Liquid Crystal Biosensors: Principles, Structure and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle of LC-Based Biosensors
2.1. Optical Anisotropy
2.2. Orientations of LCs
3. Geometries of LCs in Biosensing
3.1. LC–Solid Interface
3.1.1. LC–Solid Interface on Glass Substrates
3.1.2. Applications of Microfluidics at LC–Solid Interface
3.2. LC–Aqueous Interface
3.2.1. LC–Aqueous Interface on Glass Substrates
3.2.2. Applications of Microfluidics at the LC–Aqueous Interface
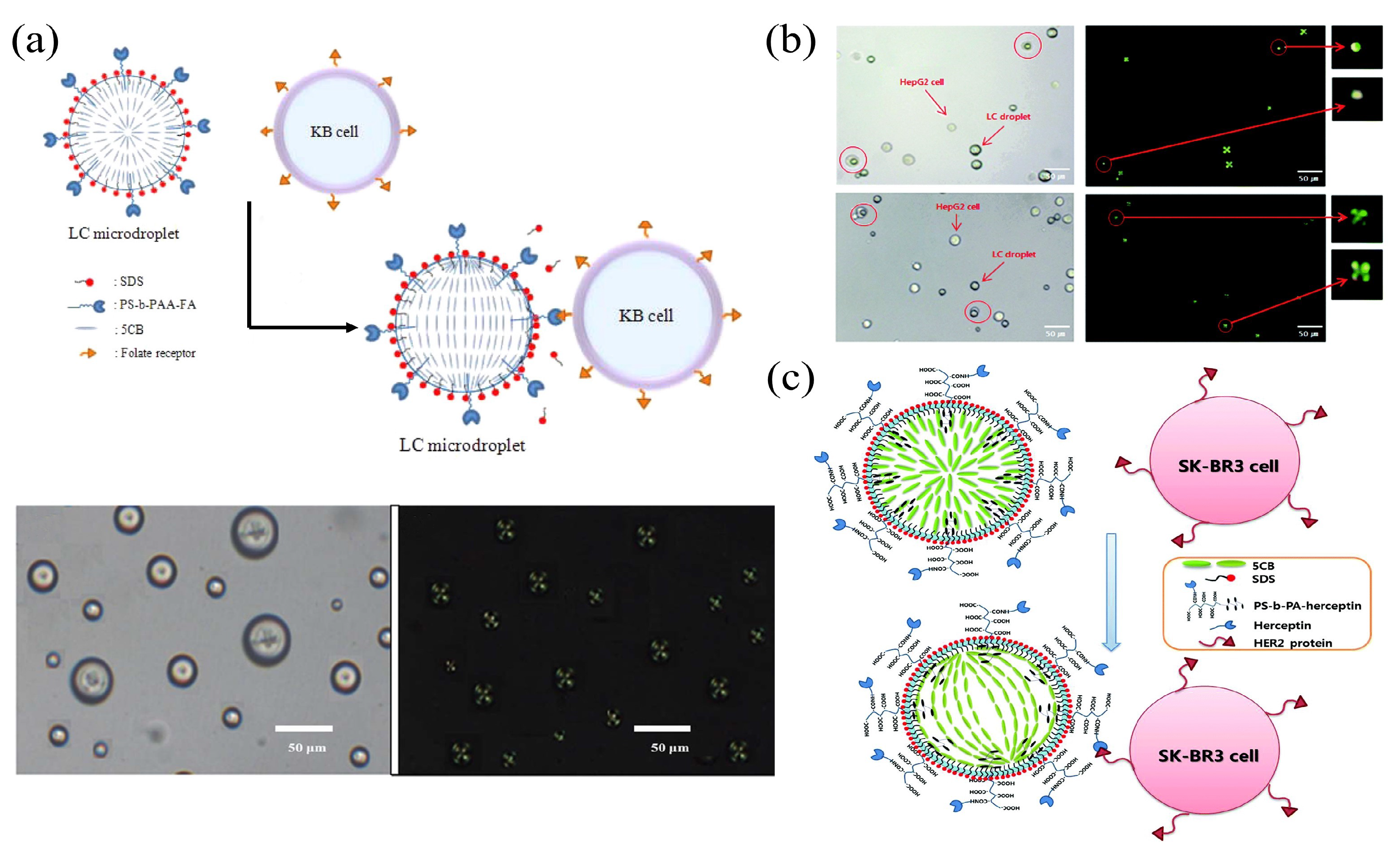
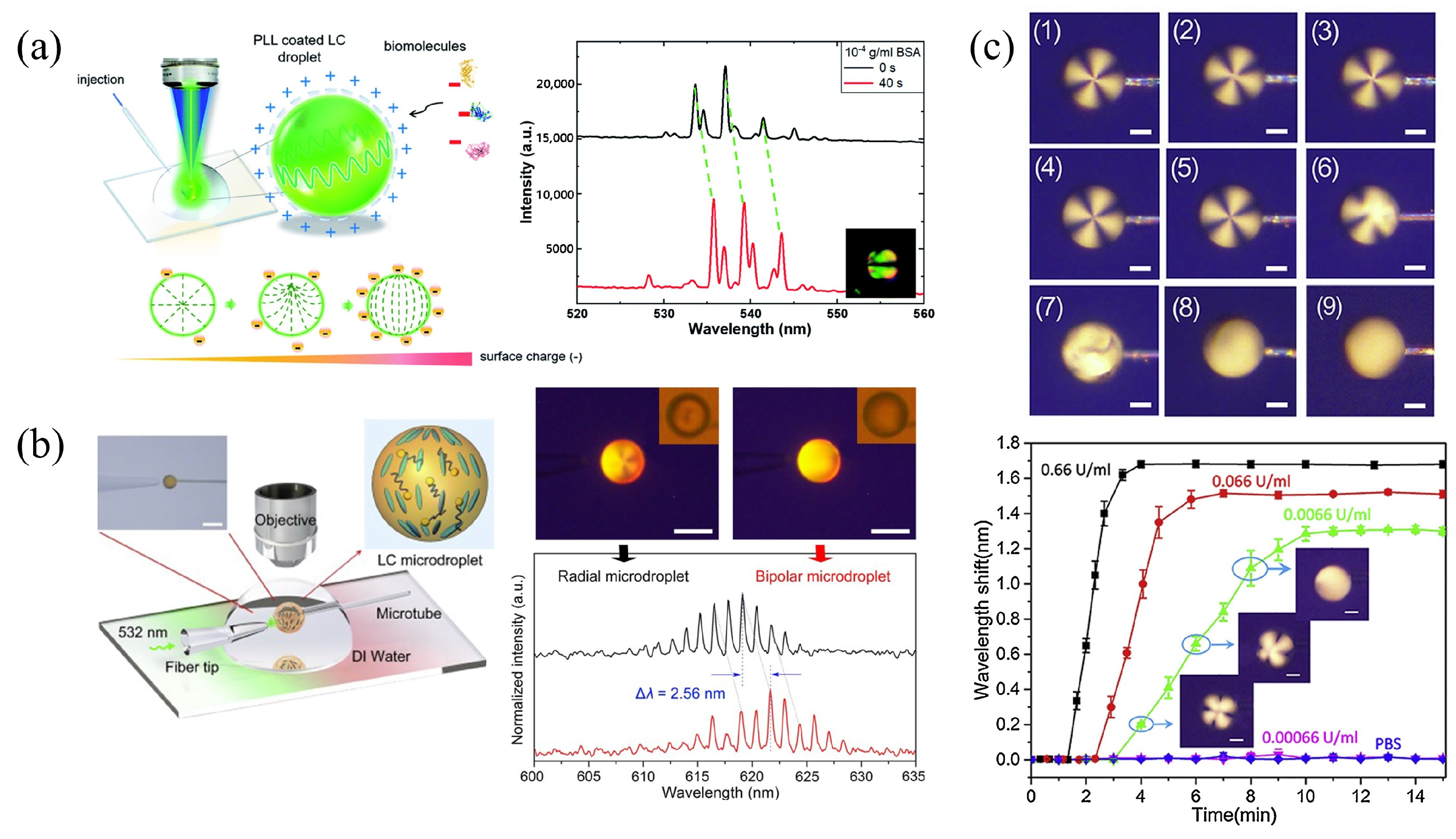
3.3. LC Droplets
3.3.1. LC Droplet Biosensing Integrated with Spectroscopy
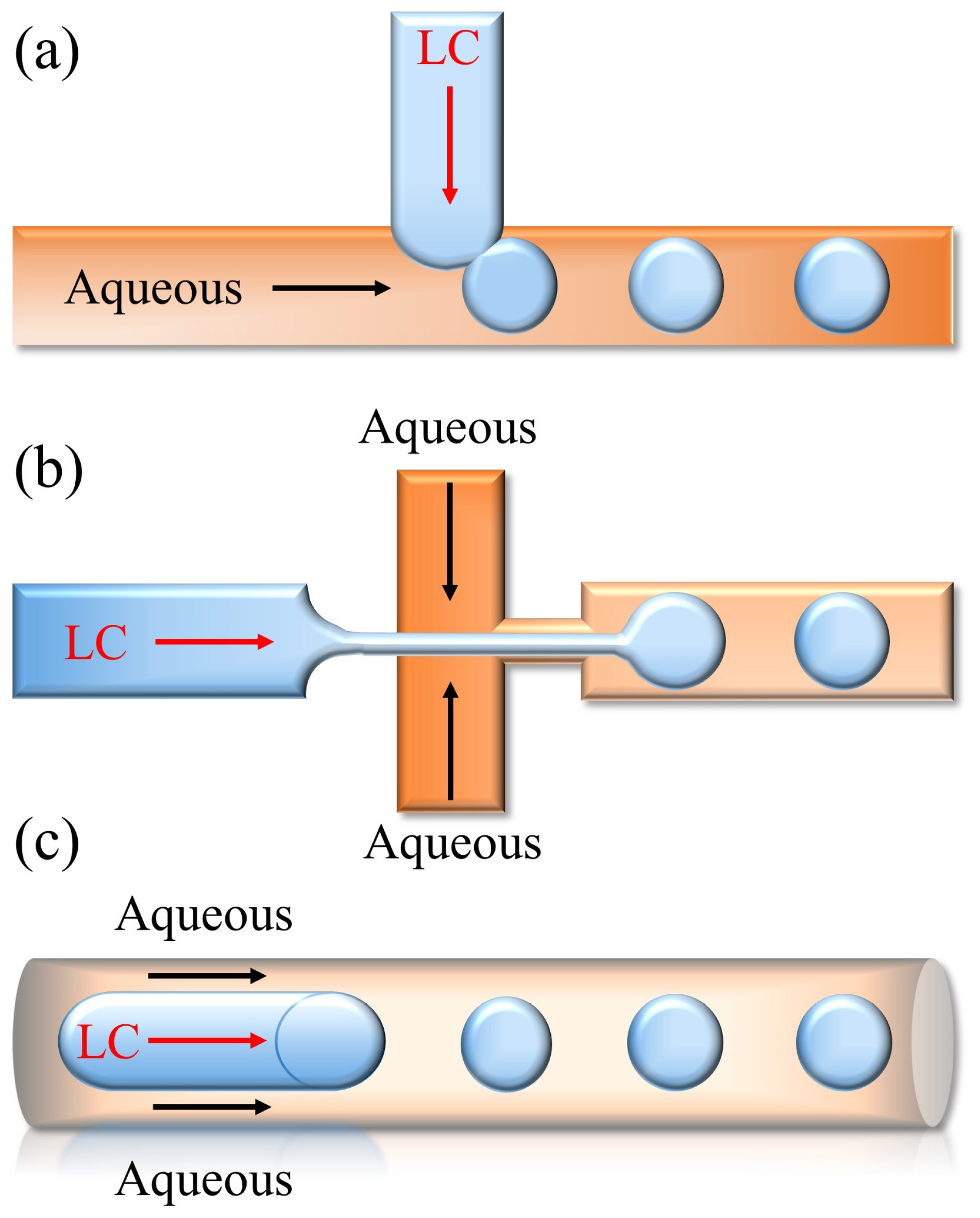
3.3.2. LC Droplet Microfluidic Biosensors
4. LC-Based Whispering Gallery Mode Microcavity Biosensing
4.1. Classification and Preparation of WGM Microcavities
4.1.1. Classification of WGM Microcavities
4.1.2. Fabrication of WGM Microcavities
4.2. Applications of LC-Based Microcavities in Biosensing
5. Conclusions and Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalita, P.; Shukla, S.S.; Singh, R.K.; Bhattacharjee, A. Potential liquid crystal-based biosensor depending on the interaction between liquid crystals and proteins. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 254, 119634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-e, M.; Zheng, D.Y. Newly discovered dimensional effects of electrodes on liquid crystal THz phase shifters enable novel switching between in-plane and out-of-plane. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prévôt, M.E.; Nemati, A.; Cull, T.R.; Hegmann, E.; Hegmann, T. A zero-power optical, ppt-to ppm-level toxic gas and vapor sensor with image, text, and analytical capabilities. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefelska, M.M.; Woliński, T.R.; Ertman, S.; Mileńko, K.; ączkowski, R.; Siarkowska, A.; Domański, A.W. Electric field sensing with photonic liquid crystal fibers based on micro-electrodes systems. J. Light. Technol. 2015, 33, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.G.; Yuan, C.L.; Hu, W.; Bisoyi, H.K.; Tang, M.J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, P.Z.; Yang, W.Q.; Wang, X.Q.; Shen, D.; et al. Light-patterned crystallographic direction of a self-organized 3d soft photonic crystal. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, S.; Farrell, G.; Semenova, Y. Directional electric field sensitivity of a liquid crystal infiltrated photonic crystal fiber. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2011, 23, 408–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, M.; De Filpo, G.; Tursi, A.; Mashin, A.I.; Nicoletta, F.P. Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystals with elongated droplets as novel pressure sensors. Liq. Cryst. 2021, 49, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Singh, S. Influence of pressure on the B2I phase transition of a banana-shaped liquid crystal. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.K.; Gupta, V.K.; Rao, D.S.; Lobo, C.V. Effect of pressure on the dynamics of the photostimulated orientational ordering transition in a liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 021705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brake, J.M.; Daschner, M.K.; Luk, Y.Y.; Abbott, N.L. Biomolecular interactions at phospholipid-decorated surfaces of liquid crystals. Science 2003, 302, 2094–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinov, L.M. Structure and Properties of Liquid Crystals; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 123. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Li, X.; Liao, S.; Yu, R.; Wu, Z. Highly-sensitive liquid crystal biosensor based on DNA dendrimers-mediated optical reorientation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Zi, Q.J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.Y.; Cao, Q. Determination of alkaline phosphatase activity and of carcinoembryonic antigen by using a multicolor liquid crystal biosensor based on the controlled growth of silver nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Peng, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L. Liquid-crystal biosensor based on nickel-nanosphere-induced homeotropic alignment for the amplified detection of thrombin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23418–23422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicari, L. Optical Applications of Liquid Crystals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, W. High-sensitivity Fabry–Perot interferometer temperature sensor probe based on liquid crystal and the Vernier effect. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 5355–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Huang, Y.; Luo, D.; Wang, C.; He, J.; Liao, C.; Yin, G.; Zhou, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J.; et al. Broadband thermo-optic switching effect based on liquid crystal infiltrated photonic crystal fibers. IEEE Photonics J. 2015, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.J.J.; Lim, J.L.; Cui, Y.; Milenko, K.; Wang, Y.; Shum, P.P.; Wolinski, T. Fabrication and characterization of a highly temperature sensitive device based on nematic liquid crystal-filled photonic crystal fiber. IEEE Photonics J. 2012, 4, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Su, X.; Yang, D.; Luan, C. Label-free liquid crystal biosensor for cecropin B detection. Talanta 2018, 186, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, T.; Fang, J. Polyelectrolyte-coated liquid crystal droplets for detecting charged macromolecules. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 6807–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, P.; Mann, E.K.; Jákli, A. Thermotropic liquid crystal films for biosensors and beyond. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5061–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Qazi, F.; Ahmed, M.I.; Usman, A.; Riaz, A.; Abbasi, A.D. Liquid crystals based sensing platform-technological aspects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.S.; Oh, S.W.; Choi, E.Y. Optical detection of deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization using an anchoring transition of liquid crystal alignment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 143901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Ding, H.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Label-free liquid crystal biosensor for L-histidine: A DNAzyme-based platform for small molecule assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.u.; Siddiqi, H.M.; Kun Lin, Y.; Hussain, Z.; Majeed, N. Bovine serum albumin protein-based liquid crystal biosensors for optical detection of toxic heavy metals in water. Sensors 2020, 20, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woltman, S.J.; Jay, G.D.; Crawford, G.P. Liquid-crystal materials find a new order in biomedical applications. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Yang, K. A liquid crystal biosensor for detecting organophosphates through the localized pH changes induced by their hydrolytic products. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, P.; Jones, T. Liquid crystal measurements of heat transfer and surface shear stress. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.K.; Jang, C.H. An acetylcholinesterase-based biosensor for the detection of pesticides using liquid crystals confined in microcapillaries. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Qi, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, L.; Lin, J.M.; Hu, Q. An integrated liquid crystal sensing device assisted by the surfactant-embedded smart hydrogel. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 187, 113313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Kang, Q.; Fang, M.; Yu, L. Label-free, rapid, and sensitive detection of carboxylesterase using surfactant-doped liquid crystal sensor. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 111921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.F.; Chan, H.P.; Yang, K.L. Planar optical waveguide platform for gas sensing using liquid crystal. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 2521–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, C.; Ramou, E.; Porteira, A.R.P.; Moura Barbosa, A.J.; Roque, A.C.A. Seeing the unseen: The role of liquid crystals in gas-sensing technologies. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 1902117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayani, K.; Rai, P.; Bao, N.; Yu, H.; Mavrikakis, M.; Twieg, R.J.; Abbott, N.L. Liquid crystals with interfacial ordering that enhances responsiveness to chemical targets. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.Y.; Yang, K.L. Dark-to-bright optical responses of liquid crystals supported on solid surfaces decorated with proteins. Langmuir 2008, 24, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaei, M.S.; Islam, R.; Ahmed, M. Applications of gold nanoparticles in ELISA, PCR, and immuno-PCR assays: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1143, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, J. Detection of heavy metal ions using whispering gallery mode lasing in functionalized liquid crystal microdroplets. Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10, 6073–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.L.; Song, L. Accurate modelling of nematic liquid crystal under the combination of microwave signal and applied voltage. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccianti, M.; Assanto, G. Signal readdressing by steering of spatial solitons in bulk nematic liquid crystals. Opt. Lett. 2001, 26, 1690–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtney, M.; Chen, X.; Chan, S.; Mohamed, T.; Rao, P.P.; Ren, C.L. Droplet microfluidic system with on-demand trapping and releasing of droplet for drug screening applications. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Tay, A.K.P.; Khoo, B.L.; Xiaofeng, X.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Malaria detection using inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crevillén, A.G.; Ávila, M.; Pumera, M.; González, M.C.; Escarpa, A. Food analysis on microfluidic devices using ultrasensitive carbon nanotubes detectors. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7408–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Rather, A.M.; Yao, Y.; Fang, J.C.; Mamtani, R.S.; Bennett, R.K.; Atta, R.G.; Adera, S.; Tkalec, U.; Wang, X. Liquid crystal–based open surface microfluidics manipulate liquid mobility and chemical composition on demand. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshbin, Z.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Verdian, A. Liquid crystal-based biosensors as lab-on-chip tools: Promising for future on-site detection test kits. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 142, 116325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaziz, S.; Saad, Y.; Gazzah, M.H.; Belmabrouk, H. 3D simulation of microfluidic biosensor for SARS-CoV-2 S protein binding kinetics using new reaction surface design. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosic, S.; Murthy, S.K.; Koppes, A.N. Microfluidic sample preparation for single cell analysis. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 354–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nge, P.N.; Rogers, C.I.; Woolley, A.T. Advances in microfluidic materials, functions, integration, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2550–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A. Topological Microfluidics: Nematic Liquid Crystals and Nematic Colloids in Microfluidic Environment; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Demus, D. 100 Years Liquid Crystal Chemistry. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Inc. Nonlinear Opt. 1988, 165, 45–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeon, S.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, H.C.; Oh, B.Y.; Han, J.M.; Lee, J.W.; Seo, D.S. Free residual DC voltage for nematic liquid crystals on solution-derived lanthanum tin oxide film. Liq. Cryst. 2017, 44, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisoyi, H.K.; Bunning, T.J.; Li, Q. Stimuli-driven control of the helical axis of self-organized soft helical superstructures. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannat, M.; Yang, K.L. Liquid crystal-enabled protease inhibition assays developed in a millifluidic device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.R.; Abbott, N.L. Principles for measurement of chemical exposure based on recognition-driven anchoring transitions in liquid crystals. Science 2001, 293, 1296–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M. Liquid crystal orientation induced by Van der Waals interaction. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, 8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikov, S.; Romanov, N.; Nomoev, A. Study of the properties of liquid crystals modified by nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 094304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladepo, S.A. Development and Application of Liquid Crystals as Stimuli-Responsive Sensors. Molecules 2022, 27, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwar, A. Measurement of order parameter, birefringence and polarizibility of liquid crystals. J. Opt. 2013, 42, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P.G.; Prost, J. The Physics of Liquid Crystals; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1993; Number 83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, T.; Noel, A.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, T. Applications of liquid crystals in biosensing. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 4675–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Li, G. Overview of Liquid Crystal Biosensors: From Basic Theory to Advanced Applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodby, J.W. The nanoscale engineering of nematic liquid crystals for displays. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 1363–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, D.; Huo, W.; He, C. Detection of Cecropin B by liquid-crystal biosensor based on AuNPs signal amplification. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, A.P.B.; Kuang, H.; Shabana, A.M.; Labuza, T.P.; Kokkoli, E. Design of an aptamer-amphiphile for the detection of β-lactoglobulin on a liquid crystal interface. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 2763–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Skaife, J.J.; Dubrovsky, T.B.; Abbott, N.L. Optical amplification of ligand-receptor binding using liquid crystals. Science 1998, 279, 2077–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Shah, R.R.; Abbott, N.L. Orientations of liquid crystals on mechanically rubbed films of bovine serum albumin: A possible substrate for biomolecular assays based on liquid crystals. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 4646–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, H.; Lee, S.D. Optical detection of the ligand–receptor binding by anchoring transitions of liquid crystals. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2004, 24, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.D.; Schwartz, D.K. DNA hybridization-induced reorientation of liquid crystal anchoring at the nematic liquid crystal/aqueous interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8188–8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Hartono, D.; Yang, K.L. Real-time liquid crystal pH sensor for monitoring enzymatic activities of penicillinase. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3760–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, C.; Tan, H.; Wu, Y.; Liao, S.; Wu, Z.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. Label-free liquid crystal biosensor based on specific oligonucleotide probes for heavy metal ions. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berreman, D.W. Solid surface shape and the alignment of an adjacent nematic liquid crystal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1972, 28, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, X.; Deng, S. Detection of pulmonary surfactant protein A by using an aptamer-based liquid crystal biosensor. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 2895–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Liao, W.; Zhang, C.X.; Yang, Z. A novel, label-free liquid crystal biosensor for Parkinson’s disease related alpha-synuclein. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5441–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Qu, J.; Xue, F.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, B.; Chang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J. Novel DNA aptamers for Parkinson’s disease treatment inhibit α-synuclein aggregation and facilitate its degradation. Mol.-Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhbakhsh, Z.; Verdian, A.; Rajabzadeh, G. Design of a liquid crystal-based aptasensing platform for ultrasensitive detection of tetracycline. Talanta 2020, 206, 120246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.D.; Hussain, Z.; Yang, K.L. Aptamer laden liquid crystals biosensing platform for the detection of HIV-1 glycoprotein-120. Molecules 2021, 26, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.K.; Griffiths, C.; Lea, S.M.; James, W. Structural characterization of an anti-gp120 RNA aptamer that neutralizes R5 strains of HIV-1. RNA 2005, 11, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.K.; Jang, C.H. A Label-Free Liquid Crystal Biosensor Based on Specific DNA Aptamer Probes for Sensitive Detection of Amoxicillin Antibiotic. Micromachines 2021, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.K.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, W. Quantitative Biosensing Based on a Liquid Crystal Marginally Aligned by the PVA/DMOAP Composite for Optical Signal Amplification. Biosensors 2022, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Kumar, A.; Ganguly, P.; Biradar, A. Highly sensitive bovine serum albumin biosensor based on liquid crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 043705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.Y.; Fan, Y.J.; Tao, L.; Li, M.L.; Zhao, N.; Wang, P.; Chen, E.Q.; Fan, F.; Xie, H.L. Alignment control of nematic liquid crystal using gold nanoparticles grafted by the liquid crystalline polymer with azobenzene mesogens as the side chains. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27269–27277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, H.; Yen, S.C.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, W. Signal amplification in an optical and dielectric biosensor employing liquid crystal-photopolymer composite as the sensing medium. Biosensors 2021, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubijankić, N.; Popović-Javorić, R.; Šćeta, S.; Šapčanin, A.; Tahirović, I.; Sofić, E. Daily fluctuation of cortisol in the saliva and serum of healthy persons. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2008, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, F.M. Some constitutive equations for anisotropic fluids. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 1966, 19, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, F.M. Some constitutive equations for liquid crystals. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 1968, 28, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, R.S.; Hao, X.; Shen, K.; Bashour, K.; Akimova, T.; Hancock, W.W.; Kam, L.C.; Milone, M.C. Substrate rigidity regulates human T cell activation and proliferation. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Polymer microstructures formed by moulding in capillaries. Nature 1995, 376, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.M.; Li, L.; Wang, J.C.; Tu, Q.; Ren, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, J.Y. Dynamic trapping and high-throughput patterning of cells using pneumatic microstructures in an integrated microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, M.A.; Chou, H.P.; Thorsen, T.; Scherer, A.; Quake, S.R. Monolithic microfabricated valves and pumps by multilayer soft lithography. Science 2000, 288, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araci, I.E.; Quake, S.R. Microfluidic very large scale integration (mVLSI) with integrated micromechanical valves. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2803–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Chen, D.L.; Ismagilov, R.F. Reactions in droplets in microfluidic channels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7336–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.J.; Chen, F.L.; Liou, J.C.; Huang, Y.W.; Chen, C.H.; Hong, Z.Y.; Lin, J.D.; Hsiao, Y.C. Label-free multi-microfluidic immunoassays with liquid crystals on polydimethylsiloxane biosensing chips. Polymers 2020, 12, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.Y.; Khan, S.A.; Yang, K.L. Exploring Optical Properties of Liquid Crystals for Developing Label-Free and High-Throughput Microfluidic Immunoassays. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, K.L. Microfluidic immunoassay with plug-in liquid crystal for optical detection of antibody. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, M.; Verma, I.; Pal, S.K. Distinct interfacial ordering of liquid crystals observed by protein–lipid interactions that enabled the label-free sensing of cytoplasmic protein at the liquid crystal-aqueous interface. Analyst 2021, 146, 7152–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, R.J.; Ma, C.D.; Gupta, J.K.; Abbott, N.L. Influence of specific anions on the orientational ordering of thermotropic liquid crystals at aqueous interfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 12796–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Lu, S.; Xie, Q.; Wang, T.; Lu, H.; Yu, L. A stable liquid crystals sensing platform decorated with cationic surfactant for detecting thrombin. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.K.; Jang, C.H. A cationic surfactant-decorated liquid crystal-based aptasensor for label-free detection of malathion pesticides in environmental samples. Biosensors 2021, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.H.; Qiong-Zheng, H.; Qi, K.; Lu-Bin, Q.; Yi-Ping, P.; Li, Y. Research on Competitive Enzymatic Hydrolysis-Assisted Liquid Crystal-based Acetylcholine Sensor. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, e21014–e21019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Guo, Y.; Qi, L.; Hu, Q.; Yu, L. Highly sensitive and label-free detection of catalase by a H2O2-responsive liquid crystal sensing platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yin, F.; Liu, X.; Jiang, T.; Ma, Y.; Gao, G.; Shi, J.; Hu, Q. Development of a liquid crystal-based α-glucosidase assay to detect anti-diabetic drugs. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, R.; Nandagopal, G.; Sreekumar, N.; Selvaraju, N. Detection principles and development of microfluidic sensors in the last decade. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 20, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, D.; Lin, I.H.; Abbott, N.L.; Jiang, H. Microfluidic sensing devices employing in situ-formed liquid crystal thin film for detection of biochemical interactions. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3746–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Fast Detection of Myricetin With the Use of Dedicated Microdroplets. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, S.; Moreno-Razo, J.; Ramírez-Hernández, A.; Díaz-Herrera, E.; Hernández-Ortiz, J.; de Pablo, J.J. Liquid crystal nanodroplets, and the balance between bulk and interfacial interactions. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Jang, C.H. Liquid crystal as sensing platforms for determining the effect of graphene oxide-based materials on phospholipid membranes and monitoring antibacterial activity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.H.; Miller, D.S.; Bertics, P.J.; Murphy, C.J.; De Pablo, J.J.; Abbott, N.L. Endotoxin-induced structural transformations in liquid crystalline droplets. Science 2011, 332, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.C.; Miller, D.S.; Jennings, J.; Wang, X.; Mahanthappa, M.K.; Abbott, N.L.; Lynn, D.M. Synthetic mimics of bacterial lipid A trigger optical transitions in liquid crystal microdroplets at ultralow picogram-per-milliliter concentrations. Langmuir 2015, 31, 12850–12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Gupta, K.C.; Borah, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, I.K. Folate ligand anchored liquid crystal microdroplets emulsion for in vitro detection of KB cancer cells. Langmuir 2014, 30, 10668–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, K.; Gupta, K.C.; Park, S.Y.; Kang, I.K. The role of ligand–receptor interactions in visual detection of HepG2 cells using a liquid crystal microdroplet-based biosensor. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8659–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Gupta, K.C.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Kang, I.K. In vitro detection of human breast cancer cells (SK-BR3) using herceptin-conjugated liquid crystal microdroplets as a sensing platform. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Gong, X.; Birowosuto, M.D.; Dang, C.H.; Chen, Y.C. Dynamic photonic barcodes for molecular detection based on cavity-enhanced energy transfer. Adv. Photonics 2020, 2, 066002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Cheng, X.; Li, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, X.; Chang, G.E.; Birowosuto, M.D.; Dang, C.; Chen, Y.C. Light-Harvesting in Biophotonic Optofluidic Microcavities via Whispering-Gallery Modes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 36909–36918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, X.; Yuan, Z.; Feng, S.; Xu, T.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y.C. Bio-electrostatic sensitive droplet lasers for molecular detection. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 2713–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xu, A.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. Detecting enzymatic reactions in penicillinase via liquid crystal microdroplet-based pH sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, H. Detection of acetylcholinesterase and its inhibitors by liquid crystal biosensor based on whispering gallery mode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 308, 127672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.S.; Abbott, N.L. Influence of droplet size, pH and ionic strength on endotoxin-triggered ordering transitions in liquid crystalline droplets. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Su, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Chen, Q. Highly sensitive and rapid detection of protein kinase C based on liquid crystal biosensor. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.D.; Khan, M.; Park, S.Y. Fabrication of temperature-and pH-sensitive liquid-crystal droplets with PNIPAM-b-LCP and SDS coatings by microfluidics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4922–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, T.; Roberts, R.W.; Arnold, F.H.; Quake, S.R. Dynamic pattern formation in a vesicle-generating microfluidic device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, C.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Drop formation in a co-flowing ambient fluid. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 3045–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Han, D.; Zeng, J.; Deng, J.; Hu, N.; Yang, J. Fabrication and performance of monodisperse liquid crystal droplet-based microchips for the on-chip detection of bile acids. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 105057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.D.; Zhang, J.F.; Hu, N.; Yang, J. Preparation and Sensing Studies of Flow Focusing Microfluidic Chip-based Liquid Crystal Droplet. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Khan, M.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S.; Wu, Z.; Lin, J.M. Monitoring H2O2 on the surface of single cells with liquid crystal elastomer microspheres. Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 9368–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Li, W.; Mao, S.; Shah, S.N.A.; Lin, J.M. Real-Time Imaging of Ammonia Release from Single Live Cells via Liquid Crystal Droplets Immobilized on the Cell Membrane. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Paterson, D.A.; Harrison, P.L.; Miller, K.; Peyman, S.; Jones, J.C.; Sandoe, J.; Evans, S.D.; Bushby, R.J.; Gleeson, H.F. Lipid coated liquid crystal droplets for the on-chip detection of antimicrobial peptides. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Khan, M.; Park, S.Y. Glucose sensor using liquid-crystal droplets made by microfluidics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 13135–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Cordoba, M.A.; Boriskina, S.V.; Vollmer, F.; Demirel, M.C. Nanoparticle-based protein detection by optical shift of a resonant microcavity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 073701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, J.D.; White, I.M.; Zhu, H.; Shi, H.; Caldwell, C.W.; Fan, X. Label-free quantitative DNA detection using the liquid core optical ring resonator. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmer, F.; Arnold, S.; Keng, D. Single virus detection from the reactive shift of a whispering-gallery mode. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20701–20704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Yang, K.Y.; Jeon, S.; Painter, O.; Vahala, K.J. Chemically etched ultrahigh-Q wedge-resonator on a silicon chip. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armani, D.; Min, B.; Martin, A.; Vahala, K.J. Electrical thermo-optic tuning of ultrahigh-Q microtoroid resonators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 5439–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linslal, C.; Kailasnath, M.; Mathew, S.; Nideep, T.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Nampoori, V.; Vallabhan, C. Tuning whispering gallery lasing modes from polymer fibers under tensile strain. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richtmyer, R. Dielectric resonators. J. Appl. Phys. 1939, 10, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Xu, T.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, T. Ultra-sensitive DNAzyme-based optofluidic biosensor with liquid crystal-Au nanoparticle hybrid amplification for molecular detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 359, 131608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gong, C.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, L.; Chang, P.; Liu, K.; Xu, T.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Y.C.; et al. Liquid crystal-amplified optofluidic biosensor for ultra-highly sensitive and stable protein assay. PhotoniX 2021, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, R.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, H. Quantitative and sensitive detection of lipase using a liquid crystal microfiber biosensor based on the whispering-gallery mode. Analyst 2020, 145, 7595–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, R.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, H. Functionalised liquid crystal microfibers for hydrogen peroxide and catalase detection using whispering gallery mode. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; White, I.M.; Fan, X. An opto-fluidic ring resonator biosensor for the detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 133, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Wu, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, L. Ultrasensitive label-free coupled optofluidic ring laser sensor. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 3873–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.y.; Li, P.; Cui, L.; Qiu, J.G.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, C.Y. Integration of nanomaterials with nucleic acid amplification approaches for biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 129, 115959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y. Machine Learning-Driven Multiobjective Optimization: An Opportunity of Microfluidic Platforms Applied in Cancer Research. Cells 2022, 11, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, G.; Yang, L. Phone-sized whispering-gallery microresonator sensing system. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 25905–25910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Zou, C.L.; Lu, J.; Le, Z.; Qin, Y.; Guo, S.; Hu, W. Dissipative sensing with low detection limit in a self-interference microring resonator. JOSA B 2019, 36, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Geometries of LC Biosensors | Fabrication Principle | Type of LC | Target | Detection Method | Detection Limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
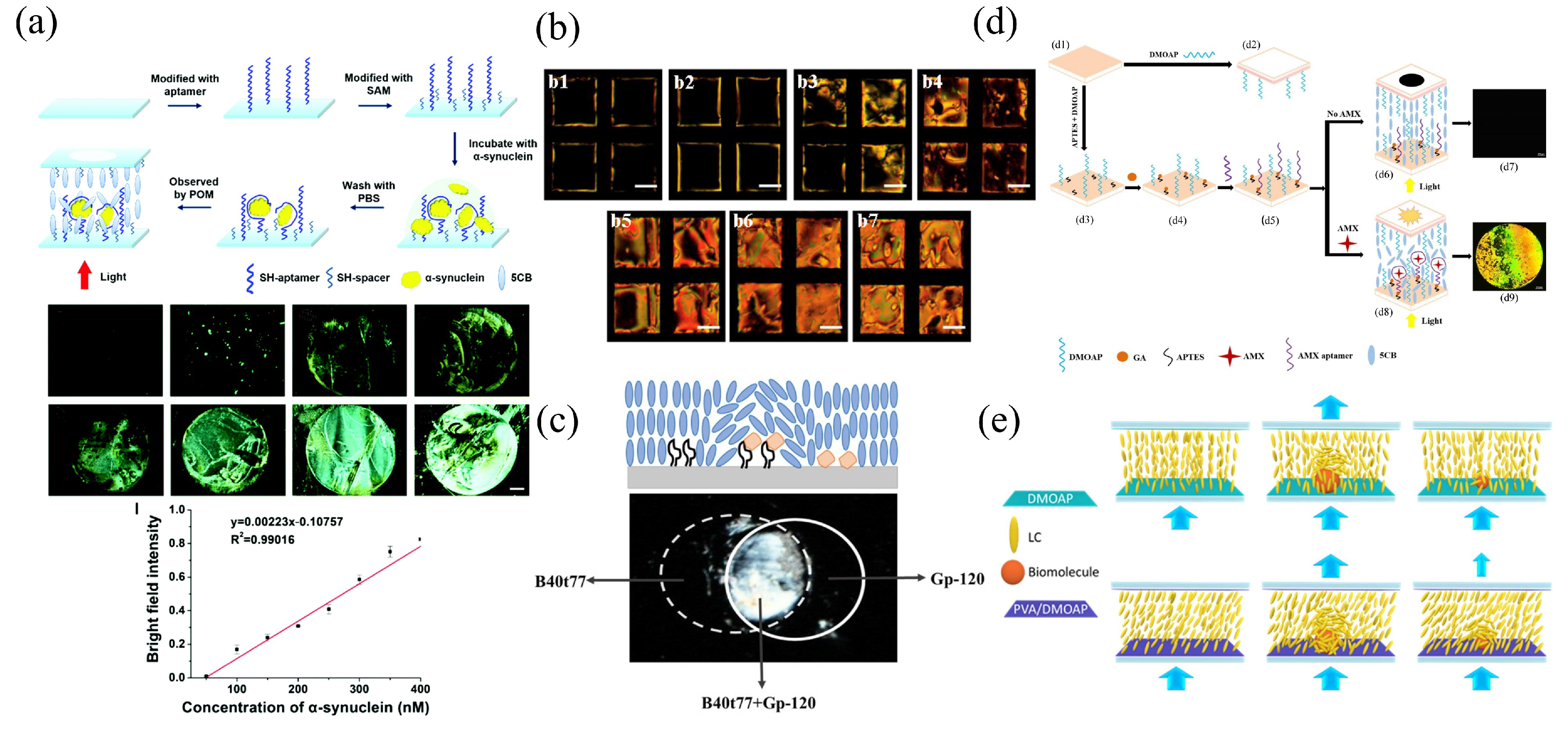
| LC–solid interface | Glass-substrate | 5CB | Alpha-synuclein | POM | 50 nM | [72] |
| 5CB | Tetracycline | POM | 0.5 pM | [74] | ||
| 5CB | Glycoprotein-120 | POM | 0.2 g | [75] | ||
| 5CB | Amoxicillin | POM | 3.5 nM | [77] | ||
| E7 | BSA | POM | g | [78] | ||
| E7 | Cortisol | POM | g | [78] | ||
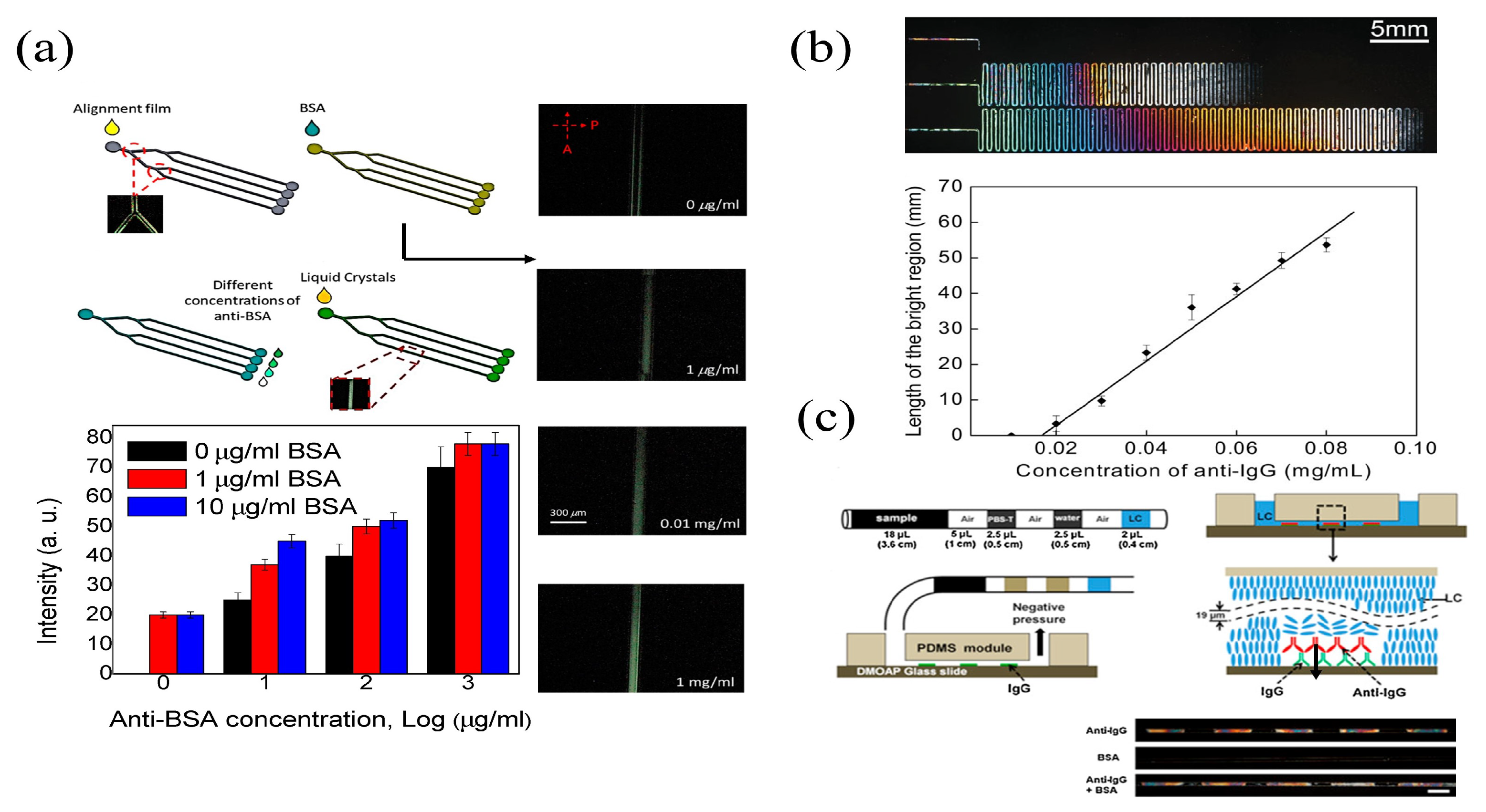
| Microfluidic | E44 | BSA | POM | 0.01 g | [91] | |
| 5CB | Anti-IgG | POM | 0.02 mg | [92] | ||
| 5CB | Anti-IgG | POM | 1 g | [93] | ||
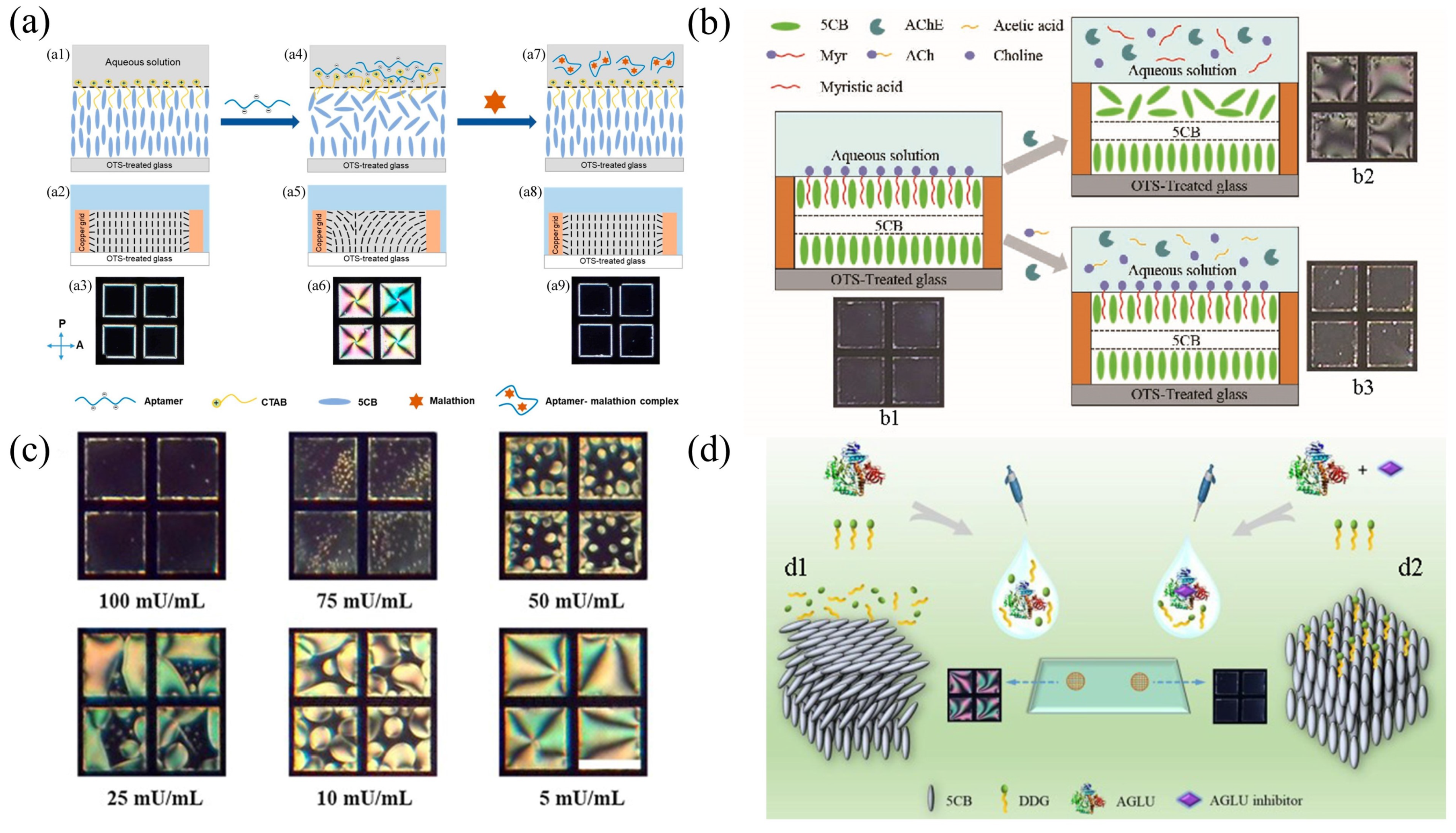
| LC–aqueous interface | Glass-substrate | 5CB | Malathion | POM and gray values | 0.465 nM | [97] |
| 5CB | Acetylcholine | POM and bright area coverage ratio | 14.5 nM | [98] | ||
| 5CB | Catalase | POM and bright area coverage ratio | 5.5 mU | [99] | ||
| 5CB | -glucosidase (AGLU) inhibitors | POM and bright area coverage ratio | Acarbose (0.57 M) Migliol (1.00 M) Voglibose (0.01 M) | [100] | ||
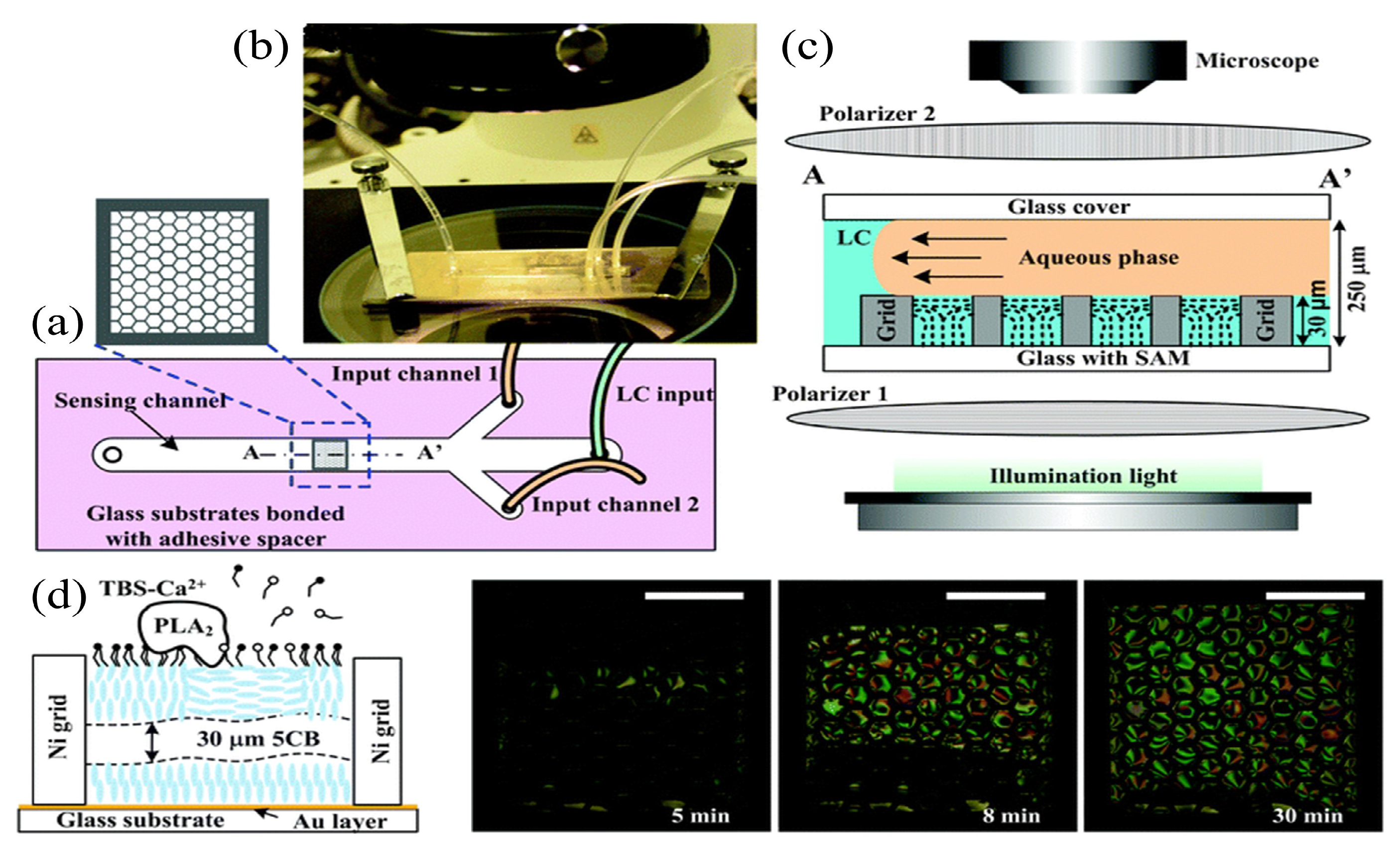
| Microfluidic | 5CB | Phospholipase | POM | 100 nM | [102] | |
| LC droplet | Glass-substrate | 5CB | KB cancer cells | POM and bright field images | 6000 cells | [108] |
| 5CB | HepG2 cells | POM and bright field images | 1.0 ± 0.01 HepG2 cells | [109] | ||
| 5CB | SK-BR3 cancer cells | POM and bright field images | 5000 cells | [110] | ||
| 5CB | BSA | Lasing spectra | 1 pM | [111] | ||
| 5CB | Penicillinase | POM and lasing spectra | M | [112] | ||
| 5CB | AChE | POM and lasing spectra | Fenobucarb (0.1 pg) Dimethoate (1 pg ) | [113] | ||
| Microfluidic | 5CB | Bile acids | POM and bright field images | Cholic acid (10 M) Deoxycholic acid (1 M) | [121] | |
| E7 | POM | M | [123] | |||
| E7 | Ammonia | POM | M | [124] | ||
| E7 | Antimicrobial peptides | POM | 3.6 M | [125] | ||
| 5CB | Glucose | POM | 0.03 mM | [126] |
| Type of Microcavity | Type of LC | Target | Interaction Principle | Detection Limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbubbles made of silicon capillaries | 5CB | L-histidine | Cleavage event of DNAzyme by the biological target leads to the shift of LC orientations | M | [134] |
| Microbubbles made of silicon capillaries | 5CB | BSA | BSA changes tilted LC molecular orientation | 1.92 fM | [135] |
| PMMA microfibers functionalized with LC | 5CB | Lipase | Enzymatic reaction between lipase and glycerol trioleate | 0.01 g | [136] |
| PMMA microfibers functionalized with LC | 5CB | Hydrogen peroxide | Hydrogen peroxide contact with dodecanal-doped LC microfibers results in the shift of LC orientation | 0.26 M | [136] |
| PMMA microfibers functionalized with LC | 5CB | Catalase | Degradation of hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by catalase | 1 ng | [137] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Xu, T.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Leeson, M.S.; Jiang, J.; Liu, T. Liquid Crystal Biosensors: Principles, Structure and Applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080639
Wang H, Xu T, Fu Y, Wang Z, Leeson MS, Jiang J, Liu T. Liquid Crystal Biosensors: Principles, Structure and Applications. Biosensors. 2022; 12(8):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080639
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haonan, Tianhua Xu, Yaoxin Fu, Ziyihui Wang, Mark S. Leeson, Junfeng Jiang, and Tiegen Liu. 2022. "Liquid Crystal Biosensors: Principles, Structure and Applications" Biosensors 12, no. 8: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080639
APA StyleWang, H., Xu, T., Fu, Y., Wang, Z., Leeson, M. S., Jiang, J., & Liu, T. (2022). Liquid Crystal Biosensors: Principles, Structure and Applications. Biosensors, 12(8), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080639






