Mechanical Sensors for Cardiovascular Monitoring: From Battery-Powered to Self-Powered
Abstract
:1. Introduction
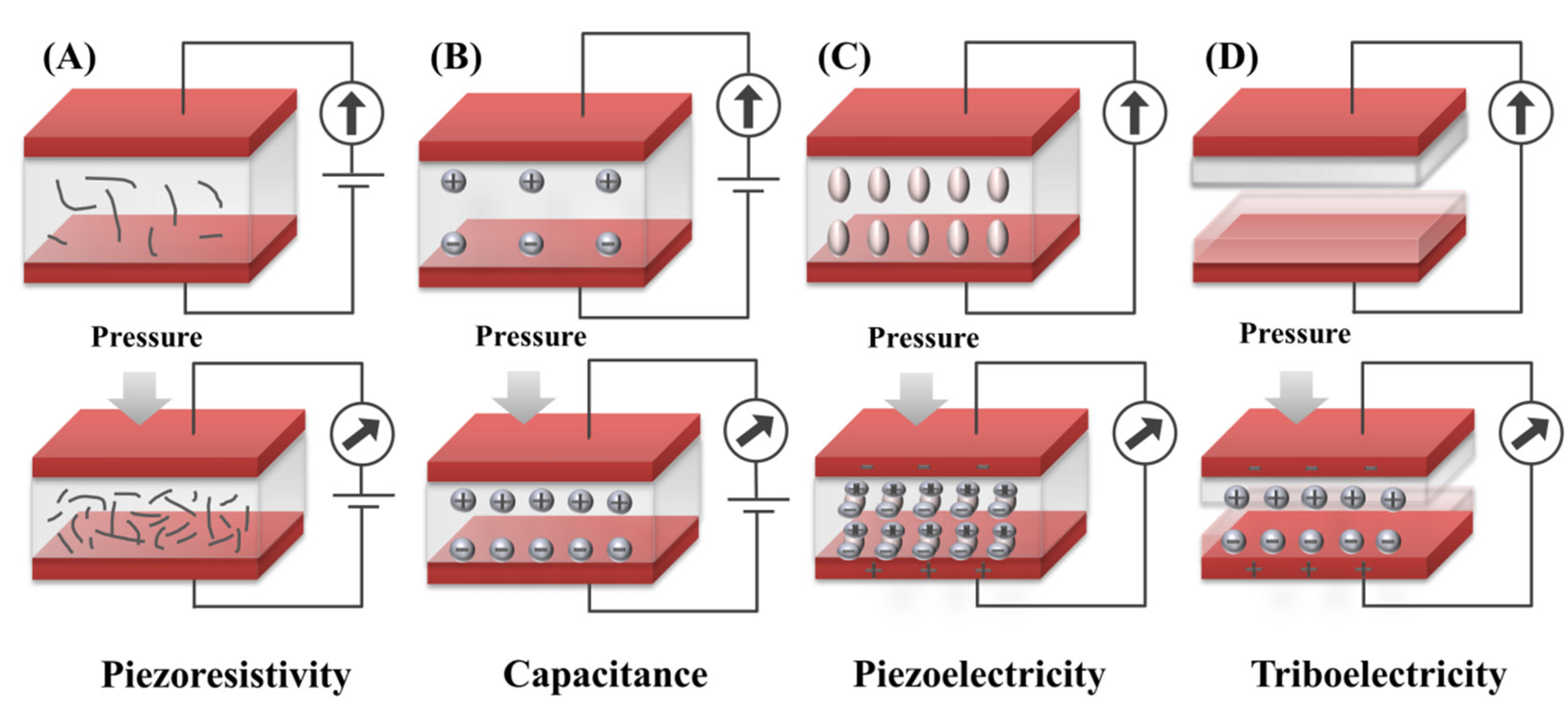
2. Sensing Mechanism
3. Biomechanical Monitoring in the Cardiovascular System
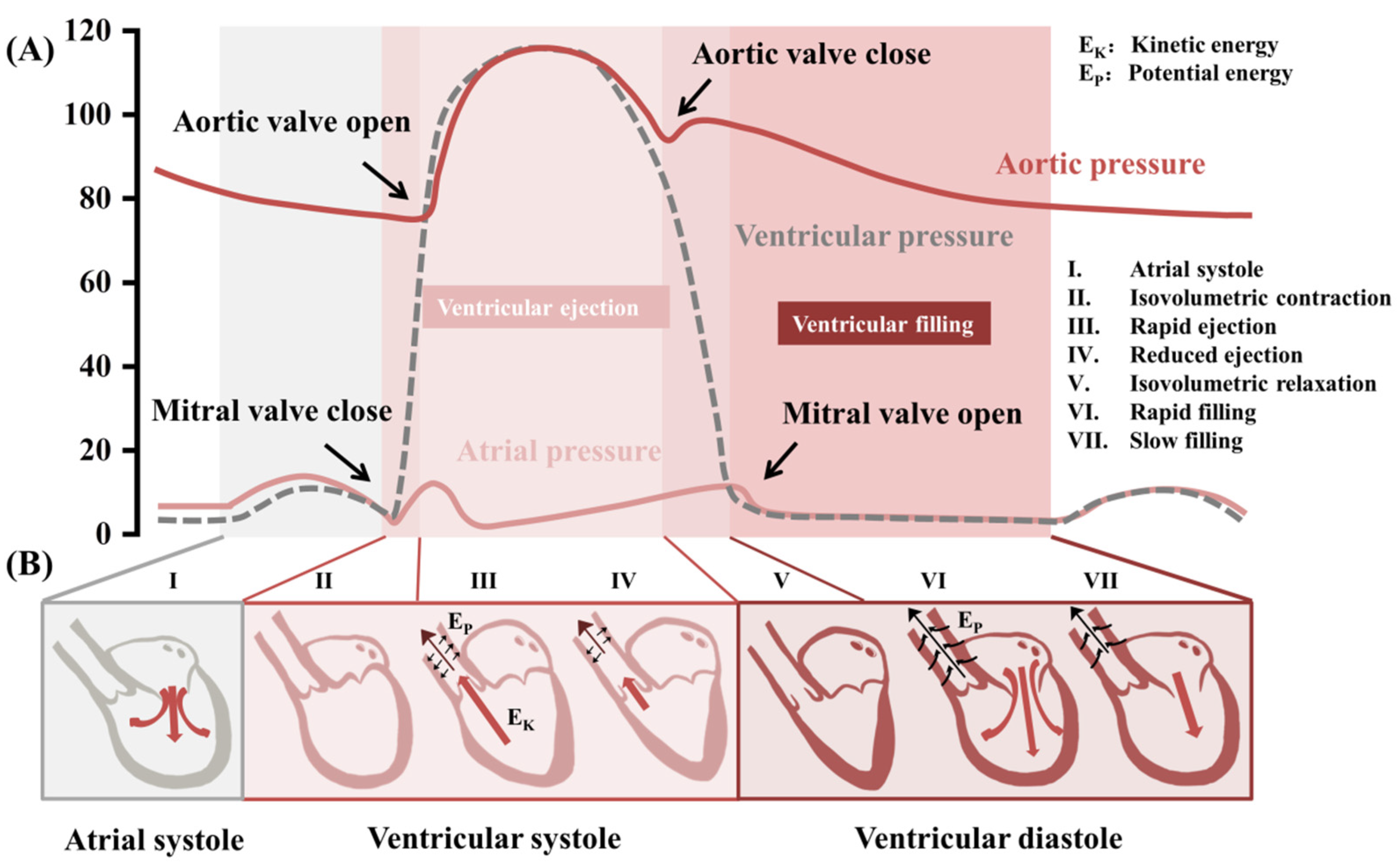
3.1. Pulse Wave
3.2. Blood Pressure
3.2.1. Wearable Blood Pressure Monitoring
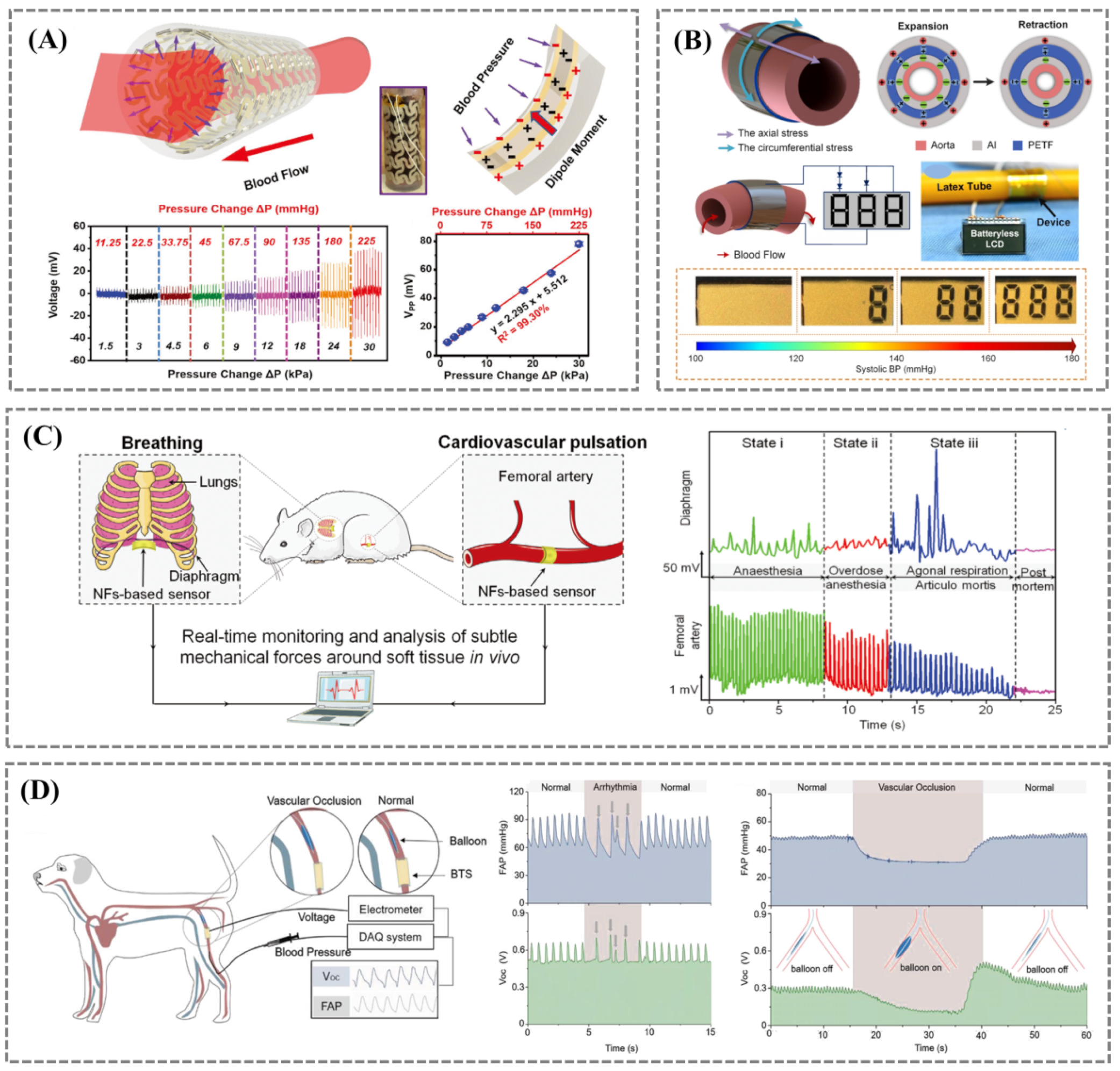
3.2.2. Implantable Blood Pressure Monitoring
3.3. Heart Rhythm and Endocardial Pressure
3.4. Cardiac Output
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Trogdon, J.G.; Khavjou, O.A.; Butler, J.; Dracup, K. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: A policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, P.W.; Ramos, C.; Matin, N.; Dorrance, A.M. The effects of hypertension on the cerebral circulation. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circul. Physiol. 2013, 304, H1598–H1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, Z. Self-powered cardiovascular electronic devices and systems. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, R.L.; Adams, R.; Albers, G.; Alberts, M.J.; Benavente, O.; Furie, K.; Goldstein, L.B.; Gorelick, P.; Halperin, J.; Harbaugh, R. Guidelines for Prevention of Stroke in Patients with Ischemic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Stroke 2006, 37, 577–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S.; Tadic, M.; Larsen, T.H.; Grassi, G.; Mancia, G. Coronavirus disease 2019 and cardiovascular complications: Focused clinical review. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, A.C.S.; Patel, M.S. Wearable Devices to Monitor and Reduce the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence and Opportunities. Annu. Rev. Med. 2020, 72, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagher, L.; Shi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Marrouche, N.F. Wearables in cardiology: Here to stay. Heart Rhythm. 2020, 17, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, E.M.; Varma, N. Remote monitoring of cardiovascular implanted electronic devices: A paradigm shift for the 21st century. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2012, 9, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oei, H.H.S.; Vliegenthart, R.; Hak, A.E.; Sol, A.I.D.; Hofman, A.; Oudkerk, M.; Witteman, J.C.M. The association between coronary calcification assessed by electron beam computed tomography and measures of extracoronary atherosclerosis: The Rotterdam Coronary Calcification Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 39, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaliaros, V.C.; Green, J.T.; Lerakis, S.; Lloyd, M.; Block, P.C. Emerging applications for transseptal left heart catheterization old techniques for new procedures. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 51, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, S.; Johnston, S.C.; Wu, F.; Oladapo, O.; Faramawi, M.F. Cardiovascular risk management and its impact on hypertension control in primary care in low-resource settings: A cluster-randomized trial. Bull. World Health Organ. 2010, 88, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannsfeld, S.C.; Tee, B.C.; Stoltenberg, R.M.; Chen, C.V.; Barman, S.; Muir, B.V.; Sokolov, A.N.; Reese, C.; Bao, Z. Highly sensitive flexible pressure sensors with microstructured rubber dielectric layers. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Oh, J.; Ryu, C.; Yoo, W.J.; Kang, C.Y.; Yoon, S.J.; et al. Highly stretchable piezoelectric-pyroelectric hybrid nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, C.; Koo, J.H.; Nguyen, A.; Caves, J.M.; Kim, M.G.; Chortos, A.; Kim, K.; Wang, P.J.; Tok, J.B.; Bao, Z. Highly skin-conformal microhairy sensor for pulse signal amplification. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Sencadas, V.; Zheng, T.; Higgins, M.J.; Middya, T.R.; Mandal, D. Human skin interactive self-powered wearable piezoelectric bio-e-skin by electrospun poly-l-lactic acid nanofibers for non-invasive physiological signal monitoring. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 7352–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Kim, J.O.; Oh, J.; Kwon, S.Y.; Sim, J.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Choi, H.B.; Park, S. Microstructured Porous Pyramid-Based Ultrahigh Sensitive Pressure Sensor Insensitive to Strain and Temperature. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 19472–19480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, M.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, Y.M. Pulse wave response characteristics for thickness and hardness of the cover layer in pulse sensors to measure radial artery pulse. Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Song, C.; Sheng, S.; Yang, L.; Yan, Z.; Hu, D.J.J.; Sun, Q. Wearable Alignment-Free Microfiber-Based Sensor Chip for Precise Vital Signs Monitoring and Cardiovascular Assessment. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntner, P.; Shimbo, D.; Carey, R.M.; Charleston, J.B.; Gaillard, T.; Misra, S.; Myers, M.G.; Ogedegbe, G.; Schwartz, J.E.; Townsend, R.R.; et al. Measurement of Blood Pressure in Humans: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension 2019, 73, e35–e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qatatsheh, A.; Morsi, Y.; Zavabeti, A.; Zolfagharian, A.; Salim, N.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Mosadegh, B.; Gharaie, S. Blood Pressure Sensors: Materials, Fabrication Methods, Performance Evaluations and Future Perspectives. Sensors 2020, 20, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Fan, X.; Chen, S.C.; Zhao, N. Emerging Technologies of Flexible Pressure Sensors: Materials, Modeling, Devices, and Manufacturing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Xiao, X.; Wei, W.; Chen, G.; Nashalian, A.; Shen, S.; Xiao, X.; Chen, J. Wearable Pressure Sensors for Pulse Wave Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2109357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, K.H.; Zhang, W.; Jang, H.; Kang, S.; Wang, L.; Tan, P.; Hwang, H.; Lu, N. Highly Sensitive Capacitive Pressure Sensors over a Wide Pressure Range Enabled by the Hybrid Responses of a Highly Porous Nanocomposite. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Lu, P.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, Z.; et al. Natural Plant Materials as Dielectric Layer for Highly Sensitive Flexible Electronic Skin. Small 2018, 14, e1801657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Chou, E.F.; Le, J.; Wong, S.; Chu, M.; Khine, M. Soft Wearable Pressure Sensors for Beat-to-Beat Blood Pressure Monitoring. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1900109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Hong, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, Y.; Cho, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, H. Tailoring force sensitivity and selectivity by microstructure engineering of multidirectional electronic skins. NPG Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, H.B.; Yeon, S.M.; Park, J.; Lee, N.K. Flexible and Stretchable Piezoelectric Sensor with Thickness-Tunable Configuration of Electrospun Nanofiber Mat and Elastomeric Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24773–24781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Shi, H.; Wu, J.; Shan, L.; Guo, S.; Dong, S. A flexible, wave-shaped P(VDF-TrFE)/metglas piezoelectric composite for wearable applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 234103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Nabulsi, N.; Zhao, W.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, M.K.; Ryou, J.H. High Durable, Biocompatible, and Flexible Piezoelectric Pulse Sensor Using Single-Crystalline III-N Thin Film. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, R.; Ma, C.; Tang, Z.; Bao, N.; Wu, W.; Fan, F.; Wu, W. Solution-synthesized chiral piezoelectric selenium nanowires for wearable self-powered human-integrated monitoring. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, R.; Li, L. Flexible MXene composed triboelectric nanogenerator via facile vacuum-assistant filtration method for self-powered biomechanical sensing. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Nie, J.; Miao, B.; Li, J.; Cui, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G.; Deng, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. Self-Powered Intracellular Drug Delivery by a Biomechanical Energy-Driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1807795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Wang, A.C.; Ding, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: A Foundation of the Energy for the New Era. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, M.; Xiang, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. High-Throughput and Self-Powered Electroporation System for Drug Delivery Assisted by Microfoam Electrode. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 15458–15467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Zou, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Teng, S.-Y.; Kelleher, J.T.; Nith, R.; Cheng, P.; Li, N.; Liu, W.; et al. A stretchable and strain-unperturbed pressure sensor for motion interference free tactile monitoring on skins. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabi4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutry, C.M.; Nguyen, A.; Lawal, Q.O.; Chortos, A.; Rondeau-Gagne, S.; Bao, Z. A Sensitive and Biodegradable Pressure Sensor Array for Cardiovascular Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6954–6961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magder, S. The meaning of blood pressure. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Huang, Y.; Ding, X.; Luo, N.; Li, C.; Zhao, N.; Chen, S.-C. Alignment-Free Liquid-Capsule Pressure Sensor for Cardiovascular Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1805045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Lee, Y.; Baek, J.; Kwon, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Strunk, K.P.; Stehlin, S.; Melzer, C.; Park, S.M.; et al. Spatiotemporal Measurement of Arterial Pulse Waves Enabled by Wearable Active-Matrix Pressure Sensor Arrays. ACS Nano 2021, 16, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.Y.; Joe, D.J.; Kim, D.H.; Park, H.; Han, J.H.; Jeong, C.K.; Park, H.; Park, J.G.; Joung, B.; Lee, K.J. Self-Powered Real-Time Arterial Pulse Monitoring Using Ultrathin Epidermal Piezoelectric Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Tian, J.; Sun, G.; Zou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Shi, B.; Fan, Y.; Fan, Y.; et al. Self-Powered Pulse Sensor for Antidiastole of Cardiovascular Disease. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Meng, K.; He, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, X.; Feng, Z.; Sun, C.; Yang, J.; et al. Enabling the Unconstrained Epidermal Pulse Wave Monitoring via Finger-Touching. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, M.E. Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Recent Evidence and Clinical Pharmacy Applications. Pharmacotherapy 2013, 33, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kario, K.; Hoshide, S.; Chia, Y.C.; Buranakitjaroen, P.; Siddique, S.; Shin, J.; Turana, Y.; Park, S.; Tsoi, K.; Chen, C.H.; et al. Guidance on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: A statement from the HOPE Asia Network. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2021, 23, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.I.; Struthers, A.D. Beyond blood pressure: Pulse wave analysis—A better way of assessing cardiovascular risk? Future Cardiol. 2005, 1, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Ruan, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W. Piezoelectric Dynamics of Arterial Pulse for Wearable Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, W.; Zhao, X.; Roustaei, M.; Hsiai, T.K.; Chen, J. Ambulatory Cardiovascular Monitoring via a Machine-Learning-Assisted Textile Triboelectric Sensor. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2104178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Zhao, X.; Xun, X.; Kang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, Y. Self-powered ultrasensitive pulse sensors for noninvasive multi-indicators cardiovascular monitoring. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhou, Z.; He, Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Flexible Weaving Constructed Self-Powered Pressure Sensor Enabling Continuous Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Disease and Measurement of Cuffless Blood Pressure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 29, 1806388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, G.; Lao, K.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Gan, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, J.; Huang, J.; Wen, J.; et al. Identifying human body states by using a flexible integrated sensor. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2020, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, J.S.; Tamis-Holland, J.E.; Bangalore, S.; Bates, E.R.; Beckie, T.M.; Bischoff, J.M.; Bittl, J.A.; Cohen, M.G.; DiMaio, J.M.; Don, C.W.; et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, E18–E114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashneh-Tala, S.; MacNeil, S.; Claeyssens, F. The Tissue-Engineered Vascular Graft-Past, Present, and Future. Tissue Eng. Part B-Rev. 2016, 22, 68–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutlip, D.E.; Windecker, S.; Mehran, R.; Boam, A.; Cohen, D.J.; Es, G.V.; Steg, P.G.; Morel, M.A.; Mauri, L.; Vranckx, P. Clinical end points in coronary stent trials: A case for standardized definitions. Circulation 2007, 115, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulsyan, N.; Kashyap, V.S.; Greenberg, R.K.; Sarac, T.P.; Clair, D.G.; Pierce, G.; Ouriel, K. The endovascular management of visceral artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 45, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutry, C.M.; Beker, L.; Kaizawa, Y.; Vassos, C.; Tran, H.; Hinckley, A.C.; Pfattner, R.; Niu, S.; Li, J.; Claverie, J.; et al. Biodegradable and flexible arterial-pulse sensor for the wireless monitoring of blood flow. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, R.; Lim, H.-R.; Rigo, B.; Yeo, W.-H. Fully implantable wireless batteryless vascular electronics with printed soft sensors for multiplex sensing of hemodynamics. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Long, Y.; Yang, F.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Carlos, C.; Dong, Y.; et al. Multifunctional Artificial Artery from Direct 3D Printing with Built-In Ferroelectricity and Tissue-Matching Modulus for Real-Time Sensing and Occlusion Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barri, K.; Jiao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Lin Wang, Z.; Alavi, A.H. Multifunctional Meta-Tribomaterial Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Active Sensing. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, M.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; Wan, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, L. Cell-Traction-Triggered On-Demand Electrical Stimulation for Neuron-Like Differentiation. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2106317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, L. Electromechanical Nanogenerators for Cell Modulation. Nanoenergy Adv. 2022, 2, 110–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xue, X.; Ma, Y.; Han, M.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H. Implantable and self-powered blood pressure monitoring based on a piezoelectric thinfilm: Simulated, in vitro and in vivo studies. Nano Energy 2016, 22, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Feng, Z.Q.; Qu, M.; Yan, K.; Yuan, T.; Gao, B.; Wang, T.; Dong, W.; Zheng, J. Core/Shell Piezoelectric Nanofibers with Spatial Self-Orientated beta-Phase Nanocrystals for Real-Time Micropressure Monitoring of Cardiovascular Walls. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10062–10073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Qu, M.; Carlos, C.; Gu, L.; Jin, F.; Yuan, T.; Wu, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, T.; Dong, W.; et al. High-Performance Poly(vinylidene difluoride)/Dopamine Core/Shell Piezoelectric Nanofiber and Its Application for Biomedical Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2006093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Li, Z.; Gu, M.; Hu, Y.; Xu, L.; Jiang, D.; Cheng, S.; Zou, Y.; Deng, Y.; Shi, B.; et al. A Bioresorbable Dynamic Pressure Sensor for Cardiovascular Postoperative Care. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2102302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X. Materials Perspectives for Self-Powered Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices toward Clinical Translation. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolina, M.; Perego, G.B.; Lunati, M.; Curnis, A.; Guenzati, G.; Vicentini, A.; Parati, G.; Borghi, G.; Zanaboni, P.; Valsecchi, S.; et al. Remote Monitoring Reduces Healthcare Use and Improves Quality of Care in Heart Failure Patients with Implantable Defibrillators: The Evolution of Management Strategies of Heart Failure Patients with Implantable Defibrillators (EVOLVO) Study. Circulation 2012, 125, 2985–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Shi, B.; Li, N.; Jiang, D.; Xie, F.; Qu, D.; Zou, Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Transcatheter Self-Powered Ultrasensitive Endocardial Pressure Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hacker, T.A.; Wei, H.; Long, Y.; Yang, F.; Ni, D.; Rodgers, A.; Cai, W.; Wang, X. Long-term in vivo operation of implanted cardiac nanogenerators in swine. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Shi, B.; Xue, X.; Ji, W.; Liu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zou, Y.; An, Z.; et al. Self-Powered, One-Stop, and Multifunctional Implantable Triboelectric Active Sensor for Real-Time Biomedical Monitoring. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6042–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Closson, A.B.; Jin, C.; Nie, Y.; Cabe, A.; Escobedo, D.; Huang, S.; Trase, I.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; et al. Multifunctional Pacemaker Lead for Cardiac Energy Harvesting and Pressure Sensing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, e2000053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yi, Z.; Ma, Y.; Xie, F.; Huang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Shao, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Direct Powering a Real Cardiac Pacemaker by Natural Energy of a Heartbeat. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, N.; Shi, B.; Zou, Y.; Xie, F.; Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Symbiotic cardiac pacemaker. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flick, M.; Bergholz, A.; Sierzputowski, P.; Vistisen, S.T.; Saugel, B. What is new in hemodynamic monitoring and management? J. Clin. Monitor. Comp. 2022, 36, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saugel, B.; Cecconi, M.; Wagner, J.Y.; Reuter, D.A. Noninvasive continuous cardiac output monitoring in perioperative and intensive care medicine. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, L.A.; Lee, A.; Ho, A.M. A critical review of the ability of continuous cardiac output monitors to measure trends in cardiac output. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 111, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouz, K.; Scheeren, T.W.L.; de Backer, D.; Saugel, B. Pulse Wave Analysis to Estimate Cardiac Output. Anesthesiology 2021, 134, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saugel, B.; Kouz, K.; Scheeren, T.W.L.; Greiwe, G.; Hoppe, P.; Romagnoli, S.; de Backer, D. Cardiac output estimation using pulse wave analysis-physiology, algorithms, and technologies: A narrative review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayat, R.; Goetzenich, A.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, H.; Jansen-Park, S.H.; Schmitz-Rode, T.; Musetti, G.; Schnoering, H.; Autschbach, R.; Hatam, N.; et al. Comparison between radial artery tonometry pulse analyzer and pulsed-Doppler echocardiography derived hemodynamic parameters in cardiac surgery patients: A pilot study. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.C.; Liu, Z.R.; Wan, X.Y.; Li, L.L. Research Progress of Chemical Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Y.; Ostfeld, A.E.; Lochner, C.M.; Pierre, A.; Arias, A.C. Monitoring of Vital Signs with Flexible and Wearable Medical Devices. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4373–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, L. Emerging polymeric electrospun fibers: From structural diversity to application in flexible bioelectronics and tissue engineering. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, L. Mechanical Sensors for Cardiovascular Monitoring: From Battery-Powered to Self-Powered. Biosensors 2022, 12, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080651
Tang C, Liu Z, Li L. Mechanical Sensors for Cardiovascular Monitoring: From Battery-Powered to Self-Powered. Biosensors. 2022; 12(8):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080651
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Chuyu, Zhirong Liu, and Linlin Li. 2022. "Mechanical Sensors for Cardiovascular Monitoring: From Battery-Powered to Self-Powered" Biosensors 12, no. 8: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080651
APA StyleTang, C., Liu, Z., & Li, L. (2022). Mechanical Sensors for Cardiovascular Monitoring: From Battery-Powered to Self-Powered. Biosensors, 12(8), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12080651



