Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Luminescent Chemosensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
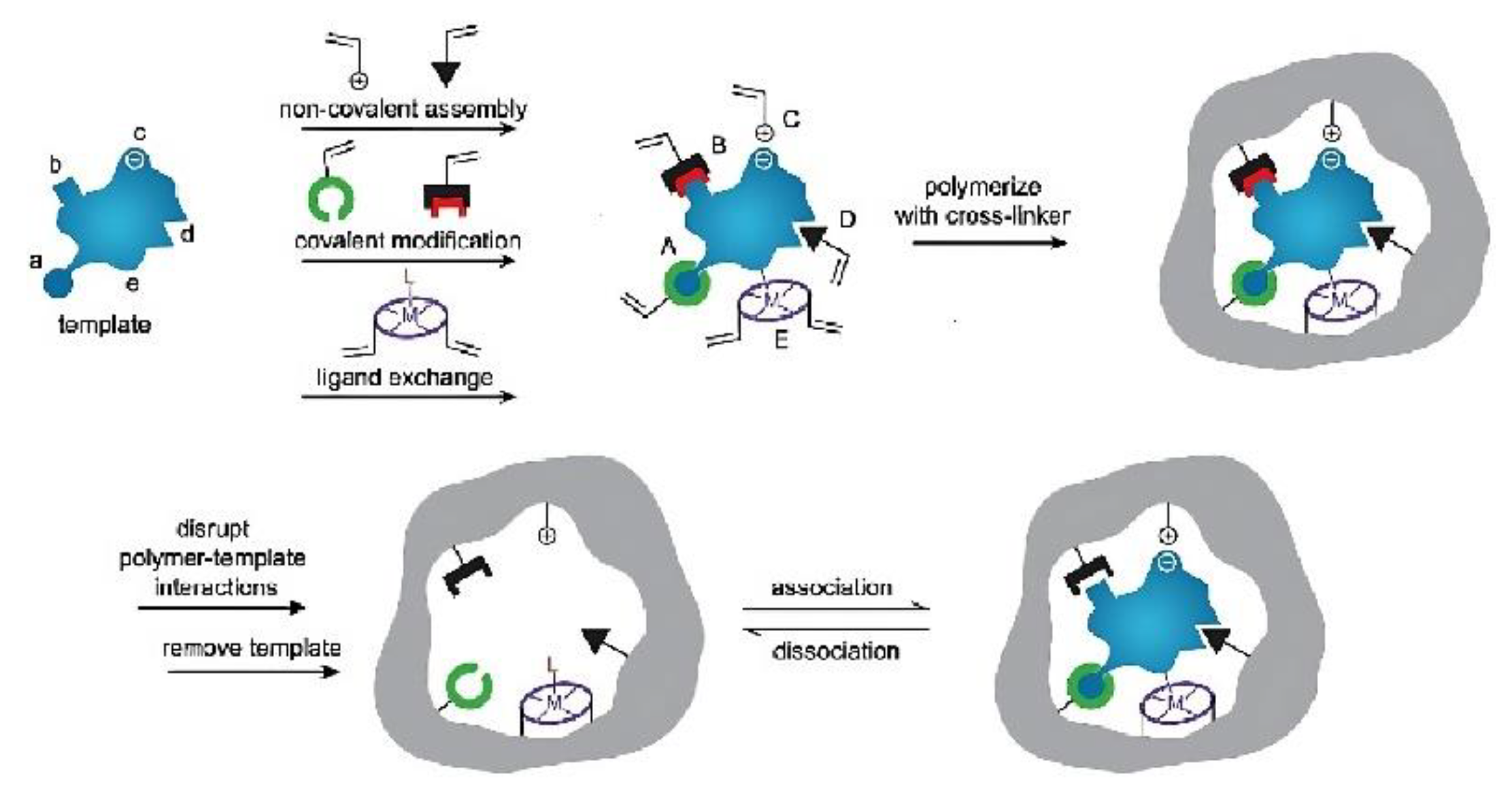
2. Molecular Imprinting Strategy
3. Design Strategies of Luminescent MIPs for Chemosensing Applications
3.1. Using Luminescent Monomer as a Building Block of MIPs
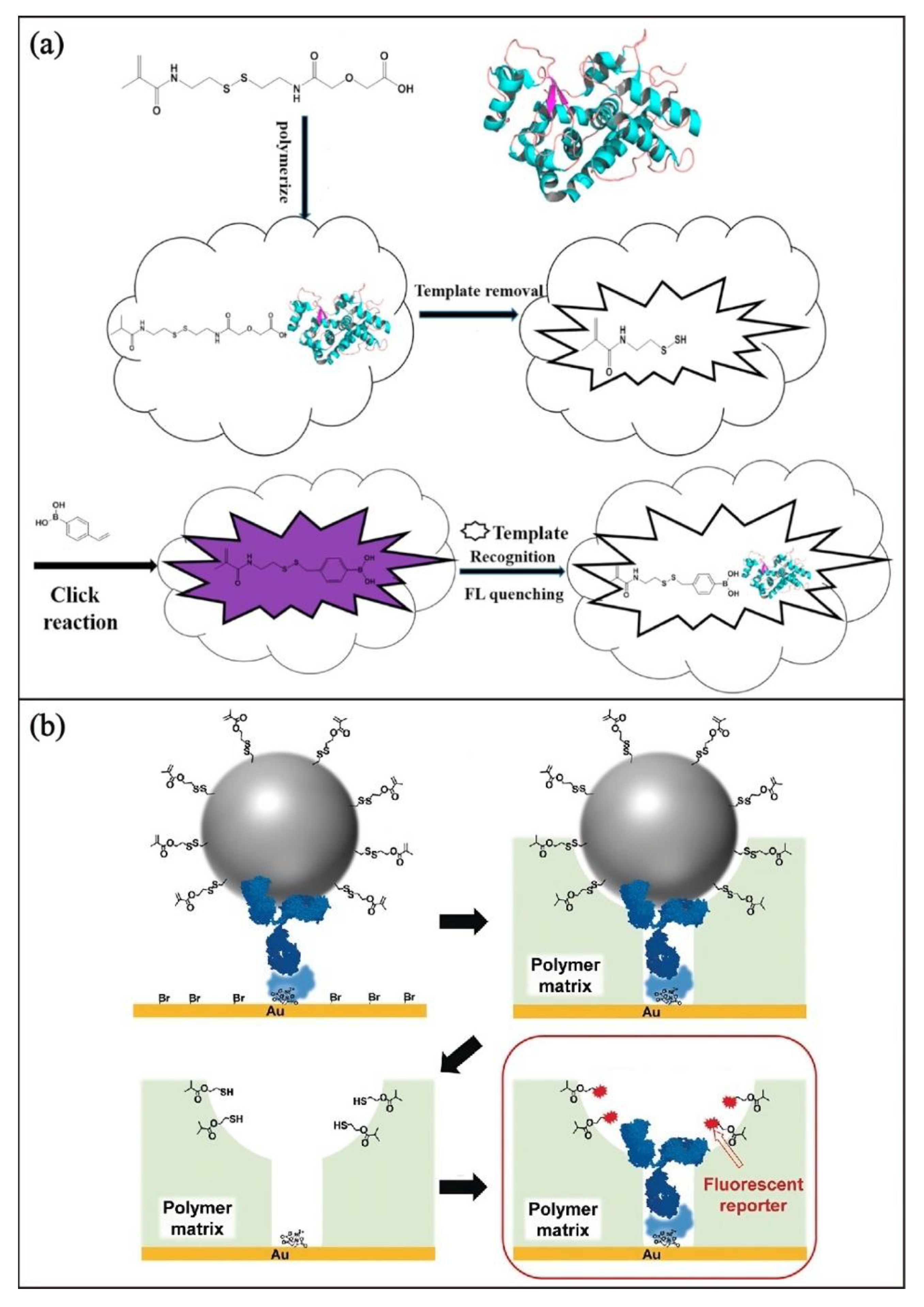
3.2. Chemical Surface Functionalization with a Luminophore
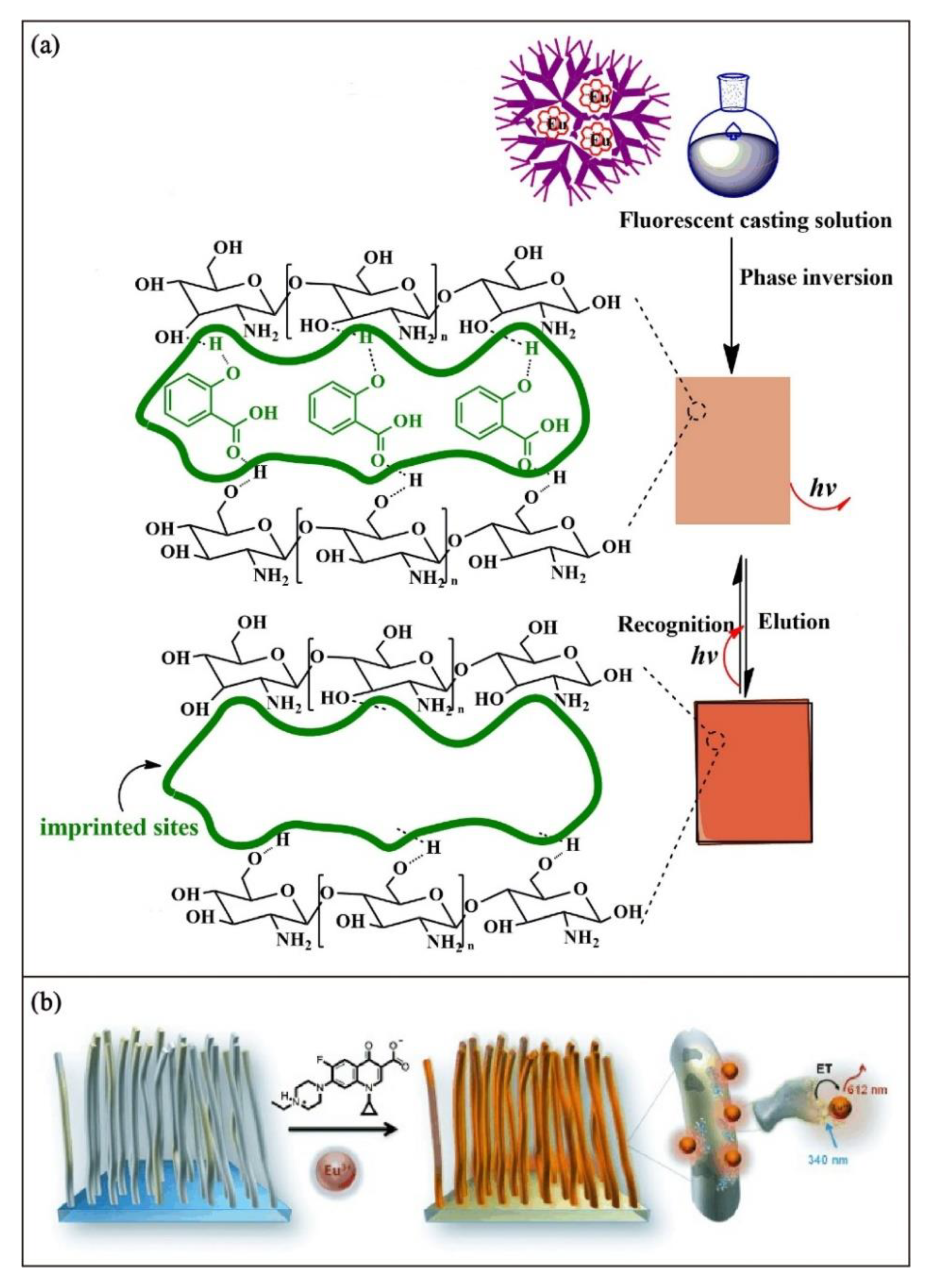
3.3. Physical Entrapment
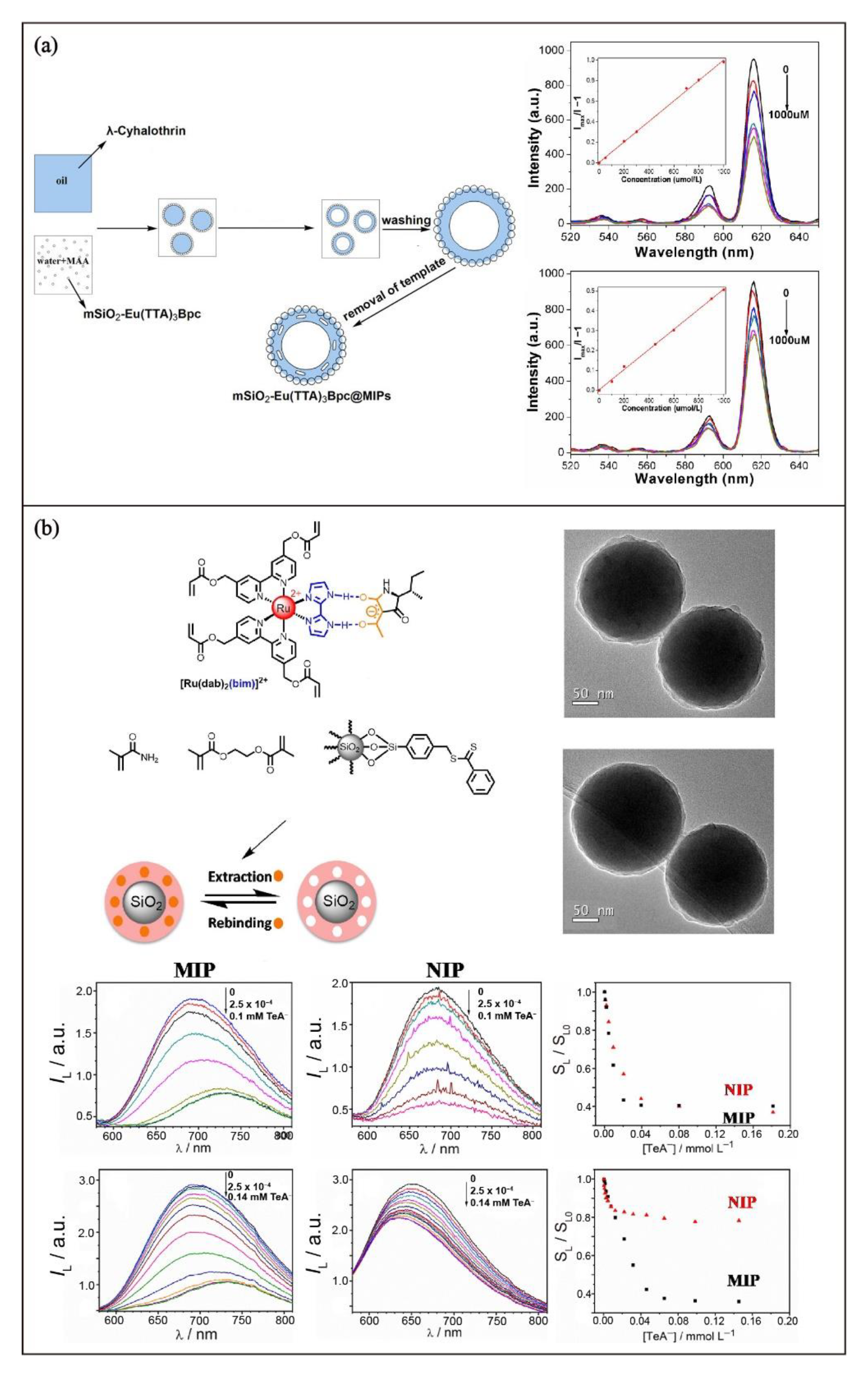
3.4. Encapsulation
4. Classifications of Luminescent MIPs Based on the Nature of Luminophore
4.1. Luminescent Transition Metal Complexes-Functionalized MIPs
4.2. Organic Fluorescent Dyes-Functionalized MIPs
4.3. MIPs Encapsulated on Luminescent Nanomaterials
5. Applications of Luminescent MIP-Based Chemosensors
5.1. Biosensors
5.2. Bio-Imaging
5.3. Food Contaminants and Spoilage Detection
5.4. Clinical Diagnosis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potyrailo, R.A. Toward High Value Sensing: Monolayer-Protected Metal Nanoparticles in Multivariable Gas and Vapor Sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5311–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansha, M.; Akram Khan, S.; Aziz, M.A.; Zeeshan Khan, A.; Ali, S.; Khan, M. Optical Chemical Sensing of Iodide Ions: A Comprehensive Review for the Synthetic Strategies of Iodide Sensing Probes, Challenges, and Future Aspects. Chem. Rec. 2022, 7, e202200059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Chi, L. Electrical Gas Sensors Based on Structured Organic Ultra-Thin Films and Nanocrystals on Solid State Substrates. Nanoscale Horizons 2016, 1, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kim, H.; Pandey, B.; James, T.D.; Yoon, J.; Anslyn, E.V. Recent advances in fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensors for the detection of chemical warfare agents: A legacy of the 21st century. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 663–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yu, J. AIEgens-Functionalized Inorganic-Organic Hybrid Materials: Fabrications and Applications. Small 2016, 12, 6478–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Dong, B.; Liu, Y.; Lin, W. Fluorescent Chemosensors Manipulated by Dual/Triple Interplaying Sensing Mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6449–6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. Multifunctional luminescent switch based on a porous PL-MOF for sensitivity recognition of HCl, trace water and lead ion. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 436, 135028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Das, S.; Kundu, S.; Rawal, I.; Anand, P.; Patra, A. Progress and perspective: Fluorescent to long-lived emissive multifunctional probes for intracellular sensing and imaging. J. Mat. Chem. C 2022, 10, 6141–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Molecular Imprinting for Selective Chemical Sensing of Hazardous Compounds and Drugs of Abuse. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 34, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular Imprinting: Perspectives and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgönüllü, S.; Kılıç, S.; Esen, C.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for Protein Detection. Polymers 2023, 15, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, Y.; Soppera, O.; Haupt, K. Photopolymerization and Photostructuring of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Sensor Applications—A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 717, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tang, S.; Zhao, P.; Tang, K.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z. One-pot synthesis of ternary-emission molecularly imprinted fluorescence sensor based on metal–organic framework for visual detection of chloramphenicol. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Jin, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z. Recent Advances and Future Prospects in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers-Based Electrochemical Biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, M.; Xie, C.; Guan, G.; Wang, D. A Surface Functional Monomer-Directing Strategy for Highly Dense Imprinting of TNT at Surface of Silica Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7859–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tan, L.; Wang, G.; Peng, G.; Kang, C.; Tang, Y. Binding Characteristics of Homogeneous Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Acyclovir Using an (Acceptor-Donor-Donor)-(Donor-Acceptor-Acceptor) Hydrogen-Bond Strategy, and Analytical Applications for Serum Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1285, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndunda, E.N. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers—A Closer Look at the Control Polymer Used in Determining the Imprinting Effect: A Mini Review. J. Mol. Recognit. 2020, 33, e2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swager, T.M. The Molecular Wire Approach to Sensory Signal Amplification. Acc. Chem. Res. 1998, 31, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, F.; Çimen, D.; Bereli, N.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer based quartz crystal microbalance sensor for the clinical detection of insulin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mako, T.L.; Racicot, J.M.; Levine, M. Supramolecular Luminescent Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 322–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toal, S.J.; Trogler, W.C. Polymer Sensors for Nitroaromatic Explosives Detection. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 2871–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na Kim, H.; Xiu Ren, W.; Seung Kim, J.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and Colorimetric Sensors for Detection of Lead, Cadmium, and Mercury Ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3210–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, K.; Hu, Y.J.; Feng, X.C.; Shi, P.D.; Zheng, H.G. A Bifunctional Photoluminescent Metal–organic Framework for Detection of Fe3+ Ion and Nitroaromatics. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2018, 89, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, S.; Pu, L. Amphiphilic Polymer-Based Fluorescent Probe for Enantioselective Recognition of Amino Acids in Immiscible Water and Organic Phases. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 18066–18073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, S.; Swager, T.M. Conjugated Amplifying Polymers for Optical Sensing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4488–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Andersson, H.S.; Andersson, L.I.; Ansell, R.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A.; O’Mahony, J.; Whitcombe, M.J. Molecular Imprinting Science and Technology: A Survey of the Literature for the Years up to and Including 2003. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 106–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcombe, M.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A. Molecular Imprinting Science and Technology: A Survey of the Literature for the Years 2004–2011. J. Mol. Recognit. 2014, 27, 297–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R.; Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Present and Future Prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adumitrăchioaie, A.; Tertiş, M.; Cernat, A.; Săndulescu, R.; Cristea, C. Electrochemical Methods Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Drug Detection. A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 2556–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Advanced Drug Delivery Systems: Synthesis, Character and Application; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mayes, A.G.; Whitcombe, M.J. Synthetic strategies for the generation of molecularly imprinted organic polymers. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2005, 57, 1742–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajini, T.; Gigimol, M.G.; Mathew, B. A brief overview of molecularly imprinted polymers supported on titanium dioxide matrices. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 11, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajini, T.; Mathew, B. A Brief Overview of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Highlighting Computational Design, Nano and Photo-Responsive Imprinting. Talanta Open 2021, 4, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reville, E.K.; Sylvester, E.H.; Benware, S.J.; Negi, S.S.; Berda, E.B. Customizable Molecular Recognition: Advancements in Design, Synthesis, and Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 3387–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautner, G.; Kaev, J.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Rappich, J.; Syritski, V.; Gyurcsányi, R.E. Selective Artificial Receptors Based on Micropatterned Surface-Imprinted Polymers for Label-Free Detection of Proteins by SPR Imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, A.; Borrull, F.; Marcé, R.M.; Cormack, P.A.G. Molecularly-Imprinted Polymers: Useful Sorbents for Selective Extractions. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Feng, T.; Xu, J.; Xue, C. Recent Advances of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors in the Detection of Food Safety Hazard Factors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Kant, K.; Chidambara, V.A.; Wolff, A.; Bang, D.D.; Sun, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Sample Preparation and Biosensing in Food Analysis: Progress and Perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Li, J. Recent Advances in Molecular Imprinting Technology: Current Status, Challenges and Highlighted Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2922–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, W.J.; Ali, F.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.O.; Yune, S.K. Recent applications of molecular imprinted polymers for enantio-selective recognition. Talanta 2013, 106, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, V.; Delaunay, N.; Combes, A. Sample preparation using molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiel, E.; Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Sample Preparation: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 668, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, W.; Yoon, J.; Tian, H. Recent Progress on Polymer-Based Fluorescent and Colorimetric Chemosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Huang, X.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, J.; Xu, D. Recent Advances and Perspectives of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Fluorescent Sensors in Food and Environment Analysis. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Jin, H. Recent Advances in Synthetic Methods and Applications of Photo-Luminescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2019, 41, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.; Xiong, H.; Chen, L. Strategies of molecular imprinting-based fluorescence sensors for chemical and biological analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, X.A.; Acha, V.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Direct Fluorimetric Sensing of UV-Excited Analytes in Biological and Environmental Samples Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles and Fluorescence Polarization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, S.; Canalejas-Tejero, V.; Navarro-Villoslada, F.; Barrios, C.A.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Cross-Linkable Linear Copolymer with Double Functionality: Resist for Electron Beam Nanolithography and Molecular Imprinting. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 1400–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletsky, S.A.; Piletskaya, E.V.; Elskaya, A.V.; Levi, R.; Yano, K.; Karube, I. Optical detection system for triazine based on molecularly-imprinted polymers. Anal. Lett. 1997, 30, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito-Peña, E.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Aparicio, S.; Orellana, G.; Cederfur, J.; Kempe, M. Molecular Engineering of Fluorescent Penicillins for Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Assays. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, S.; Nahavandifard, F. Molecular Imprinting-Based Fluorescent Optosensor Using a Polymerizable 1,8-Naphthalimide Dye as a Florescence Functional Monomer. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2014, 197, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descalzo, A.B.; Somoza, C.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Orellana, G. Luminescent Core-Shell Imprinted Nanoparticles Engineered for Targeted Förster Resonance Energy Transfer-Based Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5316–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Xiao, H.; Wang, H.; Tang, B. A Fluorescence Nanosensor for Glycoproteins with Activity Based on the Molecularly Imprinted Spatial Structure of the Target and Boronate Affinity. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12489–12493. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, A.L.; Murray, G.M. Ultratrace Determination of Lanthanides by Luminescence Enhancement. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 2974–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, M.K.-P.; Chow, C.-F.; Lam, M.H.-W. A sol–gel derived molecular imprinted luminescent PET sensing material for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 2985–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Biyikal, M.; Wagner, R.; Sellergren, B.; Rurack, K. Fluorescent Sensory Microparticles That “Light-up” Consisting of a Silica Core and a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Shell. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7023–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunayama, H.; Ooya, T.; Takeuchi, T. Fluorescent Protein Recognition Polymer Thin Films Capable of Selective Signal Transduction of Target Binding Events Prepared by Molecular Imprinting with a Post-Imprinting Treatment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.-Y. Toward Biocompatible Semiconductor Quantum Dots: From Biosynthesis and Bioconjugation to Biomedical Application. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11669–11717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H. Efficient One-Pot Synthesis of Hydrophilic and Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Direct Drug Quantification in Real Biological Samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, T.; Jin, Y.; Ling, B.; Li, Q.; Li, J. A Simple Approach to Prepare Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 7732–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, R.; Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Takano, E.; Takeuchi, T. A Programmable Signaling Molecular Recognition Nanocavity Prepared by Molecular Imprinting and Post-Imprinting Modifications. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13023–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moczko, E.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Perez De Vargas Sansalvador, I.; Caygill, S.; Canfarotta, F.; Whitcombe, M.J.; Piletsky, S. Surface-Modified Multifunctional MIP Nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3733–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunayama, H.; Ooya, T.; Takeuchi, T. Fluorescent Protein-Imprinted Polymers Capable of Signal Transduction of Specific Binding Events Prepared by a Site-Directed Two-Step Post-Imprinting Modification. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1347–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Kamra, T.; Ye, L. A Modular Approach for Assembling Turn-on Fluorescence Sensors Using Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12237–12240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Wagner, S.; Rurack, K. Fluorescent Monomers: “Bricks” that Make a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer “Bright”. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1753–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Deng, Q.; Wang, S. One-Step Post-Imprint Modification Achieve Dual-Function of Glycoprotein Fluorescent Sensor by “Click Chemistry”. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Hirase, M.; Morishige, T.; Takano, E.; Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Inubushi, S.; Sasaki, R.; Yashiro, M.; Takeuchi, T. A Pretreatment-Free, Polymer-Based Platform Prepared by Molecular Imprinting and Post-Imprinting Modifications for Sensing Intact Exosomes. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1612–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, A.L.; Uy, O.M.; Murray, G.M. Polymer Based Lanthanide Luminescent Sensors for the Detection of Nerve Agents. Anal. Commun. 1997, 34, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosef, I.; Abu-Reziq, R.; Avnir, D. Entrapment of an Organometallic Complex within a Metal: A Concept for Heterogeneous Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11880–11882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Bai, M.; Da, Z.; Cui, Y.; Li, B.; Pan, J. Selective Recognition of Salicylic Acid Employing New Fluorescent Imprinted Membrane Functionalized with Poly(Amidoamine) (PAMAM)-Encapsulated Eu(TTA)3phen. J. Lumin. 2019, 208, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdunek, J.; Benito-Peña, E.; Linares, A.; Falcimaigne-Cordin, A.; Orellana, G.; Haupt, K.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Surface-Imprinted Nanofilaments for Europium-Amplified Luminescent Detection of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2013, 19, 10209–10216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, L.; Han, D.; Pan, J.; Qiu, H.; Li, H.; Wei, X.; Dai, J.; Yang, J.; Yao, H.; et al. Optical Detection of λ-Cyhalothrin by Core-Shell Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Chinese Spirits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 2392–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent Carbon Nanodots: Emergent Nanolights. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Luminescent Molecularly-Imprinted Polymer Nanocomposites for Sensitive Detection. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 67, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tan, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liang, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Mesoporous Silica Embedded with Perovskite CsPbBr3 Quantum Dots for the Fluorescence Sensing of 2,2-Dichlorovinyl Dimethyl Phosphate. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2020, 325, 128751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Chang, J.Y. Preparation of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Containing Europium(III) Ions for Luminescent Sensing. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 4990–4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Yuste, A.; Abouhany, R.; Urraca, J.L.; Descalzo, A.B.; Orellana, G.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Eu(III)-Templated Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Used as a Luminescent Sensor for the Determination of Tenuazonic Acid Mycotoxin in Food Samples. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür, E.; Patra, H.K.; Turner, A.P.F.; Denizli, A.; Uzun, L. Lanthanide [Terbium(III)]-Doped Molecularly Imprinted Nanoarchitectures for the Fluorimetric Detection of Melatonin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 16068–16076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quílez-Alburquerque, J.; Descalzo, A.B.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Orellana, G. Luminescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanocomposites for Emission Intensity and Lifetime Rapid Sensing of Tenuazonic Acid Mycotoxin. Polymer 2021, 230, 124041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southard, G.E.; Van Houten, K.A.; Ott, E.W.; Murray, G.M. Luminescent Sensing of Organophosphates Using Europium(III) Containing Imprinted Polymers Prepared by RAFT Polymerization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 581, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Pan, J.; Gao, L.; Wei, X.; Dai, J.D.; Shi, W.D.; Yan, Y. Silica Nanoparticles Doped with a Europium(III) Complex and Coated with an Ion Imprinted Polymer for Rapid Determination of Copper(II). Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armelao, L.; Quici, S.; Barigelletti, F.; Accorsi, G.; Bottaro, G.; Cavazzini, M.; Tondello, E. Design of Luminescent Lanthanide Complexes: From Molecules to Highly Efficient Photo-Emitting Materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Song, Z.; Pan, J.; Wei, X.; Gao, L.; Yan, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Dai, J.; et al. Molecular Imprinting in Fluorescent Particle Stabilized Pickering Emulsion for Selective and Sensitive Optosensing of λ-Cyhalothrin. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 10445–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subat, M.; Borovik, A.S.; König, B. Synthetic Creatinine Receptor: Imprinting of a Lewis Acidic Zinc(II)Cyclen Binding Site to Shape Its Molecular Recognition Selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3185–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recillas Mota, J.J.; Bernad Bernad, M.J.; Mayoral-Murillo, J.A.; Gracia Mora, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers with Metallic Zinc Center for Enrofloxacin Recognition. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, S.; Benito-Peña, E.; Walt, D.R.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Fiber-Optic Array Using Molecularly Imprinted Microspheres for Antibiotic Analysis. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 3139–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, G. Disposable Terbium (III) Salicylate Complex Imprinted Membrane Using Solid Phase Surface Fluorescence Method for Fast Separation and Detection of Salicylic Acid in Pharmaceuticals and Human Urine. Talanta 2013, 107, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneckova, T.; Bezdekova, J.; Han, G.; Adam, V.; Vaculovicova, M. Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Artificial Receptors for Imaging. Acta Biomater. 2020, 101, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheubong, C.; Takano, E.; Kitayama, Y.; Sunayama, H.; Minamoto, K.; Takeuchi, R.; Furutani, S.; Takeuchi, T. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanogel-Based Fluorescence Sensing of Pork Contamination in Halal Meat Extracts. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.; El-Schich, Z.; Malakpour, A.; Wan, W.; Dizeyi, N.; Mohammadi, R.; Rurack, K.; Gjörloff Wingren, A.; Sellergren, B. Sialic Acid-Imprinted Fluorescent Core-Shell Particles for Selective Labeling of Cell Surface Glycans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13908–13912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Medina Rangel, P.X.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Antibody Mimics for Bioimaging and Therapy. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 9554–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrum, K.F.; Lancaster, J.M.; Johnston, S.E.; Gilman, S.D. Monitoring Electroosmotic Flow by Periodic Photobleaching of a Dilute, Neutral Fluorophore. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 4317–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunath, S.; Panagiotopoulou, M.; Maximilien, J.; Marchyk, N.; Sänger, J.; Haupt, K. Cell and Tissue Imaging with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Plastic Antibody Mimics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1322–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, C. CdTe Quantum Dots@luminol as Signal Amplification System for Chrysoidine with Chemiluminescence-Chitosan/Graphene Oxide-Magnetite-Molecularly Imprinting Sensor. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 153, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.V.; Mirata, F.; Pérollier, C.; Arotcarena, M.; Bayoudh, S.; Resmini, M. Smart Coumarin-Tagged Imprinted Polymers for the Rapid Detection of Tamoxifen. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, K.; Sunayama, H.; Kitayama, Y.; Takano, E.; Nakamachi, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Takeuchi, T. Fluorescent Signaling of Molecularly Imprinted Nanogels Prepared via Postimprinting Modifications for Specific Protein Detection. Adv. NanoBiomed. Res. 2021, 1, 2000079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Deng, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Hu, W.; Guo, L.; Li, L.; Wan, S.; et al. Highly Sensitive Determination of 4-Nitrophenol with Coumarin-Based Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Poly (Ionic Liquid). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Fei, Y.; Gao, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, T.; Zhou, X.S.; Shao, Y.; Yin, Z.Z. G-Quadruplex DNA with an Apurinic Site as a Soft Molecularly Imprinted Sensing Platform. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5552–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Li, B.; Zhao, J.; Qi, J.; Hao, G.; Jianhui, R.; Yang, X. Fluorescence Detection of 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid by Ratiometric Fluorescence Imaging on Paper-Based Microfluidic Chips. Analyst 2020, 145, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shinde, S.; Grasso, G.; Caroli, A.; Abouhany, R.; Lanzillotta, M.; Pan, G.; Wan, W.; Rurack, K.; Sellergren, B. Selective Detection of Phospholipids Using Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Sensory Core-Shell Particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Haupt, K.; Tse Sum Bui, B. Core–shell molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles as synthetic antibodies in a sandwich fluoroimmunoassay for trypsin determination in human serum. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24476–24483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Song, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the fluorescent detection of trace 17β-estradiol in environmental water. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; Feng, X.; Sun, Y. A multifunctional molecularly imprinted polymer-based biosensor for direct detection of doxycycline in food samples. Talanta 2018, 182, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Luo, J.; Yin, G.; Xu, Z.; Le, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Q. Selective determination of dimethoate via fluorescence resonance energy transfer between carbon dots and a dye-doped molecularly imprinted polymer. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Tan, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, D.; Fei, J. A mesoporous silica-based probe with a molecularly imprinted polymer recognition and Mn: ZnS QDs@rhodamine B ratiometric fluorescence sensing strategy for the analysis of 4-nitrophenol. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 3881–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Feng, T.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, S.; Yang, B. Carbonized Polymer Dots: A Brand New Perspective to Recognize Luminescent Carbon-Based Nanomaterials. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 5182–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Liu, S.L.; Pang, D.W. Quantum Dots: A Promising Fluorescent Label for Probing Virus Trafficking. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 2991–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Saeed, M.H.; Zhang, S.; Wei, H.; Gao, Y.; Zou, C.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Luminescence Enhancement, Encapsulation, and Patterning of Quantum Dots Toward Display Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Jin, H.; Wang, Z.; Tan, L. Recent Advances in Optical Properties and Applications of Colloidal Quantum Dots under Two-Photon Excitation. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 338, 141–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, H.R.; Schiffman, J.D.; Balakrishna, R.G. Quantum Dots as Fluorescent Probes: Synthesis, Surface Chemistry, Energy Transfer Mechanisms, and Applications. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 1191–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Assi, N.; Rypar, T.; Macka, M.; Adam, V.; Vaculovicova, M. Microfluidic paper-based fluorescence sensor for L-homocysteine using a molecularly imprinted polymer and in situ-formed fluorescent quantum dots. Talanta 2023, 255, 124185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H. Biological Sample-Compatible Ratiometric Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microspheres by RAFT Coupling Chemistry. Langmuir 2020, 36, 12403–12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantada-Vázquez, M.P.; Sánchez-González, J.; Peña-Vázquez, E.; Tabernero, M.J.; Bermejo, A.M.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Simple and Sensitive Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Mn-Doped ZnS Quantum Dots Based Fluorescence Probe for Cocaine and Metabolites Determination in Urine. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2734–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; You, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers-Coated Gold Nanoclusters for Fluorescent Detection of Bisphenol A. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015, 211, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, A. Carbon Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6921–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Nasr-Esfahani, P.; Rezaei, B. Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer on Carbon Quantum Dots as an Optical Sensor for Selective Fluorescent Determination of Promethazine Hydrochloride. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018, 257, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, E.; Üzek, R.; Merkoçi, A. Paper Based Photoluminescent Sensing Platform with Recognition Sites for Tributyltin. ACS Sensors 2019, 4, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahid, B. Specific Fluorescence Probe for Direct Recognition of Dimethoate Using Molecularly Imprinting Polymer on ZnO Quantum Dots. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, H.; Cui, J.; Liu, S.; Yan, Y.; Li, C. SiO2-MIP Core-Shell Nanoparticles Containing Gold Nanoclusters for Sensitive Fluorescence Detection of the Antibiotic Erythromycin. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Min, H.; Xu, X.; Li, Y. Sensitive Determination of Ofloxacin by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Containing Ionic Liquid Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots and Europium Ion. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 8467–8474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, K.; Jothi, V.K.; Rajaram, A.; Natarajan, A. Novel Metal-Free Fluorescent Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer N-CDs@MIP for Highly Selective Detection of TNP. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, H.; Zhang, H. Direct and Highly Selective Drug Optosensing in Real, Undiluted Biological Samples with Quantum-Dot-Labeled Hydrophilic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Microparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15741–15749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Guo, M.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, R.; Yang, X. A Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Sensor Based on the ZnO Quantum Dot Core-Shell Structure for High Selectivity and Photolysis Function of Methylene Blue. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20664–20673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Guo, M.; Tan, J.; Geng, Y.; Wu, J.; Tang, Y.; Su, C.; Lin, C.C.; Liang, Y. Novel Fluorescence Sensor Based on All-Inorganic Perovskite Quantum Dots Coated with Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Highly Selective and Sensitive Detection of Omethoate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 39056–39063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masteri-Farahani, M.; Mashhadi-Ramezani, S.; Mosleh, N. Molecularly imprinted polymer containing fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a new fluorescent nanosensor for detection of methamphetamine. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 229, 118021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Li, Z.; Jin, Y.; Ren, T.; Wang, X.; Zhong, K.; Tang, L.; Tang, Y.; Cao, M. Novel magnetic fluorescence probe based on carbon quantum dots-doped molecularly imprinted polymer for AHLs signaling molecules sensing in fish juice and milk. Food Chem. 2020, 328, 127063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistani, S.; Shekarchizadeh, H. Fabrication of fluorescence sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer on amine-modified carbon quantum dots for fast and highly sensitive and selective detection of tannic acid in food samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1186, 339122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abha, K.; Nebu, J.; Devi, J.A.; Aparna, R.S.; Anjana, R.R.; Aswathy, A.O.; George, S. Photoluminescence sensing of bilirubin in human serum using L-cysteine tailored manganese doped zinc sulphide quantum dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Ren, Y.; Fan, J. Cu-Mn codoped ZnS quantum dots-based ratiometric fluorescent sensor for folic acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1040, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton, X.A.; Tse Sum Bui, B.; Resmini, M.; Bonomi, P.; Dika, I.; Soppera, O.; Haupt, K. A Versatile Fiber-Optic Fluorescence Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Microstructures Polymerized in Situ. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8317–8321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Zhang, C.; Yu, F.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly CdTe Quantum Dots and Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Modified Chemiluminescence Sensor for Deltamethrin Detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Kuwahara, A.; Ohmori, K.; Sunayama, H.; Ooya, T.; Takeuchi, T. Fluorescent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Thin Films for Specific Protein Detection Prepared with Dansyl Ethylenediamine-Conjugated O-Acryloyl l-Hydroxyproline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, J.; Xu, Y.; Dai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Sellergren, B.; Pan, G. Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescent Test Strip for Direct, Rapid, and Visual Dopamine Detection in Tiny Amount of Biofluid. Small 2019, 15, 1803913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-álvarez, M.; Martín-Esteban, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Quantum Dot Materials in Optical Sensors: An Overview of Their Synthesis and Applications. Biosensors 2021, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, Z. Recent advances in protein-imprinted polymers: Synthesis, applications and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 6571–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ma, Y.; He, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y. Tumor-Sensitive Biodegradable Nanoparticles of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Stabilized Fluorescent Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 for Targeted Imaging and Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24585–24598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, F.; Lezina, L.; Guerreiro, A.; Czulak, J.; Petukhov, A.; Daks, A.; Smolinska-Kempisty, K.; Poma, A.; Piletsky, S.; Barlev, N.A. Specific Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells with Double-Imprinted Nanoparticles against Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 4641–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Cao, P.P.; He, Z.Y.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.K. Targeted Imaging and Targeted Therapy of Breast Cancer Cells: Via Fluorescent Double Template-Imprinted Polymer Coated Silicon Nanoparticles by an Epitope Approach. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17018–17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.T.; Peng, H.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Highly Effective Drug Delivery and Cell Imaging Using Fluorescent Double-Imprinted Nanoparticles by Targeting Recognition of the Epitope of Membrane Protein. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12696–12703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Qin, Y.T.; He, X.W.; Li, W.Y.; Zhang, Y.K. Epitope Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles for Chemo-/Photodynamic Synergistic Cancer Therapy Guided by Targeted Fluorescence Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13360–13370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Cheng, S.; Xiao, Y.; Chan, K.; Tong, K.; Ko, C. Recyclable Polymer-Supported Iridium-Based Photocatalysts for Photoredox Organic Transformations. J. Catal. 2022, 407, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, T.; Ding, H.; Ding, L. Rapid Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers on Carbon Quantum Dots for Fluorescent Sensing of Tetracycline in Milk. Talanta 2016, 146, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, J.; Kang, R.; Grimm, L.M.; De Cola, L.; Picchetti, P.; Biedermann, F. Molecular Probes, Chemosensors, and Nanosensors for Optical Detection of Biorelevant Molecules and Ions in Aqueous Media and Biofluids. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 3459–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Gupta, N.; Raghuwanshi, R. Epitope Imprinting Approach to Monitor Diseases. J. Mol. Genet. Med. 2017, 11, 1000270. [Google Scholar]
- Tawfik, S.M.; Elmasry, M.R.; Sharipov, M.; Azizov, S.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, Y.I. Dual Emission Nonionic Molecular Imprinting Conjugated Polythiophenes-Based Paper Devices and Their Nanofibers for Point-of-Care Biomarkers Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 160, 112211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




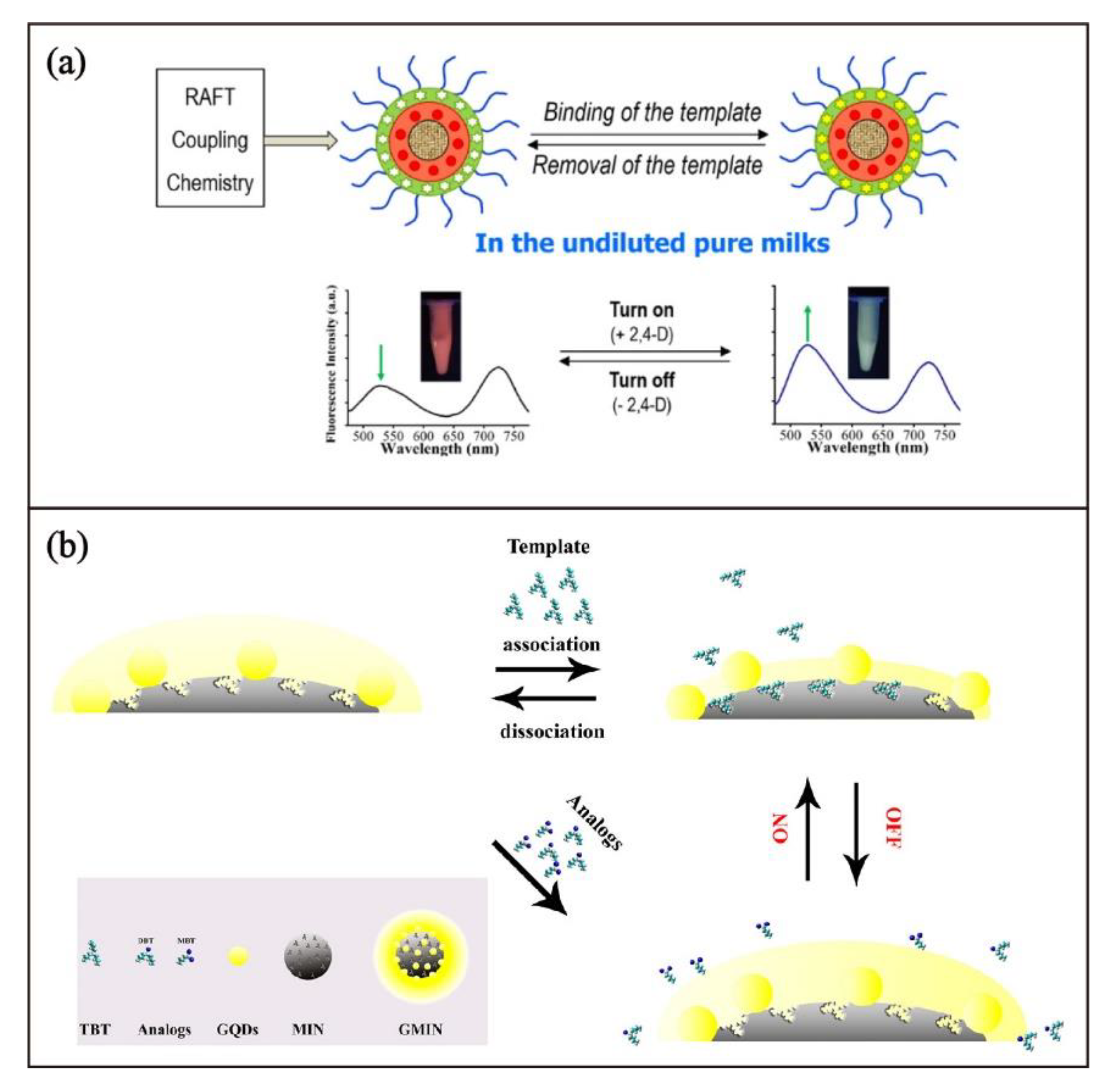
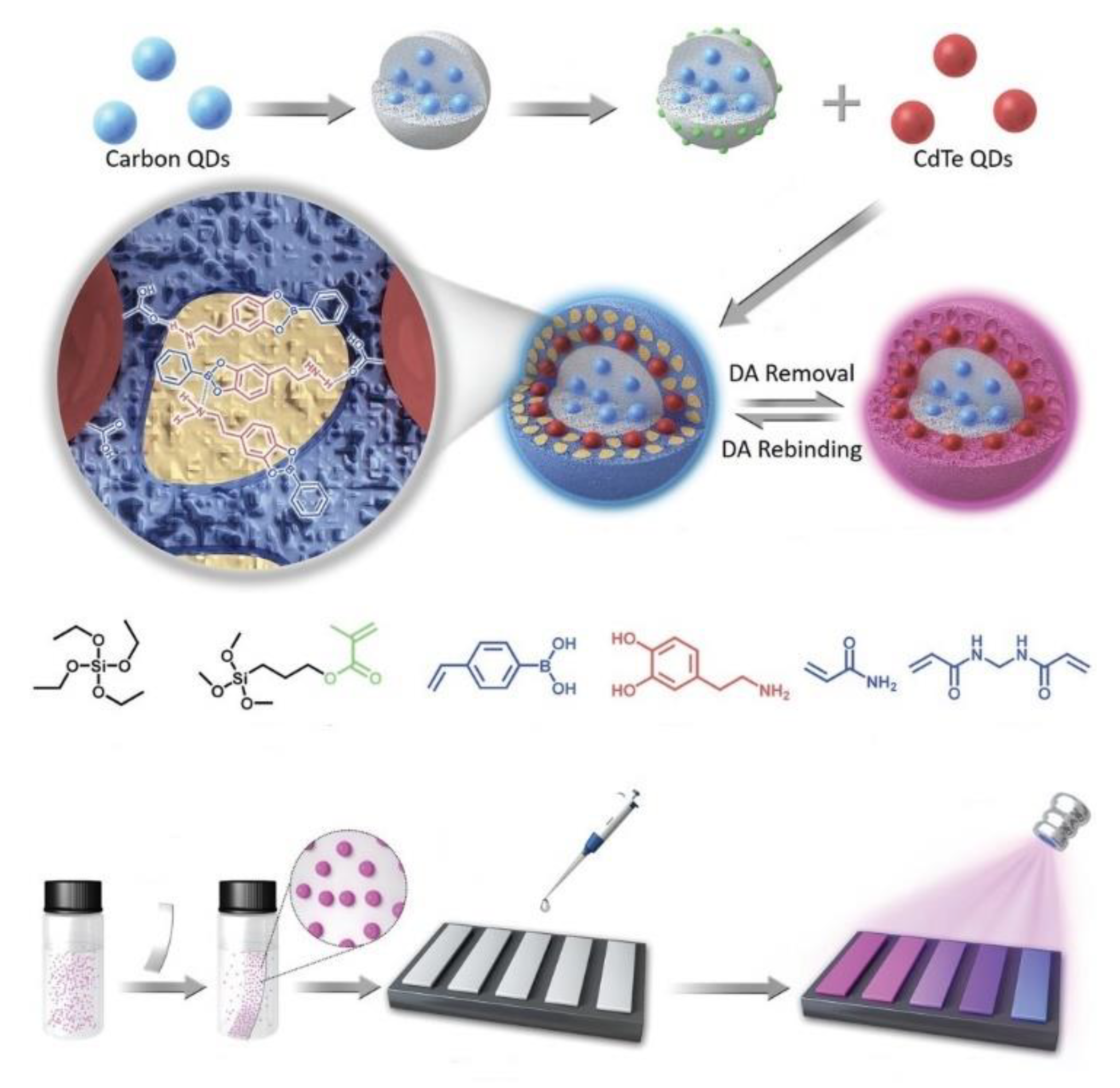
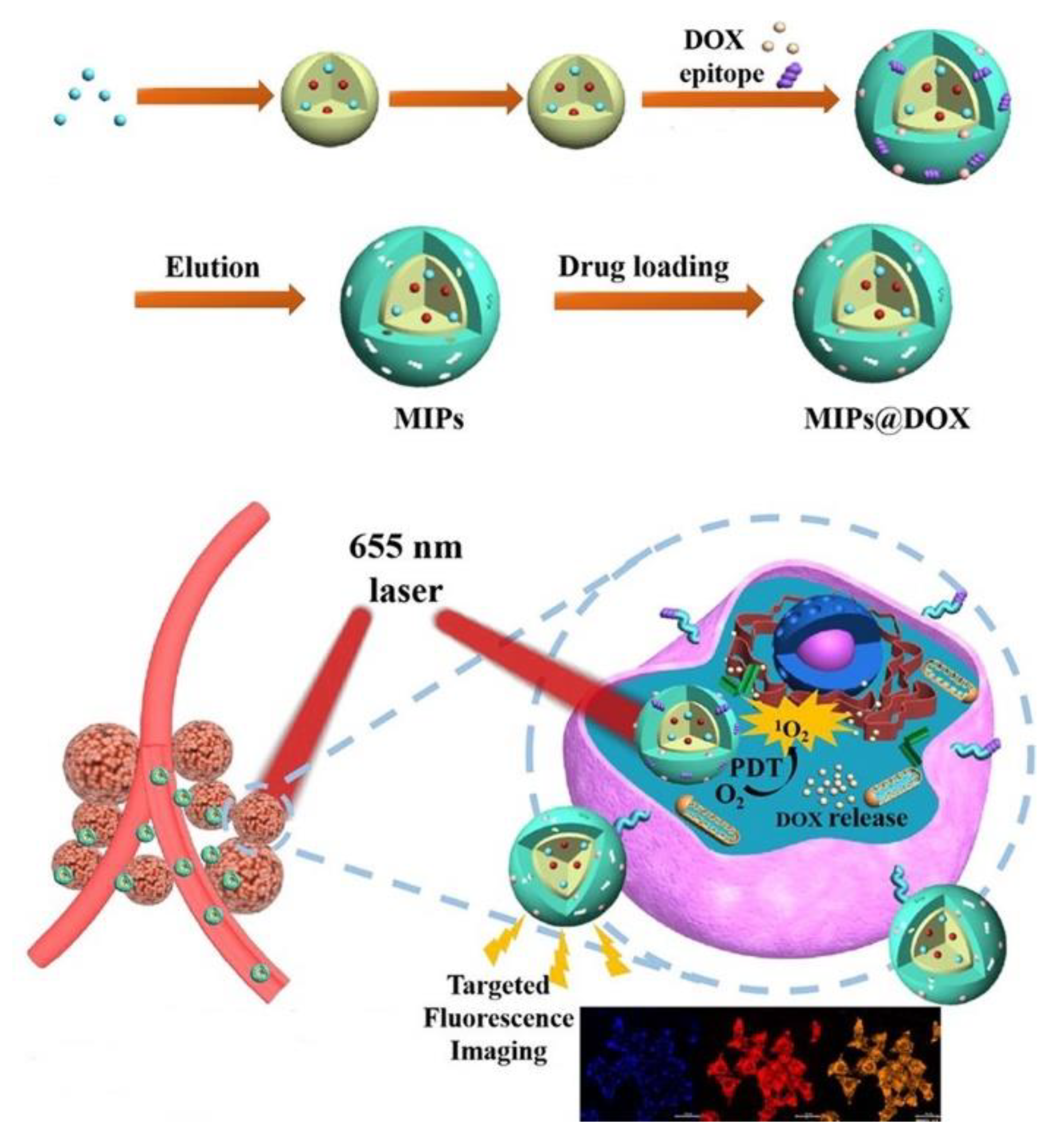

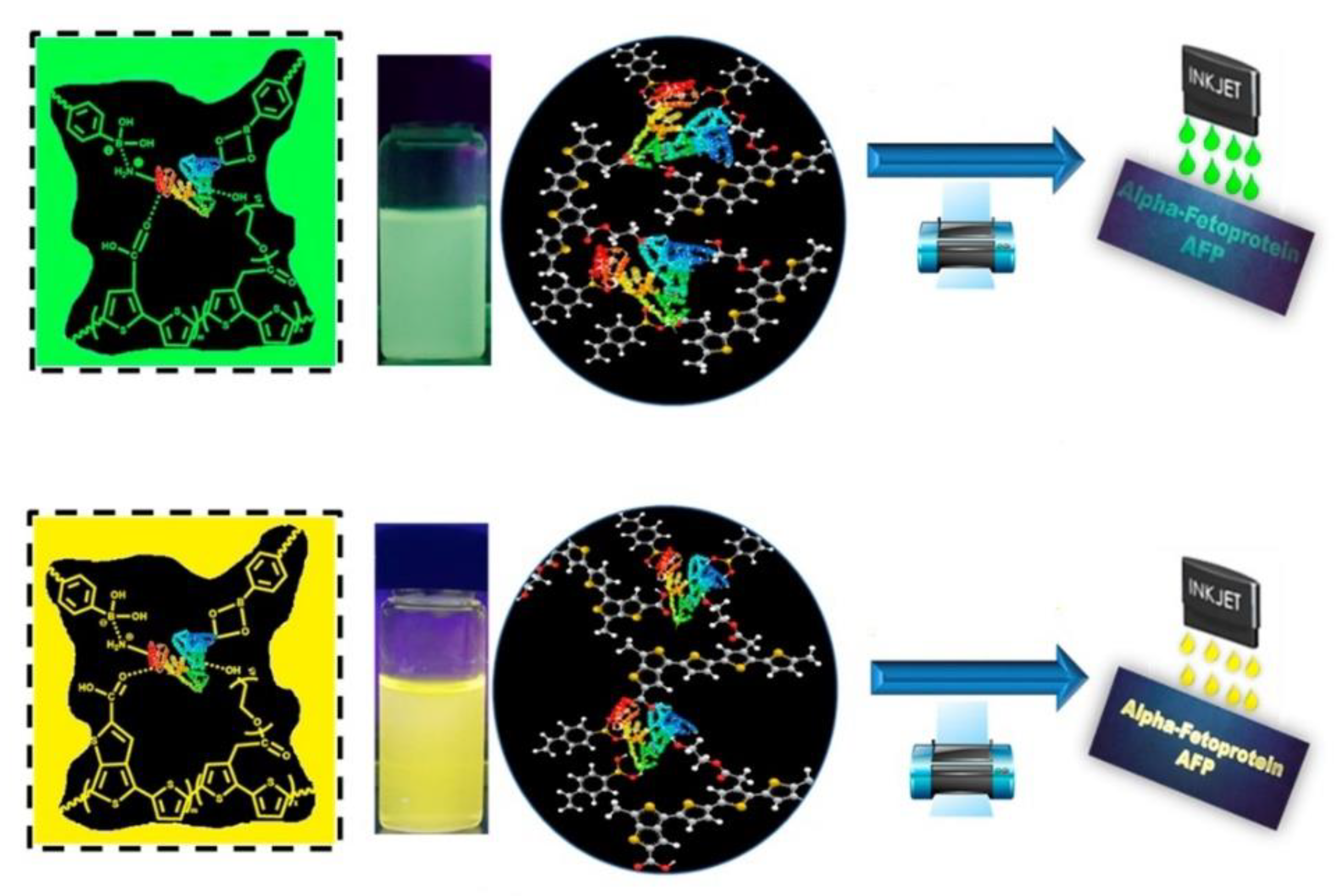
| Components | Examples |
|---|---|
| Monomer | Acrylic acid |
| Methacrylic acid | |
| 2-Vinylpyridine | |
| Styrene | |
| 4-Vinylaniline | |
| Methyl methacrylate | |
| 1-Vinylimidazole | |
| Acrylamide | |
| Crosslinker | Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| Divinylbenzene | |
| 1,1,1-Trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate | |
| 1,3-Diisopropenyl benzene | |
| Pentaerythritol triacrylate | |
| Solvent | Acetonitrile |
| 2-Methoxyethanol | |
| Methanol | |
| Chloroform | |
| Tetrahydrofuran | |
| N,N-Dimethylformamide | |
| Initiator | Benzoyl peroxide |
| Azobisisobutyronitrile | |
| Ammonium persulfate | |
| Ethyl 2-chloro-propionate |
| Lanthanide Complex | Sensing Target | λem | Detection Range | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Eu(TTA)3phen] | Salicylic acid | 614 nm | 0–724 µM | 174 µM | [70] |
| EuCl3 | Fluoroquinolone antibiotics | 612 nm | 0.5–50 µM | 0.58 µM | [71] |
| EuCl3·6H2O | Picloram herbicide | 616 nm | –a | –a | [76] |
| EuCl3·6H2O | Tenuazonic acid | 615 nm | 88.4–1040 µM | 26 µM | [77] |
| Tb(NO3)3·5H2O | Melatonin | 748 nm | 0.004–2.153 nM | 0.048 pM | [78] |
| EuCl3·6H2O | Pinacolyl methylphosphonate | 618 nm | 0–4.44 µM | –a | [80] |
| [Eu(TTA)3phen] | Copper(II) | 616 nm | 10–100 µM | –a | [81] |
| TbCl3·6H2O | Salicylic acid | 545 nm | 0.14–72.4 µM | 0.290 µM | [87] |
| Fluorescent Dye | Sensing Target | λem/nm | Detection Range | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FITC | λ-Cyhalothrin | 531 | 0–60 nM | 9.17 nM | [72] |
| ATTO 647N | Porcine serum albumin | 668 | 0.25–5 nM | 40 pM | [89] |
| FITC | Lysozyme | 520 | 0.1–0.7 µM | –a | [57] |
| Nitrobenzoxadiazole | Sialic acid | 509 | –a | –a | [90] |
| Rhodamine | Hyaluronan | –a | –a | –a | [93] |
| Luminol | Chrysoidine | –a | 0.1–10 µM | 0.032 µM | [94] |
| Coumarin | Tamoxifen | 521 | –a | 10 mM | [95] |
| ATTO 647N | Human serum albumin | 664 | 12–192 nM | 13 nM | [96] |
| Coumarin | 4-Nitrophenol | 461 | 0.001–7.5 µM | 0.5 nM | [97] |
| Thioflavin T | Guanosine | 488 | –a | 5 µM | [98] |
| Nitrobenzoxadiazole | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid | 528 | 0.56–80 µM | 90 nM | [99] |
| Nitrobenzoxadiazole | Phospholipids | 512 | 18–60 µM | 5.6 µM | [100] |
| FITC | Trypsin | 515 | –a | 50 pM | [101] |
| FITC | 17β-Estradiol | –a | 0.10–70 µM | 0.03 uM | [102] |
| FITC | Doxycycline | 520 | 0.2–6 µM | 117 nM | [103] |
| Methyl red | Dimethoate | 450 | 0.6–34 nM | 18.3 pM | [104] |
| Rhodamine | 4-Nitrophenol | 582 | 0.01–10 µM | 3.0 nM | [105] |
| Luminescent Nanomaterials | Sensing Target | λem/nm | Detection Range | Limit of Detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdTe QDs | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid | 528 | 0–15 μM | 0.28 μM | [112] |
| Mn-ZnS QDs | Cocaine | 590 | 0–3.296 μM | 0.250 μM | [113] |
| AuNCs | Bisphenol A | –a | 0–13.1 μM | 0.10 μM | [114] |
| Carbon QDs | Promethazine hydrochloride | 431 | 2.0–250 μM | 0.5 μM | [116] |
| Graphene QDs | Tributyltin | 440 | 0.687 pM–0.687 nM | 0.79 pM | [117] |
| ZnO QDs | Dimethoate | 536 | 0.087–13.92 μM | 0.026 μM | [118] |
| AuNCs | Erythromycin | 585 | 0.1 μM–11.9 μM | 12 nM | [119] |
| Carbon QDs | Ofloxacin | 614 | 1–50 nM | 0.25 nM | [120] |
| Nitrogen CDs | 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol | 408 | 0.5–2.5 nM | 0.15 nM | [121] |
| CdTe QDs | Tetracycline | –a | 0.5–15 µM | 0.14 µM | [122] |
| ZnO QDs | Methylene blue | 554 | 0–100 µM | 1.27 µM | [123] |
| CsPbBr3 QDs | Omethoate | 510 | 0.23–1.88 pM | 0.09 pM | [124] |
| Graphene QDs | Methamphetamine | 420 | 5–50 µM | 0.011 µM | [125] |
| Carbon QDs | N-Acyl homoserine lactones | –a | 2.66–127 nM | 0.033 nM | [126] |
| Carbon QDs | Tannic acid | 440 | 1–200 nM | 0.6 nM | [127] |
| Mn-ZnS QDs | Bilirubin | 590 | 10.99–63.84 µM | 1.8 µM | [128] |
| Cu-Mn-ZnS QDs | Folic acid | 490, 595 | 0.01–5 µM | 6 nM | [129] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Ko, C.-C. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Luminescent Chemosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13, 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020295
Liu R, Ko C-C. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Luminescent Chemosensors. Biosensors. 2023; 13(2):295. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020295
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ruoyang, and Chi-Chiu Ko. 2023. "Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Luminescent Chemosensors" Biosensors 13, no. 2: 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020295
APA StyleLiu, R., & Ko, C.-C. (2023). Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Luminescent Chemosensors. Biosensors, 13(2), 295. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13020295






