Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein Based on AIEgen Nanosphere Labeled Aptamer Combined with Sandwich Structure of Magnetic Gold Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents and Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Instruments
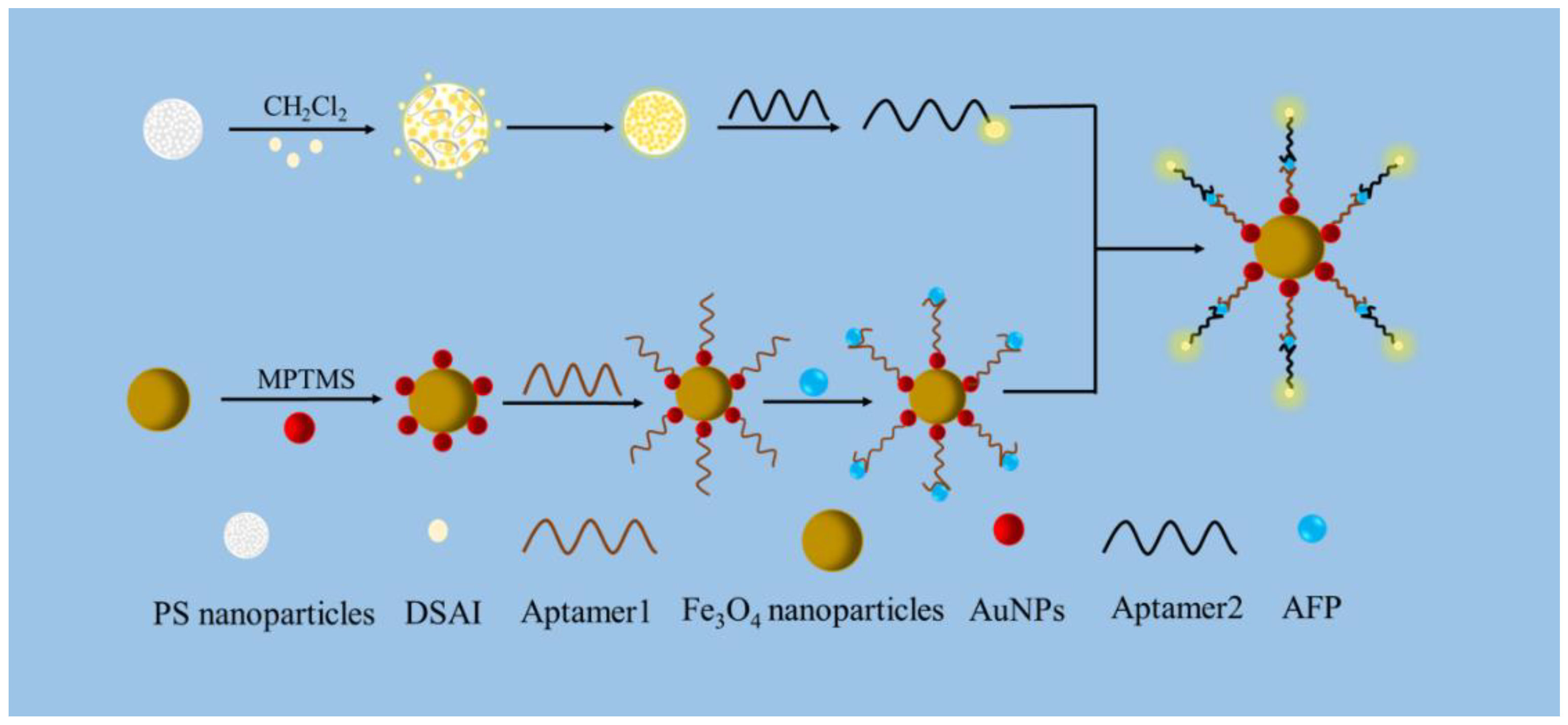
2.3. Preparation of Fe3O4@MPTMS@AuNPs
2.4. Preparation of AIEgen
2.5. Preparation of Carboxyl Functionalized AIEgen Nanospheres
2.6. Preparation of AIEgen Nanosphere Labeled Aptamer (AIEgen Aptamer)
2.7. Sensor Fabrication Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sensor Detection Principle
3.2. Characterization of Fe3O4@MPTMS @ AuNPs and AIEgen Nanospheres
3.3. Fluorescence Spectra and Characterization of AIEgen Nanospheres
3.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
3.4.1. Optimization of Fe3O4@MPTMS @ AuNPs Concentration
3.4.2. Optimization of Aptamer 1 Concentration
3.4.3. Optimization of AIEgen Aptamer 2 Concentration
3.5. Sensitivity Test
3.6. Selective Detection
3.7. Serum Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, C.; Cao, K.; Ma, C.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Qiao, X.; Hong, C. Ultrasensitive immunosensor for AFP detection based on Cu2O to generate electrical signals. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, H. Conjugated polymer sensitized hyperbranched titanium dioxide based photoelectrochemical biosensor for detecting AFP in serum. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 24, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, L.; He, W.; Song, D.; Ji, X.; Shao, J. The diagnostic value of serum PIVKA-II alone or in combination with AFP in Chinese hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 8868370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, T.; Gu, S.; Zhi, J.; Yang, J.; Li, G. An electrochemical biosensor for the assay of alpha-fetoprotein-L3 with practical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L. Chemical redox-cycling for improving the sensitivity of colorimetric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowska-Ciemny, J.; Pankiewicz, J.; Malewski, Z.; von Kaisenberg, C.; Kocylowski, R. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)—New aspects of a well-known marker in perinatology. Ginekol. Pol. 2022, 93, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, M. Development of graphite carbon nitride based fluorescent immune sensor for detection of alpha fetoprotein. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 196, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Q. A graphene oxide-based label-free electrochemical aptasensor for the detection of alphafetoprotein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 112, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdin, A.; Malherbe, C.; Eppe, G. Spatially resolved determination of the abundance of the HER2 marker in microscopic breast tumors using targeted SERS imaging. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, A. A simple electrochemical immunosensor based on worm-like platinum for highly sensitive determination of alpha-fetoprotein. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 140, 107804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chi, B.; Wu, F.; Ma, S.; Zhan, S.; Yi, M.; Xu, H.; Mao, C. A sensitive label-free immunosensor for detection alpha Fetoprotein in whole blood based on anticoagulating magnetic nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 95, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M. Blame it on the antibodies. Nature 2015, 521, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalra, P.; Dhiman, A.; Cho, W.C.; Bruno, J.G.; Sharma, T.K. Simple methods and rational design for enhancing aptamer sensitivity and specificity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimjee, S.M.; White, R.R.; Becker, R.C.; Sullenger, B.A. Aptamers as therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 57, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senf, B.; Yeo, W.H.; Kim, J.H. Recent advances in portable biosensors for biomarker detection in body fluids. Biosensors 2020, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Schadt, M.; Wang, L.; Lim, I.; Njoki, P.; Kim, S.; Jiang, M.; Luo, J.; Zhong, C. Fabrication of magnetic core@shell Fe oxide@Au nanoparticles for interfacial bioactivity and bio-separation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9050–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Hao, T. Removal of organic dye by air and macroporous ZnO/MoO3/SiO2 hybrid under room conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 7913–7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizmann, Y.; Patolsky, F.; Katz, E.; Willner, I. Amplified DNA sensing and immunosensing by the rotation of functional magnetic particles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3452–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Drug Develop. Res. 2006, 67, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.; Nagar, A.; Chaudhary, S.; Pal, S. Advanced properties and applications of AIEgens-inspired smart materials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 10721–10736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, S.; Lu, Y. Size-dependent modulation of graphene oxide-aptamer interactions for an amplified fluorescence-based detection of aflatoxin B1 with a tunable dynamic range. Analyst 2016, 141, 4029–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jun, J. Time-resolved fluorescence immunochromatographic assay developed using two idiotypic nanobodies for rapid, quantitative, and simultaneous detection of aflatoxin and zearalenone in maize and its products. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11520–11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.; Kwok, R.; Lam, J.; Tang, B. Aggregation-induced emission: Together we shine, united we soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, L.; Ma, K.; Xu, B.; Liu, L.; Tian, W. Label-Free Aptamer-based biosensor for specific detection of chloramphenicol using AIE probe and graphene oxide. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 12886–12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lam, J.; Mahtab, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Hong, Y.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, Q.; Tang, B. Biotin-decorated fluorescent silica nanoparticles with aggregation-induced emission characteristics: Fabrication, cytotoxicity and biological application. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, M.; Allafchian, A.; Jalali, S.; Kameli, P. Synthesis and characterisation of Fe3O4 at MPTMS at Au nanocomposite by sol–gel method for the removal of methylene blue. Micro Nano Lett. 2018, 13, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, D.; Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, B.; Li, P. AIEgens enabled ultrasensitive point-of-care test for multiple targets of food safety: Aflatoxin B1 and cyclopiazonic acid as an example. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 182, 113188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Wang, J.; Yu, M.; Zhuang, X. Preparation of aptamer responsive DNA functionalized hydrogels for the sensitive detection of alpha-fetoprotein using SERS method. Bioconjug. Chem. 2020, 31, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ji, F.; Zhang, T.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Jin, X.; Ruan, B. An fluorescent aptasensor for sensitive detection of tumor marker based on the FRET of a sandwich structured QDs-AFP-AuNPs. Talanta 2019, 197, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zeng, J.; Liu, H.; Ding, P.; Liang, J.; Nie, X.; Zhou, Z. A fluorometric aptamer nanoprobe for alpha-fetoprotein by exploiting the FRET between 5-carboxyfluorescein and palladium nanoparticles. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Ding, H.; Chen, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhang, K. Prussian blue nanoparticle-labeled aptasensing platform on graphene oxide for voltammetric detection of α-fetoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma with target recycling. Analyst 2019, 144, 4858–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Xue, Y.; Dong, C.; Zeng, J.; Huang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhou, Z. Label-free electrochemical aptasensor for detection of alpha-fetoprotein based on AFP-aptamer and thionin/reduced graphene oxide/gold nanoparticles. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 547, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, N.; Khoshsafar, H.; Ghanei, M.; Ghazvini, A.; Bagheri, A.H. Dual-template rectangular nanotube molecularly imprinted polypyrrole for label-free impedimetric sensing of AFP and CEA as lung cancer biomarkers. Talanta 2022, 239, 123146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Method | Analyst | Linear Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) | AFP aptamer/IgG | 50~100 ng/mL | 50 pg/mL | [29] |
| Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) | AFP aptamer/QDs-AuNPs | 0.5~45 ng/mL | 400 pg/mL | [30] |
| FRET | FAM-labeled AFP aptamer/PdNP | 5~150 ng/mL | 1.38 ng/mL | [31] |
| Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) | AFP aptamer/PBNPs | 0.01~300 ng/mL | 6.3 pg/mL | [32] |
| CV | AFP aptamer/TH/RGO/AuNPs | 0.1~100.0 μg/mL | 0.050 μg/mL | [33] |
| Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) | Methyl orange doped polypyrrole | 10~104 pg/mL | 3.3 pg/mL | [34] |
| EIS | Aptamer/graphene oxide | 0.01~100 ng/mL | 3 pg/mL | [8] |
| FRET | Aptamer/sandwich structure of AuNPs magnetic composite | 0.005–0.1 ng/mL | 1.429 pg/mL | This work |
| Samples | Added | Obtained | Recovery | RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ng/mL) | (ng/mL) | (%) | (%) | |
| 1 | 0.01 | 0.00967 | 96.69 | 1.863 |
| 2 | 0.08 | 0.0825 | 103.18 | 4.484 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 0.105 | 105.224 | 1.856 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Sulemana, H.; Xie, B.; Gao, L. Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein Based on AIEgen Nanosphere Labeled Aptamer Combined with Sandwich Structure of Magnetic Gold Nanocomposites. Biosensors 2023, 13, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030351
Liu L, Wang H, Sulemana H, Xie B, Gao L. Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein Based on AIEgen Nanosphere Labeled Aptamer Combined with Sandwich Structure of Magnetic Gold Nanocomposites. Biosensors. 2023; 13(3):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030351
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lei, Huixing Wang, Husseini Sulemana, Bing Xie, and Li Gao. 2023. "Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein Based on AIEgen Nanosphere Labeled Aptamer Combined with Sandwich Structure of Magnetic Gold Nanocomposites" Biosensors 13, no. 3: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030351
APA StyleLiu, L., Wang, H., Sulemana, H., Xie, B., & Gao, L. (2023). Detection of Alpha Fetoprotein Based on AIEgen Nanosphere Labeled Aptamer Combined with Sandwich Structure of Magnetic Gold Nanocomposites. Biosensors, 13(3), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13030351




