Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Virus N Protein Based on p-Toluenesulfonyl Modified Fluorescent Microspheres Immunoassay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Synthesis of Eu(TTA)3Phen
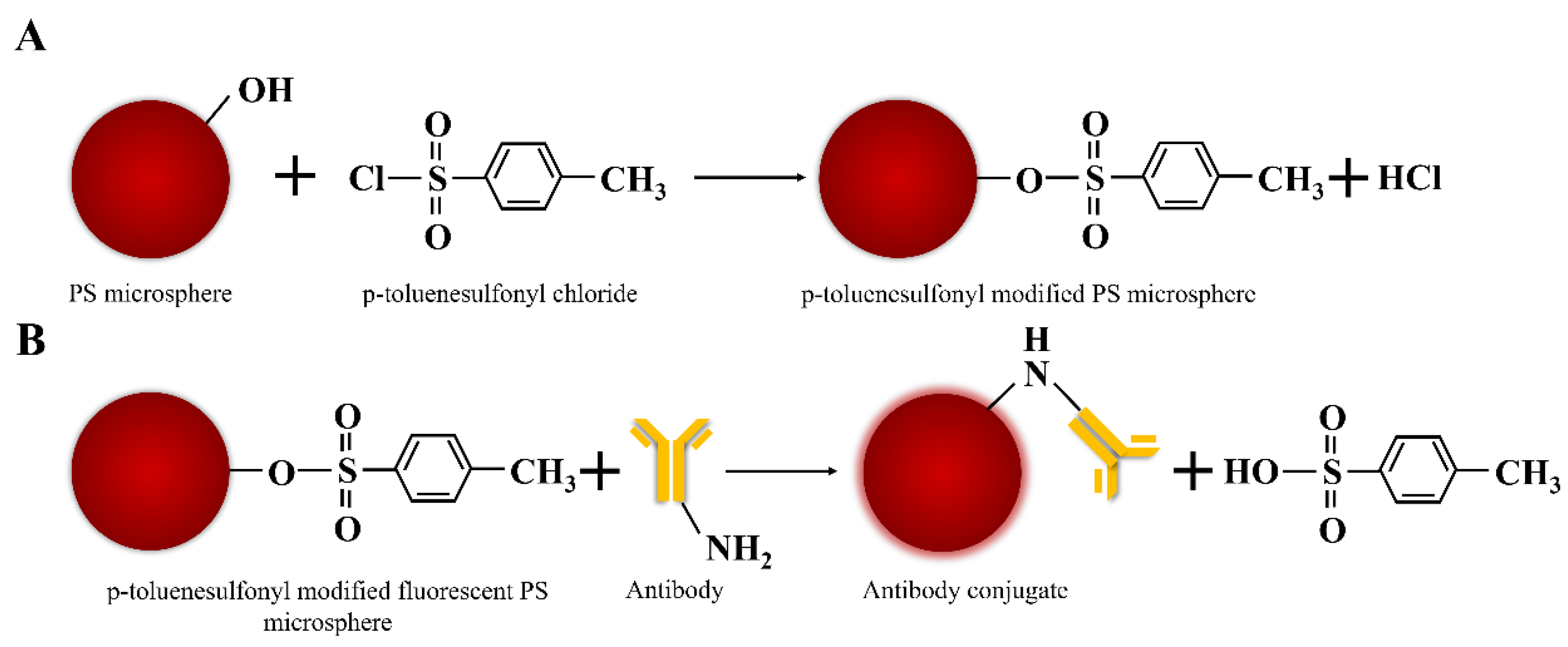
2.1.2. Synthesis of p-Toluenesulfonyl Modified PS Microspheres
2.1.3. Synthesis of Fluorescent PS Microspheres
2.1.4. Preparation of COVID-19 N Protein Monoclonal Antibody
2.1.5. Preparation of p-Toluenesulfonyl Modified Fluorescent PS Microspheres Antibodies Conjugates
2.1.6. Preparation of p-Toluenesulfonyl Fluorescent Microspheres Immunochromatographic Assay Test Strips
2.2. Analytical Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of p-Toluenesulfonyl Modified PS Microspheres
3.2. Properties of Fluorescent PS Microspheres
3.3. Properties of p-Toluenesulfonyl Fluorescent Microspheres Immunochromatographic Assay Test Strips
3.4. Conjugation of Antibodies to Fluorescent Microspheres
3.5. Specificity of COVID-19 N Protein LFIA Strips
3.6. Stability Testing of COVID-19 N Protein LFIA Strips
3.7. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Weekly Epidemiological Update and Weekly Operational Update. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Chang, D.; Lin, M.; Wei, L.; Xie, L.; Zhu, G.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Sharma, L. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of novel coronavirus infections involving 13 patients outside Wuhan. China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1092–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, L.J.; Garner, L.V.; Smoot, J.W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Saveson, C.J.; Sasso, J.M.; Gregg, A.C.; Soares, D.J.; Beskid, T.R.; et al. Assay Techniques and Test Development for COVID-19 Diagnosis. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 591–605. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, H. The Importance of diagnostic testing for COVID-19. Infectious Diseases Hub, 2 April 2020. Available online: https://www.id-hub.com/2020/04/02/the-importance-of-diagnostic-testing-for-covid-19/(accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Xia, J.; Tong, J.; Liu, M.; Shen, Y.; Guo, D. Evaluation of coronavirus in tears and conjunctival secretions of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American College of Physicians. COVID-19 Found in Sputum and Feces Samples after Pharyngeal Specimens No Longer Positive; Science Daily: Rockville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawski, S.A.; Wong, K.K.; Collins, J.P. Clinical and virologic characteristics of the first 12 patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the United States. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 861–868. [Google Scholar]
- Kacian, D.L.; Fultz, T.J. Kits for Nucleic Acid Sequence Amplification Methods. U.S. Patent 5,888,779, 3 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- What Is CRISPR? Ask the Brain; The McGovern Institute for Brain Research, Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://mcgovern.mit.edu/2019/01/01/crispr-in-a-nutshell/ (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Zhang, F.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Gootenberg, J.S. A Protocol for Detection of COVID-19 Using CRISPR Diagnostics (v. 20200321); Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Broughton, J.P.; Deng, X.; Yu, G.; Fasching, C.L.; Servellita, V.; Singh, J.; Miao, X.; Streithorst, J.A.; Granados, A.; Sotomayor-Gonzalez, A.; et al. CRISPR−Cas12-based detection of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.; Nakajima, R.; Jain, A.; de Assis, R.R.; Jasinskas, A.; Obiero, J.M.; Adenaiye, O.; Tai, S.; Hong, F.; Milton, D.K.; et al. Prometheus Study Group, Analysis of serologic cross-reactivity between common human coronaviruses and SARS-CoV-2 using coronavirus antigen microarray. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diao, B.; Wen, K.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Han, C.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, L.; Dan, Y.; et al. Diagnosis of acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection by detection of nucleocapsid protein. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sletten, E.M.; Bertozzi, C.R. Bioorthogonal chemistry: Fishing for selectivity in a sea of functionality. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6974–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takaoka, Y.; Ojida, A.; Hamachi, I. Protein organic chemistry and application for labeling and engineering in live-cell systems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4088–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, F.A.; Sundberg, R.J. Conversion of Alcohols to Alkylating Agents; Sulfonate Esters Advanced Organic Chemistry, Part B: Reactions and Synthesis, 5th ed.; Springer Science + Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 216. [Google Scholar]
- Otieno, B.A.; Krause, C.E.; Rusling, J.F. Bioconjugation of Antibodies and Enzyme Labels onto Magnetic Beads. Methods Enzymol. 2016, 571, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Mao, M.; Cen, Y.; Yang, H.; Qin, Z.; Ma, L. Copolymerization of Eu(TTA)3Phen doped styrene and methyl methacrylate nanoparticles and use in quantitative detection of pepsinogen. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Wu, F.; Cen, Y.; Ye, L.; Shi, X.; Huang, Y.; Fang, S.; Ma, L. Comparative research on nucleocapsid and spike glycoprotein as the rapid immunodetection targets of COVID-19 and establishment of immunoassay strips. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 131, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Heim, A.; Riether, D.; Yee, D.; Milgrom, Y.; Gawinowicz, M.A.; Sames, D. Reactivity of functional groups on the protein surface: Development of epoxide probes for protein labeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8130–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, B.; Wen, K.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Han, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, G.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Y. Accuracy of a nucleocapsid protein antigen rapid test in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 289.e1–289.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, L.; Du, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Lyu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Huo, J.; et al. Foundation and clinical evaluation of a new method for detecting SARS-CoV-2 antigen by fluorescent microsphere immunochromatography. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 553837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, B.D.; Anderson, C.E.; Williford, J.R.; Alonzo, L.F.; Glukhova, V.A.; Boyle, D.S.; Weigl, B.H.; Nichols, K.P. SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus nucleocapsid antigendetecting half-strip lateral flow assay toward the development of point of care tests using commercially available reagents. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11305–11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, P.; De Vos, N.; Martiny, D.; Jassoy, C.; Mirazimi, A.; Cuypers, L.; Van den Wijngaert, S.; Monteil, V.; Melin, P.; Stoffels, K.; et al. Development and potential usefulness of the COVID-19 Ag respi-strip diagnostic assay in a pandemic context. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.K.; Kim, K.; Park, J.; Im, H.; Maher, S.; Kim, M.G. Plasmon color-preserved gold nanoparticle clusters for high sensitivity detection of SARS-CoV-2 based on lateral flow immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 205, 114094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Concentration (ng/mL) | TEST 1 | TEST 2 | TEST 3 | Average | STDEV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 19,252 | 20,629 | 20,582 | 20,154.33 | 781.7969 |
| 100 | 20,498 | 20,678 | 20,526 | 20,567.33 | 96.85728 |
| 10 | 20,910 | 21,133 | 21,172 | 21,071.67 | 141.3589 |
| 1 | 6102 | 6493 | 6490 | 6361.667 | 224.8829 |
| 0.1 | 1294 | 1362 | 1285 | 1313.667 | 42.09909 |
| 0.01 | 872 | 896 | 804 | 857.3333 | 47.72141 |
| 0.001 | 368 | 400 | 365 | 377.6667 | 19.39931 |
| 0 | 265 | 254 | 344 | 287.6667 | 49.09515 |
| No. | Probe | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Assay Time | Detection Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fluorescent microparticles | - | 10 min | Fluorescence analyzer | Diao et al. (2021) [21] |
| 2 | Fluorescent microsphere | 100 ng/mL | 15 min | UV-LED/detector | Zhang et al. (2020a) [22] |
| 3 | Latex beads | 0.65 ng/mL | 30 min | Optical reader | Grant et al. (2020) [23] |
| 4 | Gold nanoparticles | 0.25 ng/mL | 15 min | - | Mertens et al. (2020) [24] |
| 5 | Colloidal gold | 0.1 ng/mL | 15 min | Optical reader | Liu et al. (2021) [19] |
| 6 | PLASCOP AuNP clusters | 0.038 ng/mL | 10 min | Optical reader | Oh et al. (2022) [25] |
| This study | Fluorescent microspheres | 0.01 ng/mL | 15 min | UV-LED/detector | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, M.; Wu, F.; Shi, X.; Huang, Y.; Ma, L. Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Virus N Protein Based on p-Toluenesulfonyl Modified Fluorescent Microspheres Immunoassay. Biosensors 2022, 12, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070437
Mao M, Wu F, Shi X, Huang Y, Ma L. Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Virus N Protein Based on p-Toluenesulfonyl Modified Fluorescent Microspheres Immunoassay. Biosensors. 2022; 12(7):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070437
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Mao, Feng Wu, Xueying Shi, Yulan Huang, and Lan Ma. 2022. "Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Virus N Protein Based on p-Toluenesulfonyl Modified Fluorescent Microspheres Immunoassay" Biosensors 12, no. 7: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070437
APA StyleMao, M., Wu, F., Shi, X., Huang, Y., & Ma, L. (2022). Ultrasensitive Detection of COVID-19 Virus N Protein Based on p-Toluenesulfonyl Modified Fluorescent Microspheres Immunoassay. Biosensors, 12(7), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12070437





