Multi-Color Two-Photon Microscopic Imaging Based on a Single-Wavelength Excitation
Abstract
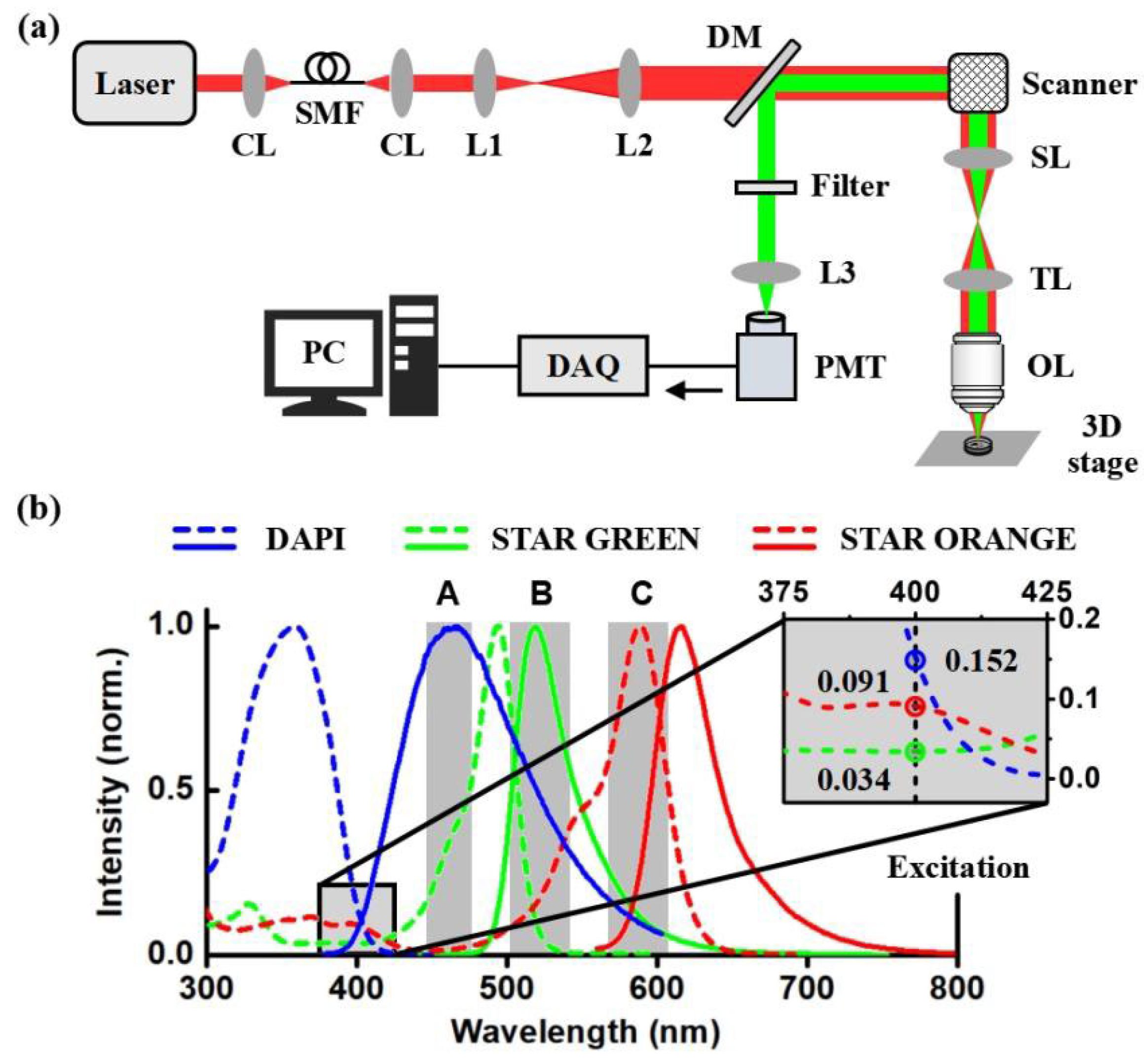
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sato, M.; Kawano, M.; Yanagawa, Y.; Hayashi, Y. In vivo two-photon imaging of striatal neuronal circuits in mice. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2016, 135, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarus, D.; Hamard, L.; Caraguel, F.; Wion, D.; Auzely-Velty, R. Design of hyaluronic acid hydrogels to promote neurite outgrowth in three dimension. Acs. Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 25051–25059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakai, T.; Kinashi, T. Microenvironmental Control of High-Speed Interstitial T Cell Migration in the Lymph Node. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luu, L.; Coombes, J.L. Dynamic two-photon imaging of the immune response to Toxoplasma gondii infection. Parasite Immunol. 2015, 37, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kang, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhuo, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J. Imaging normal and cancerous human gastric muscular layer in transverse and longitudinal sections by multiphoton microscopy. Scanning 2016, 38, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Cui, K.; Mancuso, J.; Federley, R.; Fischer, K.; Teng, G.; Mittal, V.; Gao, D.; Zhao, H.; et al. In Vivo Visualization and Characterization of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Tumors. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herz, J.; Siffrin, V.; Hauser, A.E.; Brandt, A.U.; Leuenberger, T.; Radbruch, H.; Zipp, F.; Niesner, R.A. Expanding Two-Photon Intravital Microscopy to the Infrared by Means of Optical Parametric Oscillator. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tragardh, J.; Murtagh, M.; Robb, G.; Parsons, M.; Lin, J.; Spence, D.J.; Mcconnell, G. Two-Color, Two-Photon Imaging at Long Excitation Wavelengths Using a Diamond Raman Laser. Microsc. Microanal. 2016, 22, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clément, R.; Lamasse, L.; Jaouen, A.; Rougon, G.; Debarbieux, F. Combination of an optical parametric oscillator and quantum-dots 655 to improve imaging depth of vasculature by intravital multicolor two-photon microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 2362–2372. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.B.; Fu, L. Enhanced self-phase modulation enables a 700–900 nm linear compressible continuum for multicolor two-photon microscopy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 2014, 20, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.H.; Boppart, S.A. Coherent fiber supercontinuum for biophotonics. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 628–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueki, H.; Wang, I.H.; Zhao, D.; Gunzer, M.; Kawaoka, Y. Multicolor two-photon imaging of in vivo cellular pathophysiology upon influenza virus infection using the two-photon IMPRESS. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1041–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, W.; Strickler, J.H.; Webb, W.W. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science 1990, 248, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanne, J.; Falk, H.J.; Gorlitz, F.; Hoyer, P.; Hell, S.W. STED nanoscopy with fluorescent quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vicidomini, G.; Moneron, G.; Eggeling, C.; Rittweger, E.; Hell, S.W. STED with wavelengths closer to the emission maxium. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 5225–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.; Yan, W.; Qu, J. Ultralow power demand in fluorescence nanoscopy with digitally enhanced stimulated emission depletion. Nanophotonics 2020, 9, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xie, W.; Yang, Z.; Weng, X.; Yan, W.; Qu, J. Low-power STED nanoscopy based on temporal and spatial modulation. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 3479–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Weng, X.; Yan, W.; Qu, J. Implementation of a fluorescence spatiotemporal modulation super-resolution microscope. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yan, W.; Qu, J. Low-power Two-color Stimulated Emission Depletion Micros-copy for Live Cell Imaging. Biosensors 2021, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryczynski, I.; Malak, H.; Lakowicz, J.R. Multiphoton excitation of the DNA stains DAPI and Hoechst. Bioimaging 1996, 4, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R.; Gryczynski, I.; Malak, H.; Schrader, M.; Engelhardt, P.; Kano, H.; Hell, S.W. Time-Resolved Fluorescence Spectroscopy and Imaging of DNA Labeled with DAPI and Hoechst 33342 Using Three-Photon Excitation. Biophys. J. 1997, 72, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Qu, J. Multi-Color Two-Photon Microscopic Imaging Based on a Single-Wavelength Excitation. Biosensors 2022, 12, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050307
Yan W, Huang Y, Wang L, Li J, Guo Y, Yang Z, Qu J. Multi-Color Two-Photon Microscopic Imaging Based on a Single-Wavelength Excitation. Biosensors. 2022; 12(5):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050307
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Wei, Yangrui Huang, Luwei Wang, Jin Li, Yong Guo, Zhigang Yang, and Junle Qu. 2022. "Multi-Color Two-Photon Microscopic Imaging Based on a Single-Wavelength Excitation" Biosensors 12, no. 5: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050307
APA StyleYan, W., Huang, Y., Wang, L., Li, J., Guo, Y., Yang, Z., & Qu, J. (2022). Multi-Color Two-Photon Microscopic Imaging Based on a Single-Wavelength Excitation. Biosensors, 12(5), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12050307






