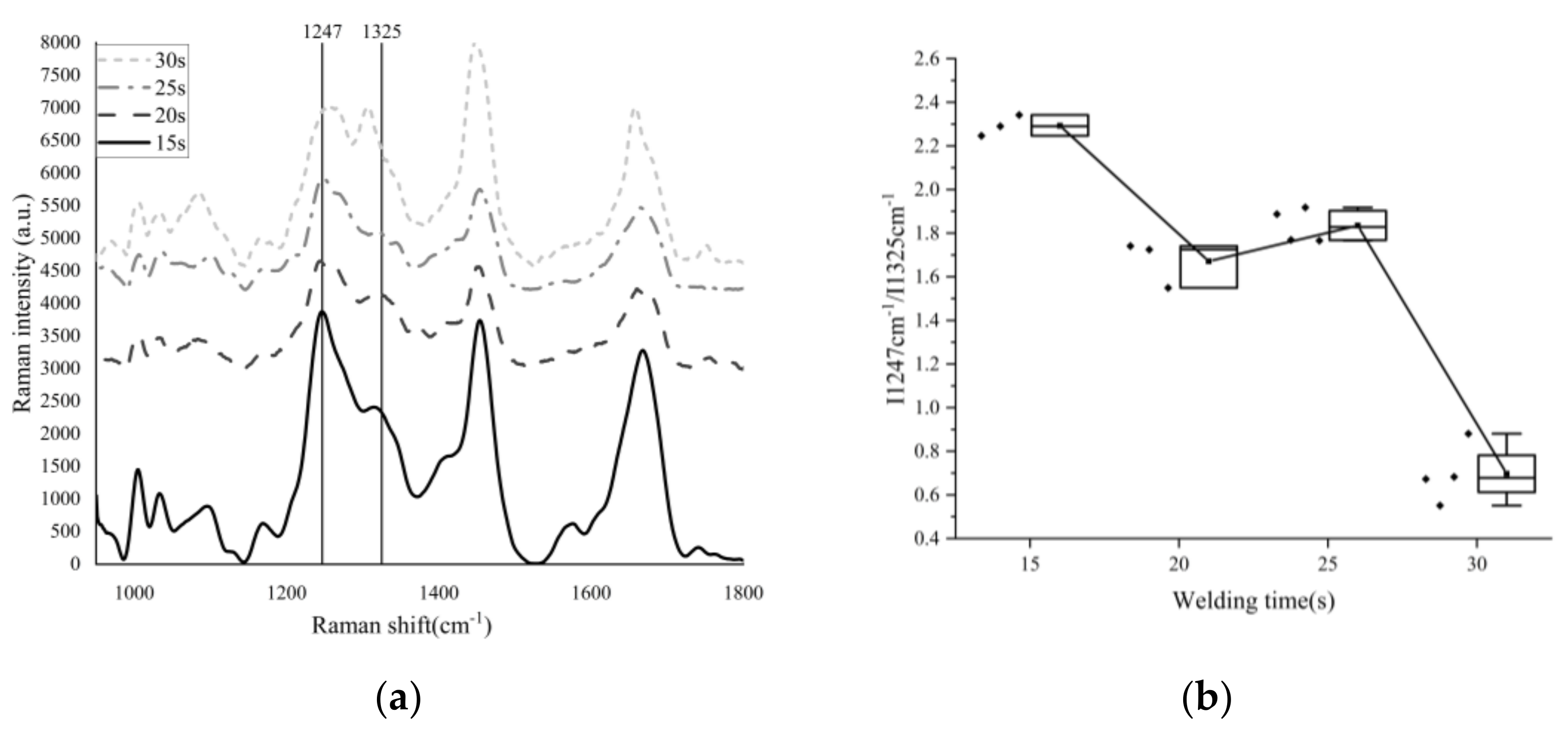
2.4. Raman Spectrum Test
3. Results
3.1. Vessel Tissue Welding Result
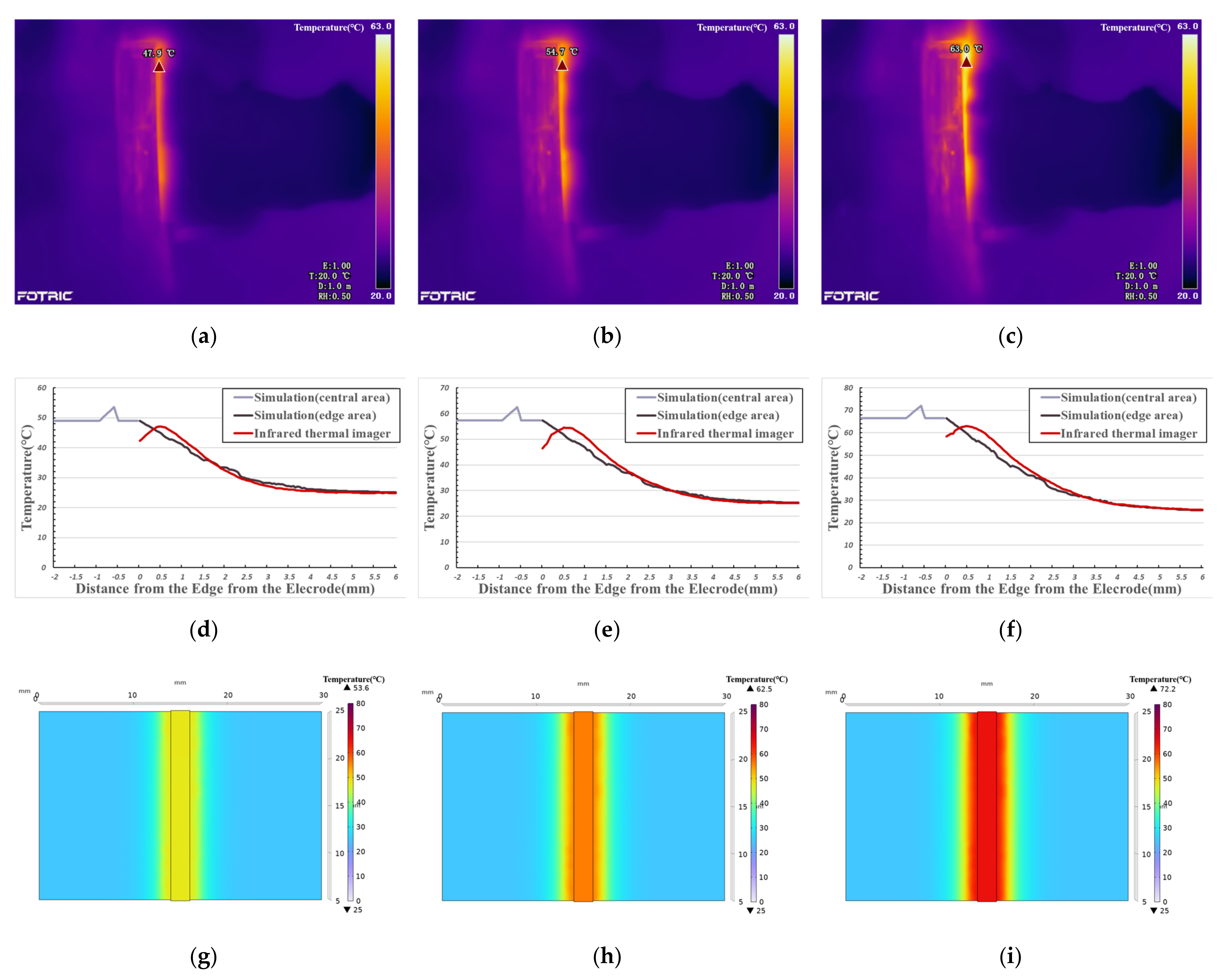
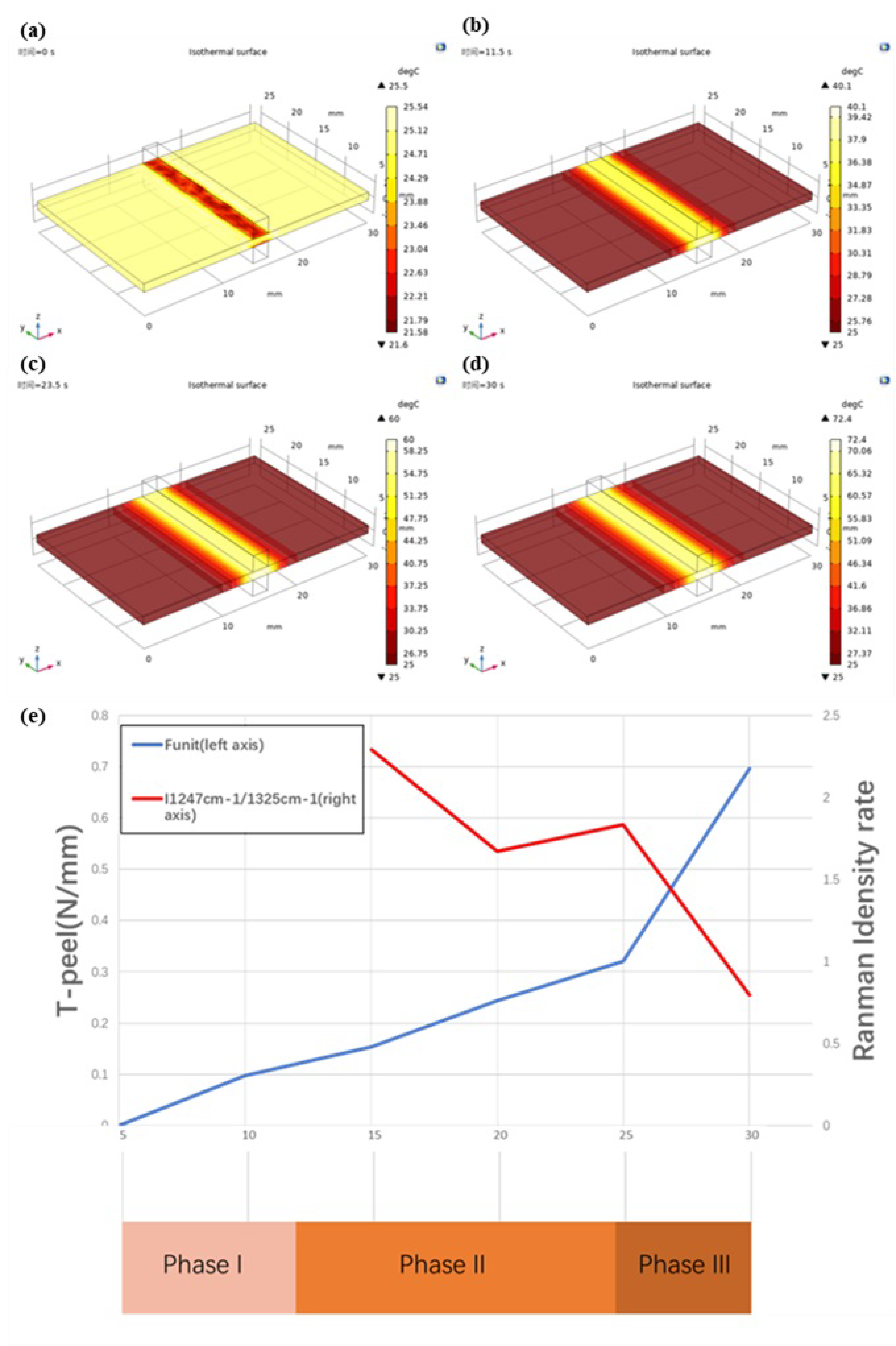
3.2. Temperature Measurement and COMSOL Simulation Result
3.3. Vessel Tissue Welding Strength Test Result
3.4. Raman Spectrum Result
4. Discussion
4.1. Phase I—Foundation Temperature Rise (Initial Temperature to 40°C)
4.2. Phase II—Denaturation (40–60 °C)
4.3. Phase III—Thermal Damage (60 °C—Maximum Temperature)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paton, B.E.; Krivtsun, I.V.; Marinsky, G.S.; Khudetsky, I.Y.; Lankim, Y.N.; Chernets, A.V. Welding, cutting and heat treatment of live tissues. Paton Weld. J. 2018, 10–11, 142–153. [Google Scholar]
- Smulders, J.F.; de Hingh, I.H.J.T.; Stavast, J.; Jackimowicz, J.J. Exploring new technologies to facilitate laparoscopic surgery: Creating intestinal anastomoses without sutures or staples, using a radio-frequency-energy-driven bipolar fusion device. Surg. Endosc. 2007, 21, 2105–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.X.; Zhuo, C.H.; Song, C.L.; Li, X.X.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, D.B. Histological characteristics of collagen denaturation and injuries in bipolar radio frequency-induced colonic anastomoses. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2015, 211, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nour-Eldin, N.A.; Exner, S.; Al-Subhi, M.; Naguib, N.N.N.; Kaltenbach, B.; Roman, A.; Vogl, T.J. Ablation therapy of non-colorectal cancer lung metastases: Retrospective analysis of tumour response post-laser-induced interstitial thermotherapy (LITT), radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA). Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 33, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Bijgaart, R.J.; Eikelenboom, D.C.; Hoogenboom, M.; Fütterer, J.J.; den Brok, M.H.; Adema, G.J. Thermal and mechanical high-intensity focused ultrasound: Perspectives on tumor ablation, immune effects and combination strategies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbonell, A.M.; Joels, C.S.; Kercher, K.W.; Matthews, B.D.; Sing, R.F.; Heniford, B.T. A comparison of laparoscopic bipolar vessel sealing devices in the hemostasis of small-, medium-, and large-sized arteries. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. 2003, 13, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabittei, D.R.; Heger, M.; van Tuijl, S.; Simonet, M.; de Boon, W.; van der Wal, A.C.; Balm, R.; de Mol, B.A. Ex vivo proof-of-concept of end-to-end scaffold-enhanced laser-assisted vascular anastomosis of porcine arteries. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015, 62, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramer, E.A.; Rentschler, M.E. Energy-Based Tissue Fusion for Sutureless Closure: Applications, Mechanisms, and Potential for Functional Recovery. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 20, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimova, A.; Chakraverty, R.; Muthukattil, R.; Elder, S.; Katz, A.; Sriramoju, V.; Stanley Lipper, R.; Alfano, R. In vivo molecular evaluation of guinea pig skin incisions healing after surgical suture and laser tissue welding using Raman spectroscopy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 2009, 96, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.H.; Li, W.; Chen, R.K. Characterization and Modeling of Tissue Thermal Conductivity During an Electrosurgical Joining Process. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezo, J.D.; Kramer, E.A.; Taylor, K.D.; Ferguson, V.; Rentschler, M.E. Temperature measurement methods during direct heat arterial tissue fusion. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.K.; Chastagner, M.W.; Dodde, R.E.; Shih, A.J. Electrosurgical Vessel Sealing Tissue Temperature: Experimental Measurement and Finite Element Modeling. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennes, H.H. Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duck, F.A. Physical Properties of Tissue: A Comprehensive Reference; Academic Press: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Compilation of the Dielectric Properties of Body Tissues at RF and Microwave Frequencies. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Compilation-of-the-Dielectric-Properties-of-Body-at-Gabriel/6de149eb3f64b7341e832023c3bf2a6eac3c8ed0 (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Haemmerich, D.; Chachati, L.; Wright, A.S.; Mahvi, D.M.; Lee, F.T.; Webster, J.G. Hepatic radiofrequency ablation with internally cooled probes: Effect of coolant temperature on lesion size. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 50, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copper (Transition Metal). Available online: https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E9%93%9C/668243 (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Winter, H.; Holmer, C.; Buhr, H.J.; Lindner, G.; Lauster, R.; Kraft, M.; Ritz, J.-P. Pilot study of bipolar radio frequency-induced anastomotic thermofusion–exploration of therapy parameters ex vivo. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2010, 25, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, D.A.G.; Brown, S.I.; Cochrane, L.; Motta, L.S.; Cuschieri, A. Thermal fusion: Effects and interactions of temperature, compression, and duration variables. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 3626–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyler, A.; Markus, R.T. Tensile testing of tubular vascular grafts produced by thermal compression fusion of flat collagenous materials. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1992, 26, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, R.L.P.; Dantas, M.S.S.; Oréfice, R.L. Thermal welding of biological tissues derived from porcine aorta for manufacturing bioprosthetic cardiac valves. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezo, J.D.; Passernig, A.C.; Ferguson, V.L.; Taylor, K.D.; Rentschler, M.E. Evaluating temperature and duration in arterial tissue fusion to maximize bond strength. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 30, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iconomidou, V.A.; Chryssikos, D.G.; Gionis, V.; Pavlidis, M.A.; Paipetis, A.; Hamodrakas, S.J. Secondary Structure of Chorion Proteins of the Teleostean Fish Dentex dentex by ATR FT-IR and FT-Raman Spectroscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 2000, 132, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, Z.Q. Raman spectroscopy of protein pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 2861–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnowski, C.P.; Stewart, S.; Holder, K.; Campbell-Clark, L.; Thoma, R.J.; Adams, A.K.; Moore, M.A.; Morris, M.D. Effects of treatment protocols and subcutaneous implantation on bovine pericardium a Raman spectroscopy study. Biomed. Opt. 2003, 8, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Chen, X.G.; Holtz, J.S.; Asher, S.A. UV resonance Raman-selective amide vibrational enhancement quantitative methodology for determining protein secondary structure. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 2854–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lednev, I.K.; Ermolenkov, V.V.; Higashiya, S.; Popova, L.A.; Topilina, N.I.; Welch, J.T. Reversible thermal denaturation of a 60-kDa genetically engineered beta-sheet polypeptide. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 3805–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gough, C.A.; Bhatnagar, R.S. Differential stability of the triple helix of (Pro-Pro-Gly)10 in H2O and D2O: Thermodynamic and structural explanations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 1999, 17, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masamitsu, D.; Yoshinori, N.; Susumu, U.; Nishiuchi, Y.J.; Nakazawa, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Kobayashi, Y.J. Characterization of Collagen Model Peptides Containing 4-Fluoroproline; (4(S)-Fluoroproline-Pro-Gly)10 Forms a Triple Helix, but (4(R)-Fluoroproline-Pro-Gly)10 Does Not. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9922–9923. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, Y.; Uchiyama, S.; Doi, M.; Nishiuchi, Y.J.; Nakazawa, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Kobayashi, Y.J. Different effects of 4-hydroxyproline and 4-fluoroproline on the stability of collagen triple helix. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 6034–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, S.K.; Bretscher, L.E.; Taylor, K.M.; Raines, R.T. A hyperstable collagen mimic. Chem. Biol. 1999, 6, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engel, J.; Bächinger, H.P. Structure, Stability and Folding of the Collagen Triple Helix. Top. Curr. Chem. 2005, 247, 7–33. [Google Scholar]




| Property | Expression | Unit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density () | 1101.5 | kg/m3 | [15] |
| Thermal conductivity () | 0.462 | W/m·K | [15] |
| Heat capacity at constant pressure () | 3306 | J/kg·K | [15] |
| Electrical conductivity () | 0.24567 | S/m | [15] |
| Property | Expression | Unit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density () | 8960 | kg/m3 | [17] |
| Thermal conductivity () | 401 | W/m·K | [17] |
| Heat capacity at constant pressure () | 381.875 | J/kg·K | [17] |
| Electrical conductivity () | 57,142,857 | S/m | [17] |
| Welding Times (s) | Strength (N/mm) | Average Change Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Average | ||
| 10 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.10 | - |
| 15 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 58.34% |
| 20 | 0.28 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 58.51% |
| 25 | 0.36 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 31.57% |
| 30 | 0.88 | 0.55 | 0.70 | 116.99% |
| Welding Times (s) | Position (cm−1) | Intensity | Half-Width (cm−1) | I1247 cm−1/I1326 cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 1247.30 | 3227.29 | 37.00 | 2.29 |
| 1322.71 | 1409.34 | 51.15 | ||
| 1246.21 | 3220.33 | 41.38 | 2.25 | |
| 1315.23 | 1433.47 | 72.50 | ||
| 1247.30 | 3038.43 | 41.37 | 2.34 | |
| 1312.01 | 1297.59 | 74.68 | ||
| 20 | 1247.30 | 1087.83 | 52.28 | 1.72 |
| 1317.37 | 630.84 | 95.95 | ||
| 1250.56 | 1856.38 | 56.61 | 1.74 | |
| 1313.08 | 1158.75 | 129.73 | ||
| 1249.47 | 1357.60 | 54.44 | 1.55 | |
| 1306.66 | 876.44 | 110.86 | ||
| 25 | 1248.38 | 1704.50 | 43.54 | 1.92 |
| 1319.51 | 888.80 | 76.68 | ||
| 1245.13 | 2165.38 | 39.20 | 1.77 | |
| 1315.23 | 1223.91 | 87.36 | ||
| 1246.21 | 2669.64 | 43.56 | 1.77 | |
| 1322.71 | 1511.89 | 78.74 | ||
| 1249.47 | 1464.48 | 43.53 | 1.89 | |
| 1314.16 | 775.89 | 85.26 | ||
| 30 | 1266.29 | 3484.08 | 75.66 | 0.68 |
| 1303.85 | 5100.98 | 38.42 | ||
| 1261.98 | 1086.55 | 71.38 | 0.72 | |
| 1304.92 | 1502.61 | 38.41 | ||
| 1255.51 | 422.15 | 47.59 | 0.67 | |
| 1310.26 | 634.66 | 31.98 | ||
| 1258.15 | 3203.23 | 97.10 | 0.99 | |
| 1307.73 | 3251.95 | 95.99 | ||
| 1253.91 | 1869.72 | 60.94 | 0.94 | |
| 1304.51 | 1999.29 | 62.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Madeniyeti, N.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, C.; Yin, L.; Liu, K. Temperature Distribution of Vessel Tissue by High Frequency Electric Welding with Combination Optical Measure and Simulation. Biosensors 2022, 12, 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040209
Wang H, Yang X, Madeniyeti N, Qiu J, Zhu C, Yin L, Liu K. Temperature Distribution of Vessel Tissue by High Frequency Electric Welding with Combination Optical Measure and Simulation. Biosensors. 2022; 12(4):209. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040209
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Xingjian Yang, Naerzhuoli Madeniyeti, Jian Qiu, Caihui Zhu, Li Yin, and Kefu Liu. 2022. "Temperature Distribution of Vessel Tissue by High Frequency Electric Welding with Combination Optical Measure and Simulation" Biosensors 12, no. 4: 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040209
APA StyleWang, H., Yang, X., Madeniyeti, N., Qiu, J., Zhu, C., Yin, L., & Liu, K. (2022). Temperature Distribution of Vessel Tissue by High Frequency Electric Welding with Combination Optical Measure and Simulation. Biosensors, 12(4), 209. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12040209







